
1
Dr.Aseel
Maternal pelvis &fetal skull
Labour :-
Success will depend on the three P’s:
■
Power
■
Passenger
■
Passage
■
Knowledge of the shape and dimensions of the normal female pelvis and of the fetal skull is
essential for proper understanding of the mechanism of labour and its abnormalities.The birth
canal consist of maternal bony pelvis and soft tissue.
BONY PELVIS :-
Hip bone (ilium , ischium , pubis)
■
Sacrum
■
Coccyx
■
Joined anteriorly by pubic symphysis
Posteriorly by sacro -iliac joint
Passageway: Bony pelvis :-
it is divided into:
-
False pelvis:
consist of the upper flared parts of the tow iliac crests
-
True pelvis:
the bony passageway through which the fetus must travel. The
obstetrician is only concerned with the latter. it is made up of three planes:

2
-
:
The Pelvic Inlet(Brim)
upper border of symphysis pubis
●
upper border of the superior pubic rami,
●
iliopectinal lines
●
●sacroiliac joints,
●Ala of the sacrum,
Sacral promontory
●
-
The pelvic cavity:
*the middle of the symphysis pubis
*the pubic bone,
*the obturator fascia,
*the inner aspect of the ischial bone,
*the junction of the 2nd and 3rd pieces of the sacrum.
-
The pelvic outlet:
*the lower margin of the symphysia pubis *the descending ramus of the pubic bone,
*the ischial tuberosity
*the sacro-tuberous ligament,
*the last piece of the sacrum
Pelvic shape:
4Types of pelvis:
■1. Gynecoid –
is considered the true female pelvis, although only about
half of all women have this type, vaginal birth is most favorable with this
type ,the inlet is rounded in shape with AP diameter slightely less than
transverse with slight projection of the sacral promontory ; the cavity is
roomy because the sacrum is inclined backwards and well curved , the side
walls straight and the sacro -sciatic notches are wide the ischeal spines are
of average prominent.
■The pelvic outlet is roughly diamond shaped the subpubic arch is wide>
90 and the tuberosities are far apart.
3
Measurement of normal gynaecoid pelvis :-
-
:
Pelvic inlet/ brim
it is the distance between mid point of sacral promontory
-
:
P diameter
-
A
to the mid point of upper border of pubic symphysis=11cm.
distance between the iliopectineal lines=13.5cm
-
:
Transverse diameter
-
:
Pelvic outlet
it is the distance between tip of sacrum to the mid point
-
:
P diameter
-
A
of inferior border of pubic symphysis=13.5cm
tance between the tip of two ischial
dis
-
:
Transverse or bispinous diameter
spine=11cm.
The average normal measurements are summarized in:-
transverse
Anterior-posterior
13.5 cm
11 cm
Brim
12 cm
12 cm
cavity
11 cm
13.5 cm
Outlet
2. Android –
30 % of women; “true male pelvis”The inlet is triangular with flat
posterior segment with progressively less space as moving down through the cavity
owing to the converging side walls with prominent spines, shallow sacral curve and
narrow subpubic arch .vaginal delivery is difficult and this shape predispose to deep
transverse arrest of fetal head.
3. Anthropoid –
resembles that of anthropoidape found in 20% of women with much
larger AP than transverse diameter creating along narrow oval inlet ,ischial spines are not
prominent but are close owing to the overall shape .The subpubic arch is narrow
,outwardly shaped.
This shape encourages an occipto-posterior(OP) position.
4. Platypelloid –
< 5 % of women;described as flattened pelvis;it has a much shorter AP
than transverse diameter creating an oval-shaped inlet,straight or divergent side walls, flat
sacrum ,a wide bispinous diameter &wide subpubic arch & associated with an increased
risk of obstructed labour.

4
Pelvic Types :-
Fetal head:-
●The fetal skull or cranium consists of the face, the base of the skull and
the vault of the cranium or roof.
●The bones of the face and cranial base are well fused and firmly fixed ,
but the bones of the vault are not so well ossified and are only joined by
unossified membranes at the sutures.
●The bones which form the vault are the two parietal bones , and parts
of the occipital, frontal and temporal bones.
