1
Forth stage
Obstetric
Lec-3
.د
ولدان
1/1/2016
ANATOMY OF NORMAL PELVIS & FETAL SKULL
Knowlage of the anatomy of normal female pelvis, fetal skull & soft tissues is essential to
understand mechanism of labour.
THE PELVIS
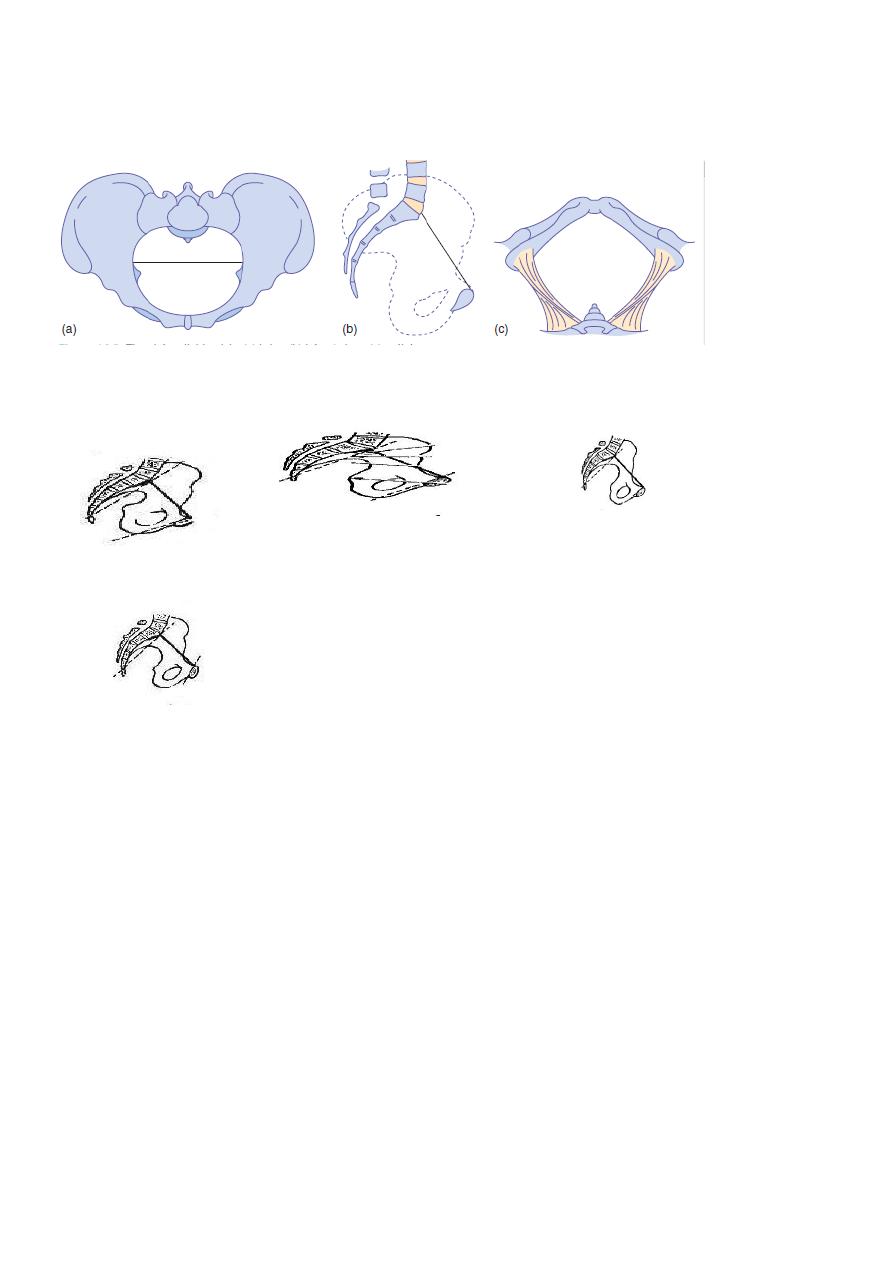
Normal female pelvis is the rounded gynaecoid pelvis occurs only in 40% of white women.
There are three other types:
android
Anthropoid & plattypelloid pelvis.
