
Karnaugh Map
First Class
Dr. AMMAR ABDUL-HAMED KHADER
Dr. AMMAR ABDUL-HAMED KHADER
1

Karnaugh Map
• Why learn about Karnaugh maps?
• A Karnaugh map is a two-dimensional truth-table. Unlike ordinary
(i.e., one-dimensional) truth tables, however, certain logical network
simplifications can be easily recognized from a Karnaugh map.
• The K- map, like Boolean algebra, is a simplification tool applicable
to digital logic.
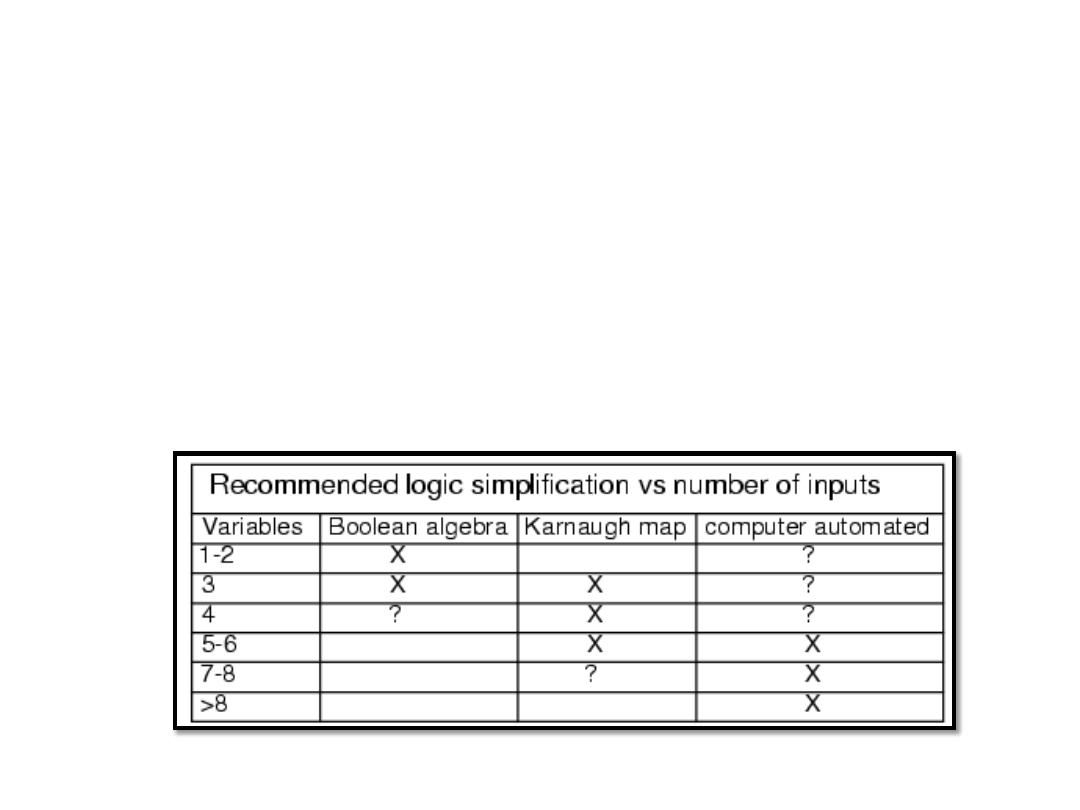
• Boolean simplification is actually faster than the Karnaugh map for
a task involving two or fewer Boolean variables. It is still quite
usable at three variables, but a bit slower. At four input variables,
Boolean algebra becomes tedious. Karnaugh maps are both faster
and easier. It is work well for up to six input variables, are usable
for up to eight variables. For more than six to eight variables,
simplification should be by CAD (Computer Automated Design).
Dr. AMMAR ABDUL-HAMED KHADER
2
Karnaugh Map
• Examples of computer automated design languages for
simplification of logic are PALASM, ABEL, CUPL, Verilog, and
VHDL.
These
programs
accept
a
hardware
descriptor
language input file which is based on Boolean equations and
produce an output file describing a reduced (or simplified) Boolean
solution.
Dr. AMMAR ABDUL-HAMED KHADER
3

Karnaugh Map (K- map)
The K-map method is easy and straightforward. It is a visual
technique for finding the minimum cost SOP (or POS) form
for a Boolean expression
A K-map for a function of n variables
consists of 2
n
cells, and,
in every row and column, two adjacent cells should differ
in the value of only one of the logic variables.