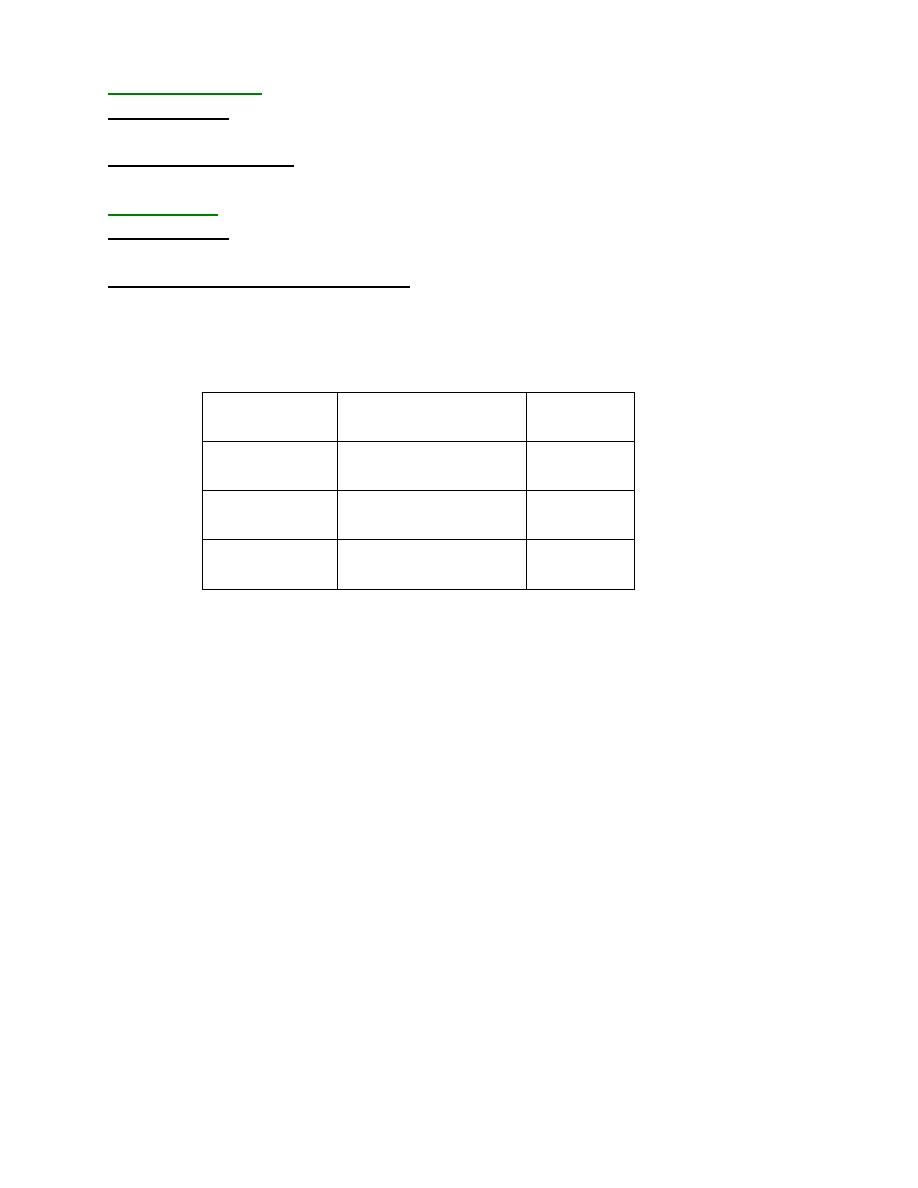
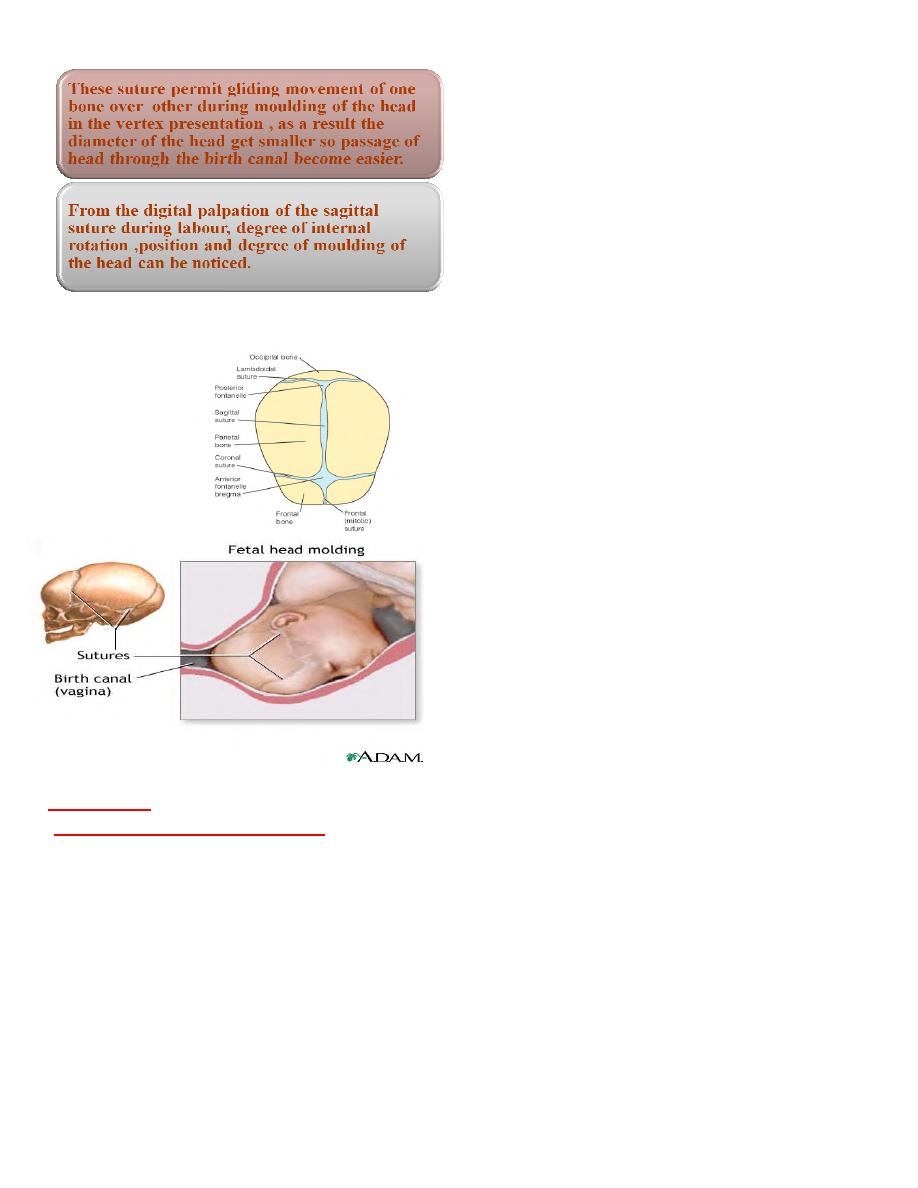
SUTURES
of the fetal skull are membranous spaces
between the cranial bones :-
5
CLINICAL IMPORTANCE OF SUTURE:-
are The points of junction of the various sutures
Fontanelles
-
:
Anterior fontanelle or bregma
∂It is a diamond shaped area of unossified membrane formed by the junction of 4 suture.
●Anteriorly:- frontal suture
●Posteriorly:- sagittal suture
●Laterally, on both side:-coronal suture.
