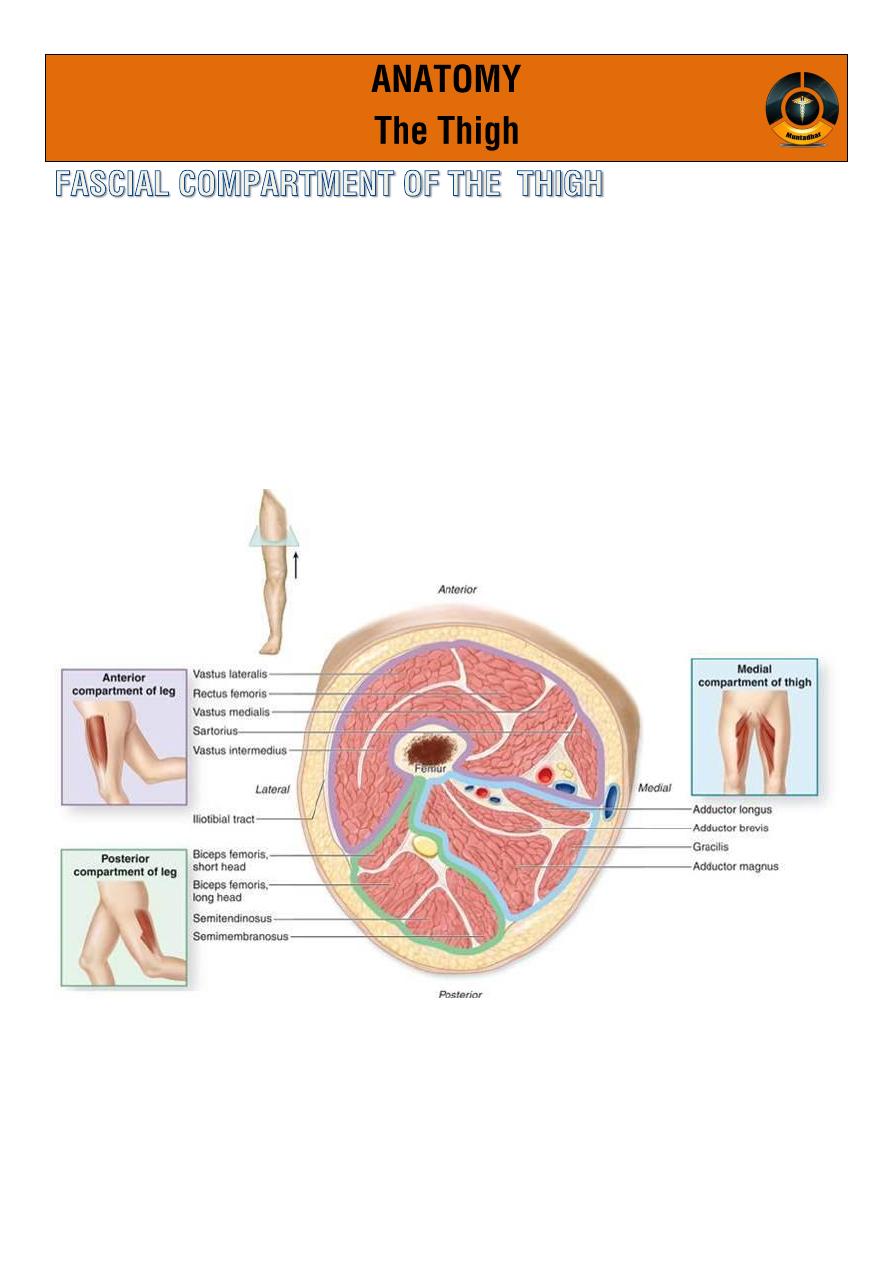
o Three fascial septa pass from the inner aspect of the deep fascial
sheath of the thigh to the linea aspera of the femur .
o by this mean the thigh is divided into 3 compartment each have
M,N,A.
ANT. POST. MED.
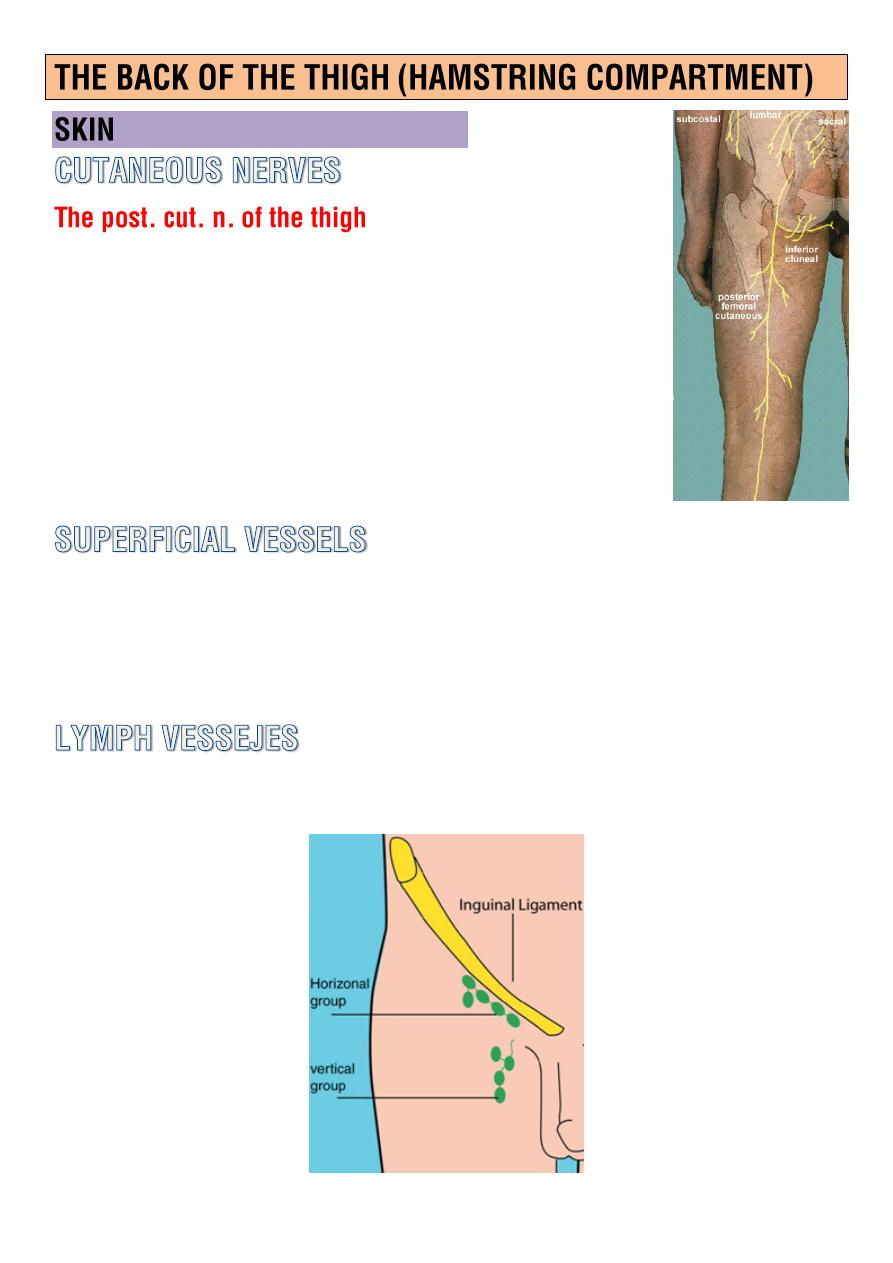
o A branch of the
sacral plexues
leaves the gluteal
region by emerging from beneath the lower border
of the gluteus maximus m.
o It descend on the back of the thigh beneath the
deep fascia pierce it supply the skin.
Small curve around the
med. and lat.
aspect of the thigh drain into the
greater saphenous v.
Drain into
vertical group of superficial inguinal lymph nodes.
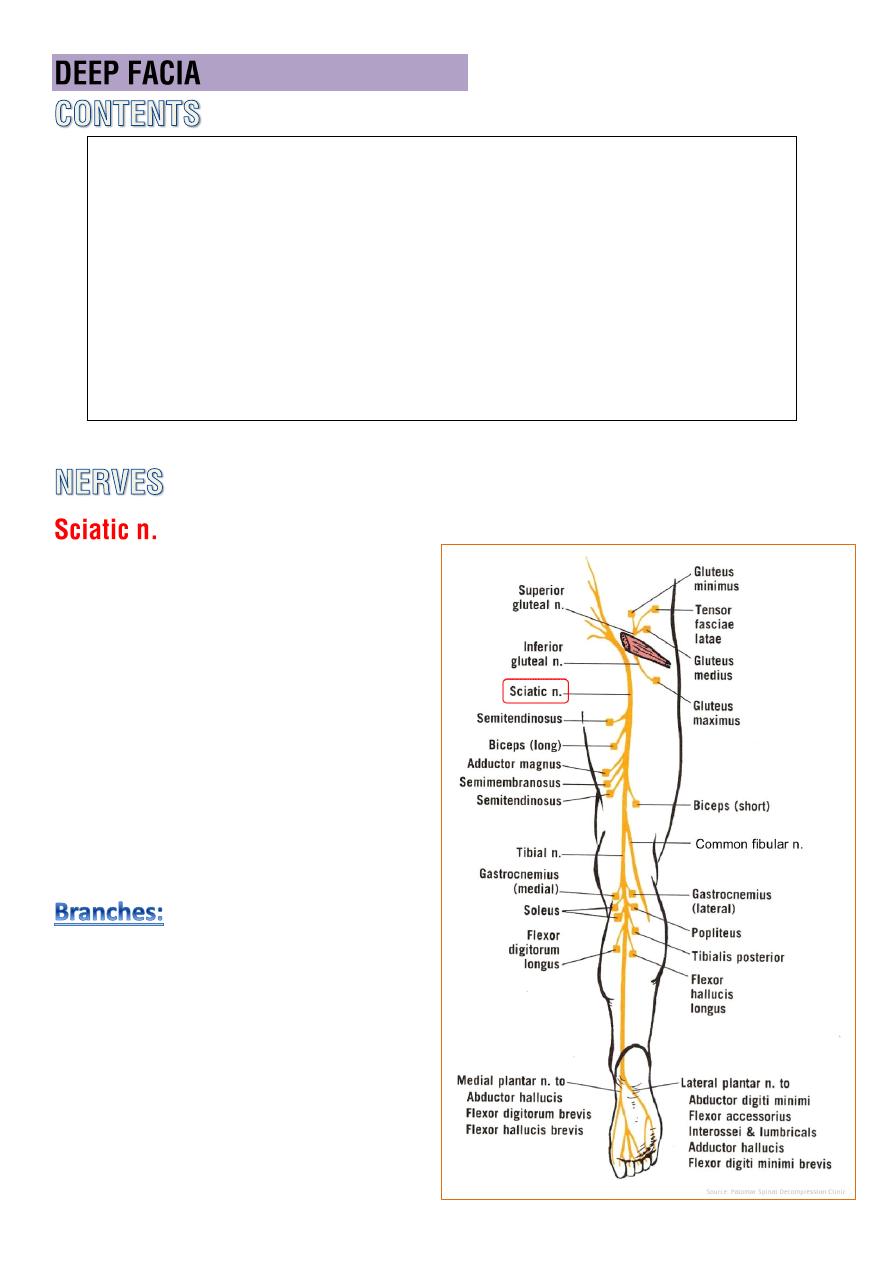
M.
Bicepsfemoris
Semitendinosis
Semimembranous
Small part of adductor magnus.
V.
Branches of Profunda femoris.
N.
Sciatic n.
o it descend in the
mid-line of
post. compartment
of the
thigh .
o ends by dividing into
tibial
and
common peroneal ns
usually just above the
popliteal fossa, sometimes
high up in the gluteal region.