This technique has limitations. i.e. works for # inputs < 7
Dr. AMMAR ABDUL-HAMED KHADER
4
Karnaugh Map (K- map)
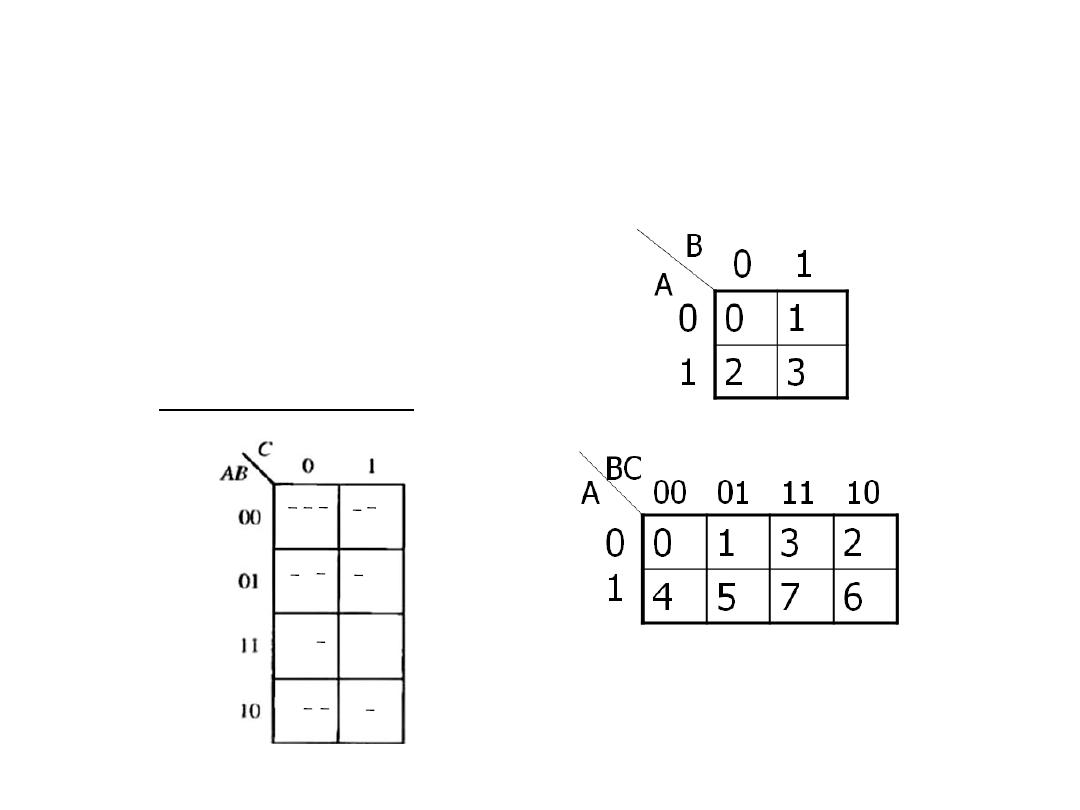
Cell numbers are written in the cells.
2-variable K-map
3-variable K-map
000
ABC
001
ABC
010
ABC
011
ABC
110
ABC
111
ABC
100
ABC
101
ABC
Dr. AMMAR ABDUL-HAMED KHADER
5
Karnaugh Map (K- map)
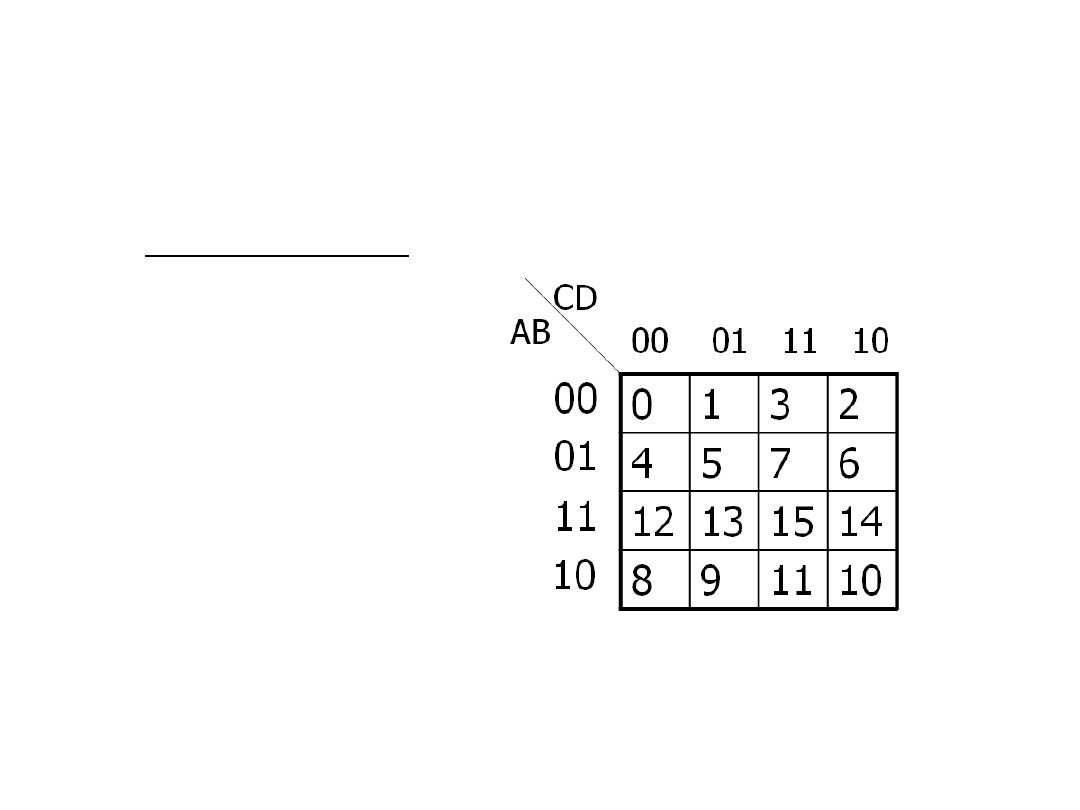
4-variable K-map
Dr. AMMAR ABDUL-HAMED KHADER
6
Karnaugh Map (K- map)
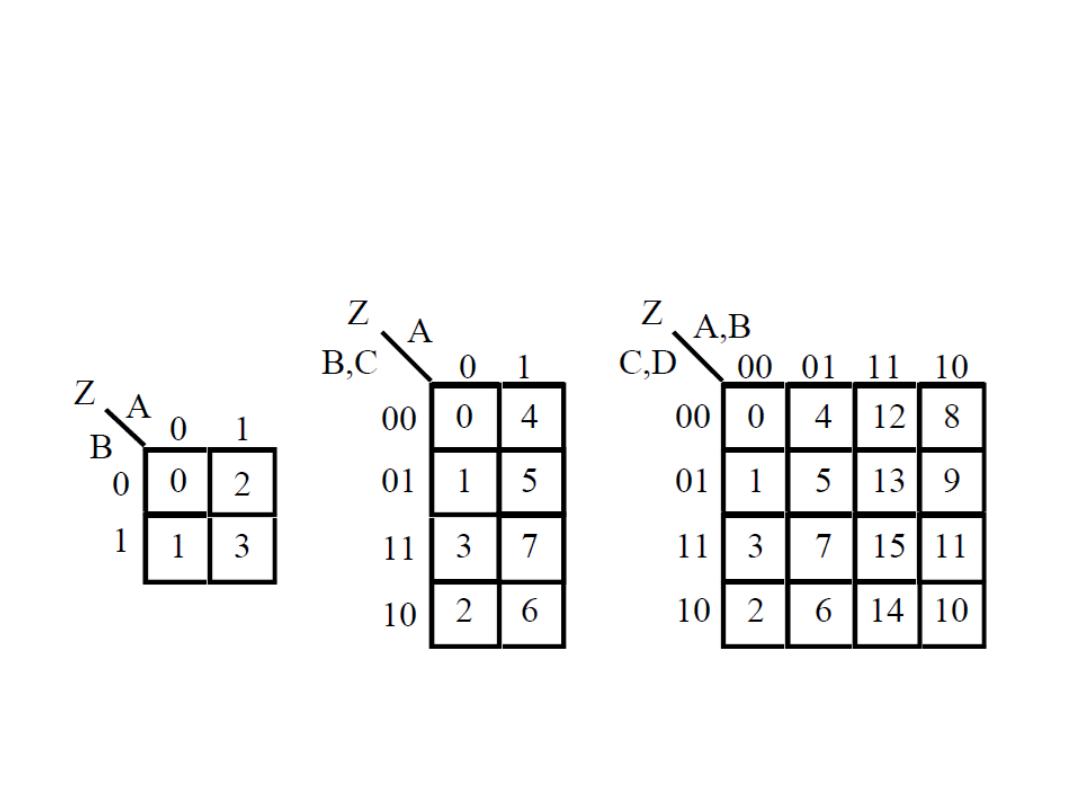
• We can numbering the K-map as follows:
Dr. AMMAR ABDUL-HAMED KHADER
7
Karnaugh Map (K- map)
• Example: Map the following standard SOP expression on a K-
map:
ABC + ABC + ABC + ABC
Solution: Evaluate the expression as follows:
001 + 010 + 110 + 111
1
1
1
1
Dr. AMMAR ABDUL-HAMED KHADER
8
Karnaugh Map (K- map)
• Example: Map the following standard SOP expression on a K-
map:
ABCD + ABCD + ABCD + ABCD + ABCD + ABCD + ABCD
• Solution:
Dr. AMMAR ABDUL-HAMED KHADER
9
1
1
1
1
1
1
1

K- map simplification of SOP
expression
• The process that results in expression containing the fewest
possible terms with the fewest possible variable is called
minimization. We can grouping the 1s on the K- map and
determine the minimum SOP expression from the map.
• The goal is to maximize the size of the groups and to minimize
the number of the groups.
