Pigmentary disorders
Dr. Qassim Al-chalabiM.B.Ch.B F.A.B.H.S
(Dermatology & Venereology)
Normal skin color
• Melanin is synthesized by epidermal melanocytes, the most important pigment in determining skin color.• Variations in the amount & distribution of melanin in the skin are the basis of the 3 racial colors: black, brown & white, which are genetically determined “constitutive melanin pigmentation”.
• Can be by UV exposure “inducible melanin pigmentation”.
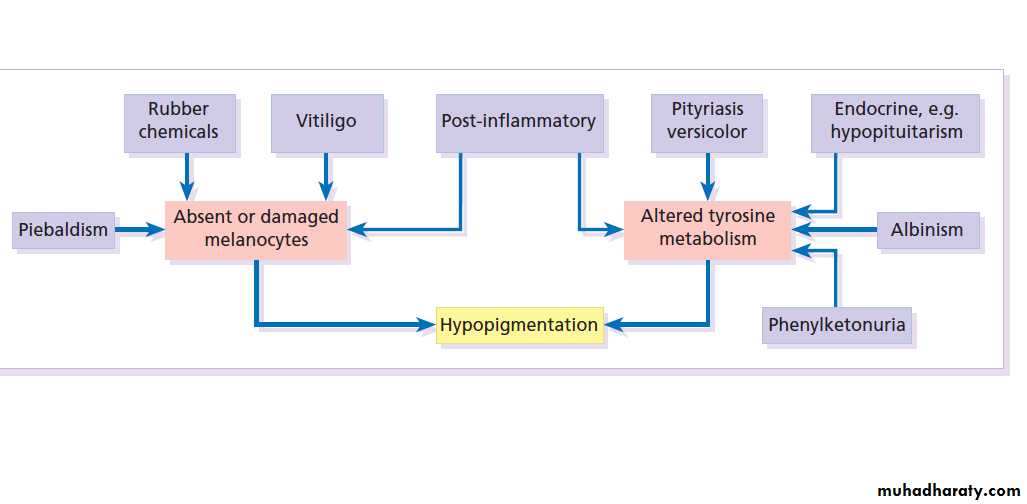
Causes of hypo and depigmentation
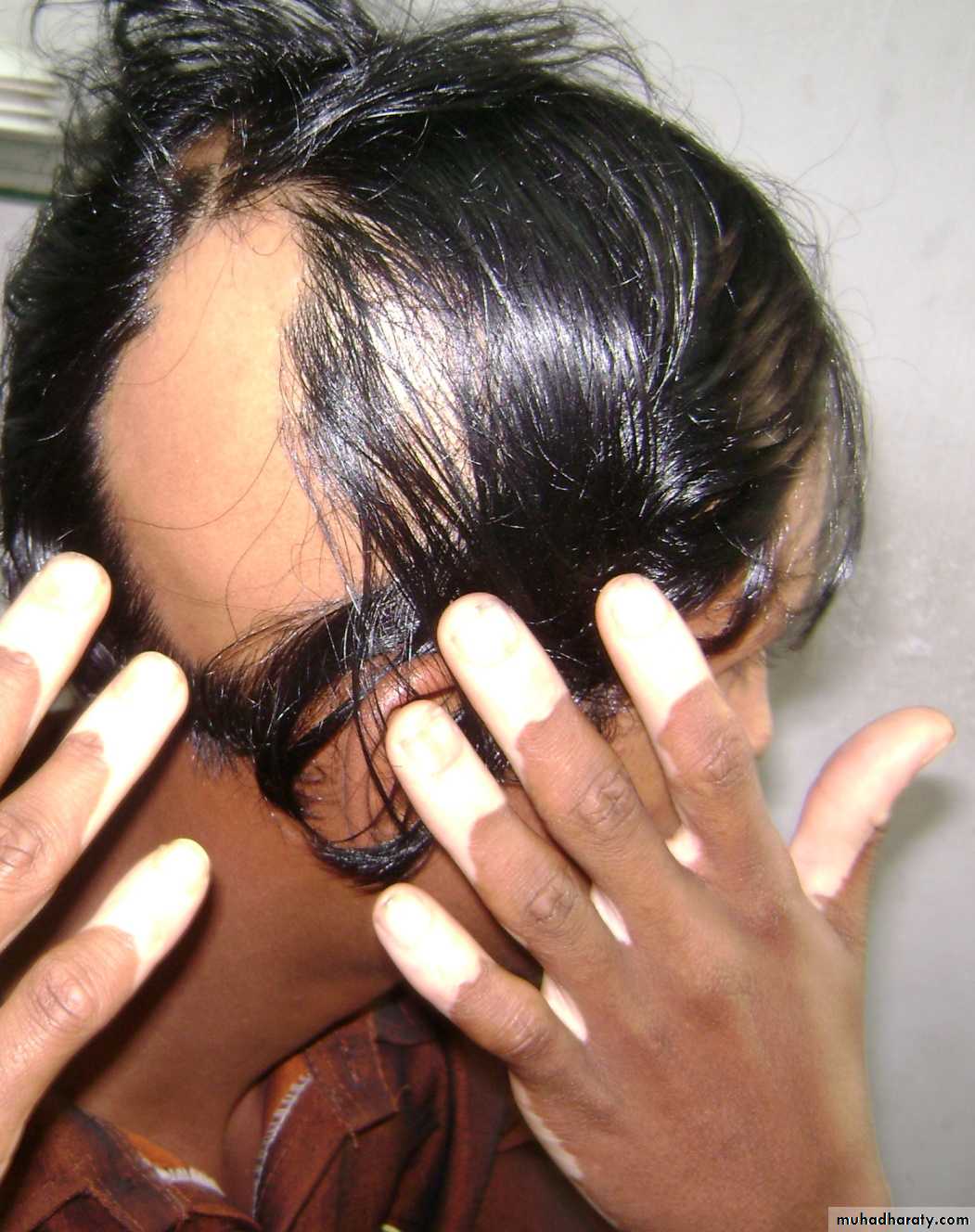
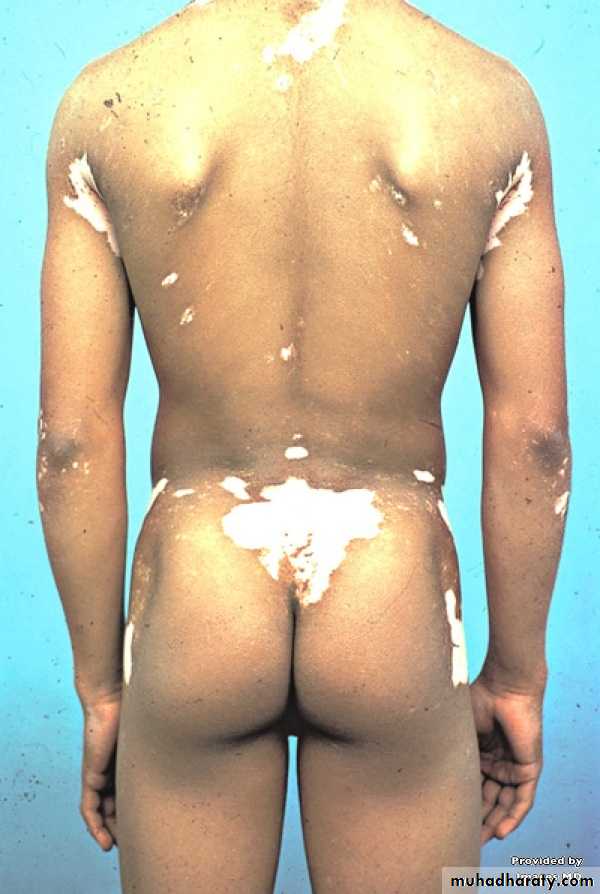
Vitiligoداء البهاق
• Prevelence
• A common disorder affecting about 1-2% of population.
• 50% of the patients develop vitiligo before the age of 20 & the incidence decreases with increasing age.• +ve family history in at least 30% of cases.
• Etiologic theories
• Autoimmune hypothesis.
• Melanocyte self-destructive hypothesis.
• Neural theory.
Clinical picture
Generalized type The sharply defined, usually symmetrical, white patches are especially common on the backs of the hands, wrists, fronts of knees, neck and around body orifices. The hair of the scalp and beard may depigmented too.The course is unpredictable: lesions may remain static or spread, sometimes following minor trauma (Köbner phenomenon).
Distribution
• Focal.• Segmental (2nd common)
• Generalized: (most common)
• Acrofacial.(resistant to treatment)
• Universal vitiligo.