1-
articular
: hip , knee
2-
muscular
: hamstring , ischial
part of add. magnus
3-
terminal
: tibial and common
peroneal
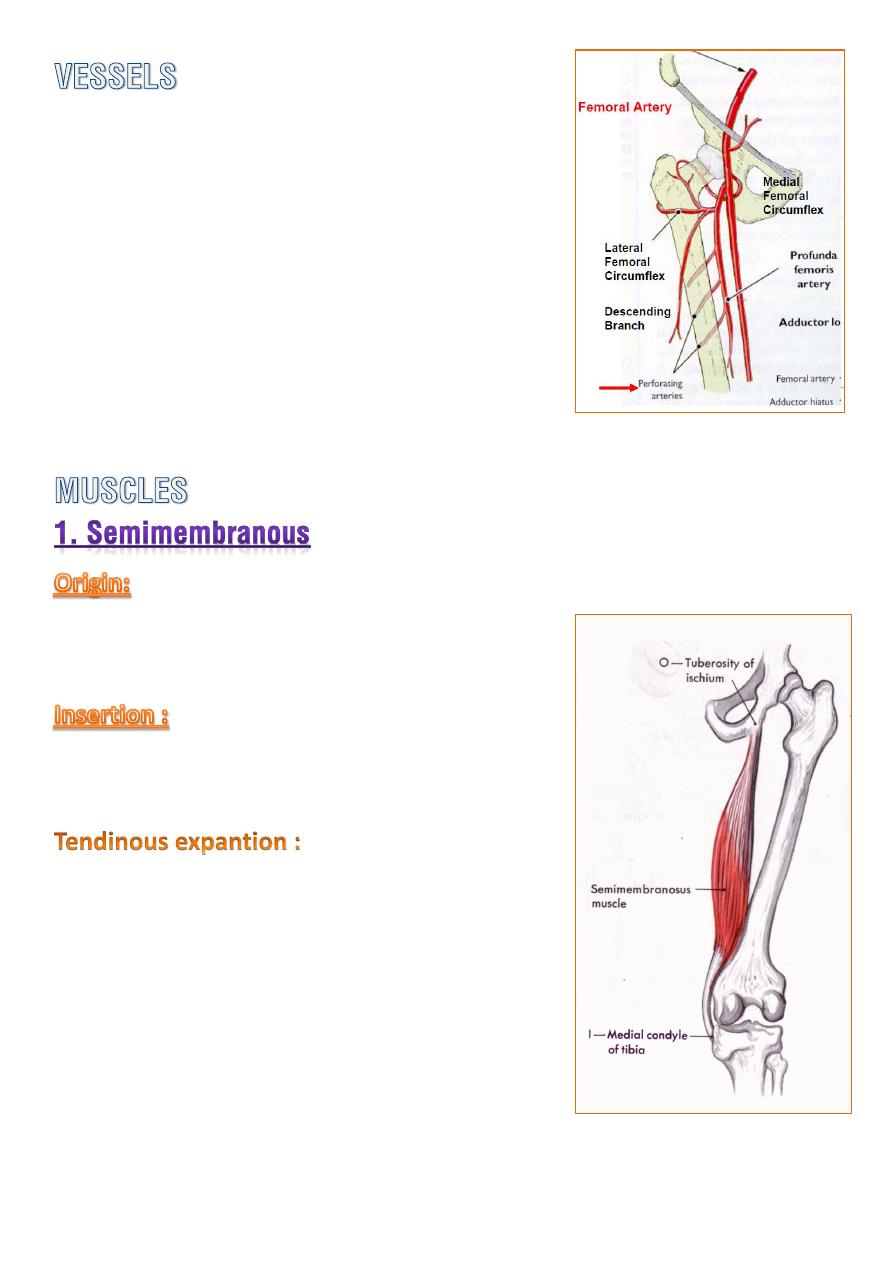
The four
perforating branches
of the
profunda femoris A. provide a rich blood
supply to this compartment.
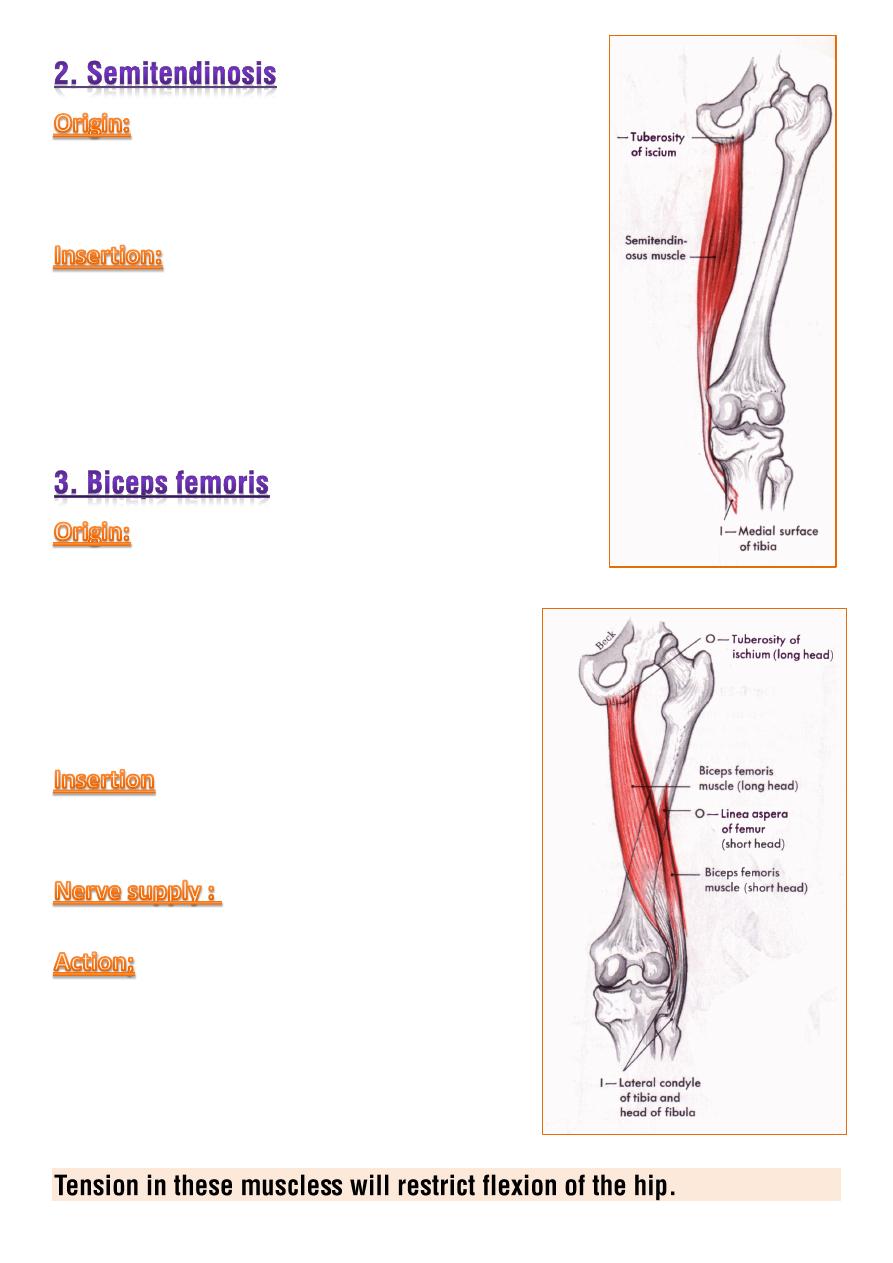
A facet on the ischial tuberosity.
posteromedial aspect of the tibial condyle.
1- up ward to the
lateral femoral condyle
(
oblique popliteal lig.
)
2- downward on to the
soleal line
of the tibia
(forming
popliteal fascia
over the
popliteus m.)
a facet on the ischial tuberosity.
upper part of the medial surface of the tibia
behind the attachment of gracillis and sartorius
tendons.
1-
long head
from a facet on the ischial
tuberosity.
2-
short head
from linea aspera near the
lateral lip and upper part of the lateral
supracondylar line of the femur.
head including apex of the fibula.
sciatic nerve.
1- powerful flexor of the knee
and
extensor of the hip.
2- when the knee is flexed the muscles can
produced a
small amount of med. and
lat. rotation at the knee.
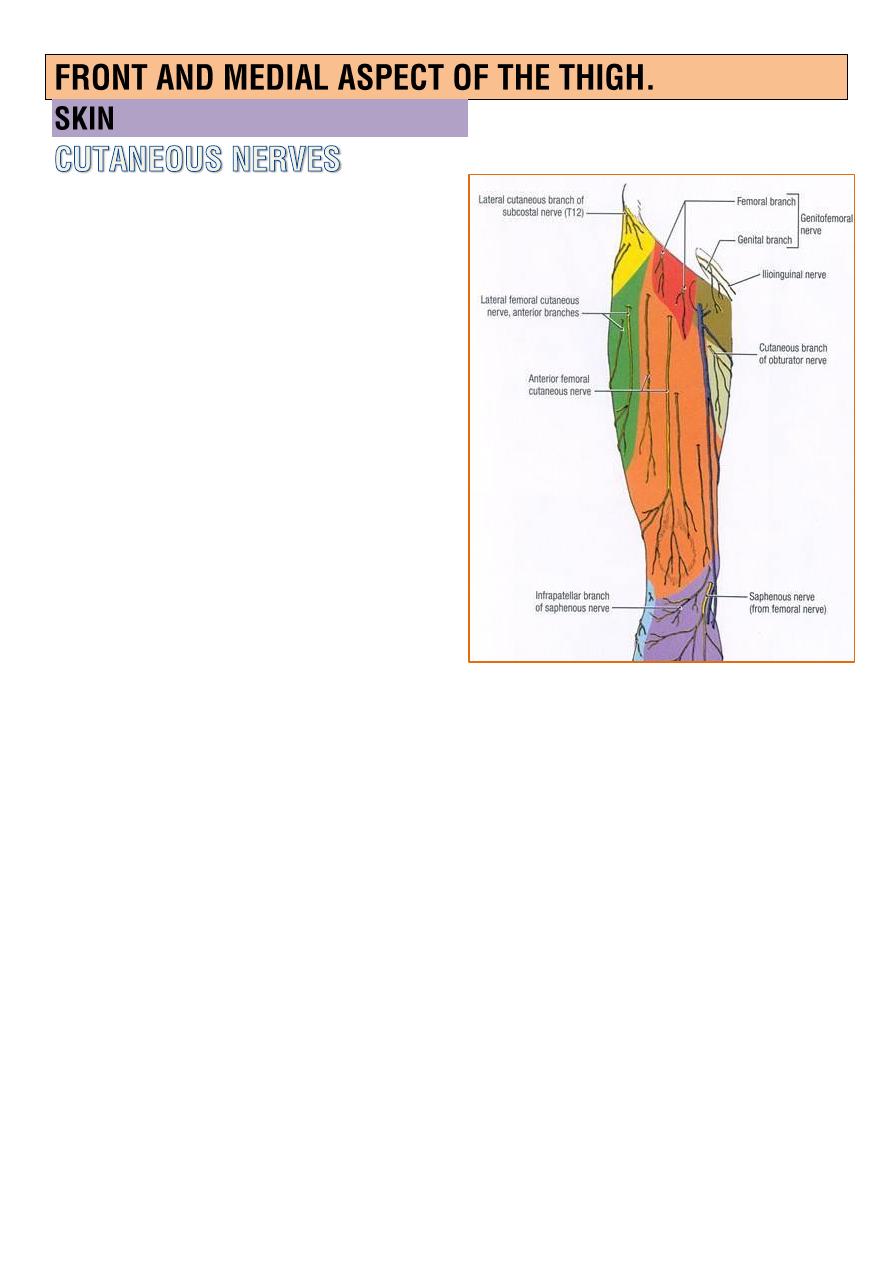
Lateral cut.n.of the thigh(L2,3)
enter the thigh behind the
lateral end of the inguinal
lig.,supplied the skin of the
lateral aspect of the thigh and
knee.
Femoral branch of the
genitofemoral n.(L1,2)
enter the thigh behind the
middle of the inguinal lig.
Ilioinguinal n.(L1)
enter the thigh through the
superficial inguinal ring, supply
the skin of root of the penis,adjacent part of scrotum(or root of
glitoris and adjacent part of labia majus in female)
Medial cut.n.of the thigh
a branch of femoral n. supply the med. aspect of the thigh.
intermediate cut.n.of the thigh
a branch of femoral n. supply the ant. aspect of the thigh.
Patellar plexus
lies in front of the knee, is formed by terminal branches of
o
(
lat. , intermediate , med. ) cut.n.of the thigh
o the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous n.
Saphenous n.
is
the largest cutaneous branch
of the femoral nerve supply the
medial aspect of the thigh..