Dr. AMMAR ABDUL-HAMED KHADER
10
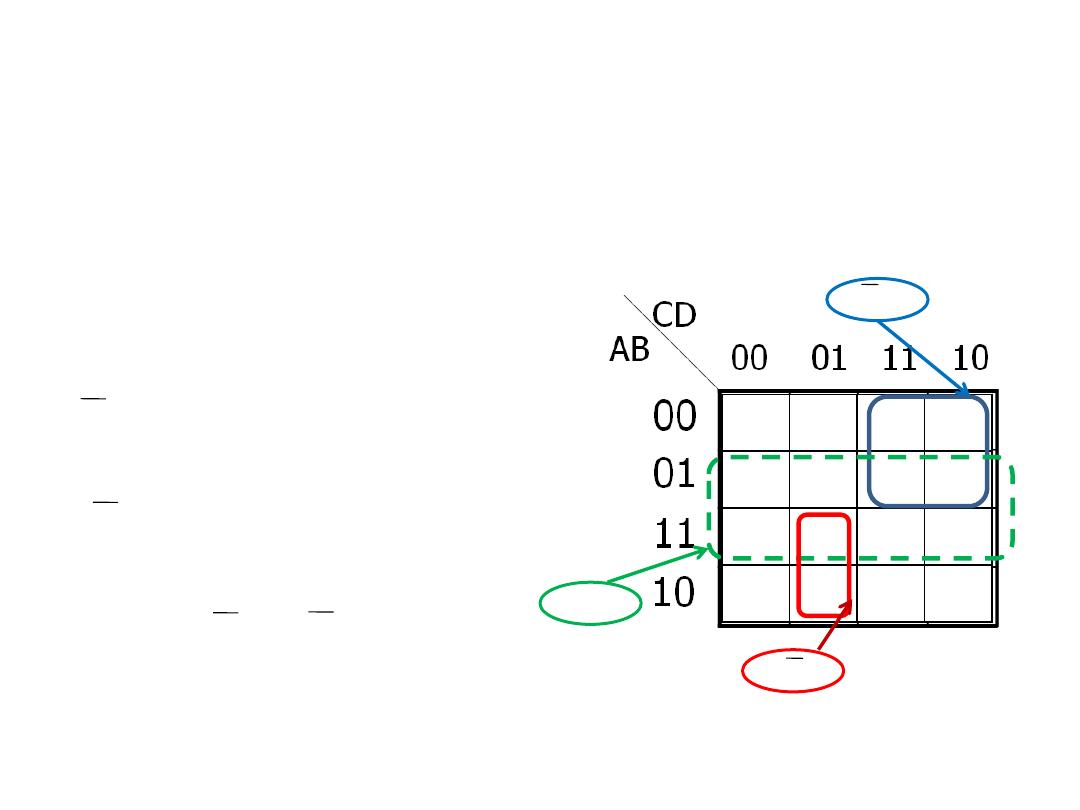
K- map simplification of SOP
expression
• Example: determine the product terms for the K-map and
write the resulting minimum SOP expression.
• Solution: the product term is:
AC
four the 4 cells,
B
for the 8 cells and
ACD
for the two cells.
The resulting minimum SOP expression is:
B
+
AC
+
ACD
Dr. AMMAR ABDUL-HAMED KHADER
11
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
B
ACD
AC
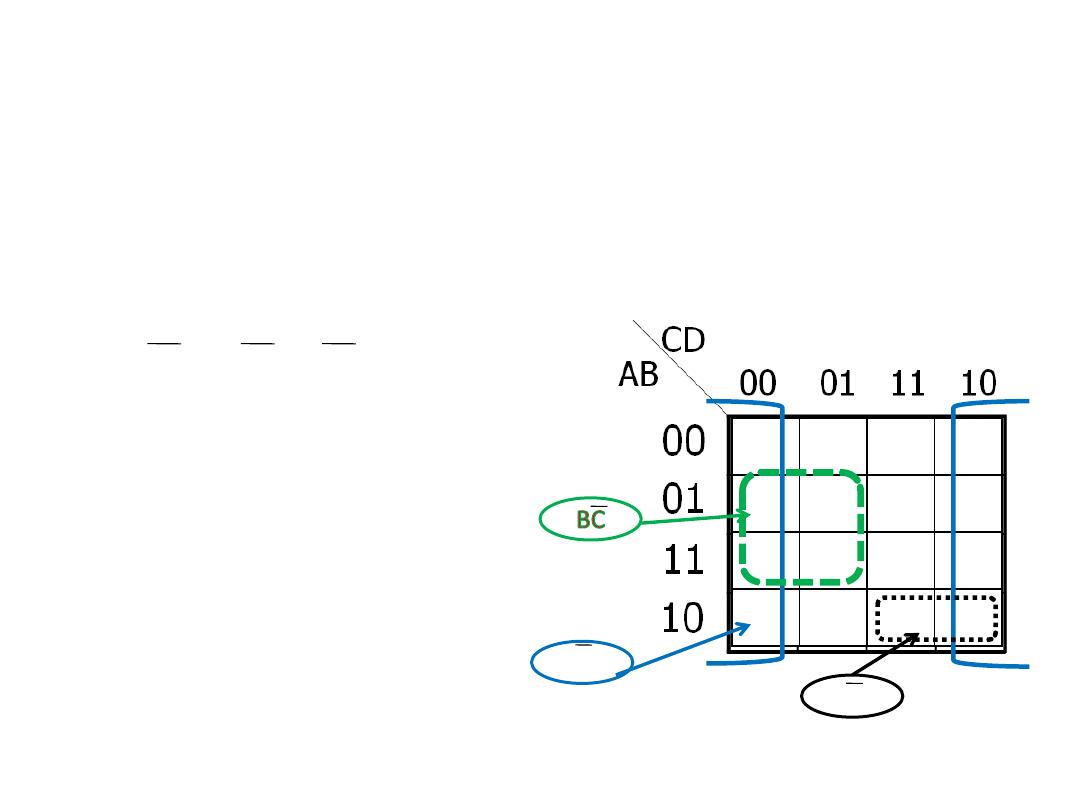
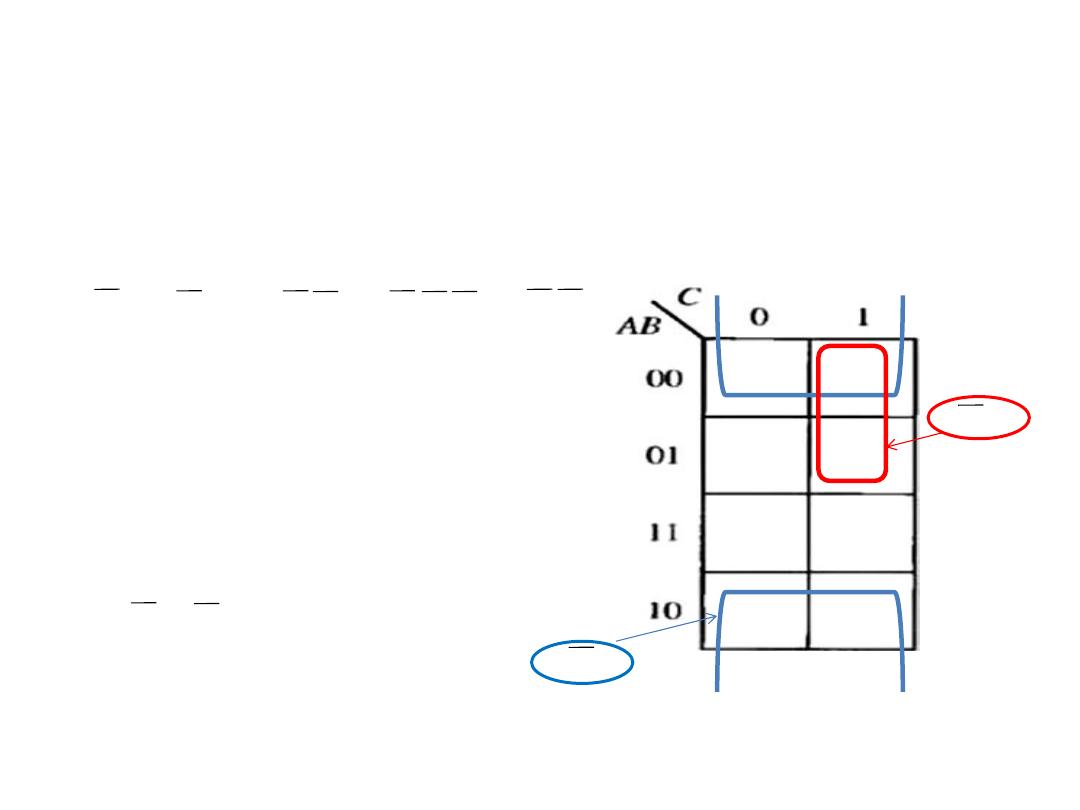
K- map simplification of SOP
