Intracranial Infections in Neurosurgical Practice
Intracranial Infections in Neurosurgical Practice• Bacterial Meningitis.
• Brain Abscess.
• Subdural Empyema.
Bacterial Meningitis
Complications:Cerebral Oedema.
Seizures.
Hydrocephalus (communicating).
Subdural Effusion.
Subdural Empyema.
Brain Abscess.
Ventriculitis.
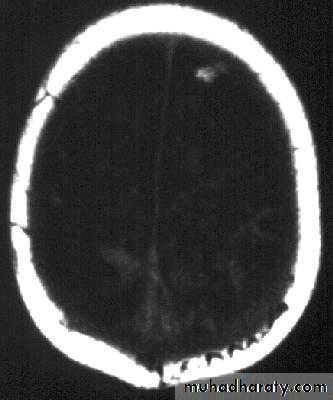
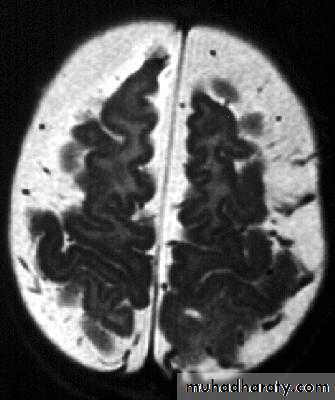
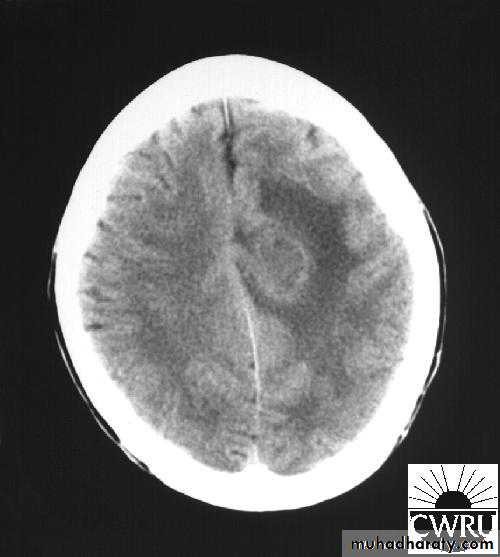
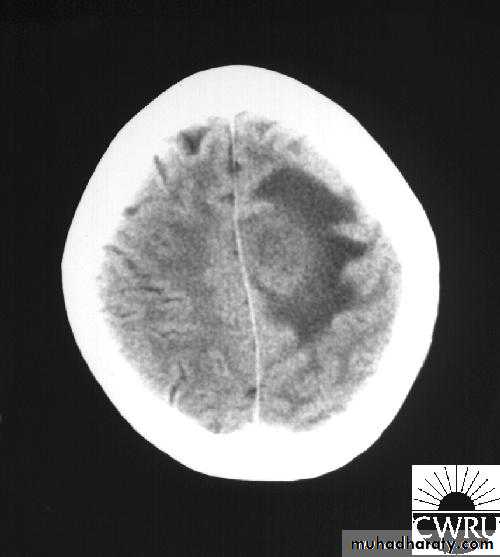
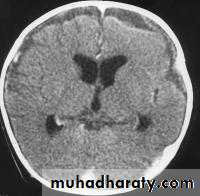
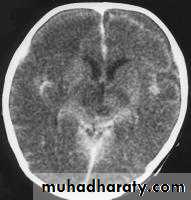
Bacterial Meningitis with cerebral oedema