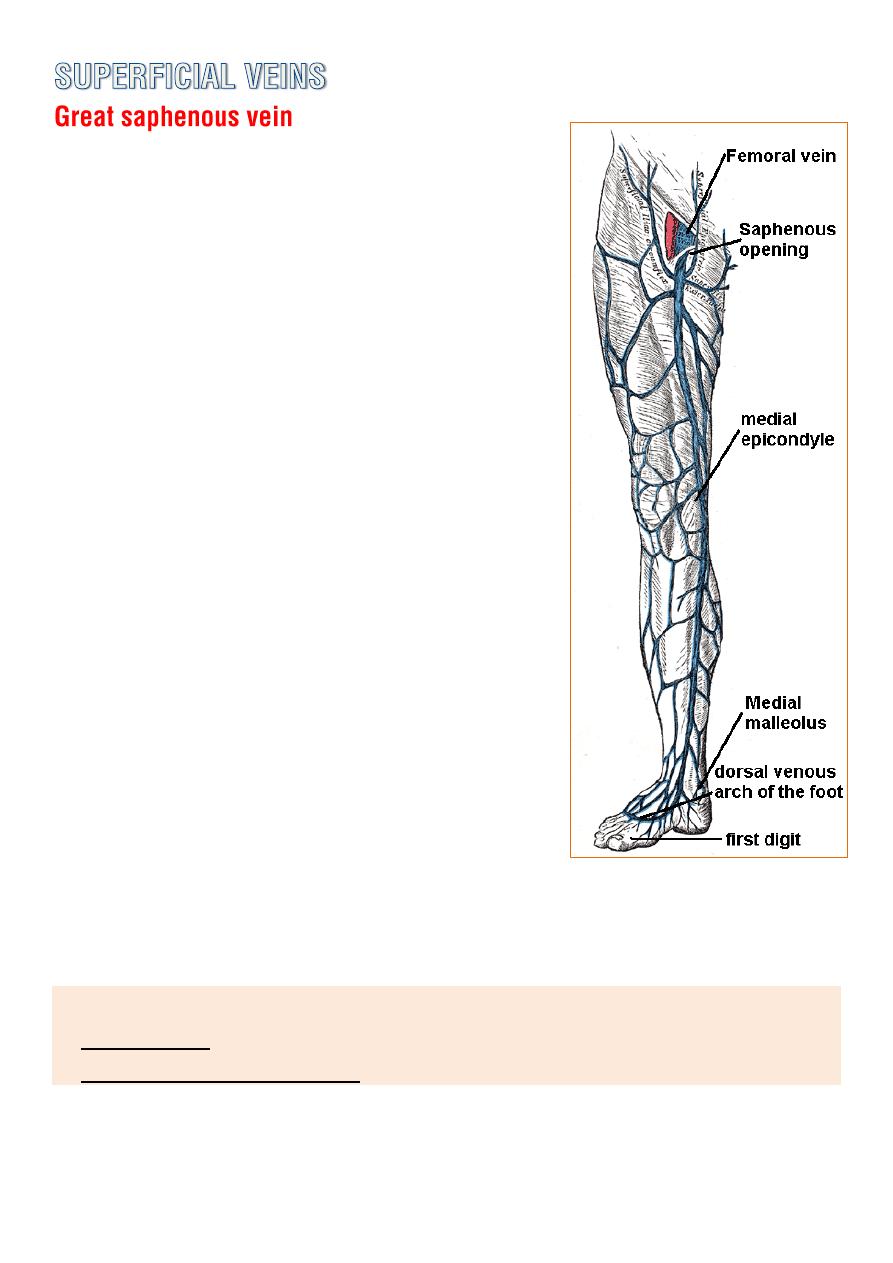
o Drain the
medial end
of the dorsal venous
arch of the foot and passes upward directly
infront of the
medial malleolus
, it pass
through the
lower part of saphenous
opening
in the deep fascia and join the
femoral vein 4cm
below and lateral to the
pubic tubercle.
o It posses numerous valves.
o It connect to the
small saphenous vein
by
one or two
branches that pass behind the
knee.
o
Number of perforating veins
, connect the
great saphenous vein with deep veins
along the medial side of the calf.
o It receive 3 tributaries at the saphenous
opening.
Sup. Circumflex iliac v.
Sup. epigastric v.
Sup. External pudendal v.
o When emergency resuscitation with fluids is necessary, and standard
intravenous access can not be achieved due to venous collapse,
saphenous vein cut down may be necessary
.

o Lies in the superficial fascia below the inguinal lig.
o divided into horizantal and vertical groups.
o lies just below and parallel to the inguinal lig.
o the
medial members
receives superficial lymph vessels from :
ant. abdominal wall below the level of umbilicus
from perineum (uretheral , external genetalia (not testis)
lower half of the anal canal.
o the
lateral
group
receive lymph vessels from :
back below the level of iliac crest.
o lies along the terminal part of great saphenous vein receive majority
of the superficial lymph vessels of the lower limb.
The efferent lymph vessel from S.I.L.N. join D.I.L.N. that lies along the
medial side of the femoral vein and then through femoral canal to
lymph nodes along the external iliac artery.
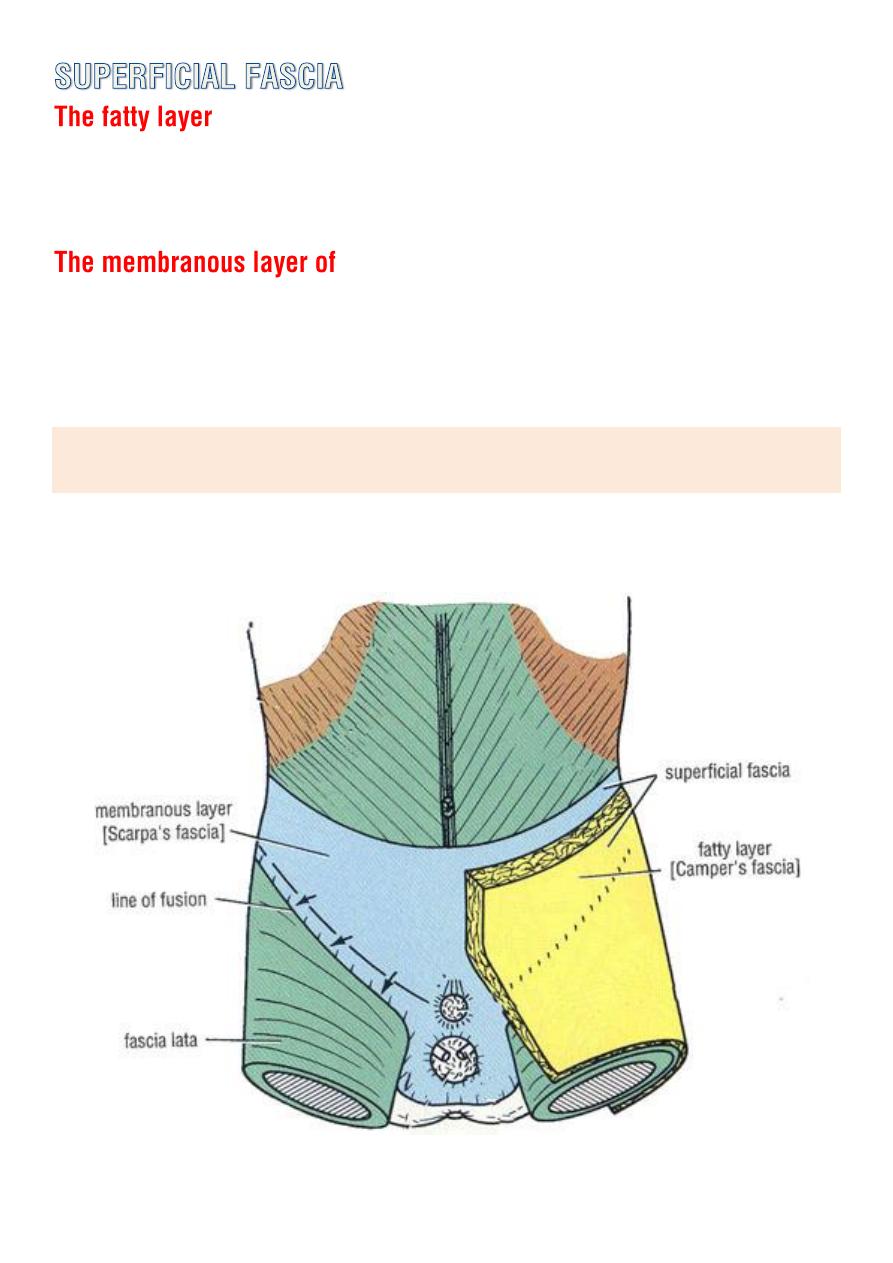
of the superficial fascia (
campers fascia
) of the anterior abdominal wall
extends into the thigh and continue down over the lower limb.
the superficial fascia (
scarpas fascia
) of the ant. abdominal wall extend
in to the thigh and is attached to the deep fascia (
fascia lata
) about
finger breadth below the inguinal ligament .
So rupture of the penile urethra may be followed by extravasations of
urine into the (
scrotum , perineum and penis
) but not the (
thigh fascia
)
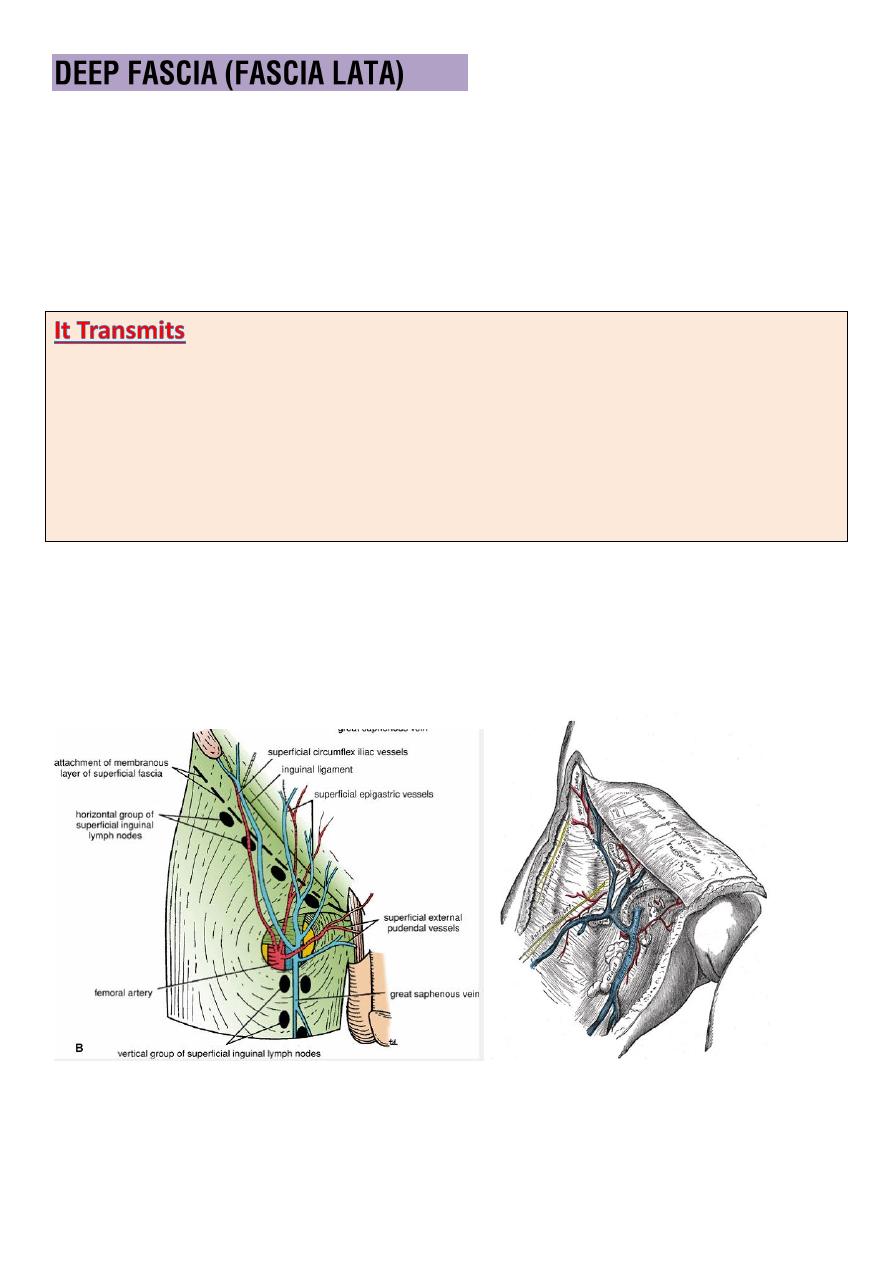
o It enclose the thigh
like a trouser
leg .
o
at its upper end is attached to the
pelvis and its associated
ligaments.
o The
saphenous opening
is an oval opening in the deep fascia in front
of the thigh
4cm below and lateral to the pubic tubercle.
1- the
.
