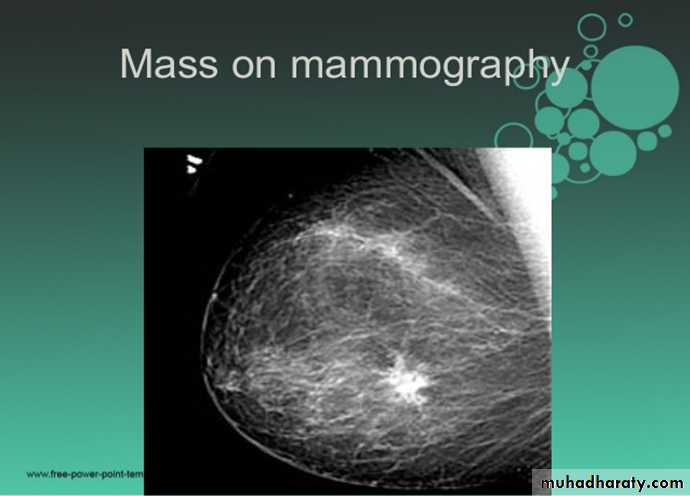
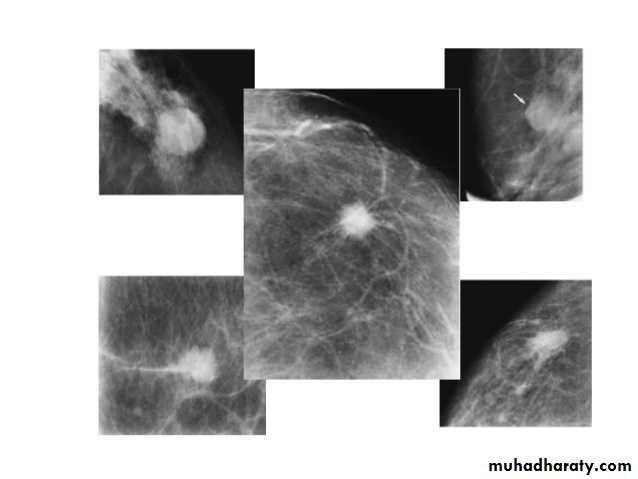
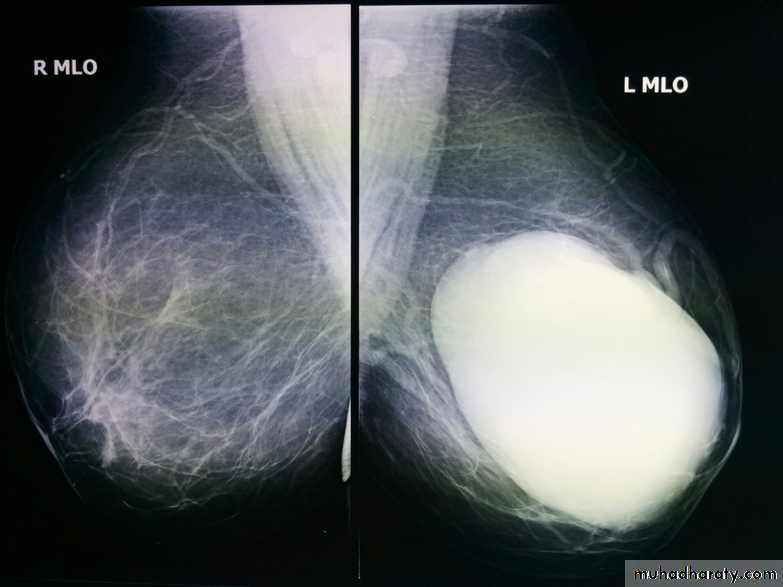
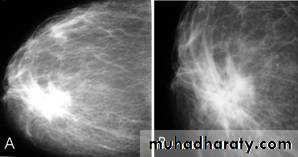
Mammogram
Collage of medicine /radiology departmentMammography
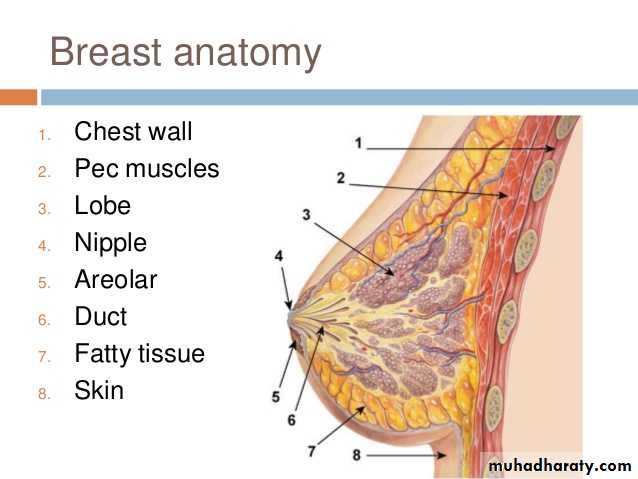
Mammography is a dedicated radiographic technique for imaging the breast . An x-ray (radiograph) is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. Imaging with x-rays involves exposing a part of the body to a small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the body.Types of mammography
In general terms, there are two types of mammography: screening and diagnostic.