Bacterial Meningitis with cerebral oedema
Bacterial Meningitis with cerebral oedema
Bacterial Meningitis with cerebral oedema
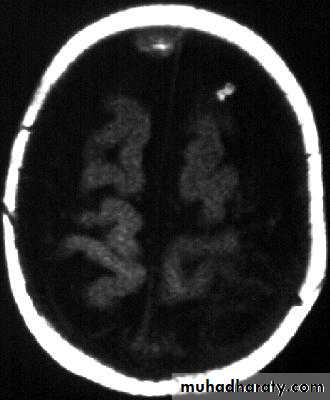
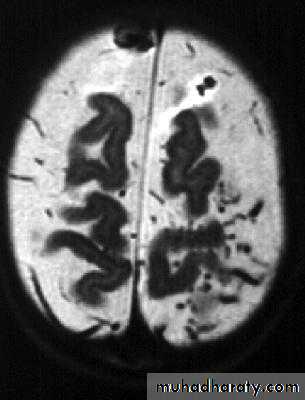
Bacterial Meningitis with suppuration
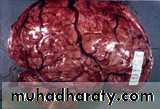
Brain Abscess
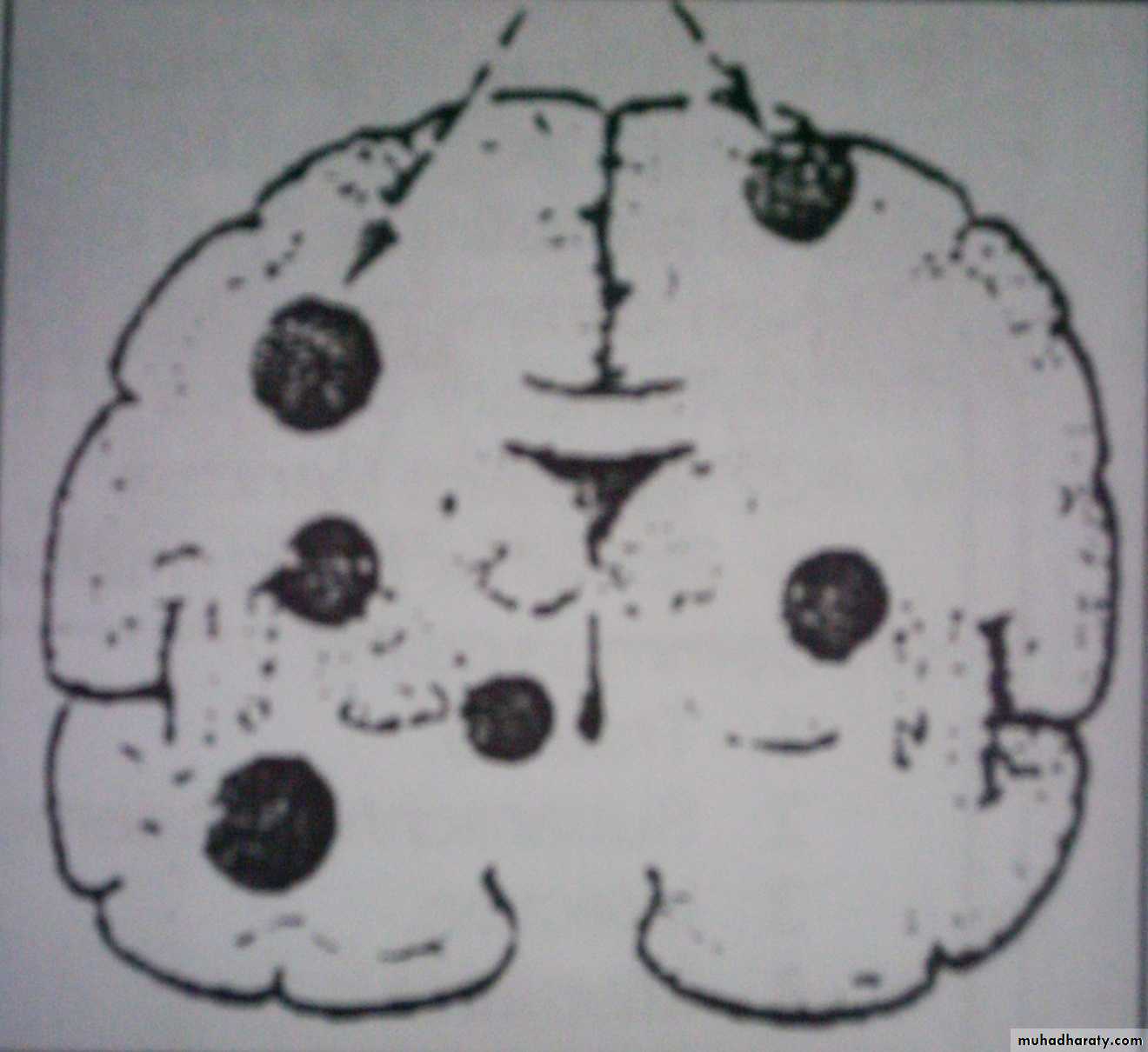
• Aetiology and Source of infection:Haematogenous spread: from a known septic site or occult focus (e.g. from dental infection, respiratory tract infection or endocarditis), usually causes multiple brain abscesses. This route is commoner in patients having congenital heart disease with right to left shunt.