2-
Smaller vessels
(like superficial epigastric artery and superficial
3-
the femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve
4-
lymph vessels.
o It is filled with loose connective tissue called cribriform fascia.
o The deep fascia is attached to the whole length of the inguinal
ligament above.
M:
Sartorius, Iliacus, Psoas, Pectineus, Quadricepsfemoris
A:
Femoral A.
N:
Femoral N.
ant.sup.iliac spine.
upper part of the medial surface of the
tibial shaft.
(
flexion , abduction , lat. rotation
)
of the thigh at the hip.
(
flexion , med.rotation
)
of the leg at the knee joint.
sup.ramus of the pubis
upper end of the linea aspera just
below the lesser trochanter.
(
flex & adduction
)
of the thigh at the hip.
fan shaped m. arise from the
iliac fossa
within the abdomen.
join the
tendon of psoas m.
insert on
lesser trochanter
(
flexion , med. rotation
) of the thigh at the hip
long fusiform m. arise
within the abdomen
and descend in the
thigh.
iliopsoas tendon to the
lesser trochanter
of the femur.
A bursa intervenes between the tendon and the joint and
may communicate with the joint.
(
flexion , med. rotation
) of the thigh at the hip
Consist of
four muscles
which have a common tendon of insertion into
the (
upper, lateral and medial
) border of the patella and then via
the
ligamentum patellae
into the
tubercle of the tibia.
o
Straight head :
from anterior inferior
iliac spine
o
Reflected head :
from ilium above
acetabulum.
from :
o intertrochanteric line
o the base of greater trochanter
o lat.lip of linea aspera of the femur
o lateral deep fascial septum.
from :
o intertrochanteric line
o medial lip of the line
a aspera
o medial fascial septum
from
ant. and lat. surface
of the shaft of
the femur.
powerful extensor of the knee joint.
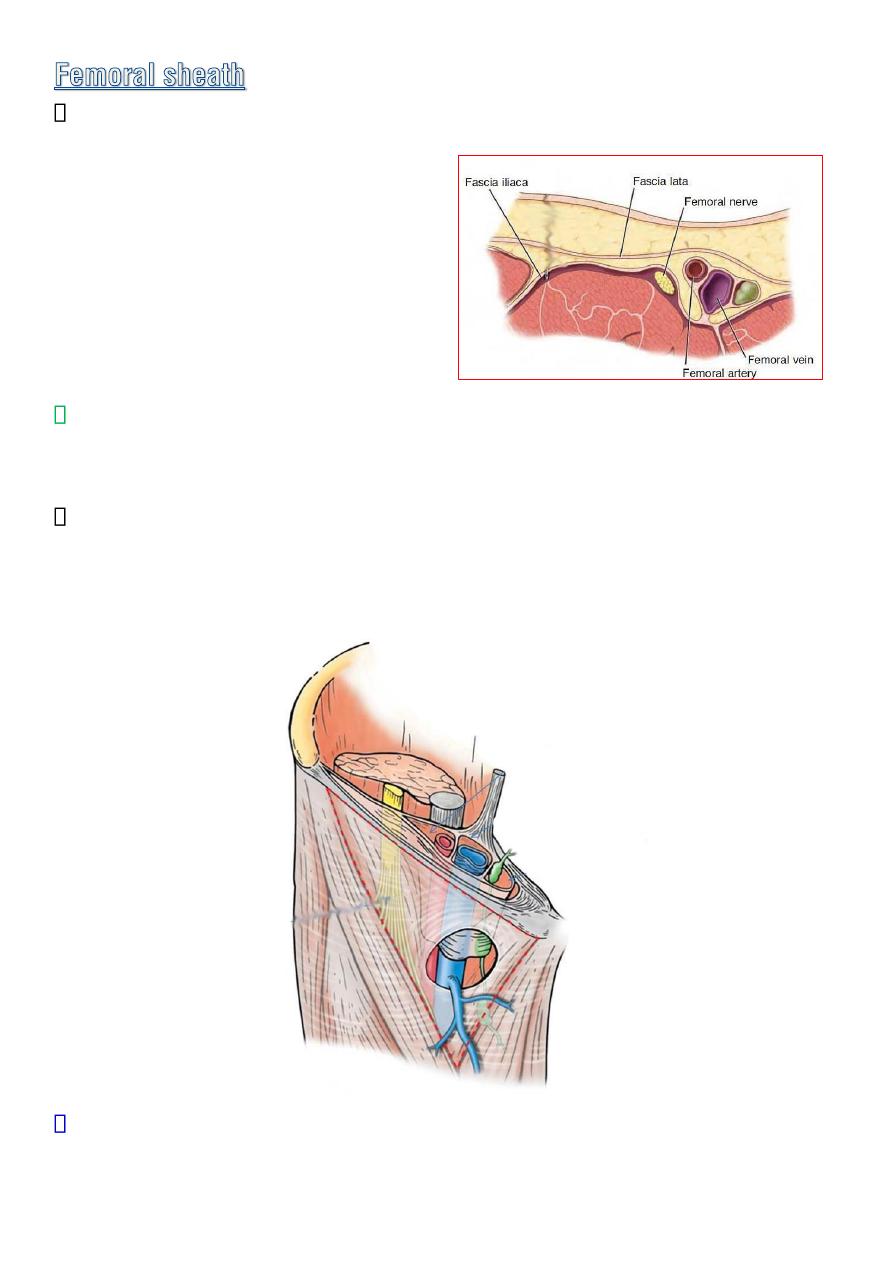
Is a downward protrusion in to the thigh of the fascial envelop lining
the abdominal wall .
Its anterior wall
:
is continues
with the
fascia transversalis
Its posterior wall :
is continues
with the
fascia iliaca .
The sheath surrounds the
femoral vessels and lymphatics
for about
2.5cm below the inguinal lig.
Septa divided it into three compartment containing :
Laterally:
the femoral
A.
Centerally:
The femoral
V.
Medially:
fatty connective tissue
and
lymph nodes
The most medial compartment is known as the
femoral canal
which
provides a
loose dead space in to which femoral vein can expand
during times of increased venous return from the lower limb.

o Small medial compartment about
1.3cm long
for lymphatic.
o its upper opening reffered as
femoral ring.
o The femoral septum which is a condensation of extraperitoneal tissue
closes the ring.
1-
fatty connective tissue
2- all the efferent
lymph vessel
from the deep inguinal lymph node
3-
one of the deep inguinal lymph nodes
drain directly from clitoris in
female and glans penis in male.
Ant.
inguinal lig.
Post.
superipr ramus of the
pubis.
Med
.
the lacunar lig.
Lat.
the fibrous septum on the medial side of the the femoral vein
.
The femoral sheath is adherent to the walls of the blood vessels and
inferiorly blend with tunica adventitia of these vessels.
The lower end of the canal is normally closed by the
adherent of its
medial wall to the tunica adventitia of the femoral vein.
It lies closes to the saphenous opening in the deep fascia of the thigh
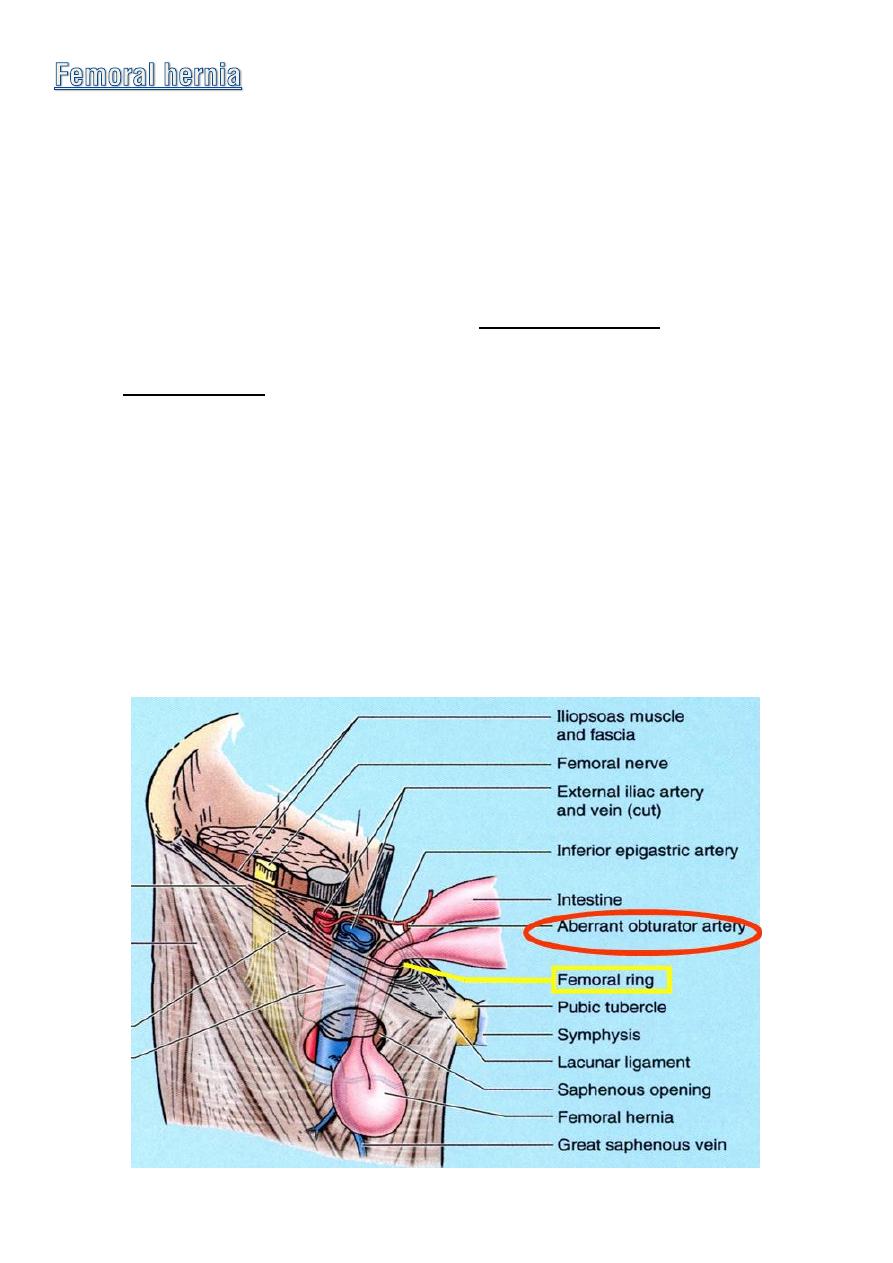
◊
The most medial part of the sheath is
not adherant
to the walls of
lymphatic vessels .
◊
it is this site that is potentially weak area in the abdomen so protusion
of peritoneum could be forced down the femoral canal pushing the
femoral septum before it ,such condition is known as a
femoral hernia.
◊
Femoral hernias occur just below the inguinal ligament, when
abdominal contents pass through a naturally occurring weakness called
the femoral canal.
◊
Femoral hernias are a relatively
uncommon type
, accounting for only
3% of all hernias.
◊
While femoral hernias can occur in
both males and females
, almost all
of them develop in women because of the
wider bone structure of the
female pelvis.
◊
Femoral hernias are more common in adults than in children.