expression
• Example: Determine the product terms for the K-map and
write the resulting minimum SOP expression
• Solution:
D + BC + ABC
Dr. AMMAR ABDUL-HAMED KHADER
12
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
ABC
D
K- map simplification of SOP
expression
• Example: Use the Karnaugh map to minimize the following
standard SOP expression.
ABC +
ABC
+
ABC
+
ABC
+
ABC
Solution: The binary values of the
expression are:
101 +
011
+
001
+
000
+
100
B
+
AC
Dr. AMMAR ABDUL-HAMED KHADER
13
1
1
1
1
1
B
AC
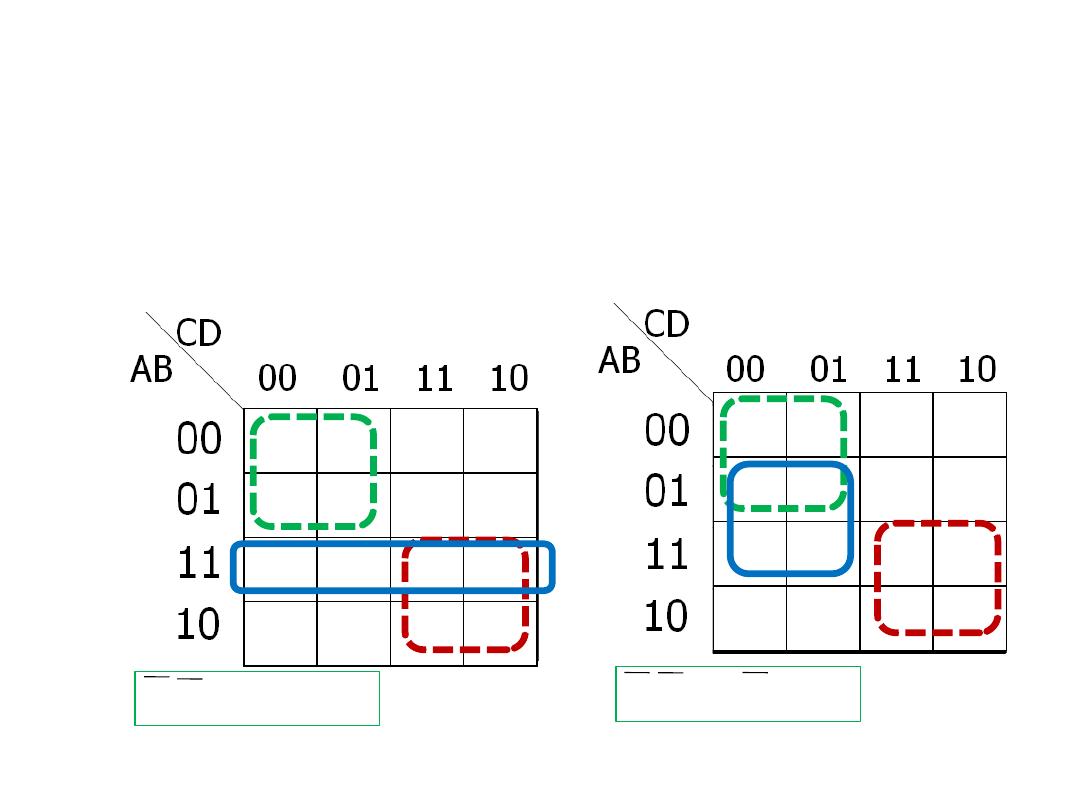