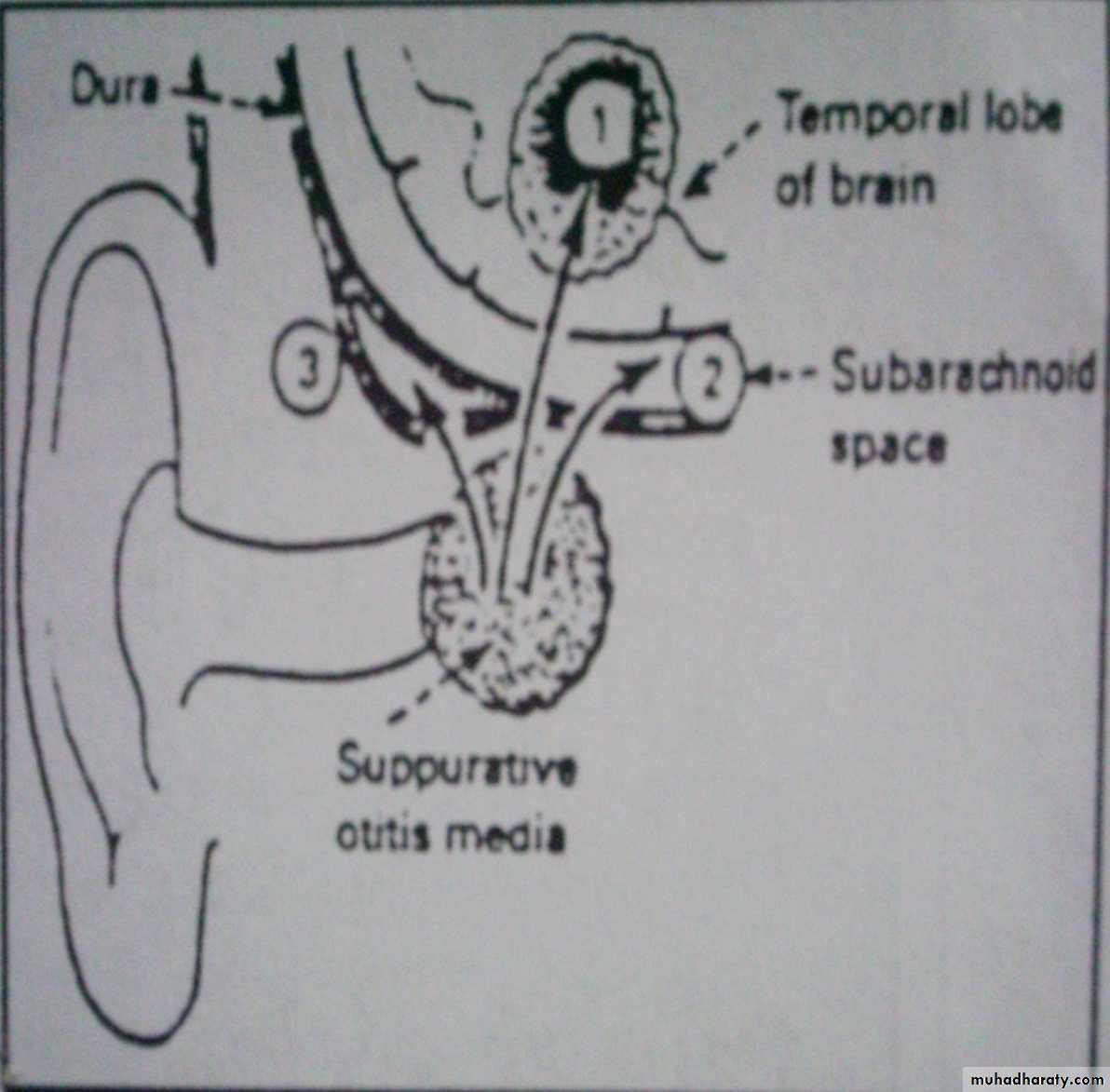
Direct spread: from an adjacent infected paranasal sinus, middle ear, or mastoid infection.
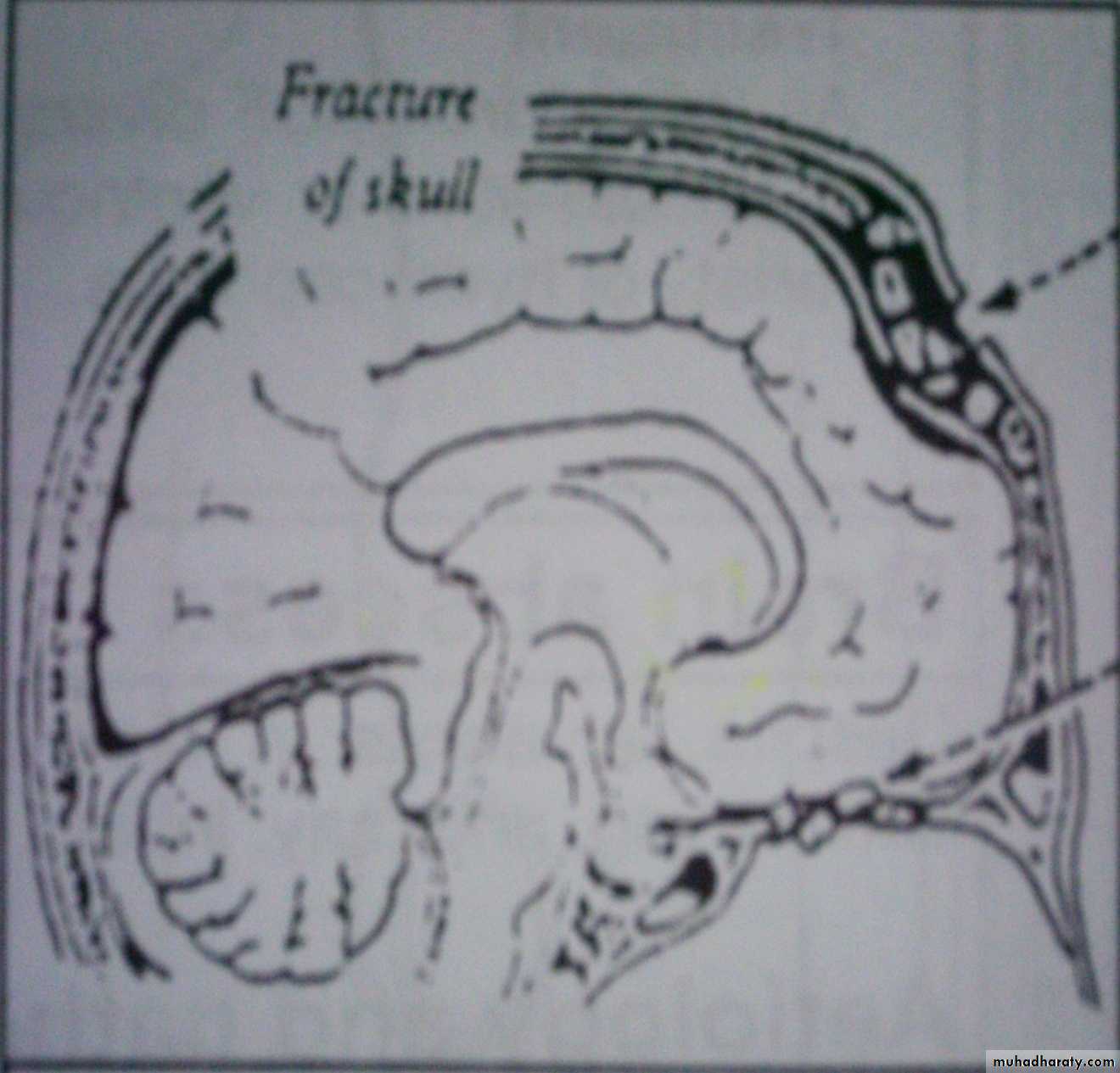
Post-traumatic: direct inoculation from trauma, or after surgery.