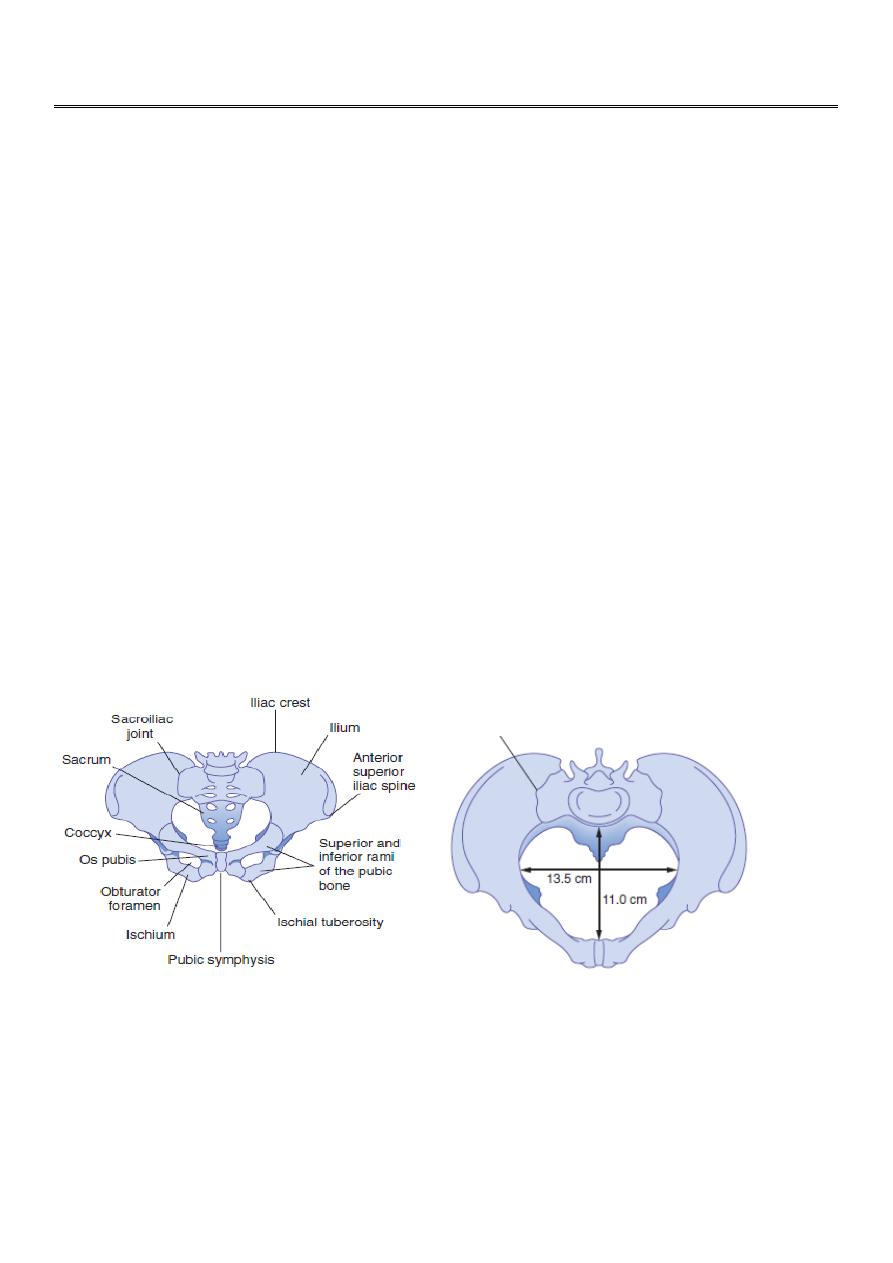
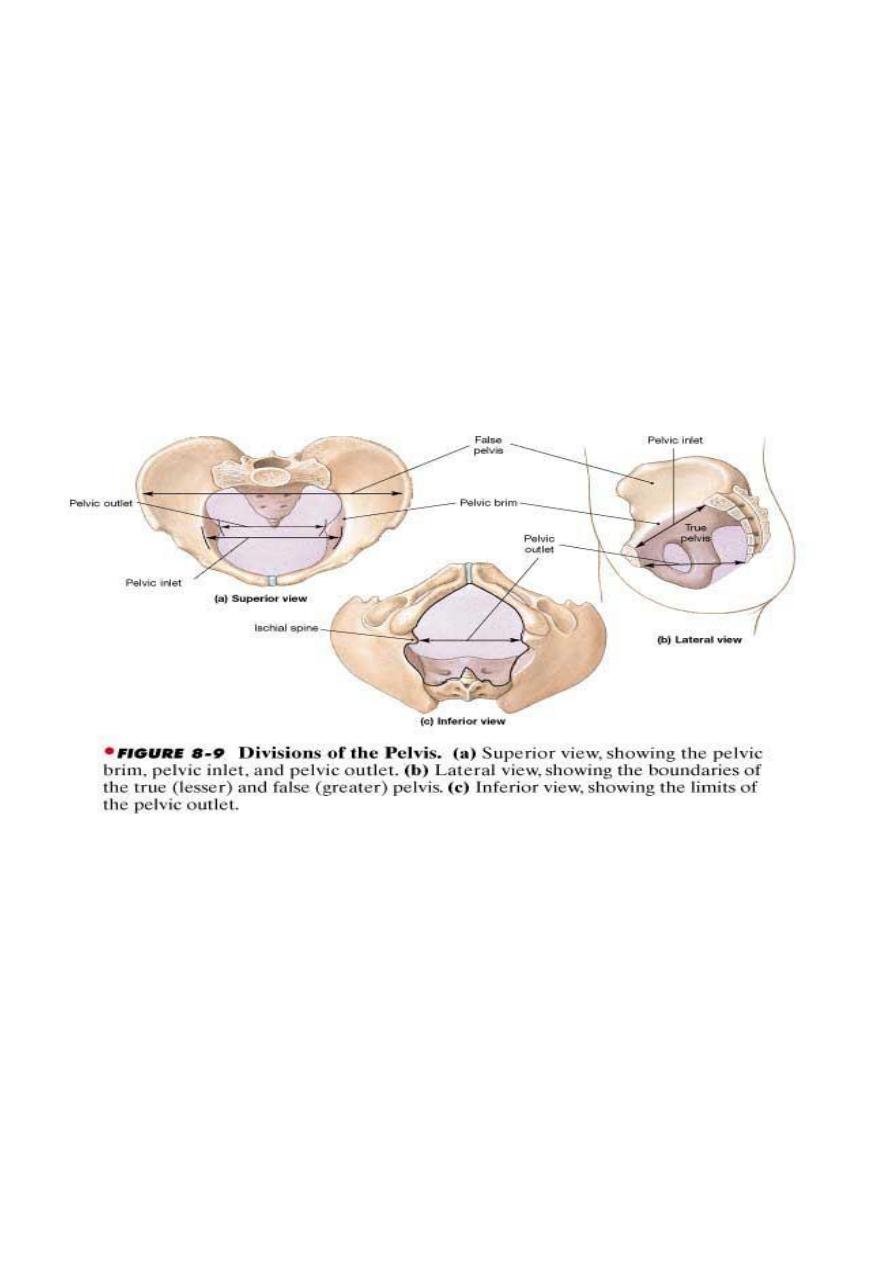
THE PELVIC BRIM OR INLET
The pelvis is divided into true & false pelvis which are separated by pelvic brim.
The plane of pelvic brim is bounded in front by the symphysis pubis [the joint separating
the two pubic bones] on each side by the upper margin of pubic bone, iliopectineal line &
ala of sacrum. Posteriorly by promontary of the sacrum.
The anteroposterior diameter of brim [true conjugate] is 11cm & the transverse diameter is
13.5cm.
THE PELVIC MID CAVITY
Can be described as an area bounded in front by the middle of symphysis pubis ,on each
side by pubic bone, obturator fascia & inner aspect of ischial bone & spines. Posteriorly
bounded by the junction of second & third pieces of sacrum.
2
The cavity is roomy circular with anterioposterior & transverse diameters both measure
12cm.
THE PELVIC OUTLET
Is roughly diamond shaped & bounded infront by the lower margin of symphysis pubis, on
each side by the descending ramus of pubic bone , ischial tuberosity & sacrotuberous
ligament & posteriorly by the last piece of the sacrum.
In gynaecoid pelvis the subpubic arch is wide & tuberosities are far apart. The anterior-
posterior diameter is 13.5cm & the transverse diameter is 11cm.
3
THE PELVIC FLOOR
It forms part of birth canal, it is formed by the two levator ani muscles which with their
fascia form amusculofascial gutter during the second stage of labour with the opening of
the vagina looking forward between sides of the gutter
THE PELVIC AXIS
Is an imaginary curve line shows the path which the centre of fetal head follows during its
passage through the pelvis, it is obtained by taking several anteroposterior diameters of the
pelvis & joining their centers.