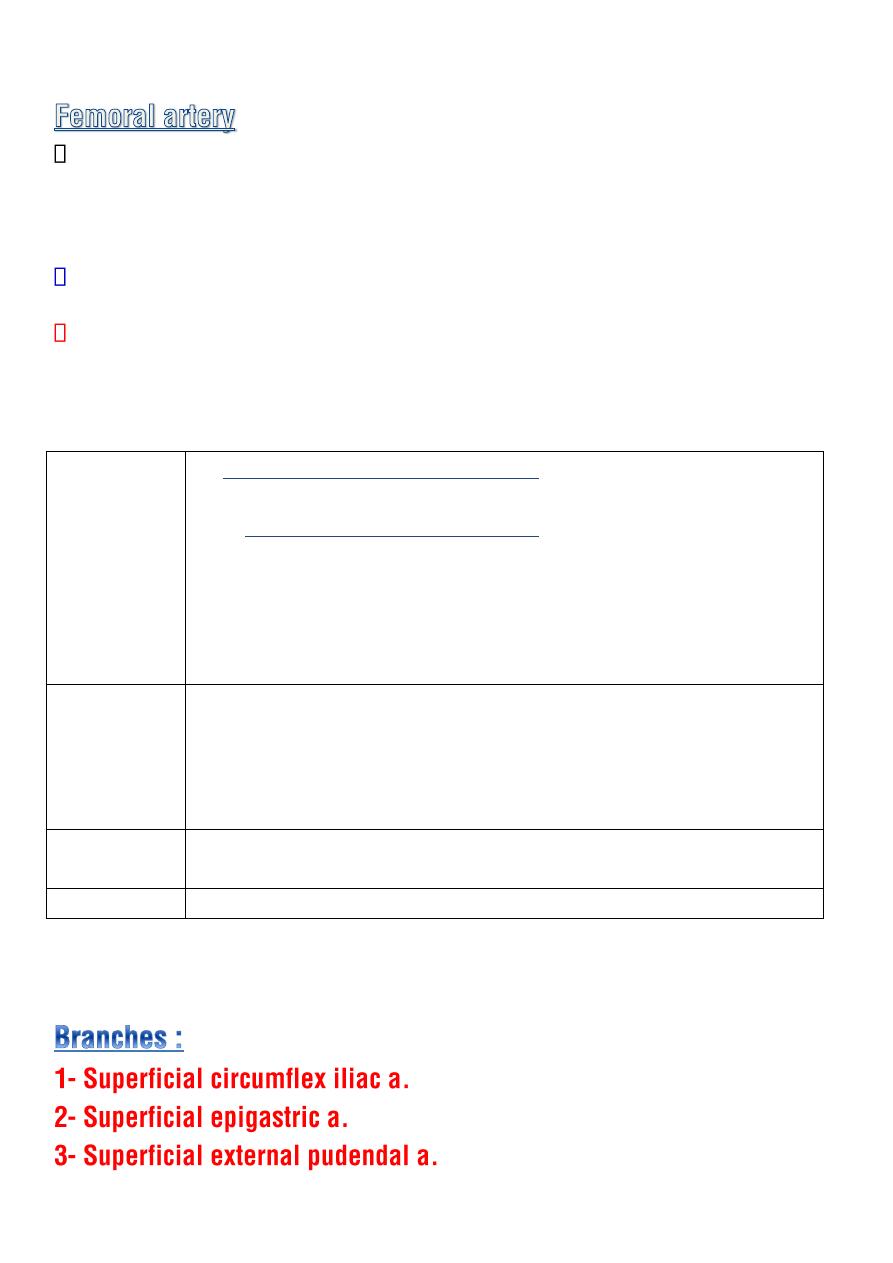
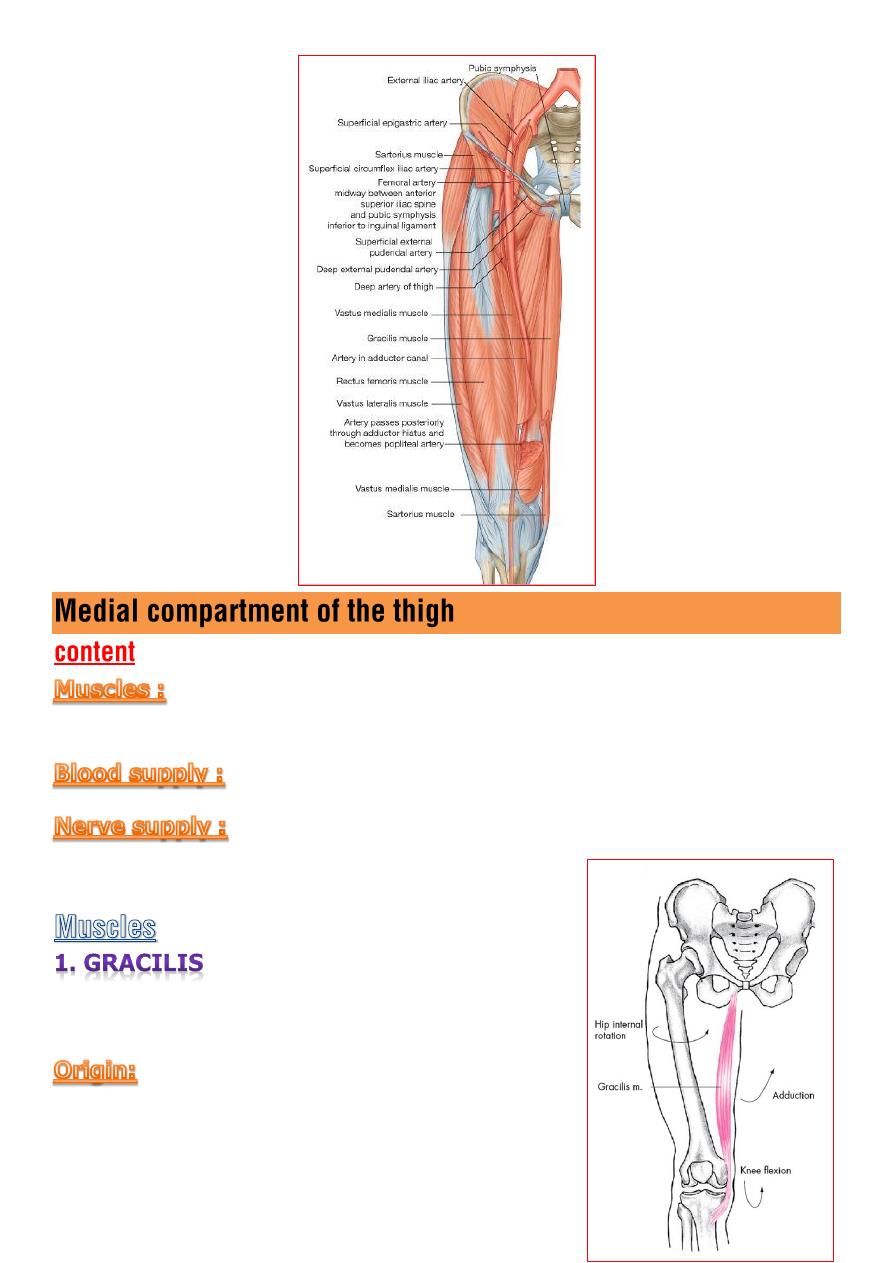
Enter the thigh behind the inguinal lig. as a continuation of the
external iliac artery
mid-way between the ASIS and the symphysis
pubis (
mid inguinal point
)
It is the main arterial supply to the lower limb.
It descend almost vertically toward the
adductor tubercle of the femur
and ends at opening in the adductor magnus
10 cm above the knee
joint
by entering the popliteal space as the
popliteal artery.
Anteriorly
♦ in the upper part of its course
it is superficial and is
covered by skin and fascia.
♦
In the lower part of its course
it passes behind the
sartorius.
♦ It is related to the ant. wall of the femoral sheath
above and is crossed by the medial cutaneous n. of the
thigh and the saphenous n. below.
Posteriorly
♦ the artery lies on the
psoas
which separate it from the
hip joint ,the
pectineus
and the
adductor longus
.
♦ the femoral vein intervenes between the artery and the
adductor longus.
Medially
it is related to the femoral vein in the upper part of its
course.
Laterally
the femoral n. and its branches.

♦ is a large and important branch that arise from the
lateral side of the
femoral a.
about
4cm below the inguinal lig
.
♦ it passes medially behind the femoral vessels and enters the medial
fascial compartment of the thigh by running
behind the adductor
longus.
♦
It ends by becoming the
fourth perforating a.
At its origin it gives off the
med. and lat. circumflex
arteries and
during the course it gives off
three perforating arteries.
♦
is a small branch that arise from the femoral a.
near its termination
♦
it assist in
supplies the knee joint.
In the femoral triangle the femoral vein lies medial to the artery.
in most of the adductor canal it is post.
and in the popliteal fossa the vein retain this relationship to the artery.
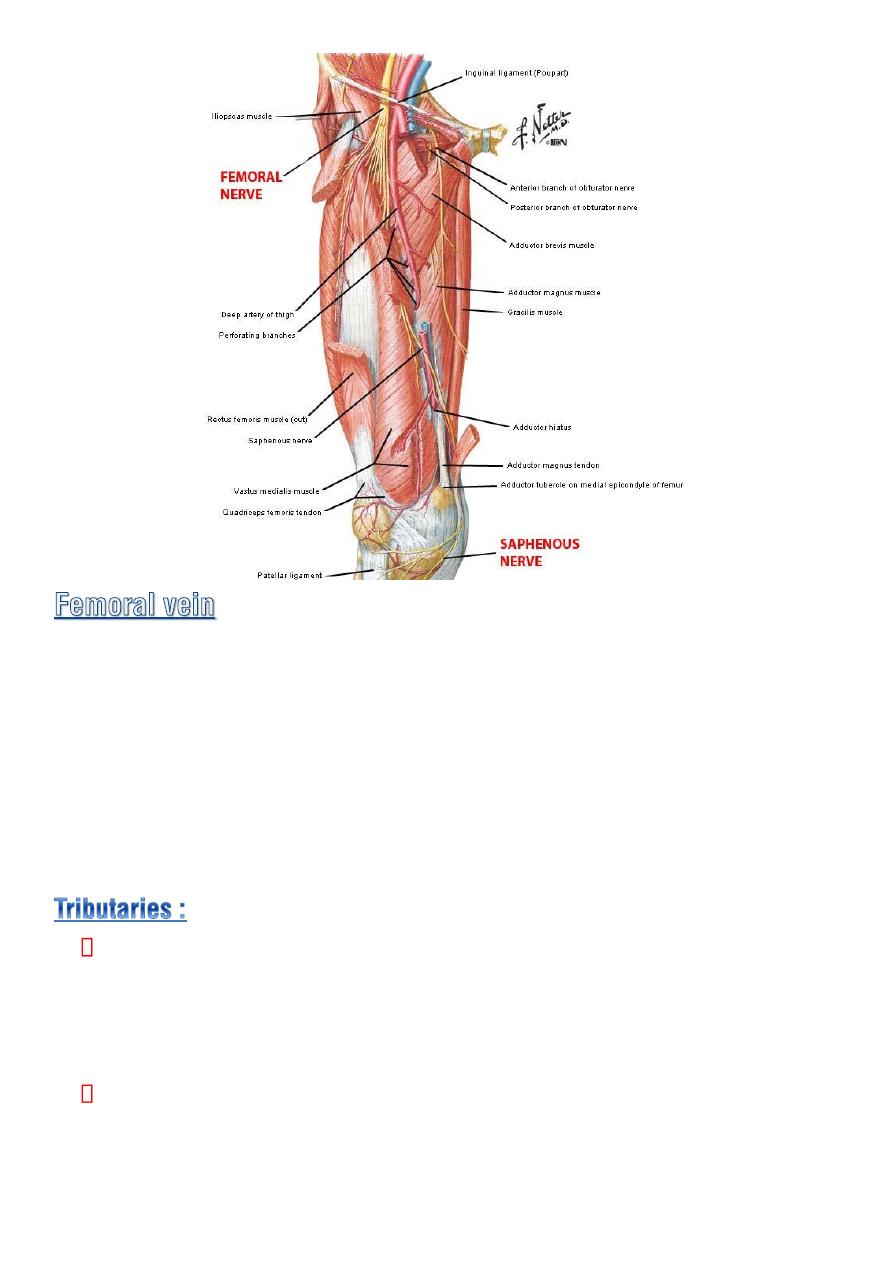
♦ It enters the thigh by passing throgh the
opening in the adductor
magnus
as a continuation of the popliteal vein .
♦ it ascend through the thigh lying at first on the lat. side of the artery
then post.to it and finally on the medial side.
♦ it leaves the thigh in the middle compartment of the femoral sheath
then pass behind the inguinal lig. to become the external iliac vein.