∂It ossifies by 18 months after birth
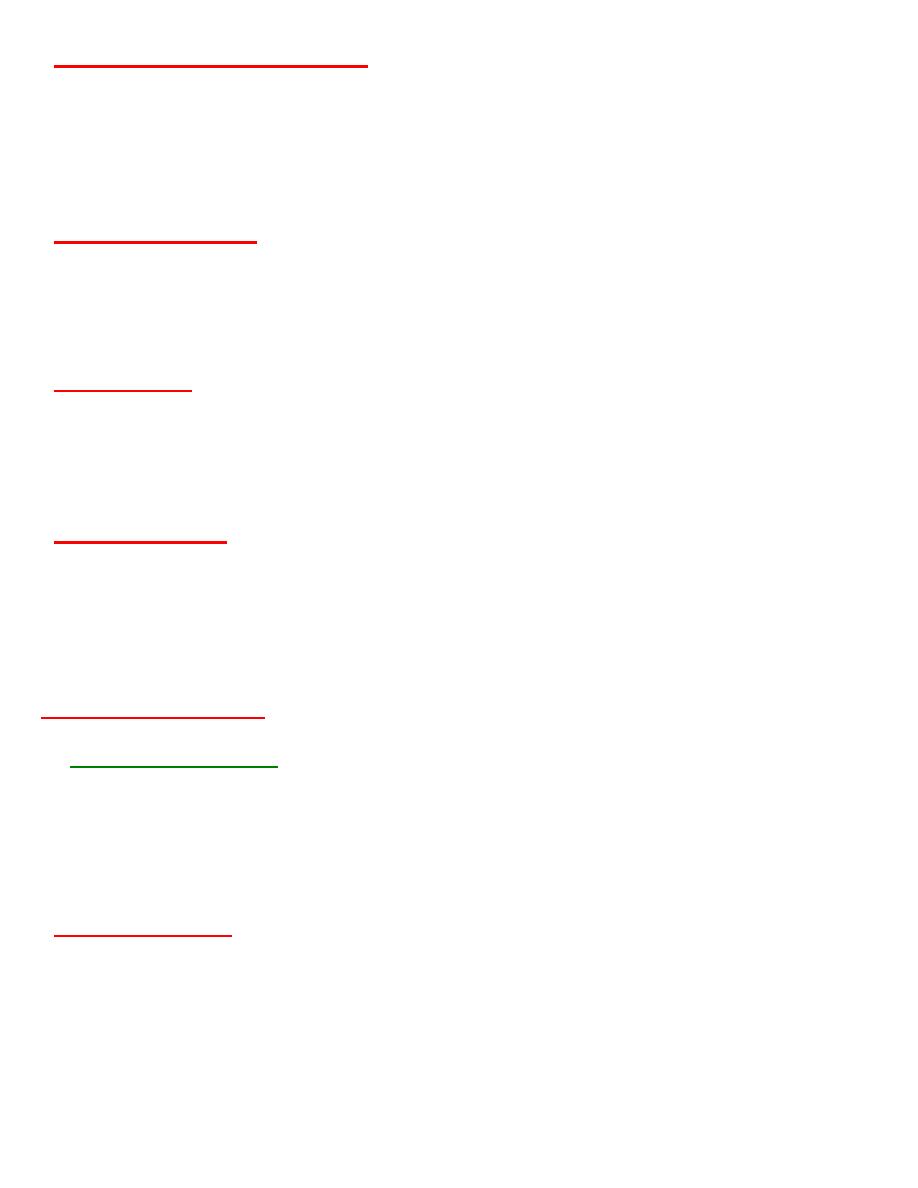
6
-
:
mbda
Posterior fontanelle or la
☼It is the triangular area at the junction of the three suture.
Anteriorly:- sagital suture
●
●Posteriorly:-2 lambdoid sutures at
both side.
☼It ossifies at 2-3 months after birth
-
:
Clinical importance
1.From their relation of the maternal pelvis, position of vertex is
determined.
2.Degree of flexion can be assessed from their position.
-
The vertex :
It is the quadrangular area bounded anteriorly by the bregma and coronal
sutures behind by the lambda and the lambdoid sutures and laterally by
the line passing through the parietal eminences.. It is the part of the head
which presents in normal labour.
-
:
Fetal attitude
■Fetal attitude is the relation of the fetal parts to one another. The normal attitude
of the fetus is one of moderate flexion of the head, flexion of the arms onto the
chest, and flexion of the legs onto the abdomen.
■The engaging diameter of the fetal skull depends on the degree of the flexion
of the presenting part.