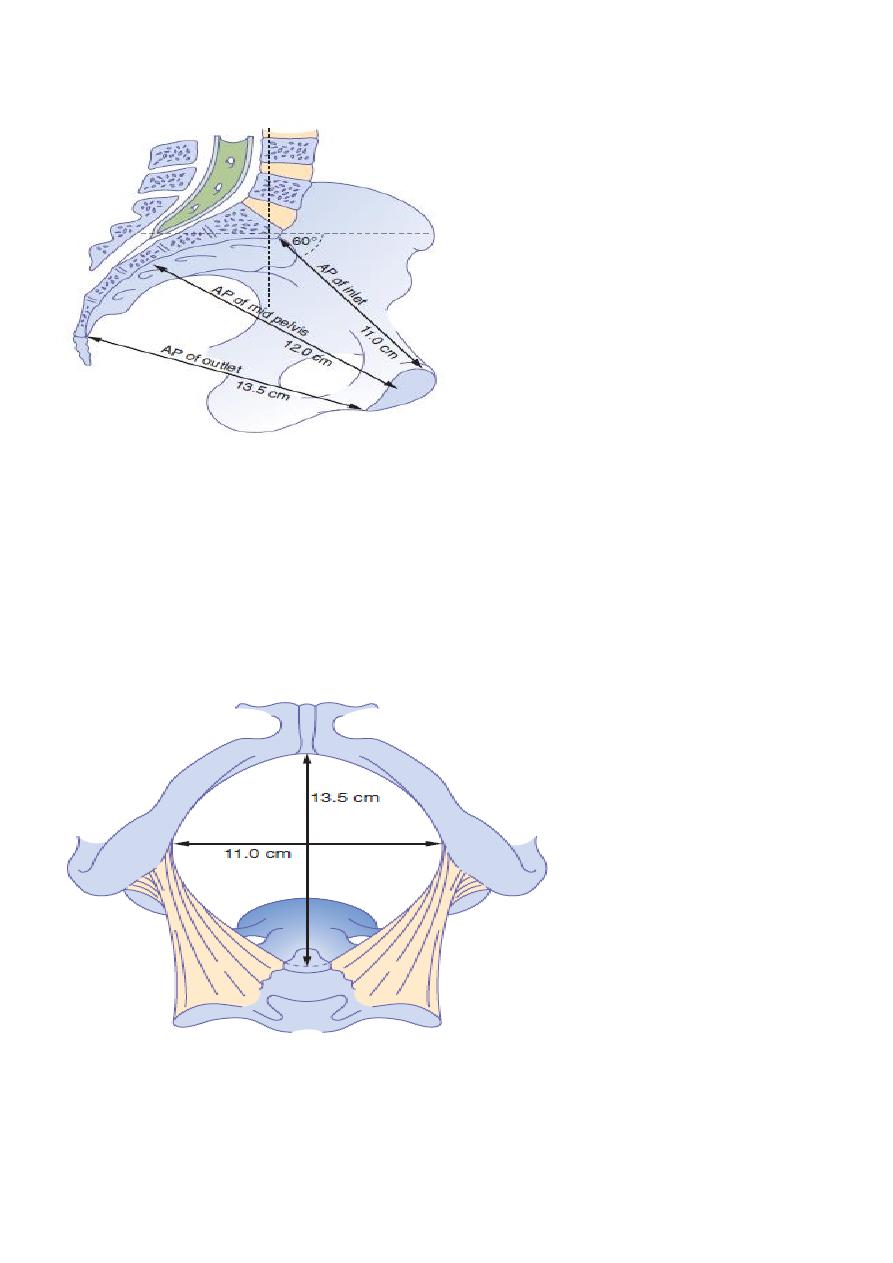
PELVIC INCLINATION
Is the angle that any pelvic plane makes with the horizontal. In the erect position the brim is
normally inclined at 60 degrees .
Pelvic outlet is inclined at about 25 degrees. On vaginal assessment sacral promontary
cannot be reached with the examining finger in normal pelvis.
It is possible to estimate the diagonal conjugate vaginally which the distance between the
promontory &lower margin of symphysis pubis is 12.5 cm.The true conjugate between the
promontory &upper margin of symphysis pubis is 11cm.
