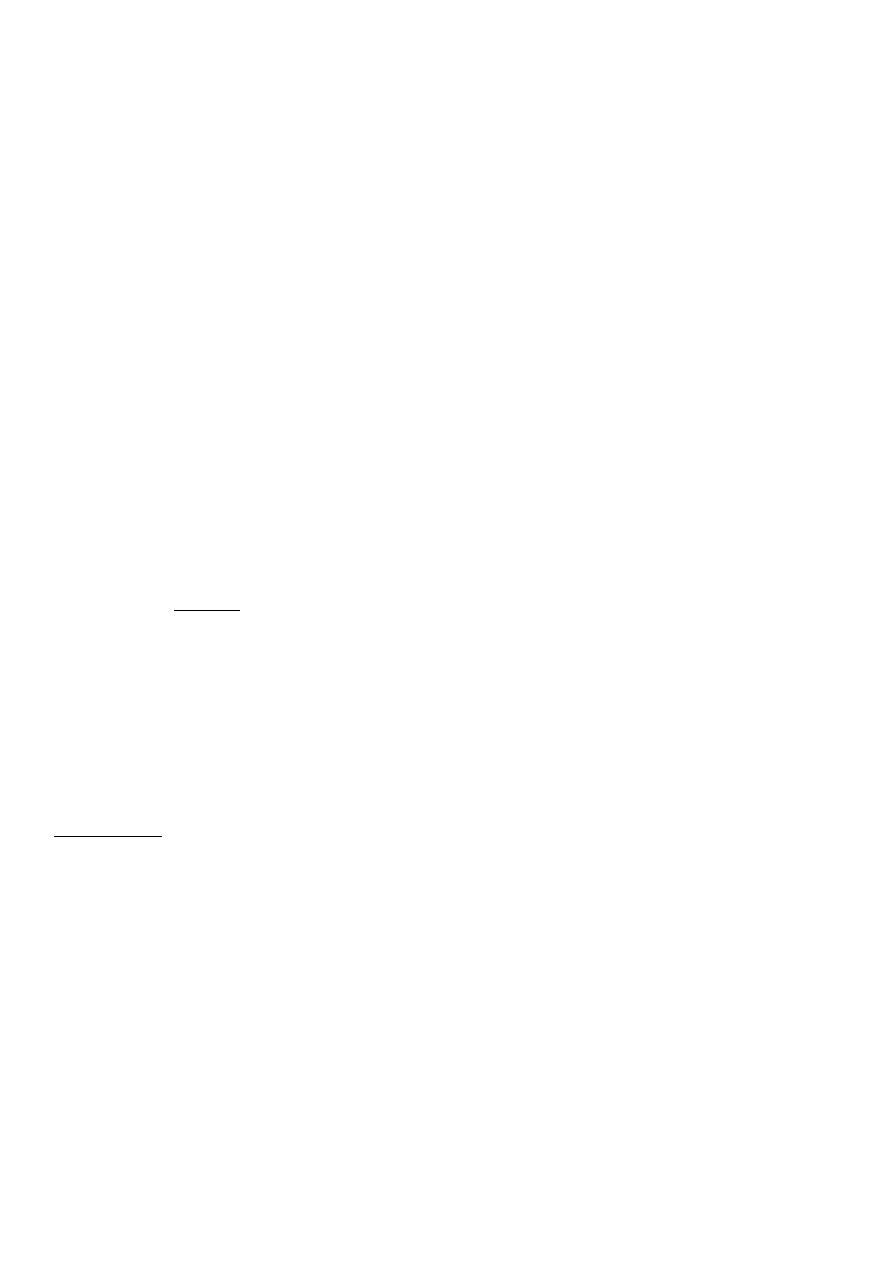
Obstetrics Dr. eman
1
Face & brow
presentation
Face presentation
Face presentation occurs in approximately 1:500 to 1000 deliveries.
The general causes for malpresentations apply for face presentation:
There is a small chance of congenital abnormality such as anencephaly.
thyroid goitre and this need to be excluded by an ultrasound examination.
In the majority it is due to extension of the head in a normal fetus.
Prematurity.
Diagnosis : The possibility of face presentation can be suspected on abdominal
examination if the prominence of the head is palpable more prominently at a
higher level on the opposite side of the fetal spine. In a thin woman a deep
groove may be palpable between the occiput and the back.
on vaginal examination when the nose, eyes and the hard gum margins are
palpated.