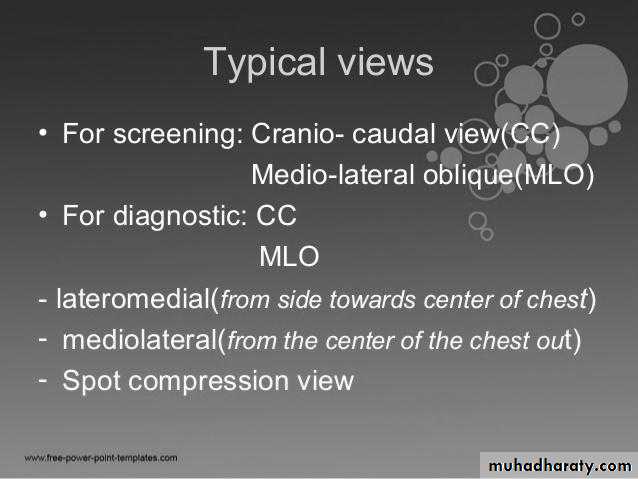
There are numerous mammography views that can broadly be split into two groups
standard views
supplementary views - additional information or problem solving
Mammography views
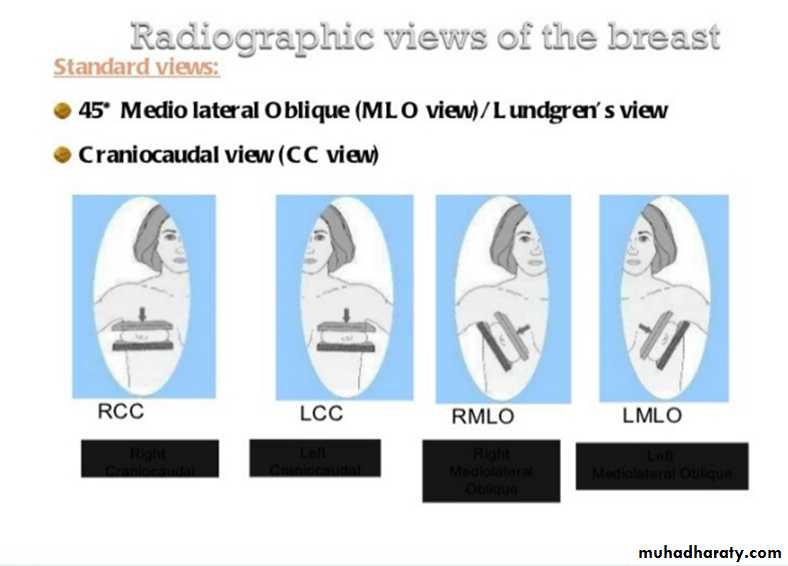
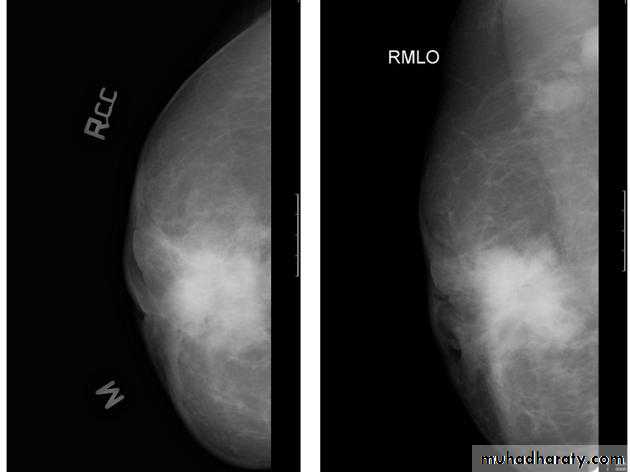
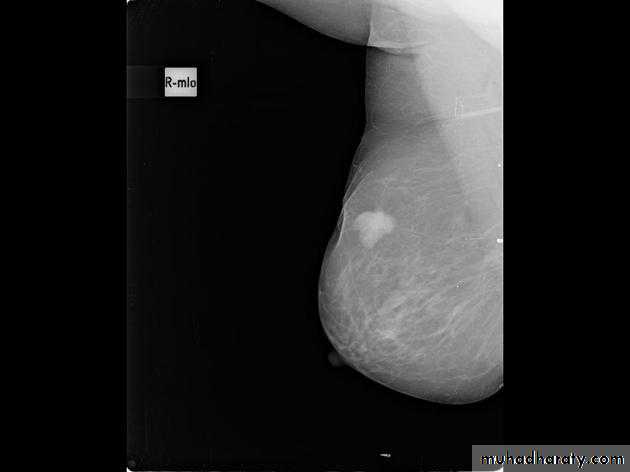
The mediolateral oblique (MLO) view is one of standard mammographic views. It is the most important projection as it allows to depict most breast tissue.The craniocaudal view (CC view), is one of the two standard projections in a screening mammography. It must show the medial part as well the external lateral portion of the breast as much as possible.