4
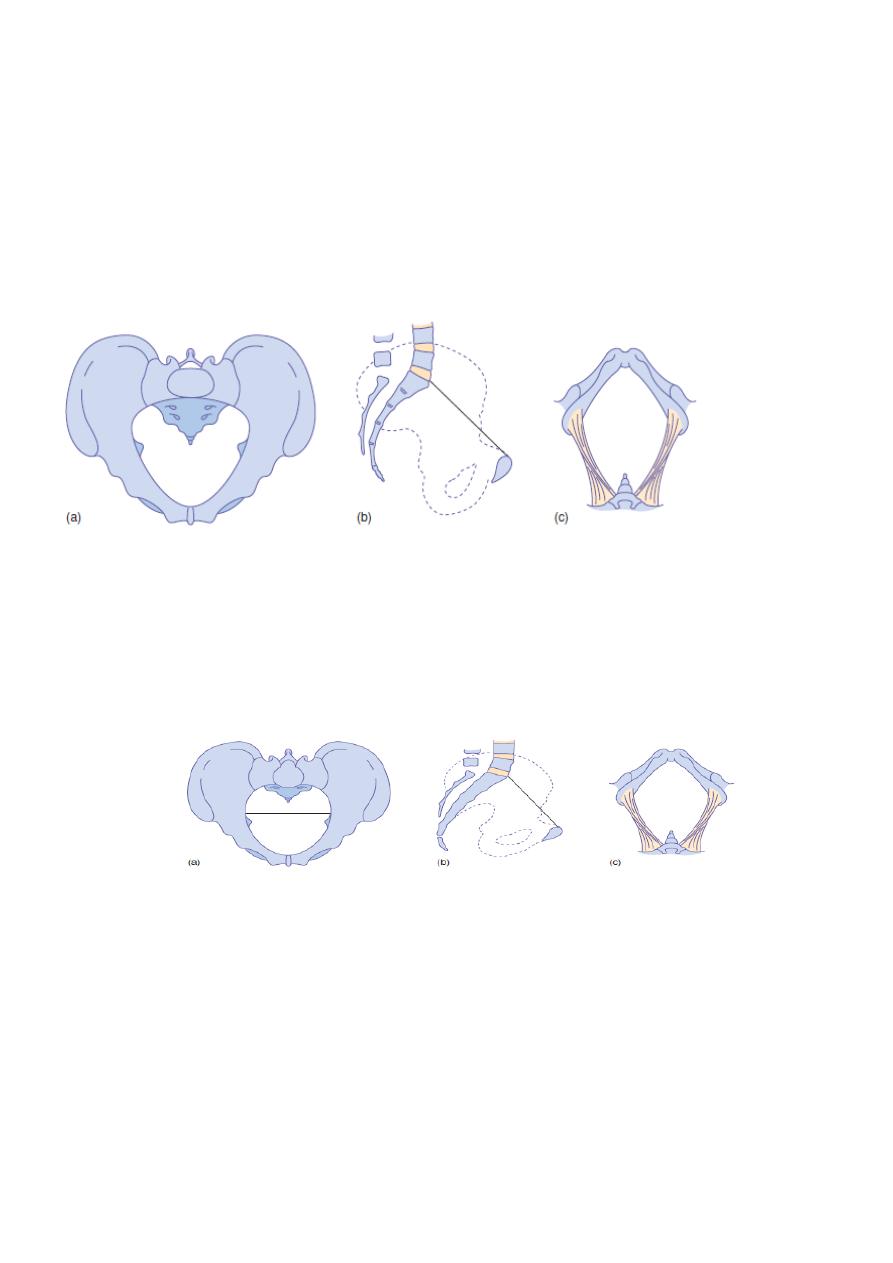
Android pelvis
It had many characteristics of male pelvis ,the brim is heart-shaped so the widest
transverse diameter is much nearer to the sacrum, the side walls tend to converge, the
ischial spines are prominent, the sacrum is straight & the subpubic arch is generally narrow
with an angle of 70 or less.
Both the anteroposterior &transverse diameters of the outlet tend to be reduced. This
type of pelvis is funnel-shaped with diameters decrease from above downwards so
disproportion become worse as labour proceeds.
Anthropoid pelvis
The anteroposterior diameter of the brim exceeds the transverse diameter. It tends to be
deep & the sacrum has six segments instead of five this is known as a high assimilation
pelvis. Sacrum & axis of pelvic cavity are less curved than in gynecoid pelvis & subpubic may
be little narrow, but the sacrosciatic notches are wide & anteroposterior diameter of the
outlet is large .
Platypelloid pelvis
Is described as the simple [non-rachitic] flat pelvis. The brim is elliptical with a wide
transverse diameter, the subpubic arch is wide & rounded.
Except in case of android pelvis, these variations have little effect on normal mechanism of
labour unless there is considerable reduction in the size of pelvis.