K- map simplification of SOP
expression
• Example: Write the resulting minimum SOP expression
• Solution: There are two possible solutions
Dr. AMMAR ABDUL-HAMED KHADER
14
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
AC
+
BC
+
AC
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
AC
+
AB
+
AC
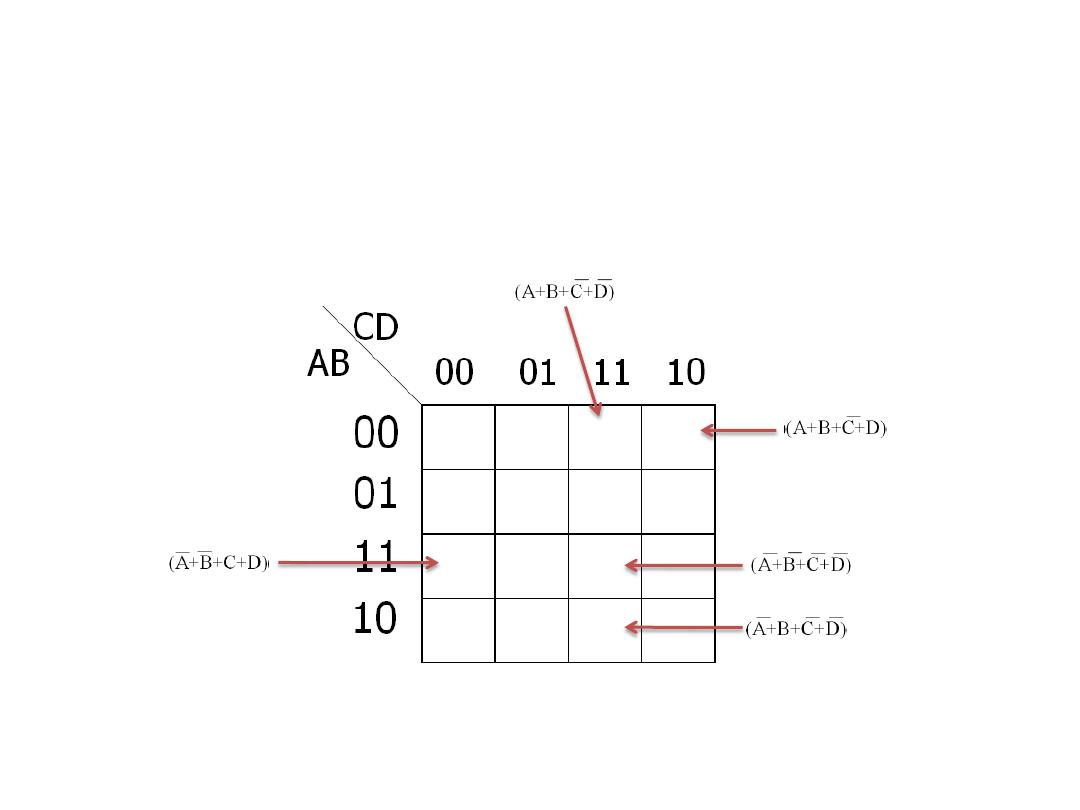
K- map simplification of POS
expression
• For a POS expression in standard form, a 0 is placed on the K-
map for each sum term in the expression. Each 0 is placed in a
cell corresponding to the value of a sum tern.