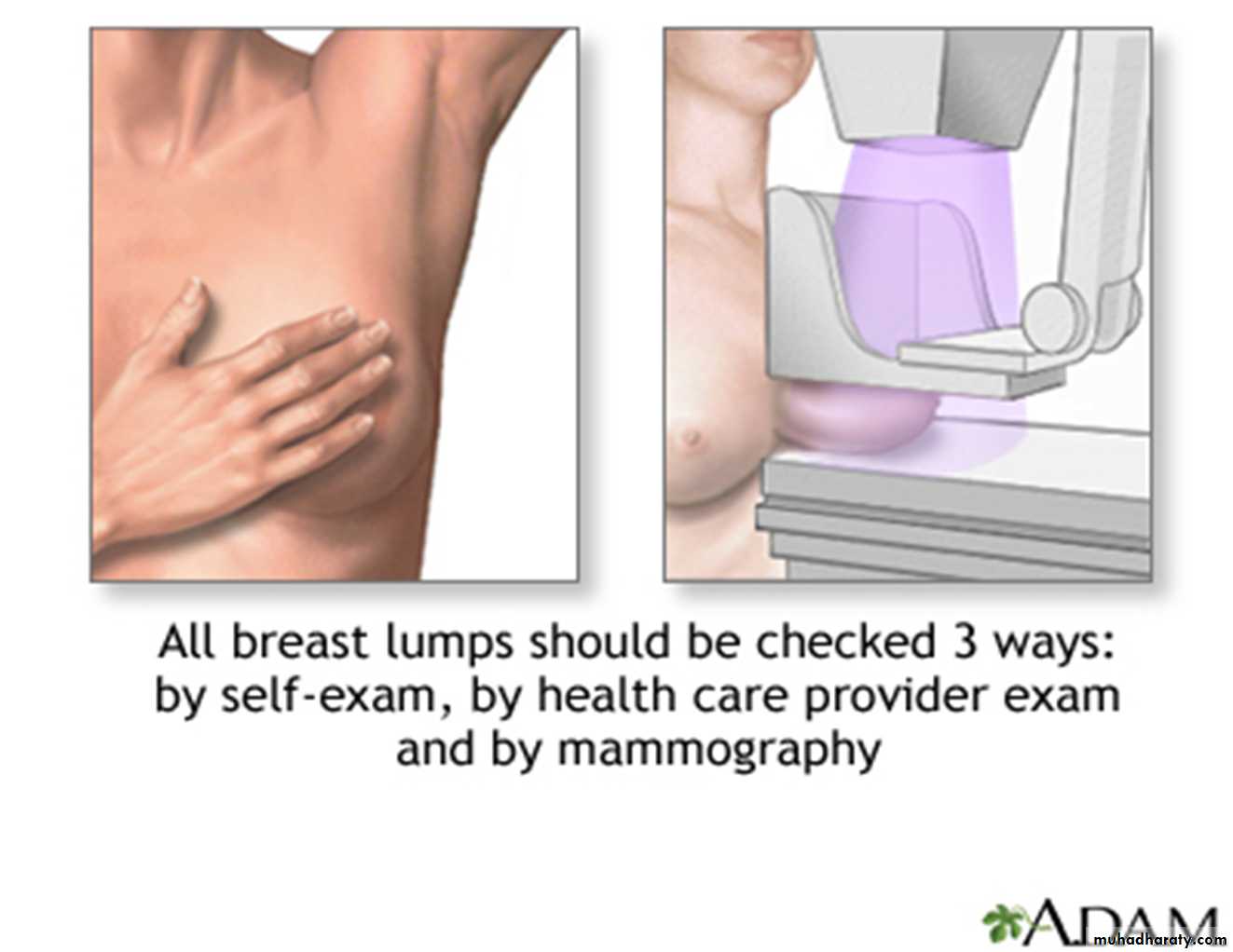
Screening mammography is the type of mammogram that checks you when you have no symptoms. It can help reduce the number of deaths from breast cancer among women ages 40 to 70. But it can also have drawbacks. Mammograms can sometimes find something that looks abnormal but isn't cancer. This leads to further testing and can cause you anxiety. Sometimes mammograms can miss cancer when it is there. It also exposes you to radiation. You should talk to your doctor about the benefits and drawbacks of mammograms. Together, you can decide when to start and how often to have a mammogram.
Mammograms are also recommended for younger women who have symptoms of breast cancer or who have a high risk of the disease.
When you have a mammogram, you stand in front of an x-ray machine. The person who takes the x-rays places your breast between two plastic plates. The plates press your breast and make it flat. This may be uncomfortable, but it helps get a clear picture. You should get a written report of your mammogram results within 30 days.
Mammogram facts
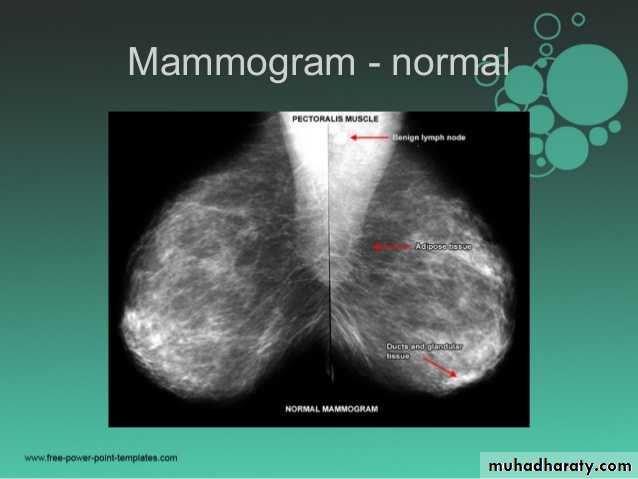
Mammograms are images of the breast tissue produced on X-ray film.Mammograms are the most efficient screening method to detect early breast cancer.
A mammogram only takes a few seconds and may be mildly uncomfortable.
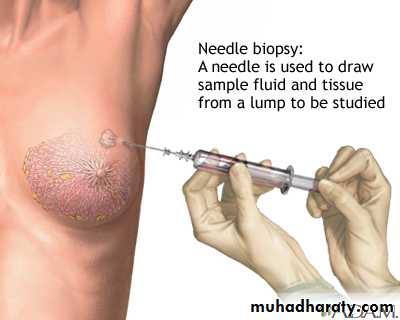
An abnormal mammogram does not necessarily mean that a cancer is present; other tests, including biopsy, MRI, or ultrasound examination may be performed for further clarification of an abnormal mammogram.