Gynecoid pelvis
Anthropoid pelvis
5
Android pelvis
Platypelloid pelvis
Android pelvis
Gynecoid pelvis
Anthropoid pelvis
Platypelloid pelvis
THE FETAL SKULL
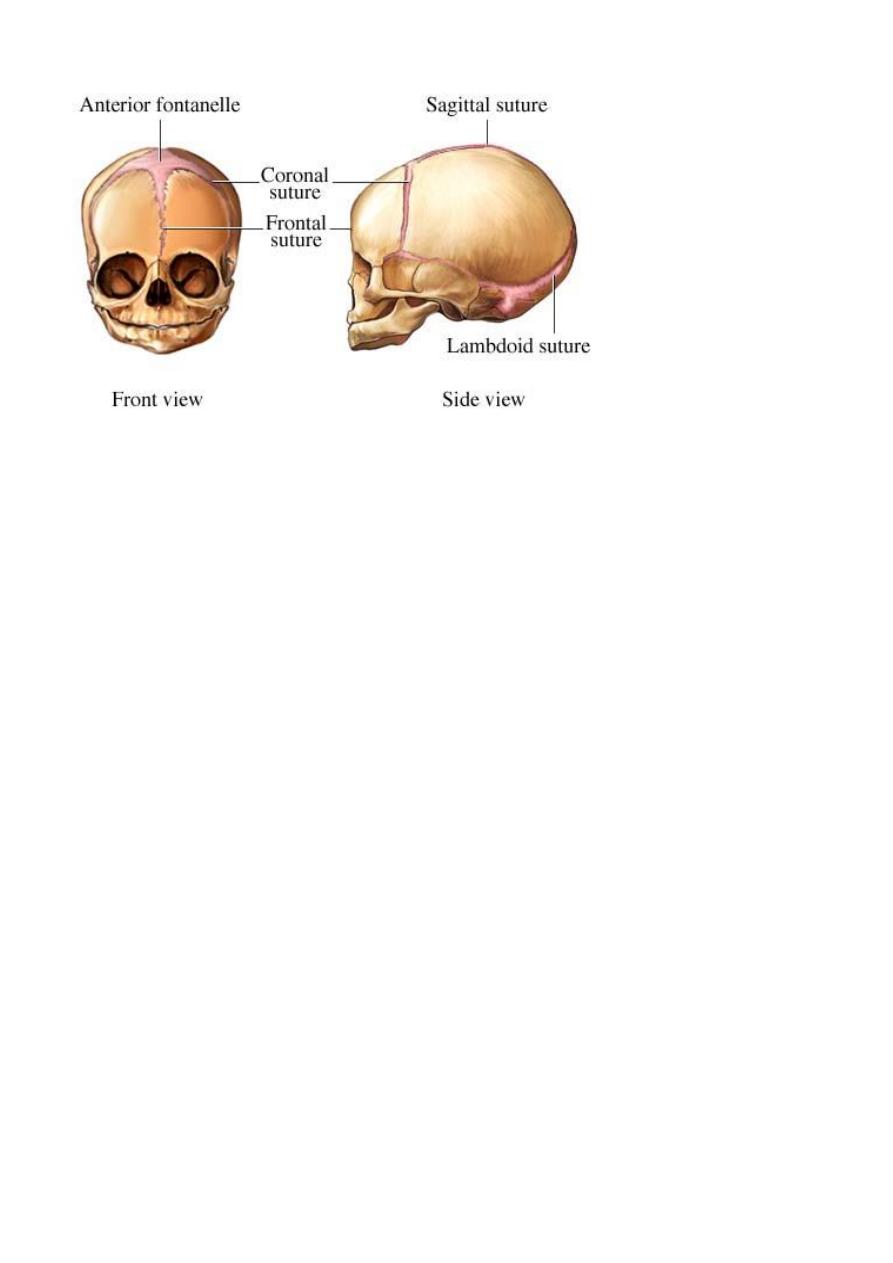
The bones ,sutures & fontanelles
Fetal skull is made of the vault, face & base. By the time of birth the bones of face & base
are firmly united but the bones of the vault are not well ossified being joined by unossified
membranes at the sutures.
The bones which form the vault are the parietal bones, parts of occipital , frontal &
temporal bones
Three sutures are of obstetric importance:
SAGITTAL SUTURE lies between the superior borders of the parietal bones
FRONTAL SUTURE is a forward continuation of the sagittal suture, lies between the two
parts of frontal bone
CORONAL SUTURE lies between the anterior borders of the parietal bones & the posterior
borders of frontal bones.