• Note: in 25% of patients, no cause can be identified.
Sources of CNS infection
Haematogenous AbscessDirect spread
Post-traumatic abscess
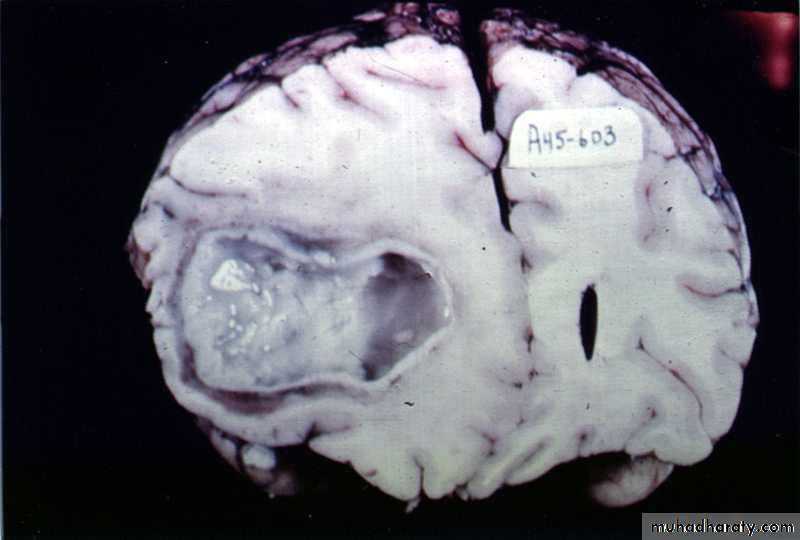
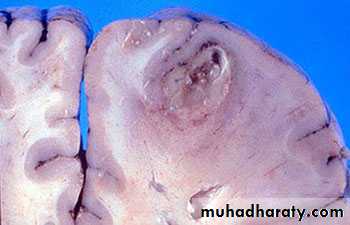
Brain Abscess Pathology
Brain abscess will pass in four stages:Early cerebritis: early 1-3 days with inflammatory cells.
Late cerebritis: days 4-9, with formation of necrotic core and increasing number of macrophages and fibroblasts.
Early capsule: days 10-13.
Late capsule (mature capsule): by day 14.
Brain Abscess
Pathology:The formation of a collagen capsule in a developing abscess is the single most important responsible that limits the spread of infection to the rest of the brain.
Collagen capsule of brain abscess
Collagen capsule of brain abscess
Brain Abscess
Clinical Features:
Features of raised intracranial pressure.
Seizures.
Meningeal irritation.
Focal neurological signs.
5.Systemic features of infection like fever is present in half of the cases and is usually of low grade
Brain Abscess
• Investigations:• Laboratory Investigations
• B. Radiological Investigations
Brain Abscess
• Laboratory Investigations:• White Blood Cells (WBC) count and Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) are usually elevated.
• Measurement of C-reactive protein is useful in differentiating brain abscess from tumour as it is elevated in case of abscess.
• Lumbar Puncture is contraindicated in case of brain abscess to avoid fatal brain herniation.