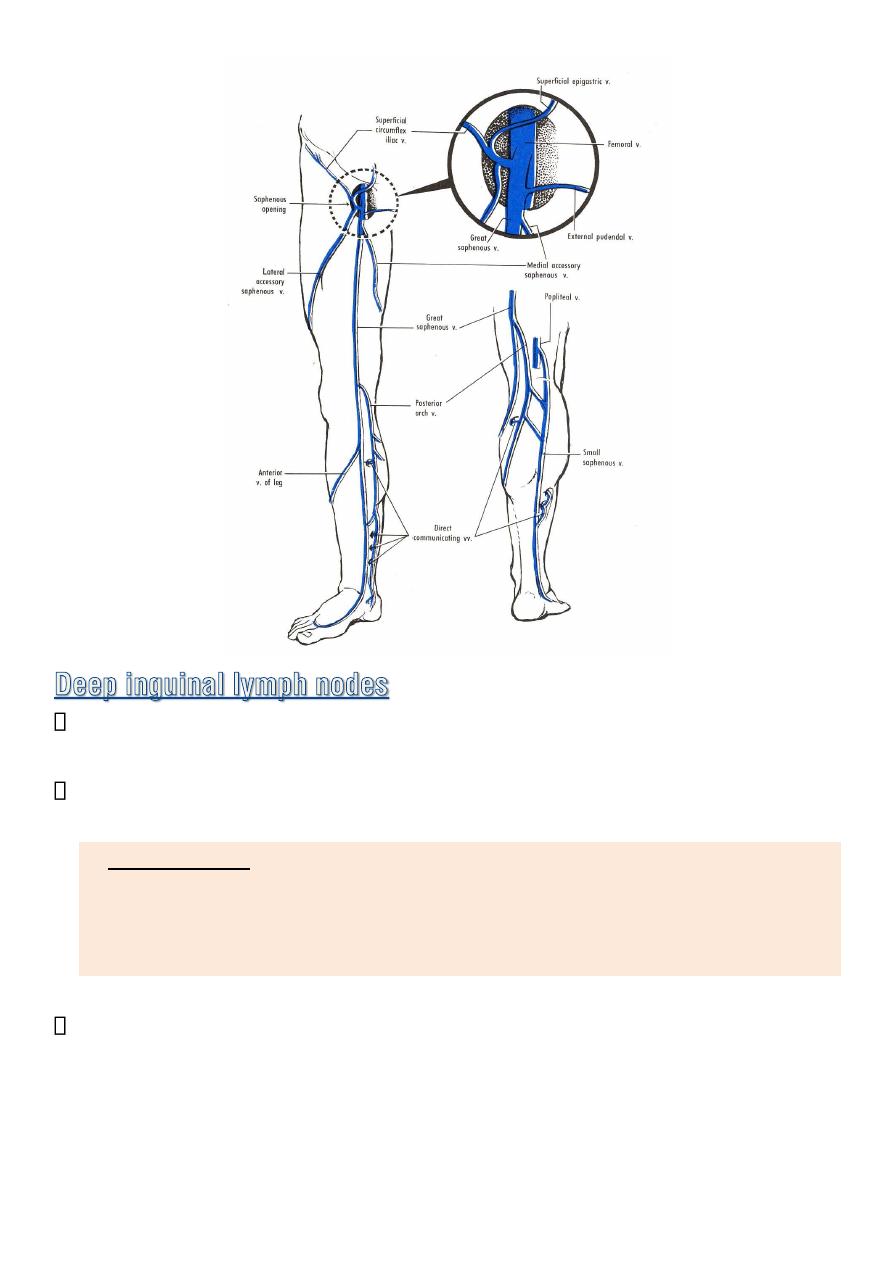
Great saphenous vein. Its tributaries
Superficial circumflex iliac v.
Superficial epigastric v.
external pudendal v.
Veins that correspond to branches of the femoral a.
Commonly are three along medial side of the terminal part of the
femoral vein.
the most superior is usually located in the femoral canal .
♦ They receive all lymph from
superficial group
via lymph vessels that
pass through the cribriform fascia of the saphenous opening.
♦ Also receive lymph from deep structures of the lower limb.
The efferant lymph from deep nodes ascend in to the abdominal cavity
through the
femoral canal
and drain into the
external iliac nodes.
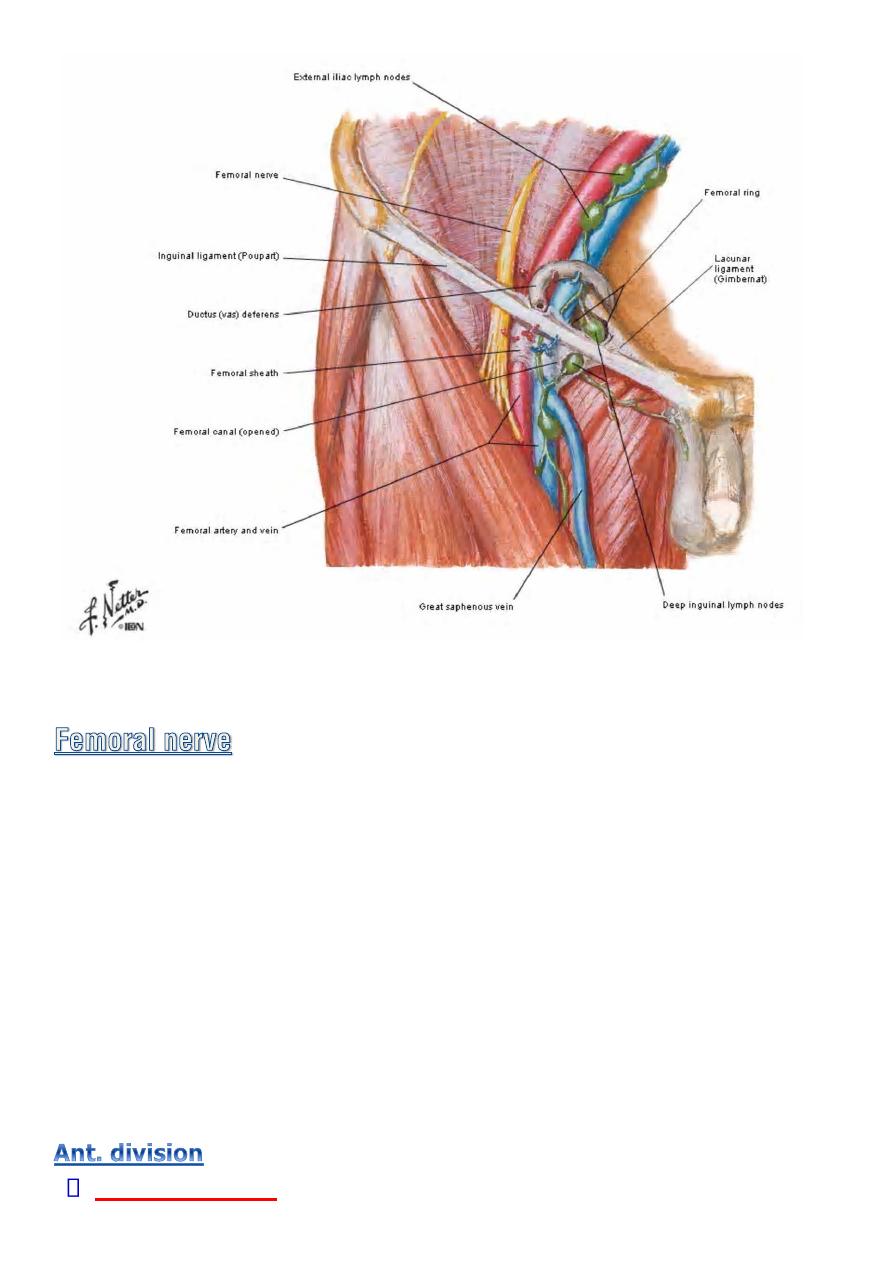
◊ Is the largest branch of the
lumbar plexus
.
◊ it emerges from the lateral border of the psoas muscle with in the
abdomen and passes down ward in the interval between psoas and
iliacus.
◊ Enter the thigh
lateral to the femoral A. and the femoral sheath
behind
the inguinal lig.
◊ About 4cm below the inguinal lig , it terminates by dividing into
anterior and posterior division.
◊ it supplies all the muscles of the ant. compartment of the thigh.
Two cutaneous

◊ medial cut. n. of the thigh
◊ intermediate cutaneous n. of the thigh.
Two muscular
◊ Sartorius
◊ Pectineus
Cutaneous
◊ Saphenous n.
♦ cross the
femoral a.
from its lateral to medial side .
♦ emerge between the tendons of
sartorius and gracilis
.
♦ then runs down the medial side of the leg compaining with
the great saphenous vein.
♦ it passes in front of the medial malleolus along the medial of
the foot.
Muscular :
◊ Rectus femoris
◊ Vasti muscles.
Articular
◊ hip and knee joints.
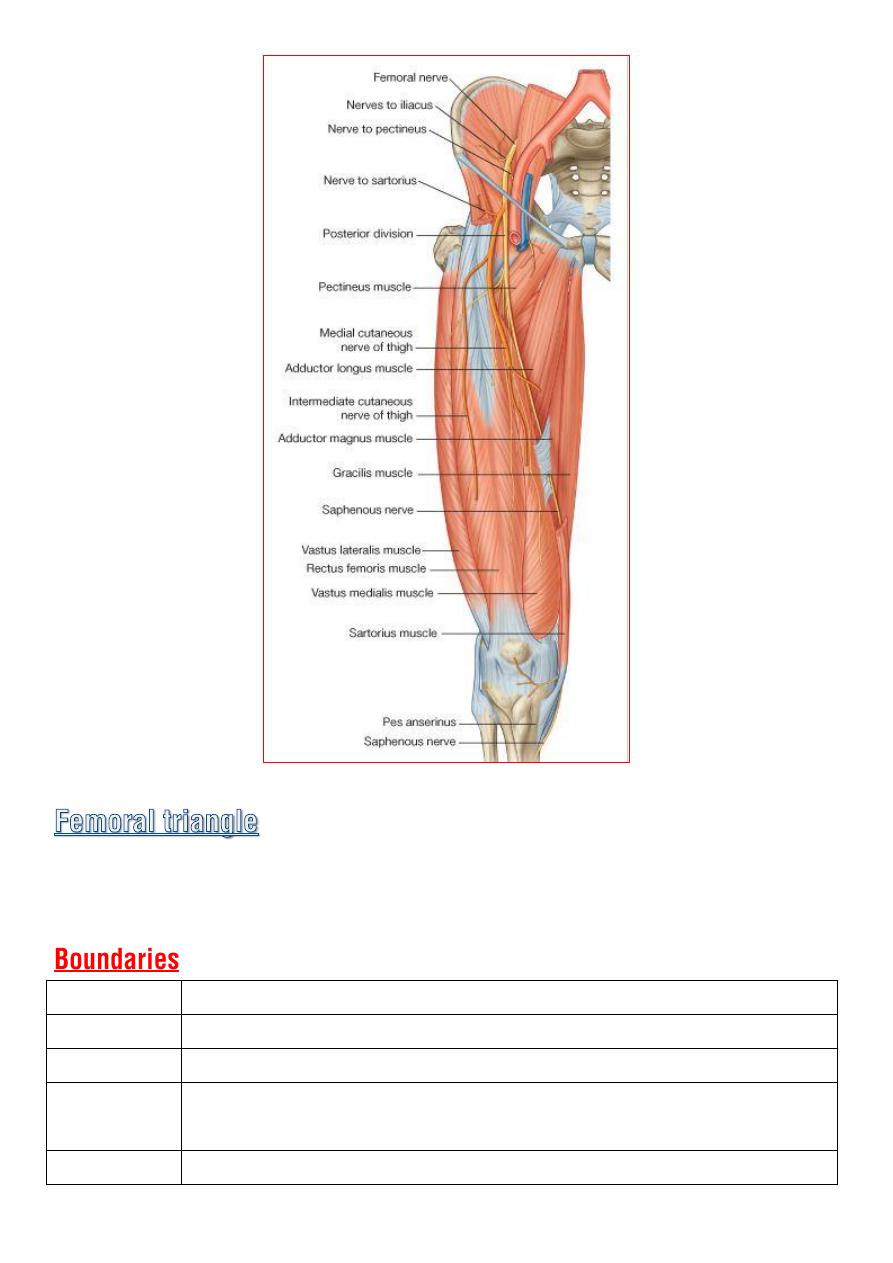
Is a triangular depressed area situated in the
upper part of the medial
aspect
of the thigh just below the inguinal lig.
Superiorly Inguinal lig.
Laterally
Sartorius m.
Medially
lateral border of the adductor longus m.
Floor
is a gutter shaped and formed from lateral to medial by :
iliopsoas , pectineus and adductor longus
Roof
Skin and fascia of the thigh.

from lateral to medial :
terminal part of the
femoral nerve
and its
branches
femoral sheath
♦
femoral
artery
and its
branches
♦
femoral
veins
and its
tributaries
♦
deep inguinal lymph nodes
1-
Since the femoral triangle provides easy access to a major artery,
is often performed by entering the femoral artery
at the femoral triangle.
2-
Heavy bleeding
in the leg can be stopped by applying pressure to
points in the femoral triangle.
3-
Medial to it lies the femoral vein. Thus the femoral vein, once located,
allows for
femoral venipuncture .
4-
The
positive pulsation
of the femoral artery signifies that the heart is
beating and also blood is flowing to the lower extremity.
5-
The nerve is more lateral than the vein. This must be remembered
when venous or arterial samples are required from the femoral vessels.
◊ Is an intermuscular cleft situated on the medial aspect of the middle
third of the thigh .