6
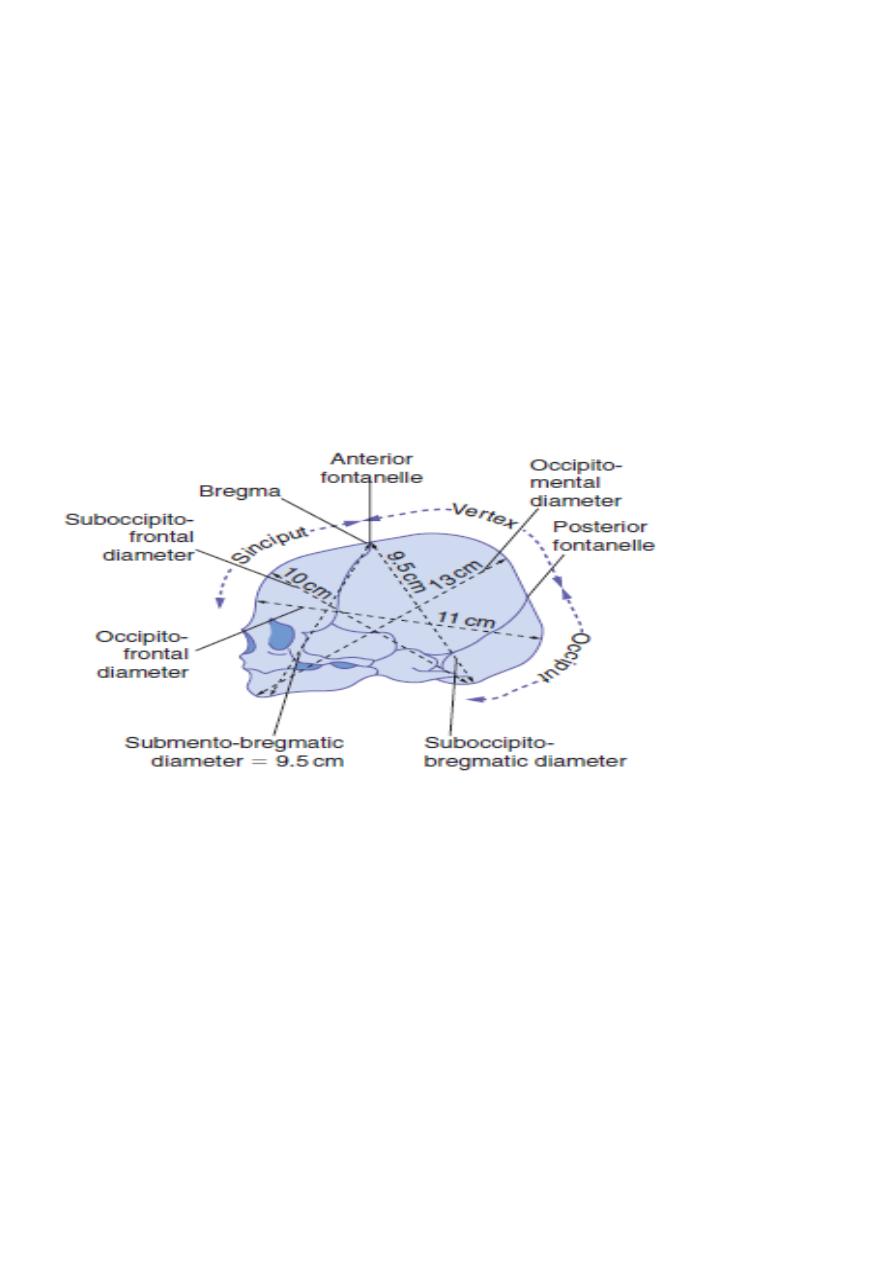
FONTANELLES
Are the junctions of various sutures;
ANTERIOR FONTANELLE OR BREGMA:
Lies where the sagittal, frontal & coronal sutures meet, is diamond shaped is present at
birth & takes about 20 months to close.
POSTERIOR FONTANELLE:
Lies at the posterior end of the sagittal suture between the two parietal bones & occipital
bone. Is triangular in shape &it closed soon after birth.
The area of fetal skull bounded by the two parietal eminences & the anterior & posterior
fontanelles is termed the vertex.