Brain Abscess
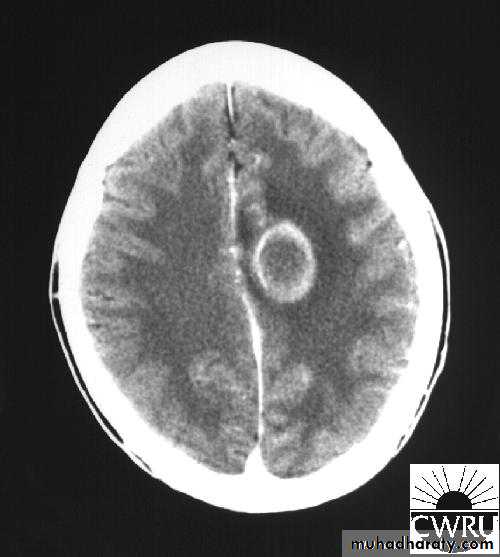
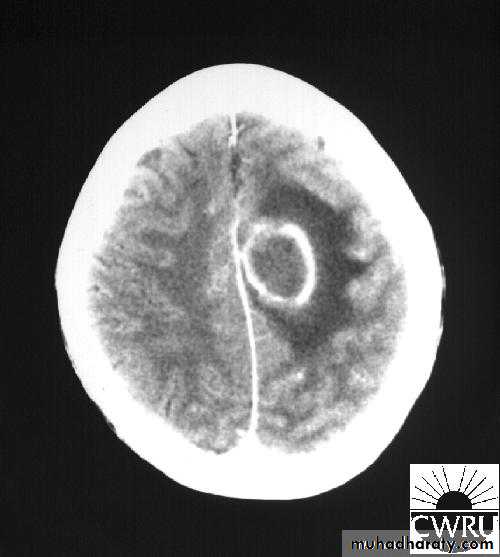
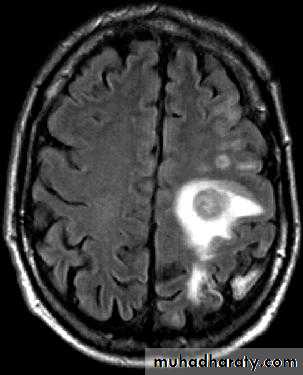
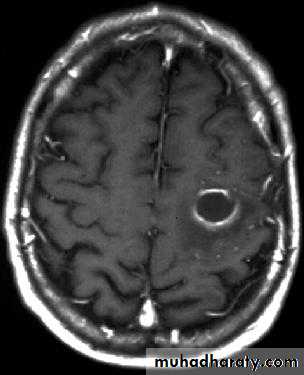
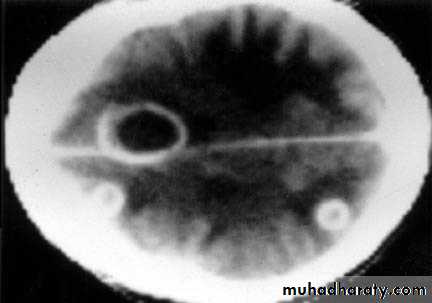
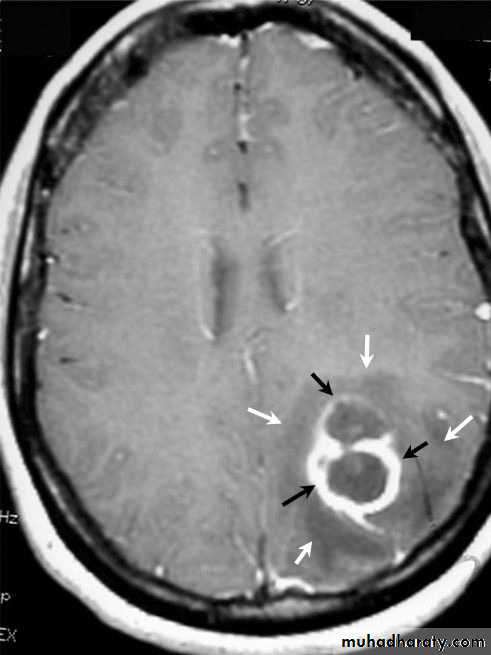
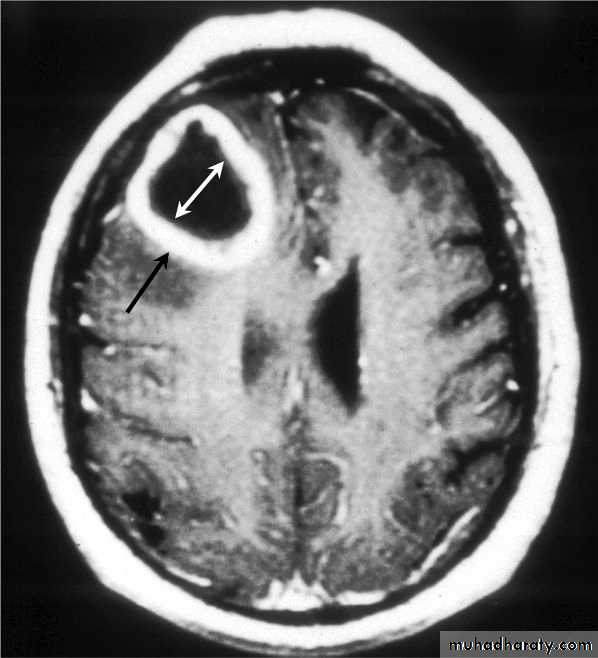
• B. Radiological Investigations:• CT or MRI is the investigation of choice.
• CT Brain is performed with and without contrast.
• MRI is done with gadolinium enhancement.