A normal mammogram does not exclude the presence of cancer.
Screening mammography is performed at regular intervals to detect abnormalities .
What are the benefits vs. risks
Benefits
Imaging of the breast improves a physician's ability to detect small tumors. When cancers are small, the woman has more treatment options.
The use of screening mammography increases the detection of small abnormal tissue growths confined to the milk ducts in the breast, called ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). These early tumors cannot harm patients if they are removed at this stage and mammography is an excellent way to detect these tumors. It is also useful for detecting all types of breast cancer, including invasive ductal and invasive lobular cancer.
No radiation remains in a patient's body after an x-ray examination.
X-rays usually have no side effects in the typical diagnostic range for this exam.
Risks
There is always a slight chance of cancer from excessive exposure to radiation. However, the benefit of an accurate diagnosis far outweighs the risk.
The effective radiation dose for this procedure
Things to consider before asses mammogram film
Finding a Lump
Remember that the majority (about 80%) of breast lumps are not due to cancer . Cysts, benign tumors, or changes in consistency due to the menstrual cycle can all cause benign breast lumps. Still, it's important to let your doctor know about any lumps or changes in your breast that you find. Early detection of breast cancer is associated with high cure rates .???????
Don’t worry
What if my mammogram is abnormal?Do not panic if you are told that your mammogram is abnormal or that there is a "spot" on your mammogram. An abnormal mammogram does not mean you have cancer. The overwhelming majority of abnormal mammograms are caused by benign (harmless) processes. In some cases, it may just be an area of thicker or denser breast tissue, a cyst, or a benign lump such as a fibroadenoma. When a mammogram detects a suspicious area, the patient may be advised to obtain further mammograms of that area, to have an ultrasound or other imaging .
Mammogram deal with the breast mass