• Example: Map the following standard POS expression on a
Karnaugh-map:
(A+B+C+D)(A+B+C+D)(A+B+C+D)(A+B+C+D)(A+B+C+D)
Solution: Evaluate the expression then place a 0 on the 4 variable
K-map for each standard sum tern in the expression
(1 1 0 0)(1 0 1 1)(0 0 1 0)(1 1 1 1)(0 0 1 1)
Dr. AMMAR ABDUL-HAMED KHADER
15
K- map simplification of POS
expression
Dr. AMMAR ABDUL-HAMED KHADER
16
0
0
0
0
0
(1 1 0 0)(1 0 1 1)(0 0 1 0)(1 1 1 1)(0 0 1 1)
K- map simplification of POS
expression
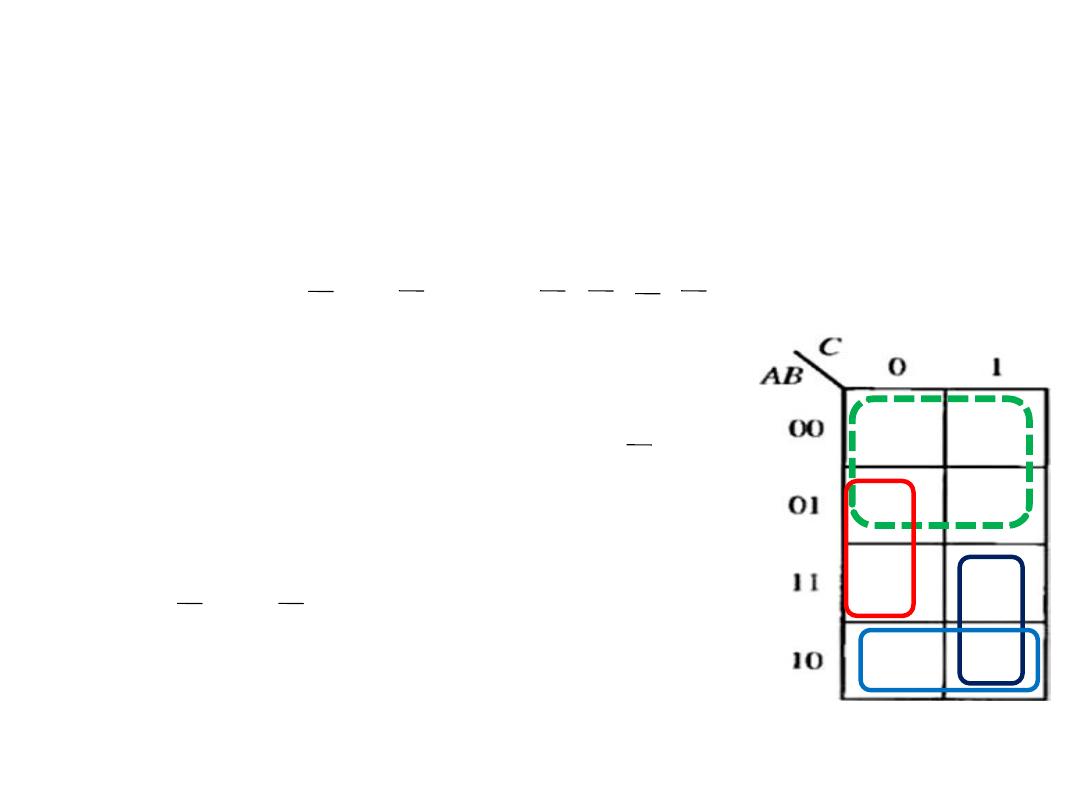
• Example: Use a Karnaugh-map to minimize the following
standard POS expression. Also derive the equivalent SOP exp..
(A+B+C)
(A+B+C)
(A+B+C)
(A+B+C)
(A+B+C)
Solution: The combination of binary values are:
(0+0+0)(0+0+1)(0+1+0)(0+1+1)(1+1+0)
The minimum POS expression is
A
(B+C)
If we group the 1s as shown, it yield an SOP
exp. that equivalent to grouping the 0s.
AC
+
AB
= A(B + C)
Dr. AMMAR ABDUL-HAMED KHADER
17
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
K- map simplification of POS
expression
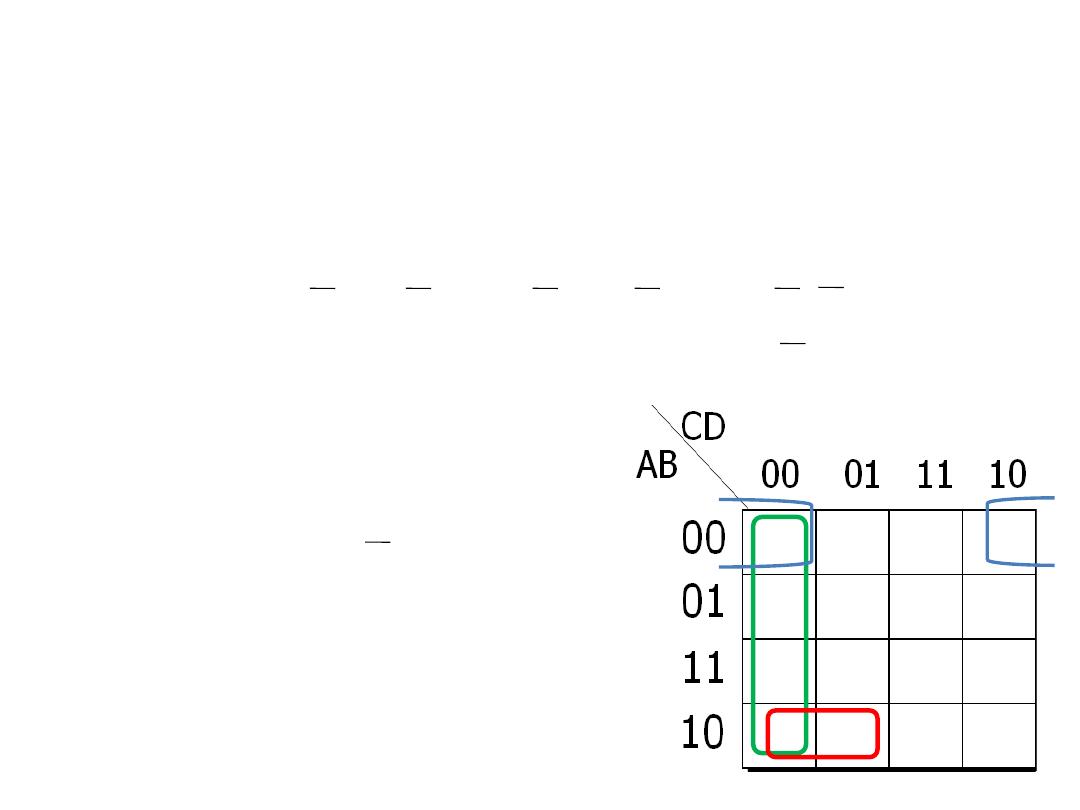
• Example: Use a Karnaugh-map to minimize the following
POS expression.