-
:
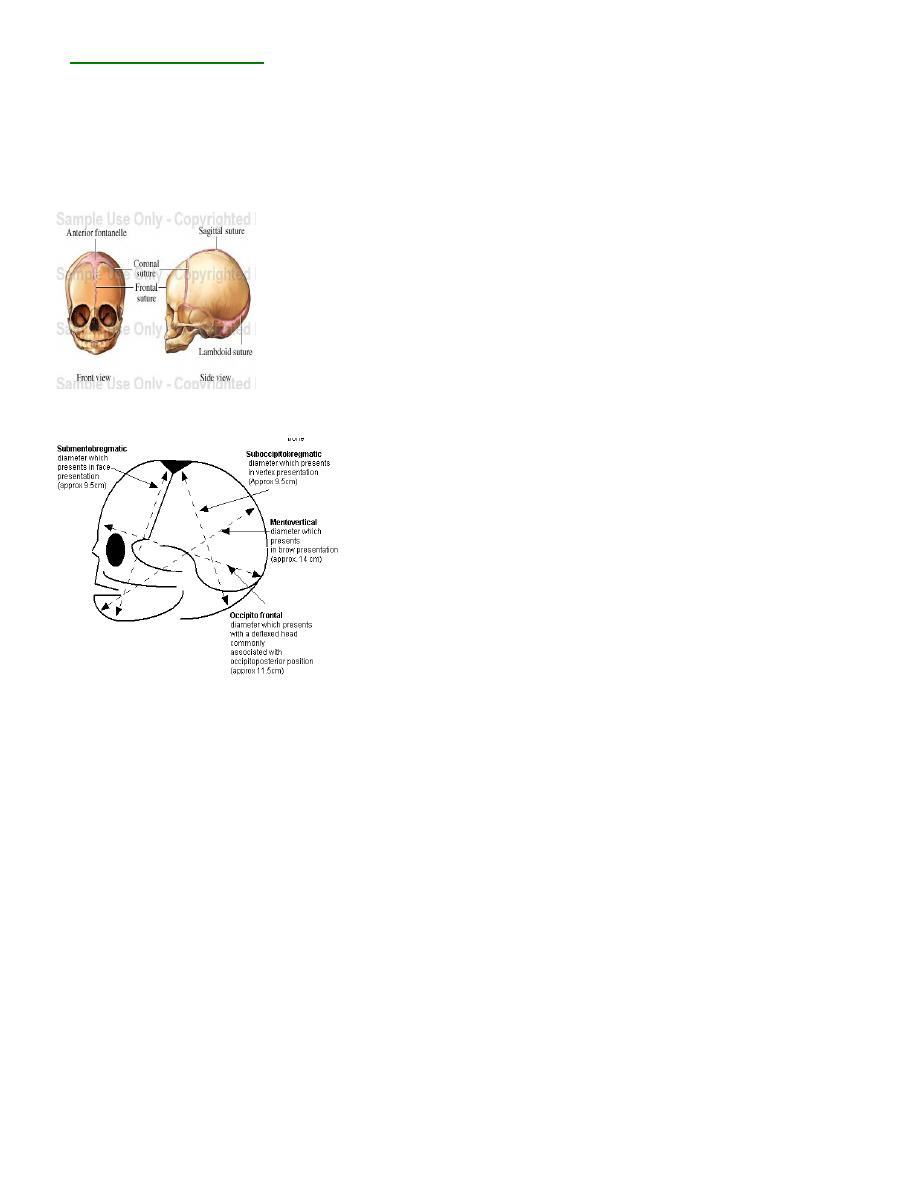
Diameter of skull
A-Anterio-posterior diameter:-
-
:
o bregmatic
occipit
-
Sub
1.
It extends from the nape of the neck to the centre of anterior fontanelle.
Length:-9.5cm
Attitude:-complete flexion
Presentation:-Vertex
-
:
Clinical importance
Smallest diameter.

7
-
:
Suboccipito frontal
2.
It extends from the nape of the neck to the prominence of forehead.
Length:-10cm
Attitude:-
Incomplete flexion.
Presentation:-Vertex.(OP)
-
:
vertical
-
Mento
4.
It extends from the mid-point of the chin to the center of the sagittal suture.
Length:-14cm
Attitude :-
Partial extension.
Presentation:- Brow
-
:
Clinical importance
In this engaging diameter, baby has to be delivered by caesarean section.
8
-
:
mento bregmatic
-
Sub
5.
It extends from below the chin to the centre of bregma.
Length:-9.5cm
Attitude:-
Complete extension
Presentation:-Face .

9