Women with a breast lump need to have a mammogram of both breasts. A mammogram is estimated to be able to detect about 90% of breast cancers. This means that about 10% of breast cancers are missed by mammography. Therefore, if a woman or her physician feels a lump and the mammogram is normal, further studies or biopsies are carried out to rule out cancer. Sometimes, a certain pattern of calcium deposits appears on the mammogram that makes the doctor suspicious of cancer. In these cases, it is often recommended that a biopsy be taken that is guided by mammogram images to be sure the correct area is sampledBreast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the tissues of the breast. There are two main types of breast cancer :Ductal carcinoma starts in the tubes (ducts) that carry milk from the breast to the nipple. Most breast cancers are of this type.
Lobular carcinoma starts in the parts of the breast, called lobules, which produce milk.
In rare cases, breast cancer can start in other areas of the breast.
Risk factors you cannot change include
Less than one-fourth of all breast lumps are found to be cancerous, so must look for risk factor ,Age and gender. Your risk of developing breast cancer increases as you get older. Most advanced breast cancer cases are found in women over age 50. Men can also get breast cancer. But they are 100 times less likely than women to get breast cancer.
Family history of breast cancer. You may also have a higher risk of breast cancer if you have a close relative who has had breast, uterine, ovarian, or colon cancer.
Genes. The most common gene defects are found in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. These genes normally produce proteins that protect you from cancer. If a parent passes you a defective gene, you have an increased risk of breast cancer. Women with one of these defects have up to an 80% chance of getting breast cancer sometime during their life.
Menstrual cycle. Women who got their periods early (before age 12) or went through menopause late (after age 55) have an increased risk of breast cancer.
When you find a lump U must adjust the following things
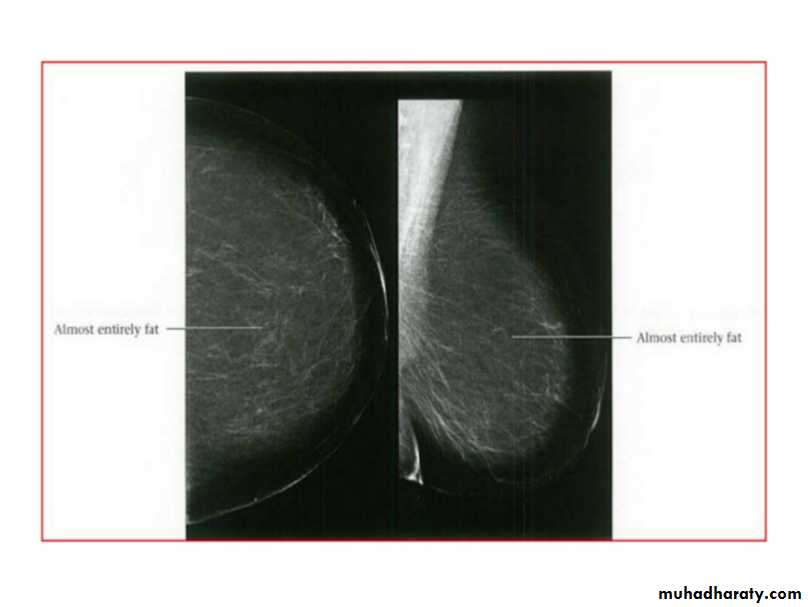
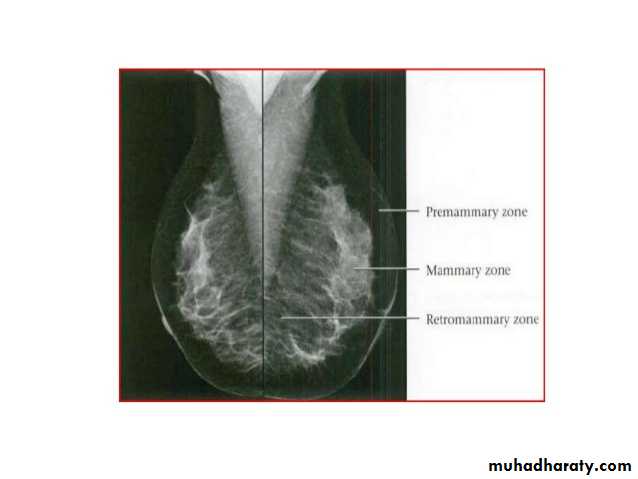
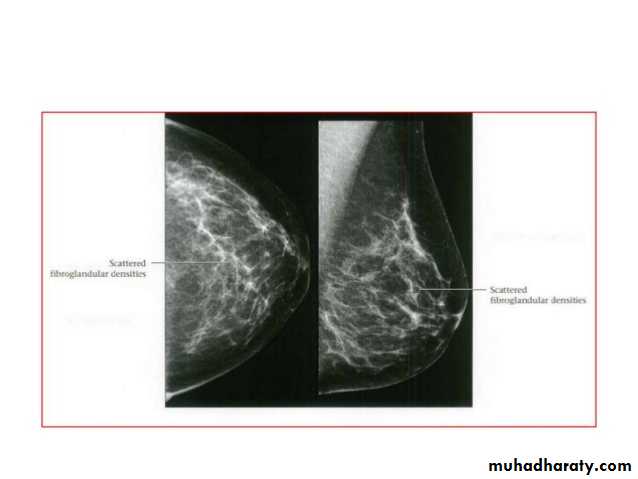