Difficulties may be encountered in recognizing the presentation when the
membranes are intact especially if the presenting part is high or in the presence
of oedema due to few hours of labour.
Obstetrics Dr. eman
2

Obstetrics Dr. eman
3
mechanism of labour.
The transverse submento-bregmatic diameter enters the pelvis.
In the majority it rotates forwards to be in the mento-anterior position with the
chin behind the symphysis pubis. The presenting lateral ( biparietal – 9.5 cm)
and antero-posterior (submentobregmatic – 9.5 cm) diameters are conducive
for vaginal delivery
Descent is possible posterior in the pelvis when the position is mento-anterior
because of large space in the lateral sacral area.
The head is born with the chin emerging under the pubic arch followed by the
forehead over the perineum
If the face rotates to a mento-posterior position, although the diameters are the
same as mento-anterior, the lateral dimensions of the frontal bones are large
and do not permit descent behind the narrow retro-pubic arch and hence a CS is
advisable.
Even with favourable mento-lateral or anterior position if there is failure to
progress the safer option for the fetus is CS in the first stage. In late second
stage of labour with the face at the outlet in mento-anterior or lateral position
outlet forceps delivery can be carried out by skilled personal if spontaneous
delivery is not forthcoming.
Brow presentation
In brow presentation the head is half extended and presents to the pelvis with
the largest anteroposterior diameter (mento-vertical-13 cm).
The incidence is rare and is about 1 in 1500–3000 deliveries.
The lower most part of the head that is palpable on vaginal examination is the
forehead but it is termed as brow because the orbital ridges and the bridge of
the nose are palpable .
The presentation may correct itself in labour by flexion and present as a vertex
or undergo further extension and presents a face and may result in vaginal
delivery.

Obstetrics Dr. eman
4
In early labour, preparations should be undertaken for CS and time allowed to
see whether flexion or extension would take place.
Failure to progress in the next few hours in labour with the persistence of brow
presentation is an indication for CS and not for augmentation of labour with
oxytocin
In extreme prematurity the fetus may descend as a brow and deliver as a brow
or may convert to a face or vertex after it reaches the pelvic floor.
Although vaginal delivery is possible in preterm fetuses there is a possibility of