◊ commences above the apex of the femoral triangle and ends below at
the opening in the adductor magnus.
The anteromedial wall (roof) :
is formed by a fibrous sheath deep to
the Sartorius .
The posterior wall :
adductor longus and magnus.
The lateral wall :
vastus medialis .
♦ Terminal part of the femoral A.
♦ Femoral V.
♦ Deep lymph vessels
♦ Saphenous N.
♦ N.to vastus medialis.
Gracilis, Adductor Longus, Adductorbrevis, Adductor magnus
and
Obturator externus.
Profunda femoral A.
and
obturator A.
Obturator N.
lies on the medial of the
thigh & knee.
outer surface of the inferior ramus of
the pubis
and
the ramus of the ischium
.
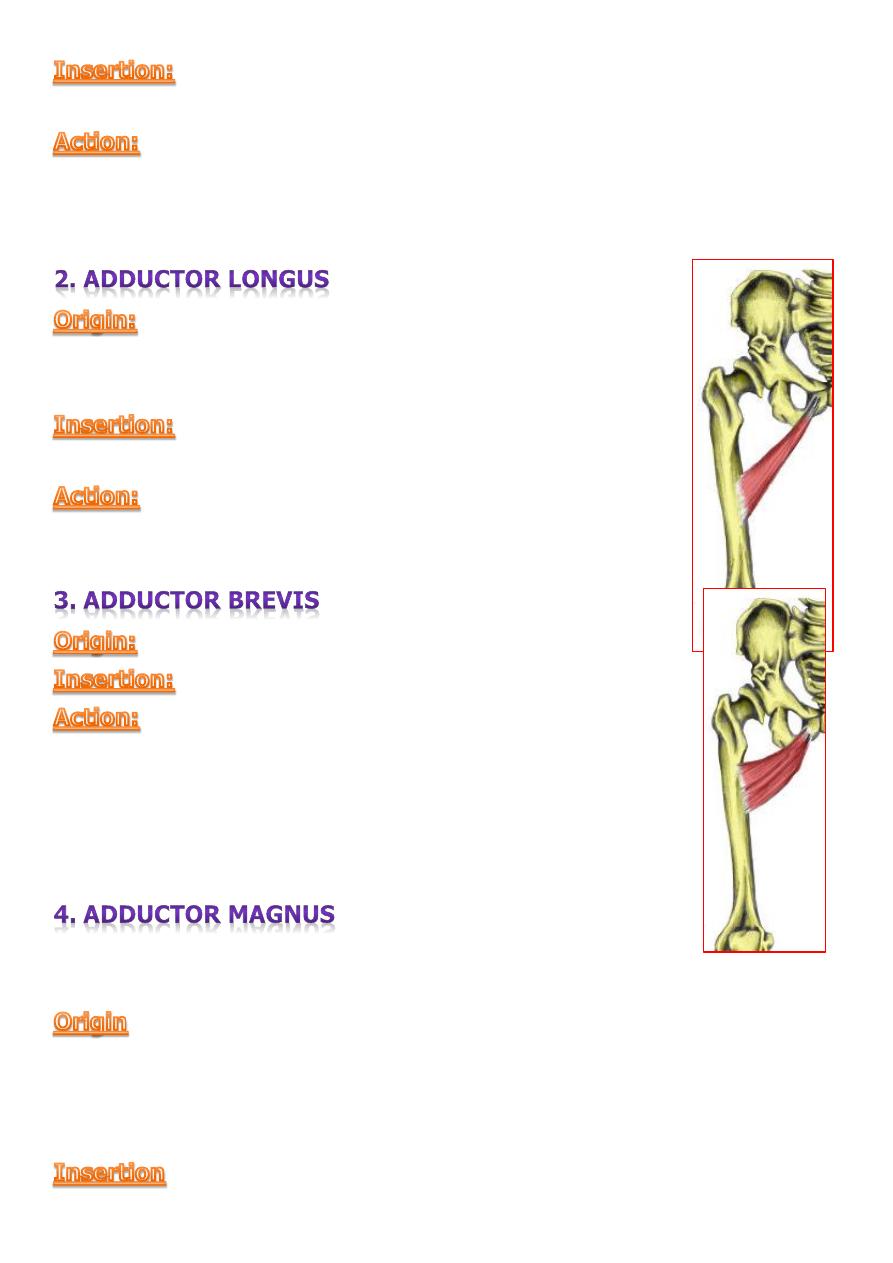
upper part of the medial surface of the tibial shaft.
adduction
of the thigh at the hip.
Flexion
of the leg at the knee.
From the front of the pubis
below and medial
to
the pubic tubercle.
medial lip of the linea aspera.
♦ adduction of the thigh at the hip
♦ Assist lateral rotation
outer surface of the inferior ramus of the pubis
linea aspera.
♦ adduction of the thigh at the hip
♦ Assist lateral rotation.
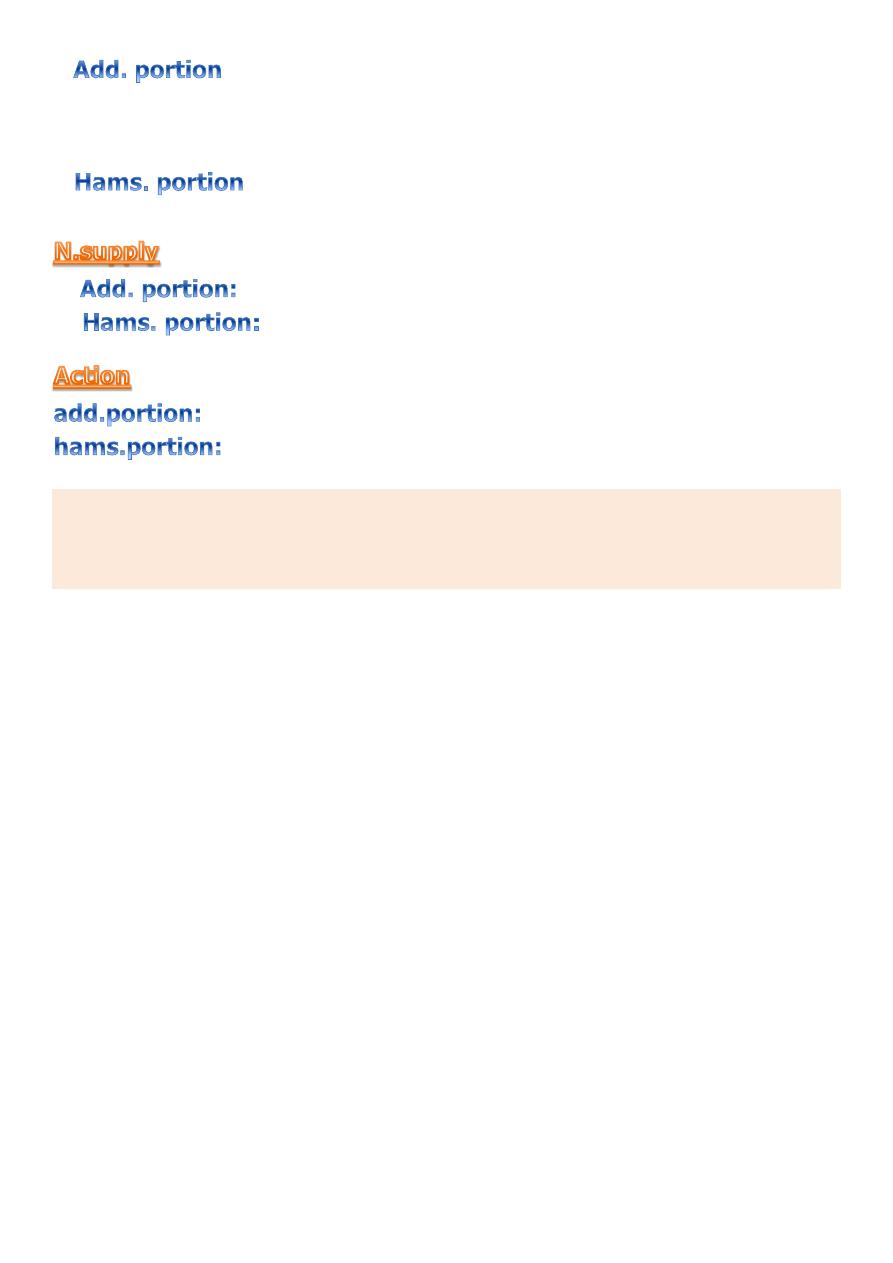
♦ It is large muscle consist of adductor and hamstring
portion.
◊ outer surface of the inferior ramus of the pubis
◊ the ramus of the ischium
◊ ischial tuberosity.
posterior surface of the femur from quadrate tubercle above along
the linea aspera to the medial supracondylar ridge below.
adductor tubercle on the medial condyle of the femur.
obturater N.
sciatic N.
adduct the thigh at the hip
and
assist lateral rotation.
extend the thigh.
There is a gap
adductor hiatus
in the attachment of the muscle to the
medial supracondylar ridge which permit the femoral vessels to pass from
the adductor canal down ward in to the popliteal space.
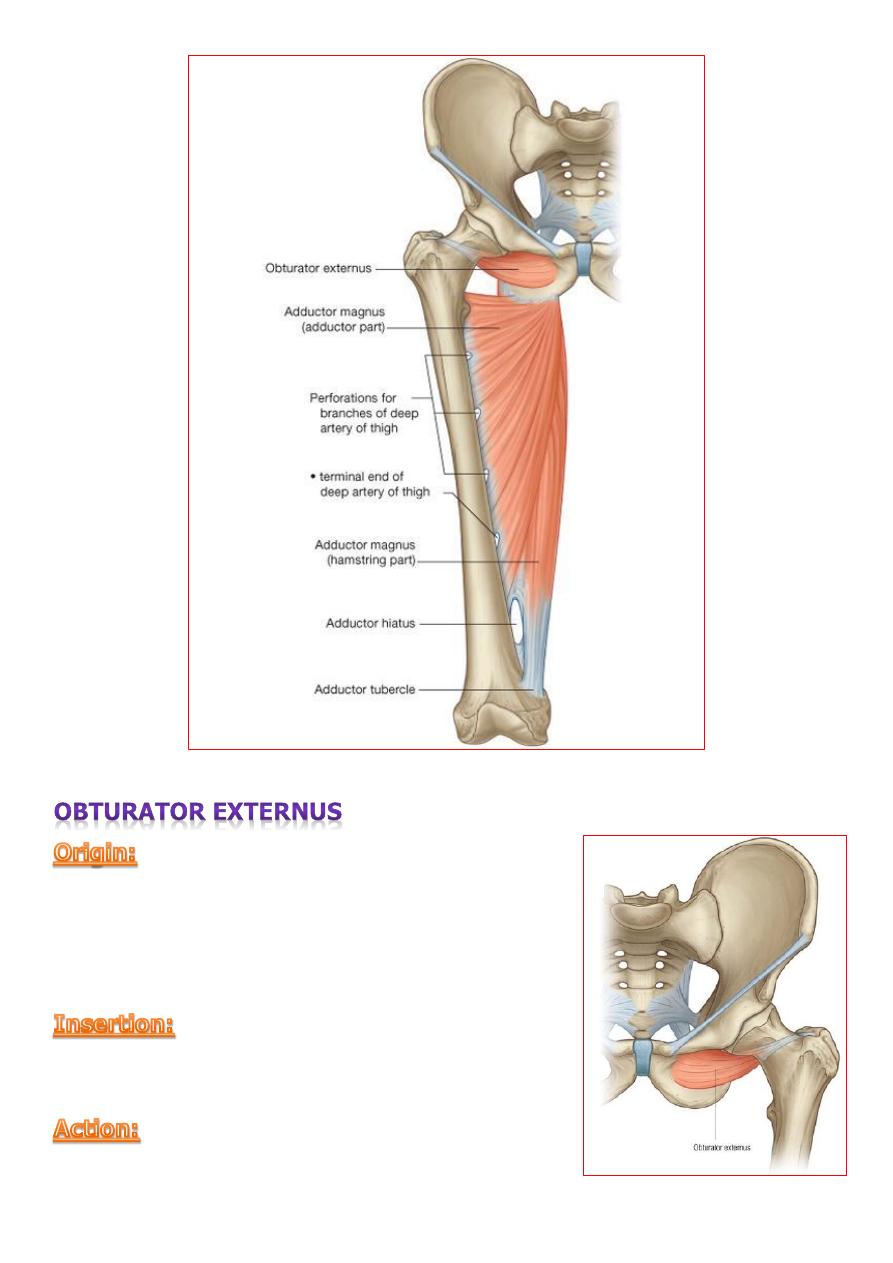
from outer surface of the obturater
membrane and the adjacent of the pubic and
ischial rami.
medial surface of the greater trochanter.
lateral rotation of the thigh at the hip..