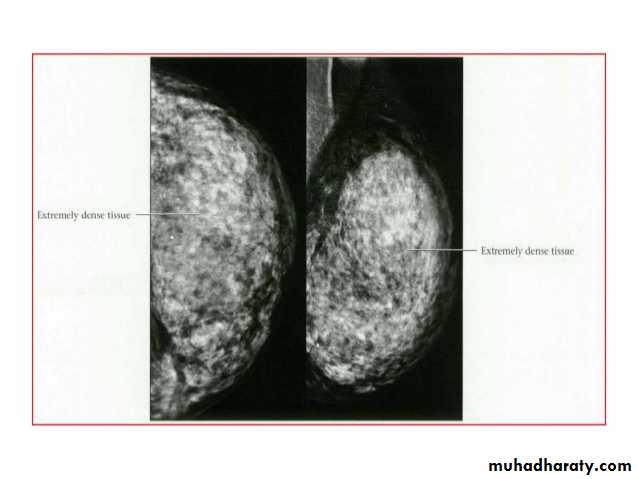
Breast density & who can U detect a mass lesionYour mammogram report must take in consideration & assessment the breast density. Breast density is based on how fibrous and glandular tissue tissues are distributed in your breast, vs. how much of your breast is made up fatty tissue.
Dense breasts are not abnormal, but they are linked to a higher risk of breast cancer. We know that dense breast tissue can make it harder to find cancers on a mammogram. Still experts do not agree what other tests, if any, should be done in addition to mammograms in women with dense breasts who aren’t in a high-risk group (based on gene mutations, breast cancer in the family, or other factors
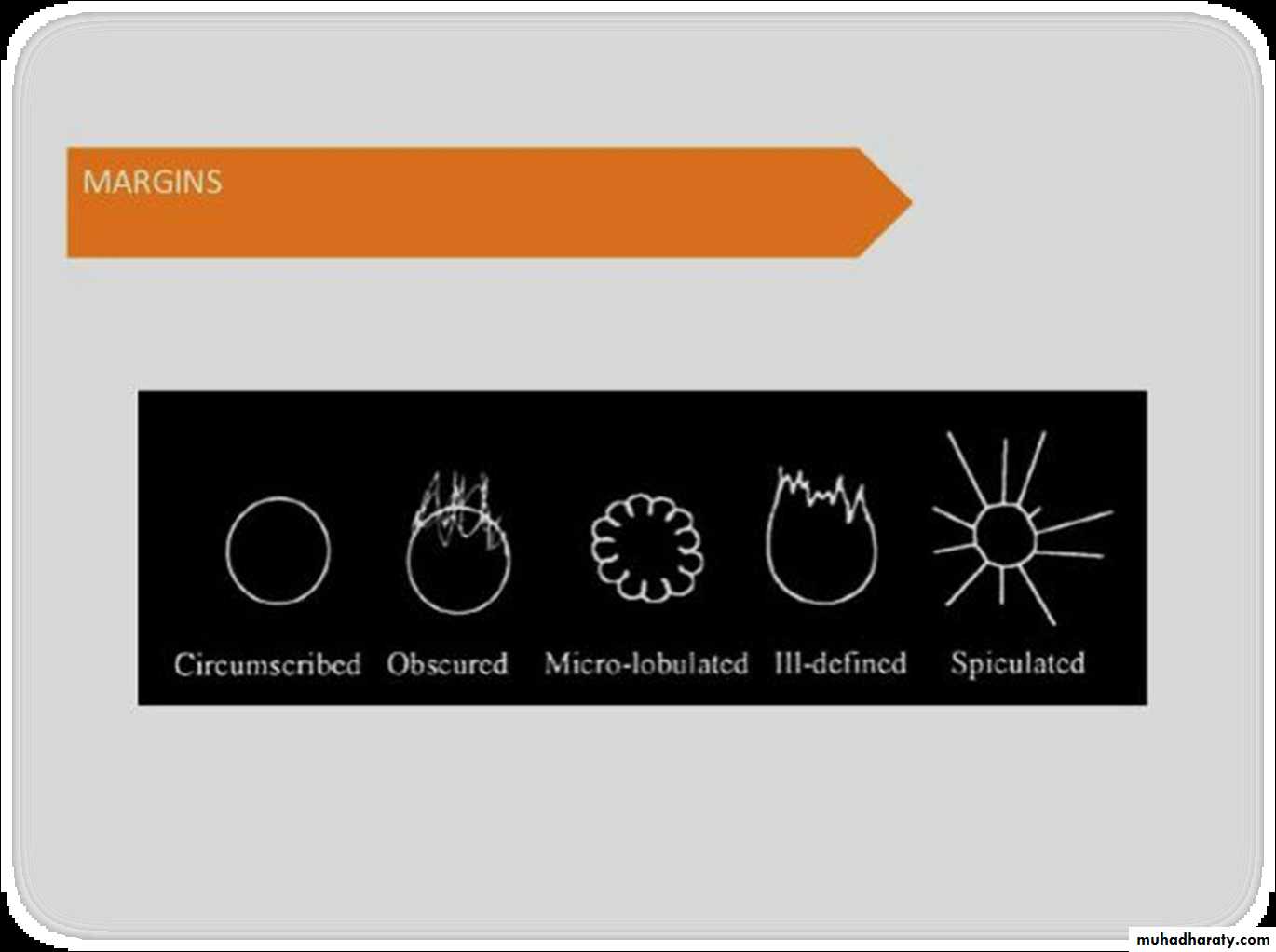
Before u asses the mass look at their margin
Ca breast
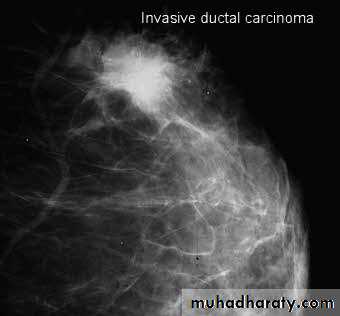
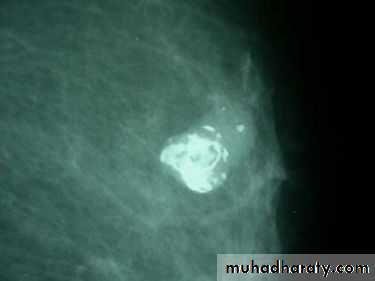
A…..Invasive ductal carcinoma is a subset of ductal carcinoma. It is an infiltrating, malignant and abnormal proliferation of neoplastic cells in the breast tissues. It is the most frequently seen breast malignancy .Radiographic features
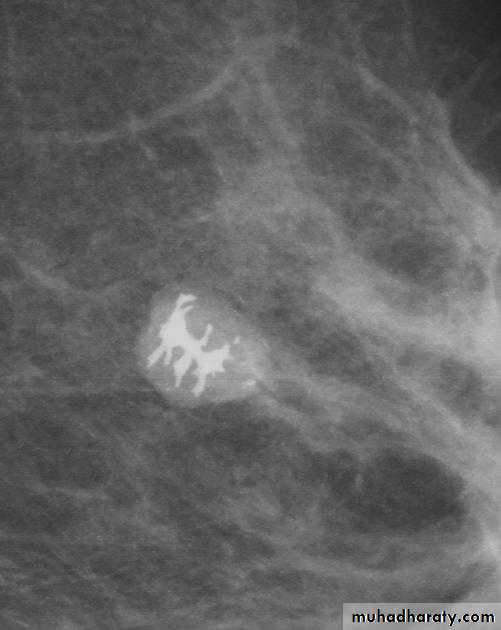
Mammogramspiculated hyperdense lesion
oval/lobulated lesion
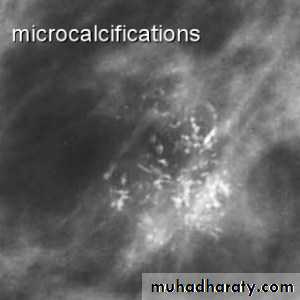
microcalicifications
Infiltrating or invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) of the breast is the second most common type of invasive breast cancer after invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) .
Radiographic features
ILC is more often multicentric and bilateral (10-15%). Therefore imaging evaluation of the contralateral breast is crucial. There can be very subtle changes such as progressive shrinkage or enlargement or reduced compressibility of the involved breast. Imaging often underestimates the disease.
Mammography
The sensitivity of mammography for the detection of ILC reportedly ranges between 55-80% 8. Because of the limitations of mammography in detecting ILC, other modalities, such as sonography and MR imaging, are being used in evaluating clinically suspicious findings and known cancers to assess the extent of disease. ILC are more commonly seen on the craniocaudal (CC), compared to the mediolateral oblique (MLO).