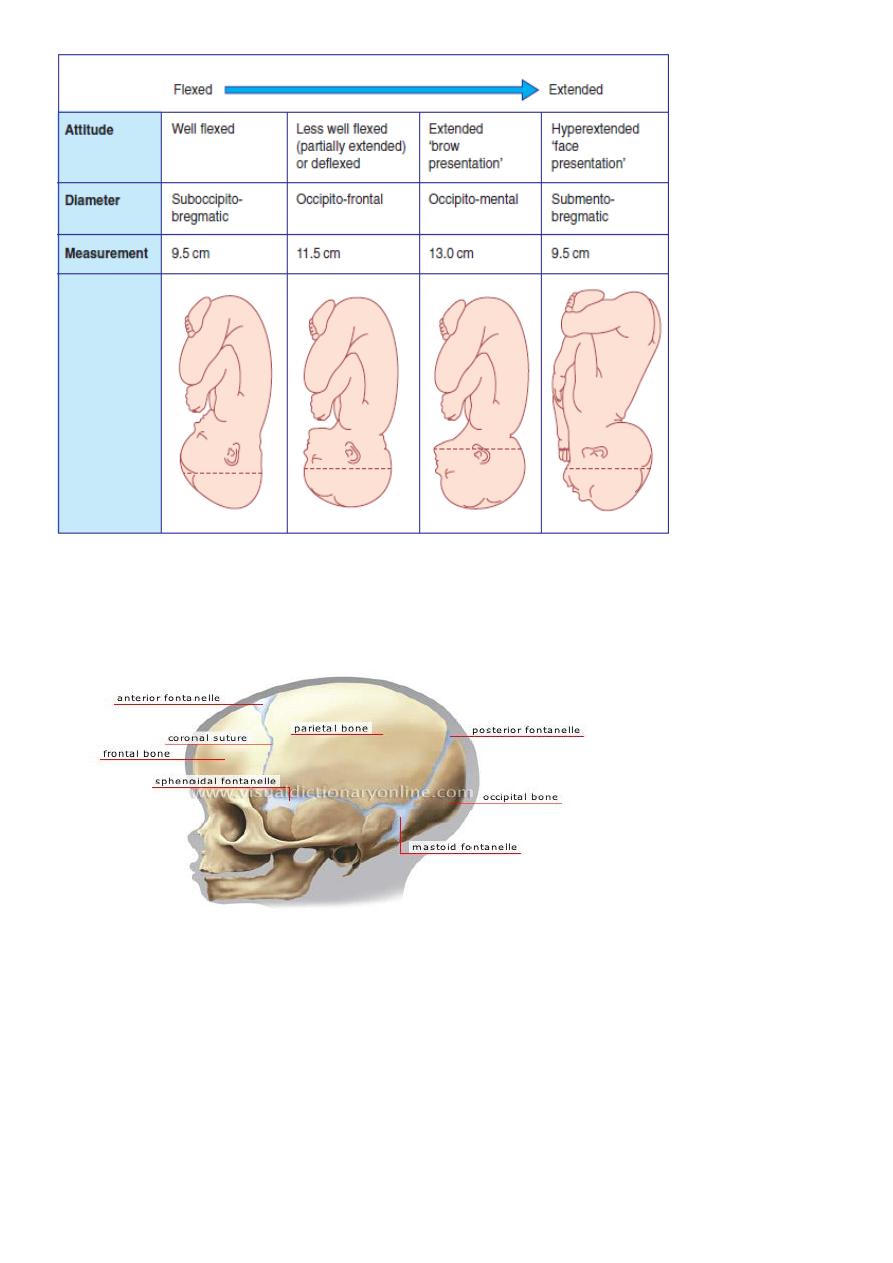
DIAMETERS OF FETAL SKULL
Is divided into vertical, longitudinal & transverse diameters. The fetal head is ovoid in
shape, there are different longitudinal diameters that may present in labour depending on
the attitude of fetal head.
The longitudinal diameter that present in a well flexed head [vertex presentation] is
suboccipito-bregmatic diameter . Ii usually 9.5 cm from suboccipital region to the centre of
the anterior fontanelle.
7
If the head is less well flexed the suboccipitofrontal diameter is involved, is taken from the
suboccipital region to the prominence of the forehead & measures 10cm.
With further extention of the head the occipitofrontal diameter presents which is
measured from the root of the nose to the posterior fontanelle &is 11.5.
The greatest longitudinal diameter that may present is the mento-vertical ,which is taken
from chin to the furthest point of vertex &measures 13cm.This is known as a brow
presentation&is too large to pass through normal pelvis.
Extention of the fetal head beyond this point results in a smaller diameter presenting. The
submento-bregmatic diameter is measured from below the chin to the anterior fontanelle
&measures 9.5 cm, this is clinically a face presentation.
TRANSVERSE DIAMETER is the biparietal diameter is measured from one parietal eminence
to the other, is 9.5cm.
8