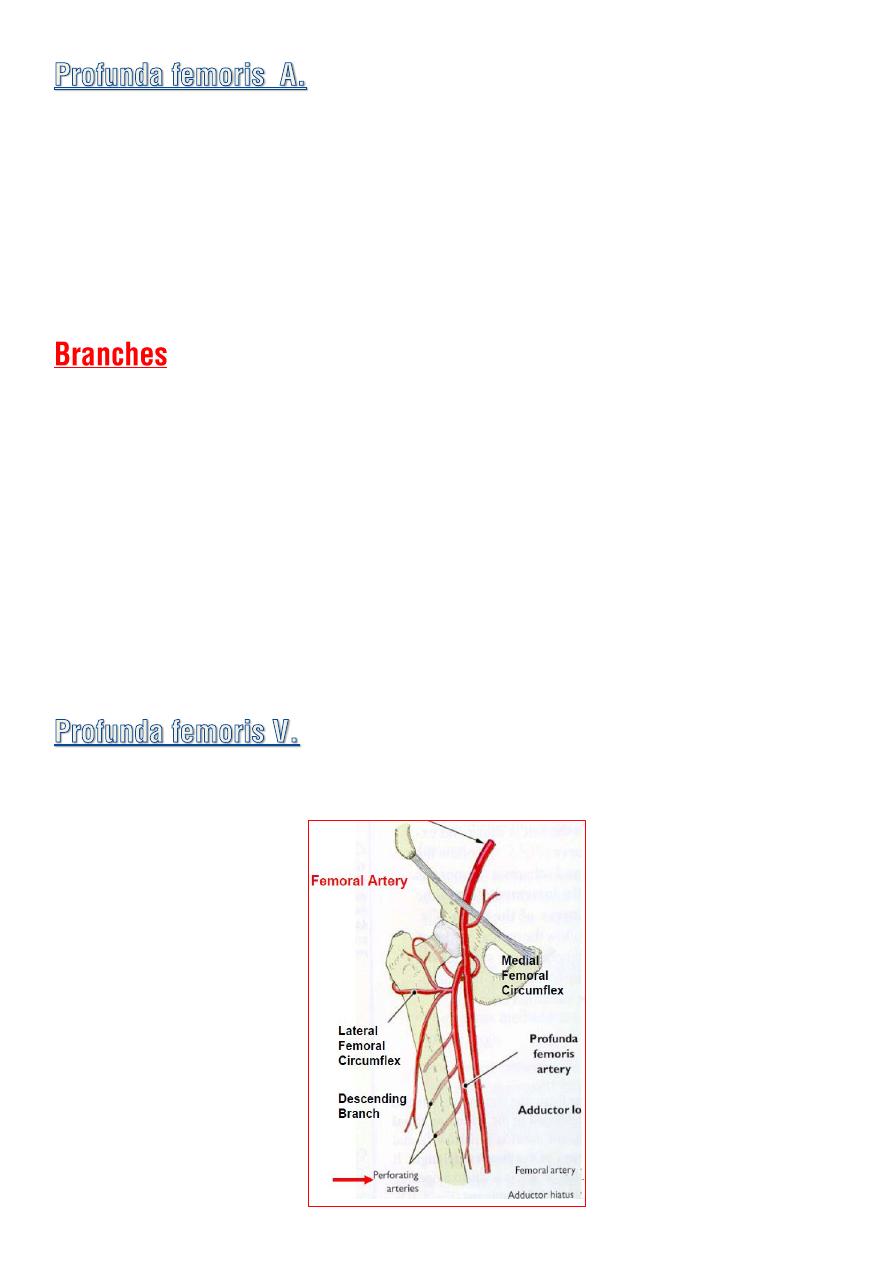
◊
Arise from lateral side of the femoral A. in the femoral triangle
4cm
below inguinal ligament .
◊
It leaves the ant. fascial compartment by passing behind the adductor
longus m.
◊
It descend in the interval between add.longus and add.brevis and then
lies on add.magnus when it ends as fourth perforating A.
1- medial femoral circumflex A.
2- lateral femoral circumflex A.
3- four perforating As.
Run backward and laterally piercing the muscle layers .
they supply the muscles and terminate by anastomosing with :
♦ One another
♦ Inferior gluteal A.
♦ The circumflex femoral As. above
♦ The muscular branches of the popliteal A. below
Recieves tributaries corresponds to the branches of A. and drain in to the
femoral vein.
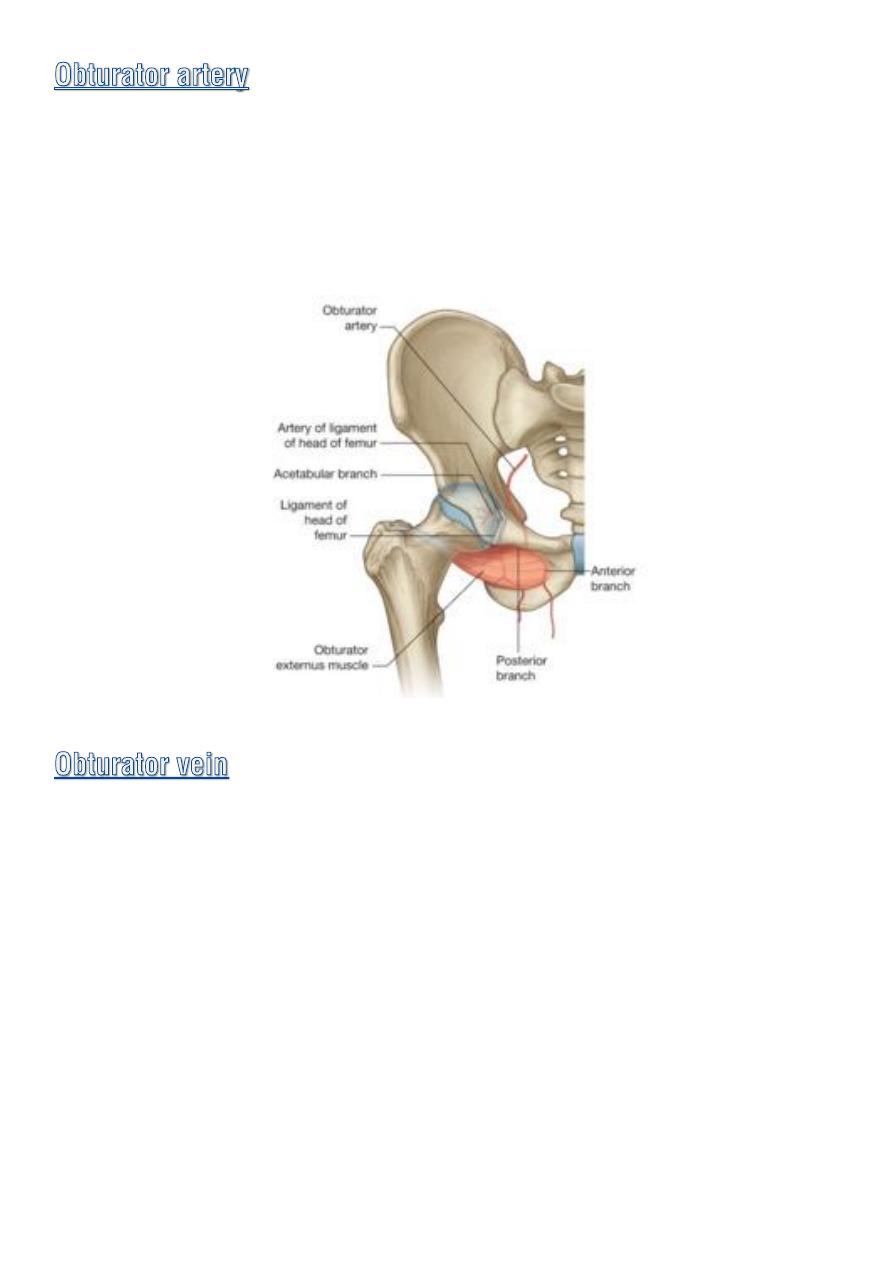
♦
Is a branch of
internal iliac A.
accompanied the obturator N. in the
obturator canal.
♦
On entering the medial compartment of the thigh it divide in to
med.
and lat. division.
♦ Receives tributaries that correspond to the branches of the artery .
♦ it drains in to the internal iliac vein.
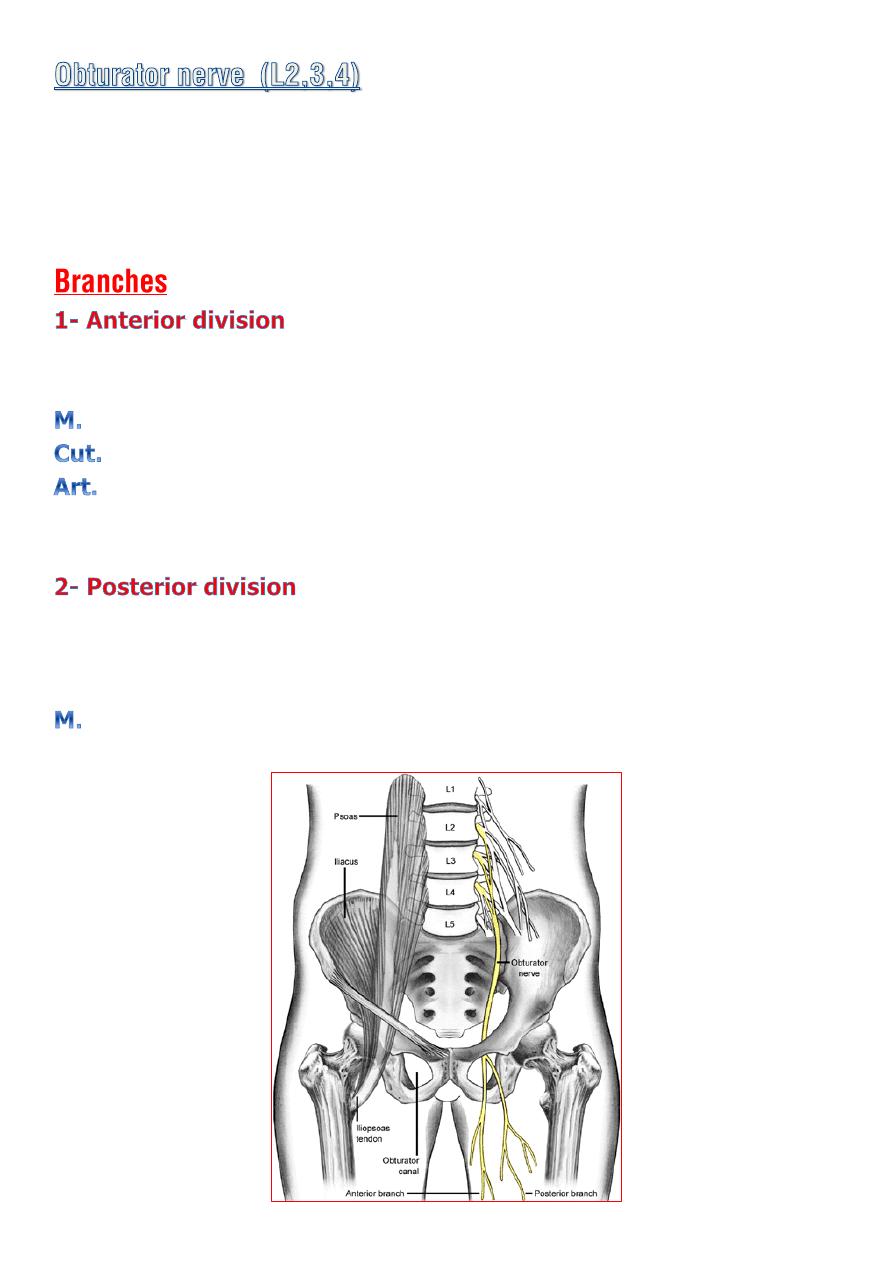
♦ Emerge on the medial border of the psoas muscle within the abdomen
.
♦
At the upper part of the obturator foramen it divides into
ant. and post.
division.
infront
: obturator externus and add. Brevis
and behind
: the pectineus and add.longus.
gracilis
,
add.longus
&
brevis
and
pectineus.
medial side of the thigh
Hip
♦
pass behind
add.brevis
infront of
the add.magnus.
♦ It terminate by descending through the opening in the add. magnus
to supply the knee.
Obturator externus , Add.magnus & brevis..