Invasive ductal Ca invasive lobular CA
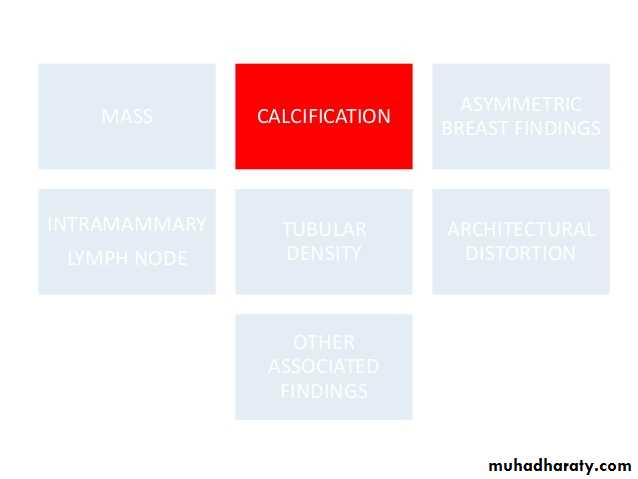
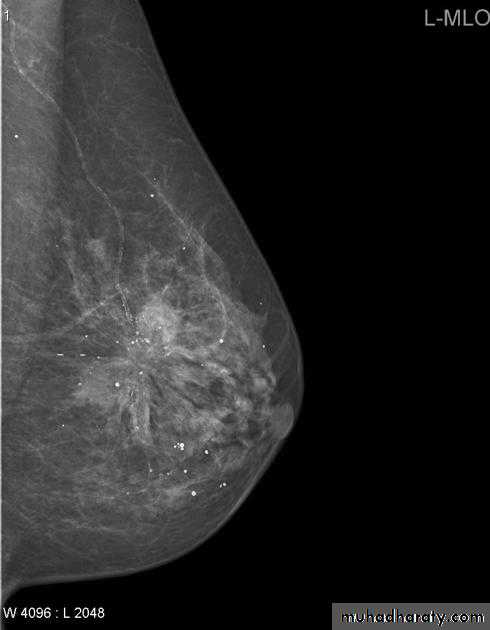
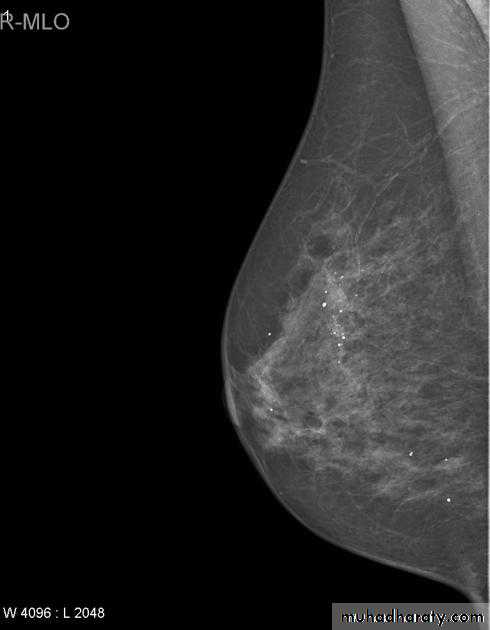
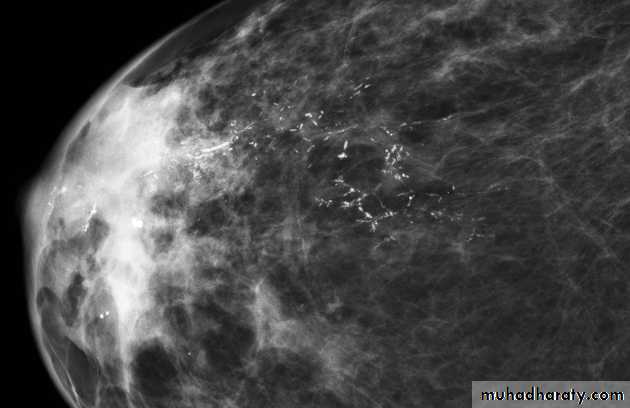
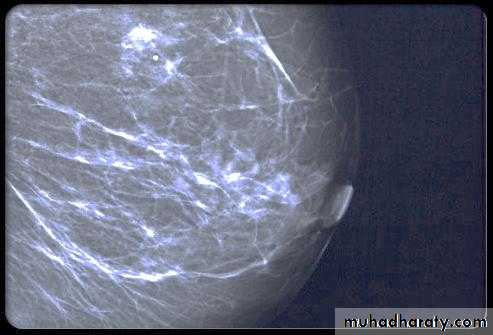
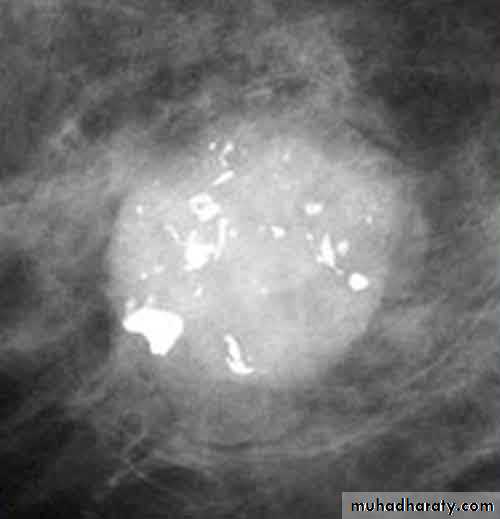
Micro calcifications
Micro calcifications are tiny specks of calcium in the breast. Micro calcifications seen on a mammogram are of more concern than macrocalcifications, but they do not always mean that cancer is present. The shape and layout of microcalcifications help the radiologist judge how likely it is that cancer is present.
In most cases, the presence of microcalcifications does not mean a biopsy is needed. But if the microcalcifications have a suspicious look and pattern, a biopsy will be recommended. (During a biopsy, the doctor removes a small piece of the suspicious area to be looked at under a microscope. A biopsy is the only way to tell if cancer is really present.)