spinal cord damage and a CS is preferred.
Complications in labour include cord prolapse with membrane rupture and rare
incidence of uterine rupture in neglected cases.
In cases of intrauterine fetal death and in those with lethal malformation in the
extreme preterm period, where injury to the fetus is not a concern, labour may
be allowed if there is good progress in anticipation of vaginal delivery.
At term, destructive operations and vaginal delivery may be possible for cases of
fetal death or lethal anomaly but CS is still preferred in the developed world for
fear of genital tract trauma in the hands of those who are not familiar with
these techniques.
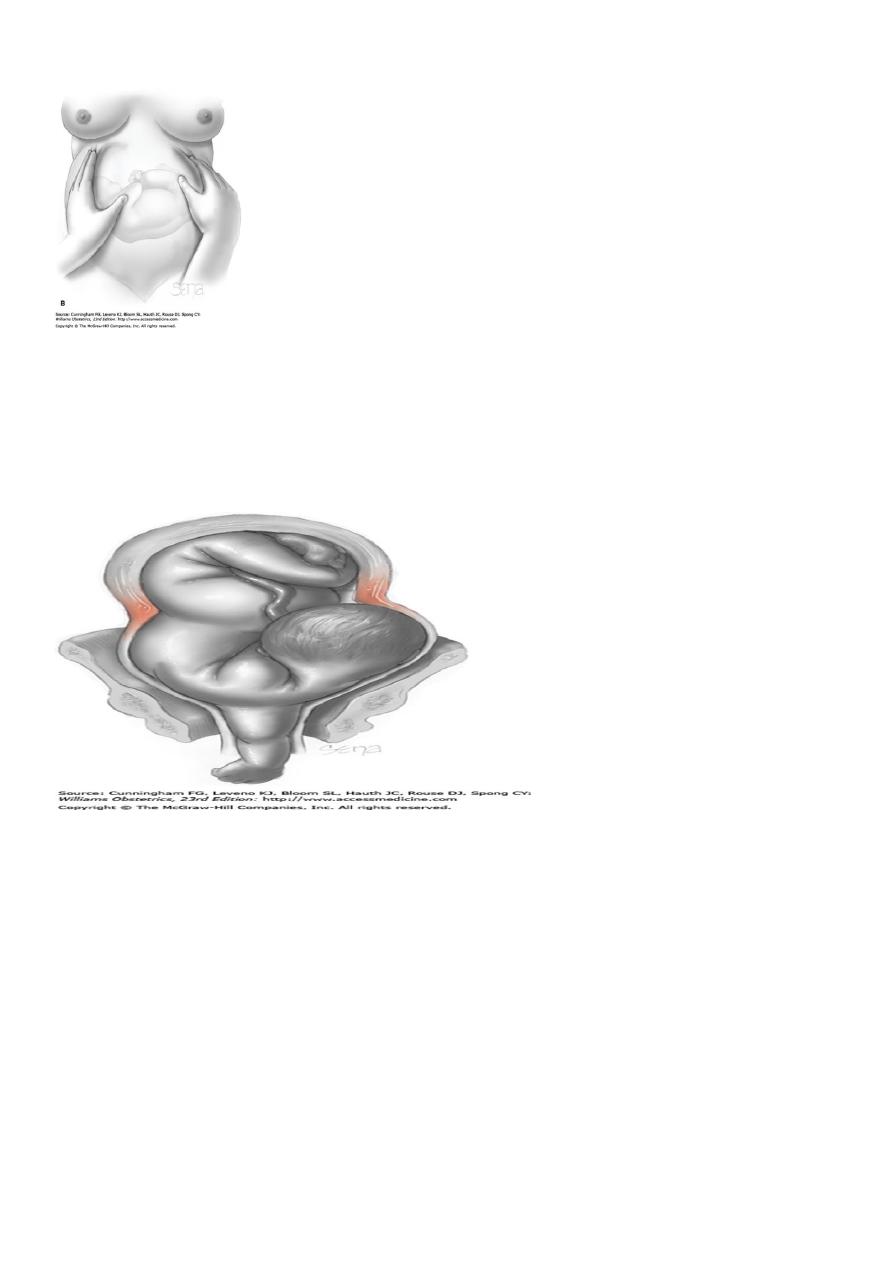
Shoulder presentation:
Causes
1-In multiparous women with singleton pregnancies shoulder presentation is
more common without any cause due to the laxity of the uterus.
2-Preterm.
3-congenital fetal or uterine malformation, fibroids, placenta praevia and
polyhydramnios.
The incidence at term is about1:400.
On abdominal examination
:
-SFH is less than expected for gestation
-Broader uterus
Obstetrics Dr. eman
5
-Empty lower uterine segment
Transverse lie with shoulder presentation in the antenatal period corrects itself
to longitudinal lie with the onset of labour due to increased muscular tone of
the uterus.if rupture of membranes take place with the fetus in the transverse
lie, cord prolapse, shoulder presentation and arm prolapse are likely possibilities
with progressive cervical dilatation.
- In early labour with the membranes intact, one could wait in anticipation of
spontaneous or assisted correction to longitudinal lie while making all the
preparation for CS. If the membranes rupture and the fetus is still in the
transverse lie, CS should be performed to avoid injury to the fetus or the uterus.
- In cases where the diagnosis is made late the fetus may be impacted in the
transverse lie and safe delivery may be only possible by a CS with a midline
vertical incision. It may be possible to deliver the fetus through a lower segment
transverse incision with acute uterine relaxation using a short acting drug (e.g.
0.25 mg terbutaline in 5 cc saline given IV over 5 min) .
- Following this treatment if the uterus does not contract despite oxytocics, a
small dose of beta blocker such as Propranolol 1 mg IV may be needed to
Obstetrics Dr. eman
6
contract the uterus and to avoid post-partum haemorrhage . Labour and
spontaneous vaginal delivery is possible in extreme preterm and macerated
fetuses.