(B+C+D)(A+B+C+D)(A+B+C+D)(A+B+C+D)(A+B+C+D)
Solution: The first term must be expanded into
(A+B+C+D)
and
(A+B+C+D)
to get a standard POS
exp., which is then mapped;
and the cells are grouped as shown:
(A+B+D)
(C+D)
(A+B+C)
Dr. AMMAR ABDUL-HAMED KHADER
18
0
0
0
0
0
0

Don’t Care Conditions
• In many application it is known in advance that some of the
input combinations will never occur. For example there are six
invalid combinations in BCD code (1010, 1011, 1100, 1101,
1110 and 1111). These combinations are marked as
“Don’t
Care
Conditions” and are used as either zero’s or one’s so that
the application is implemented with the most simplified
circuit.
• In such cases we fill in the Karnaugh map with and X (don't
care).
• – When minimizing an X is like a "joker”
Dr. AMMAR ABDUL-HAMED KHADER
19
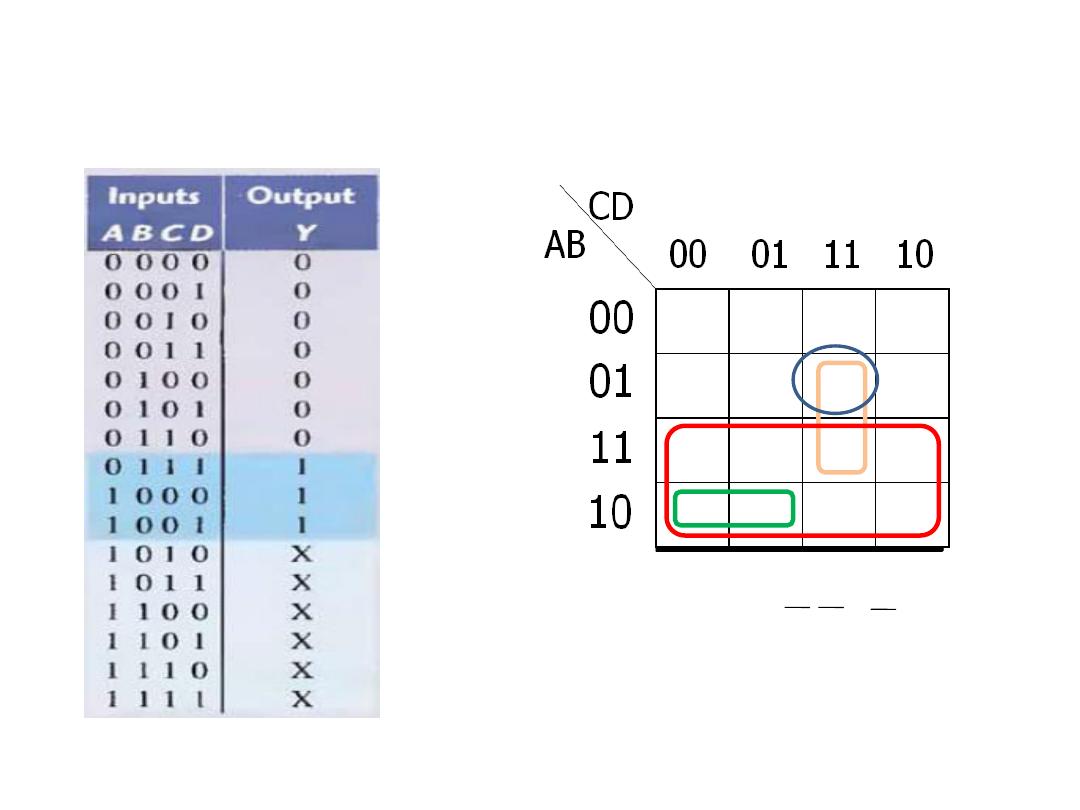
Don’t Care Conditions
•
• Without don't care: Y=
ABC
+
ABCD
• With don’t care: Y=
BCD
+
A
Dr. AMMAR ABDUL-HAMED KHADER
20
1
X
X
X
X
1
1
X
X