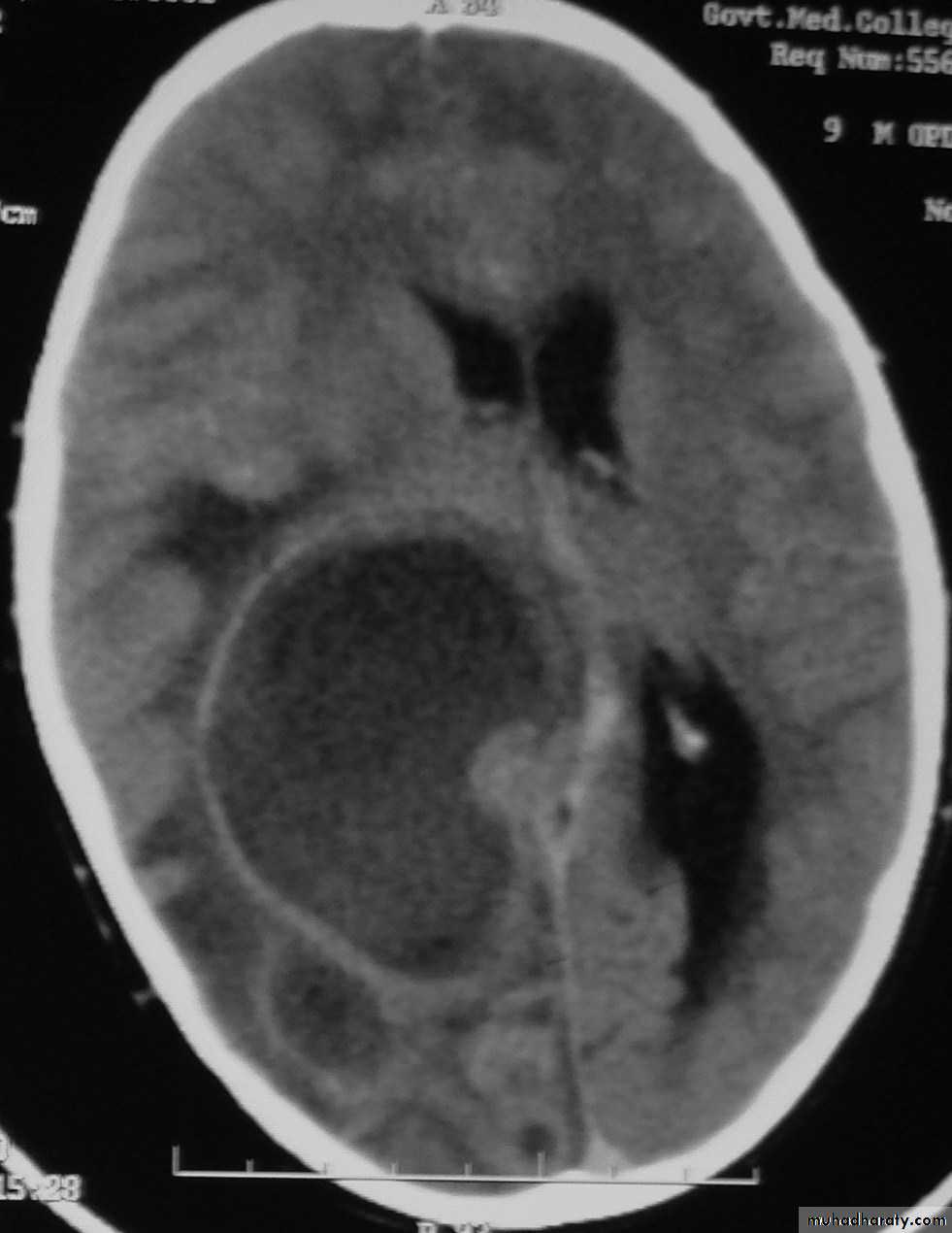
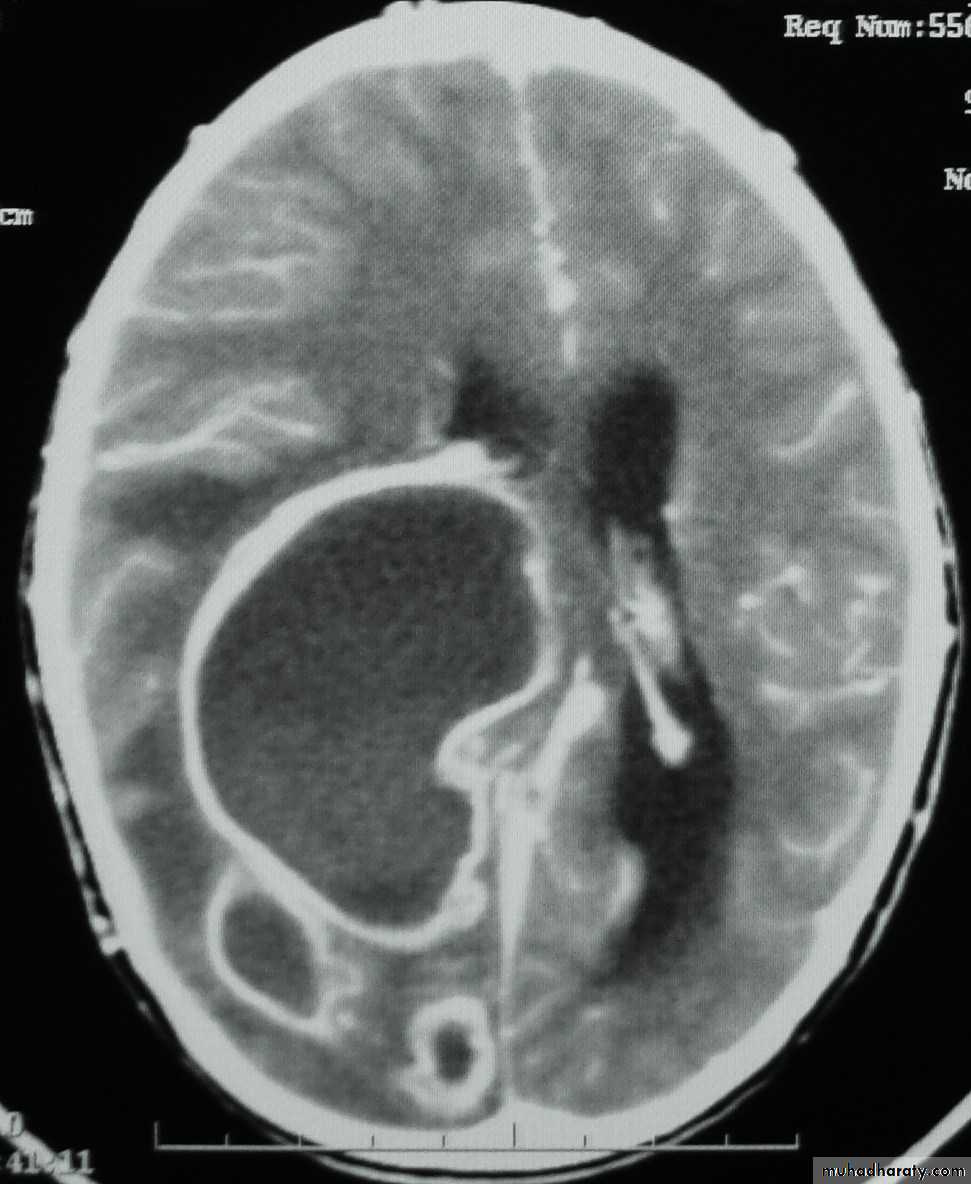
• They will show a single (or multiple) space occupying lesion that is well delineated with an enhancing wall, with variable surrounding oedema.
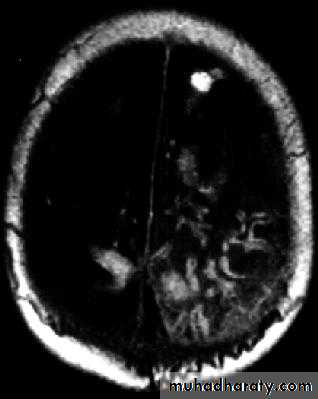
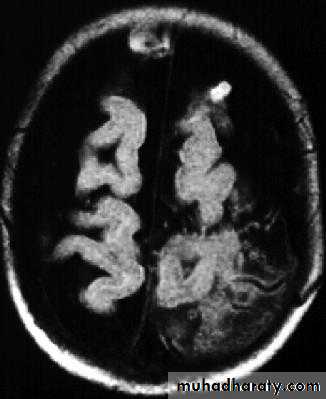
Brain Abscess CT without contrast
Brain Abscess CT with contrast
Brain Abscess MRI
Brain Abscess
• B. Radiological Investigations:• The differential diagnosis of a single brain abscess in CT or MRI is a solitary metastasis or cerebral infarction.
• The differential diagnosis of multiple brain abscesses is from multiple metastasis and tuberculoma.
Brain Abscess
• Treatment of Brain Abscess:
• Non-surgical treatment (medical treatment)
• B. Surgical treatment
Brain Abscess
• Non-surgical treatment (medical treatment):• This is indicated for an abscess that is less than 2.5 cm. It includes:
• Antibiotics: Appropriate antibiotic selection is based on culture and sensitivity results, e.g. penicillin-G, trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole, and aminoglycoside.
• Corticosteroids: help to reduce cerebral oedema.
• Anticonvulsants Therapy.
Brain Abscess
• B. Surgical treatment:• Aspiration versus excision.
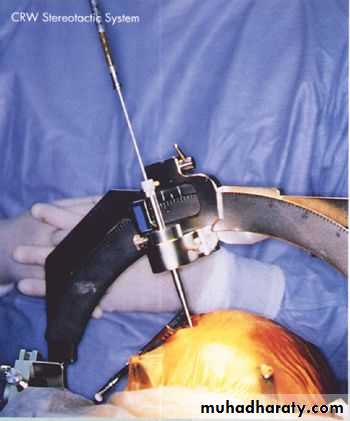
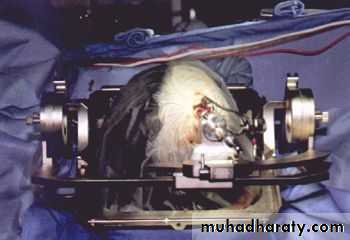
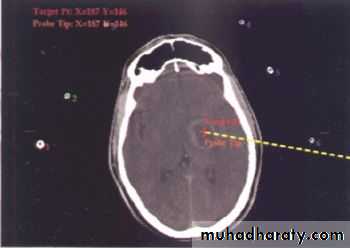
• Indications for Aspiration (Burr hole ± Stereotaxis):
• Multiple abscesses.