Associations
• Insulin-dependent diabetes
• Pernicious anemia
• Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
• Grave’s disease
• Addison’s disease
• Alopecia areata
Treatment
Sunscreen and cosmetic cover-up.Topical corticosteroids
Ultraviolet phototherapy(NB UVB)
Laser (308 mn excimer)
Topical tacrolimus(TCI)
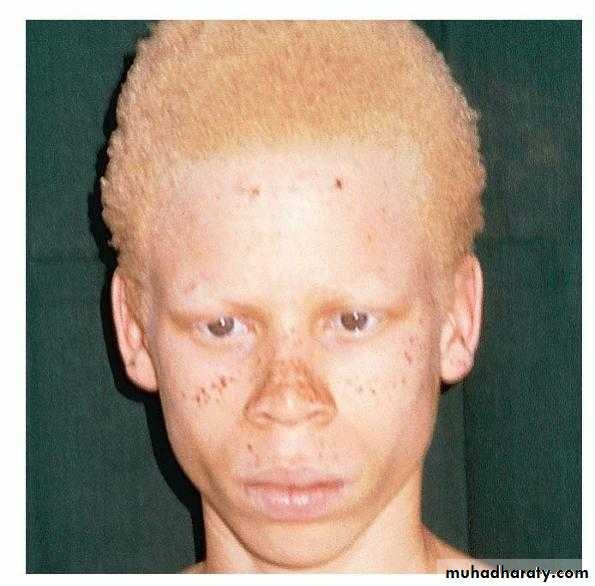
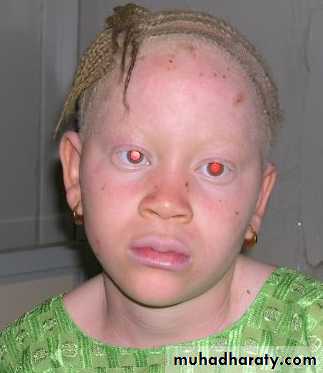
Oculocutaneous albinism
It is a genetic(AR) disorder characterized by absence of melanin in the skin and/ or eyes.The prevalence of albinism of all types ranges from 0.01% to 5% in some communities.
oculocutaneous albinism divided into two main types: tyrosinase negative and tyrosinase positive.
Clinical feature
The whole epidermis is white and pigment is also lacking in the hair, iris and retina.Albinos have poor sight, photophobia and a rotatory nystagmus.
Tyrosinase-positive albinos may also develop freckles. Sunburn is common on unprotected skin. As melanocytes are present, albinos have non-pigmented melanocytic naevi and may develop amelanotic malignant melanomas.
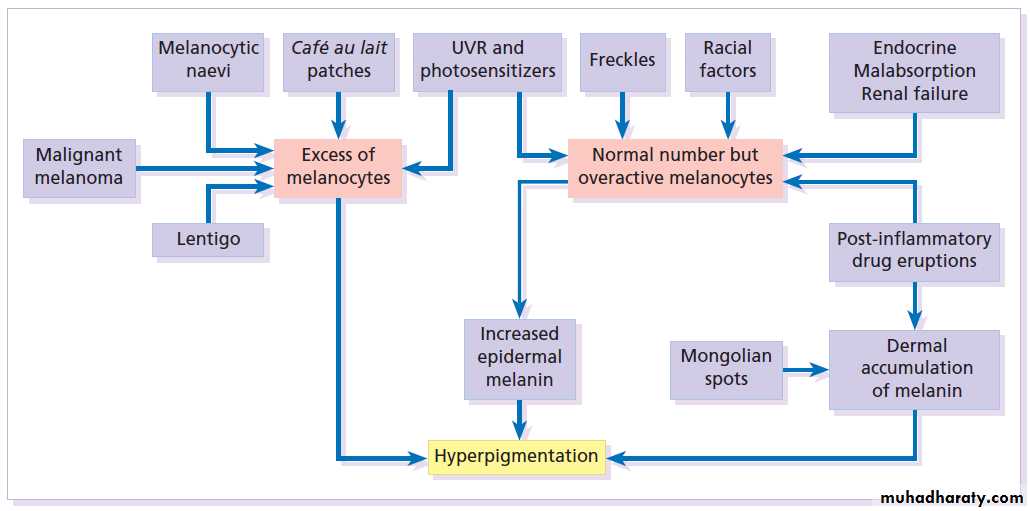
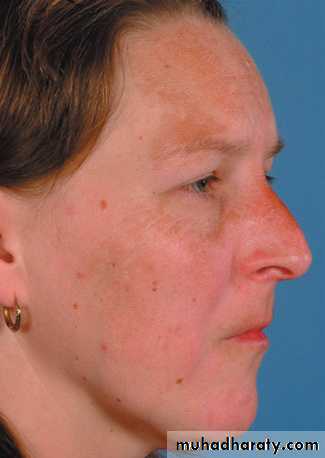
Melasma
It is an acquired, symmetrical well defined hyperpigmentation their edges may be scalloped occurring on sun-exposed skin, especially the face.The condition is much more common in women, affects all races but is most prevalent in dark-skinned individuals with skin types IV–VI .
There are many causes including sunlight, pregnancy ‘the mask of pregnancy, estrogens and oral contraceptives, scented cosmetics, thyroid dysfunction and photosensitizing drugs .
Wood`s light may be useful in the determining the presence of melanin either in the epidermis or dermal.
Treatment
This is unsatisfactory.A sunscreen will make the pigmentation less obvious.
Some improvement achieved with preparations containing 2–5% hydroquinone applied for 6–10 weeks.
Chemical peels have become popular. α-Hydroxy acids, especially glycolic acid.