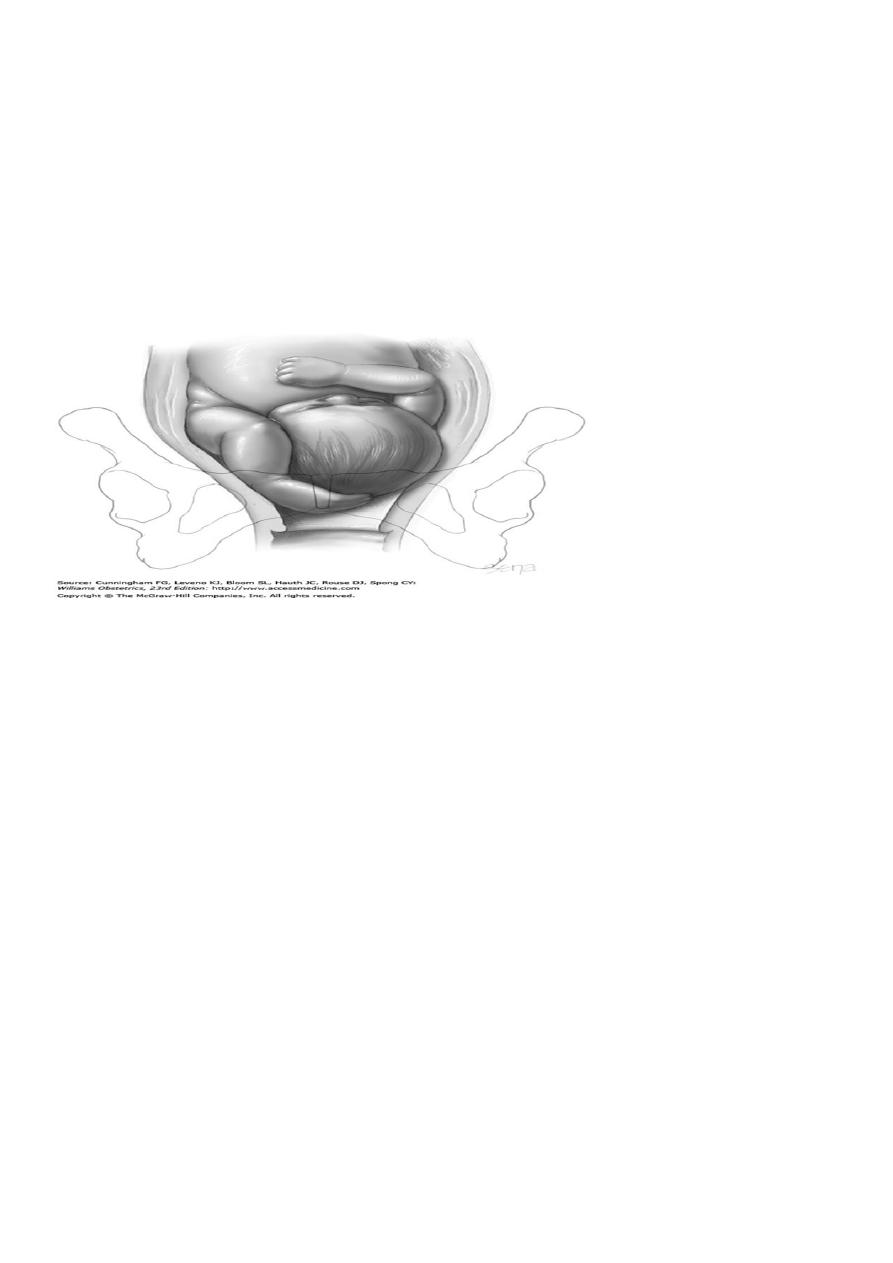
Compound presentation
:
In a compound presentation, an extremity prolapses alongside the presenting
part, and both present simultaneously in the pelvis.
Incidence 1 every 1000.
Causes of compound presentations are conditions that prevent complete
occlusion of the pelvic inlet by the fetal head, including preterm labor.
Management:
In most cases, the prolapsed part should be left alone, because most often it will
not interfere with labor. If the arm is prolapsed alongside the head, the
condition should be observed closely to ascertain whether the arm retracts out
of the way with descent of the presenting part.
If it fails to retract and if it appears to prevent descent of the head, the
prolapsed arm should be pushed gently upward and the head simultaneously
downward by fundal pressure.
Prognosis
:
In general, rates of perinatal mortality and morbidity are increased as a result of
concomitant preterm delivery, prolapsed cord, and traumatic obstetrical
procedures.
By:TWANA NAWZAD