• A deeply seated abscess.
• A critical location (e.g. motor or speech area).
• Poor general condition of the patient.
Stereotactic Aspiration of Brain Abscess
Stereotactic Aspiration of Brain Abscess
Stereotactic Aspiration of Brain Abscess
Multiple Abscesses
Multiple Abscesses
Deep Seated Abscess
Brain Abscess
• B. Surgical treatment:• Indications for Excision (Craniotomy):
• Multilocular abscess.
• A superficial abscess.
• The presence of a foreign body.
• Fungal abscess.
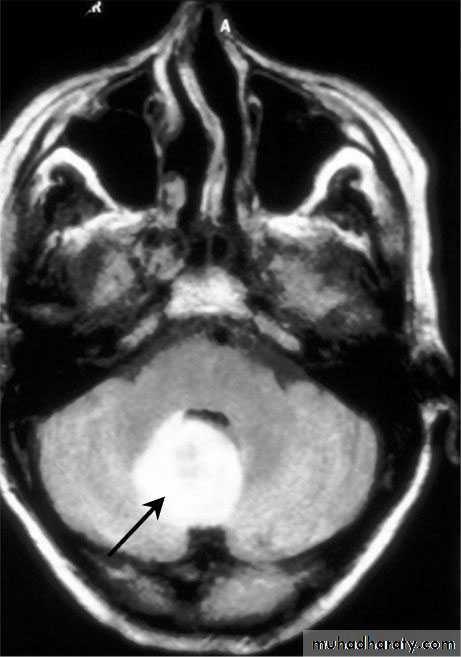
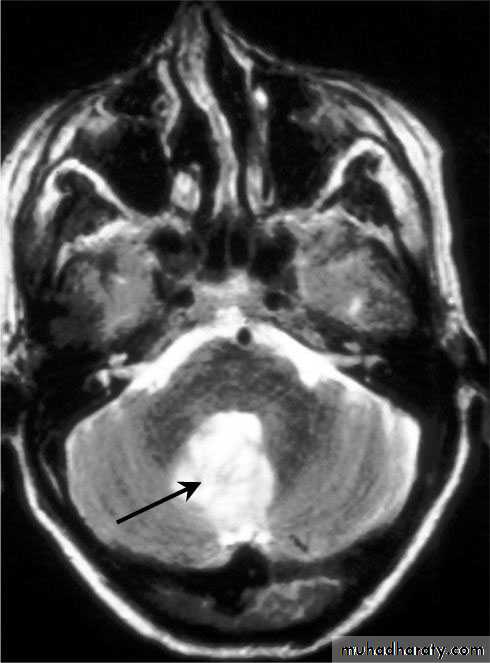
• Cerebellar Abscesses.
• Abscesses containing air.
• Abscesses with CSF leak.
Multilocular Abscess
Superficial Abscess
Foreign Body
Cerebellar Abscess
Cerebellar Abscess
SUBDURALEMPYEMA
Subdural EmpyemasSource of infection:
Although uncommon, may develop following sinusitis or mastoiditis.
It carries a high mortality (5-10 %)Subdural Empyemas
• Clinical picture:Headache, fever and meningism.
Seizures are common.
Focal neurological deficits which may progress rapidly to:
Altered mental state and coma.
• NOTE: The combination of fever and seizures with background of sinusitis is usually diagnostic of this lesion.
Subdural Empyemas
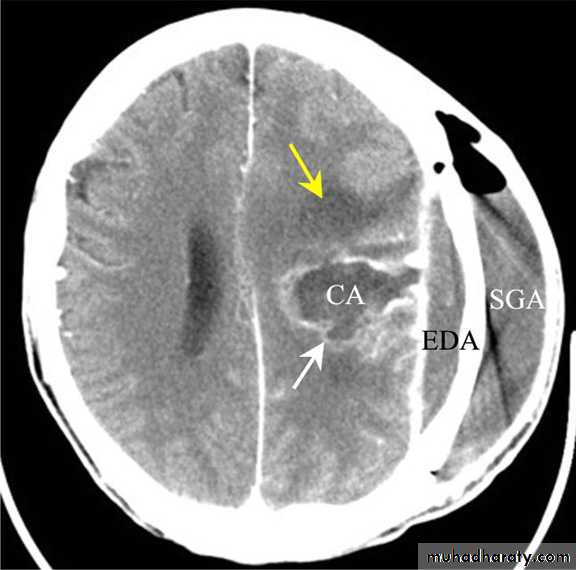
Investigations:
CT scanning;
Despite subdural empyema is a neurosurgical emergency, diagnosis is often delayed as the collection on CT is usually so slight and frequently missed.Subdural Empyemas
Subdural Empyemas
• Treatment:Craniotomy and thorough drainage of the pus, followed by:
Intravenous antibiotic.
Anticonvulsants.
Subdural Empyemas
Complications:Refractory status epilepticus.
Cortical vein/ venous sinus thrombosis.