After all description who can U asses the mass lesion ????
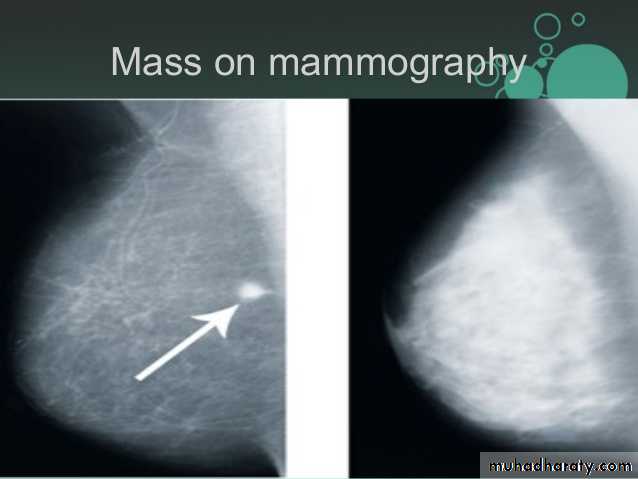
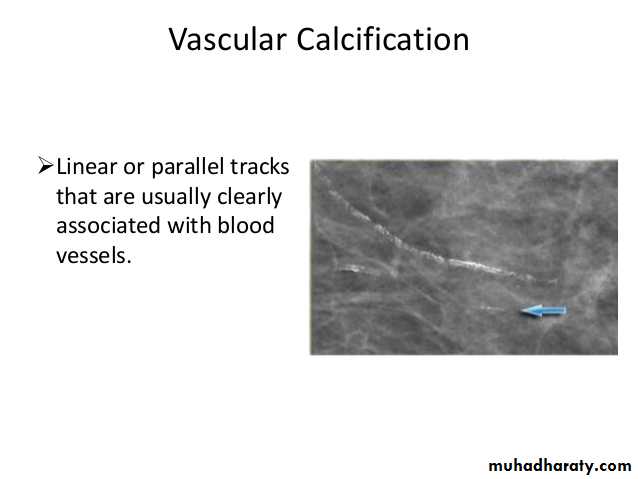
A mass it is calcification & margin
>>>>>> A mass will detected>>>>>> if it is with or without calcifications, change seen on a mammogram.
>>>>>> it is Margin
Masses are areas that look abnormal in mammogram that can be many things, not only CA
including cysts (non-cancerous, fluid-filled sacs) and non-cancerous solid tumors (such as fibro adenomas),
but must aware they sometimes may be a sign of cancer
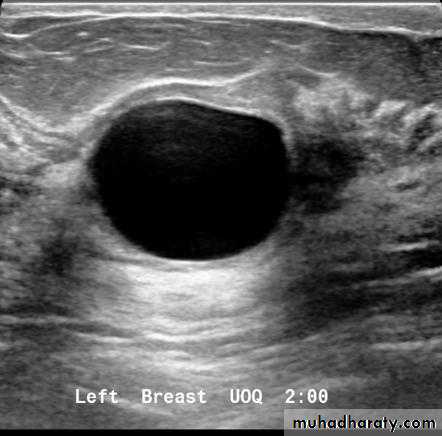
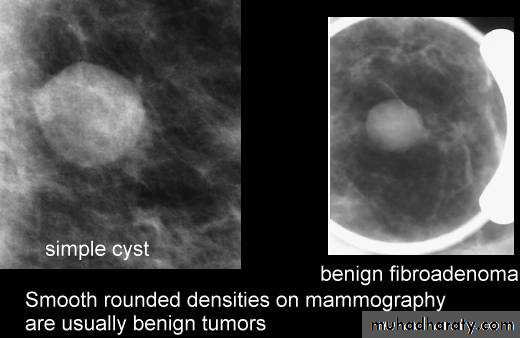
Cysts can be simple fluid-filled sacs (known as simple cysts) or can be partially solid (known as complex cystic and solid masses). Simple cysts are benign (not cancer) and don’t need to be biopsied. If a mass is not a simple cyst, it is of more concern and might need to be biopsied to be sure it isn’t cancer
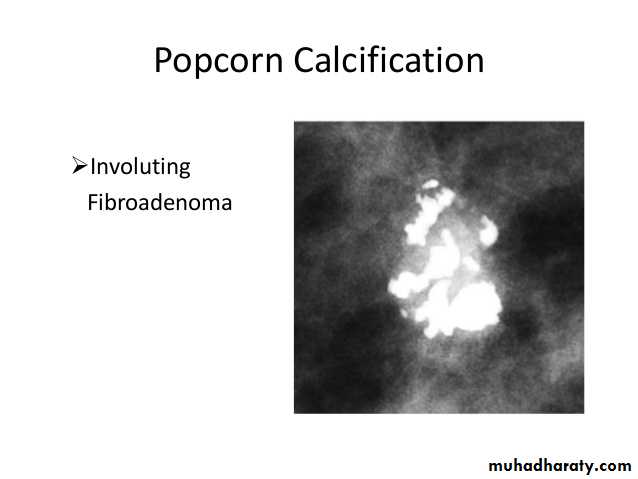
Solid benign ( non cystic lesion ) fibro adenoma
Fibroadenoma is a common benign breast lesion and results from excess proliferation of connective tissue. Fibroadenomas characteristically contain both stromal and epithelial cells.