Head and Neck

• Mesenchyme for formation of the head region
derived from paraxial & lateral plate mesoderm,
neural crest, and thickened regions of ectoderm
known as ectodermal placodes.
• Paraxial mesoderm- floor of brain case & a
small portion of the occipital region, all voluntary
muscles of craniofacial region, dermis &
connective tissues in the dorsal region of head, &
^meninges caudal to prosencephalon.
• Lateral plate mesoderm- laryngeal cartilages
(arytenoid & cricoid) & connective tissue in this
region.

• Neural crest cells- neuroectoderm of forebrain,
midbrain & hindbrain and migrate ventrally into
pharyngeal arches & rostrally around forebrain
&optic cup into facial region. In these location
they form midfacial & pharyngeal arch skeletal
structures & all other tissues including bone,
cartilage, de ti , der is…..etc.
• Ectodermal placodes together with neural crest
form neurons of 5
th
, 7
th
, 9
th
& 10
th
cranial sensory
ganglia.
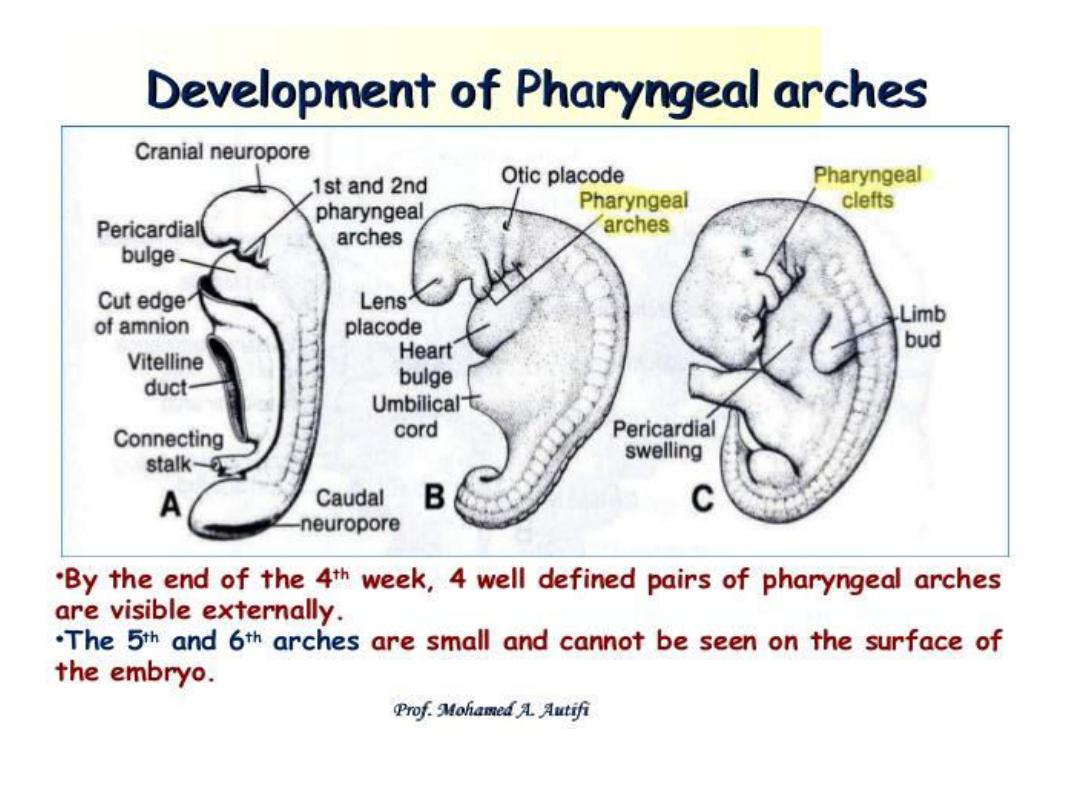

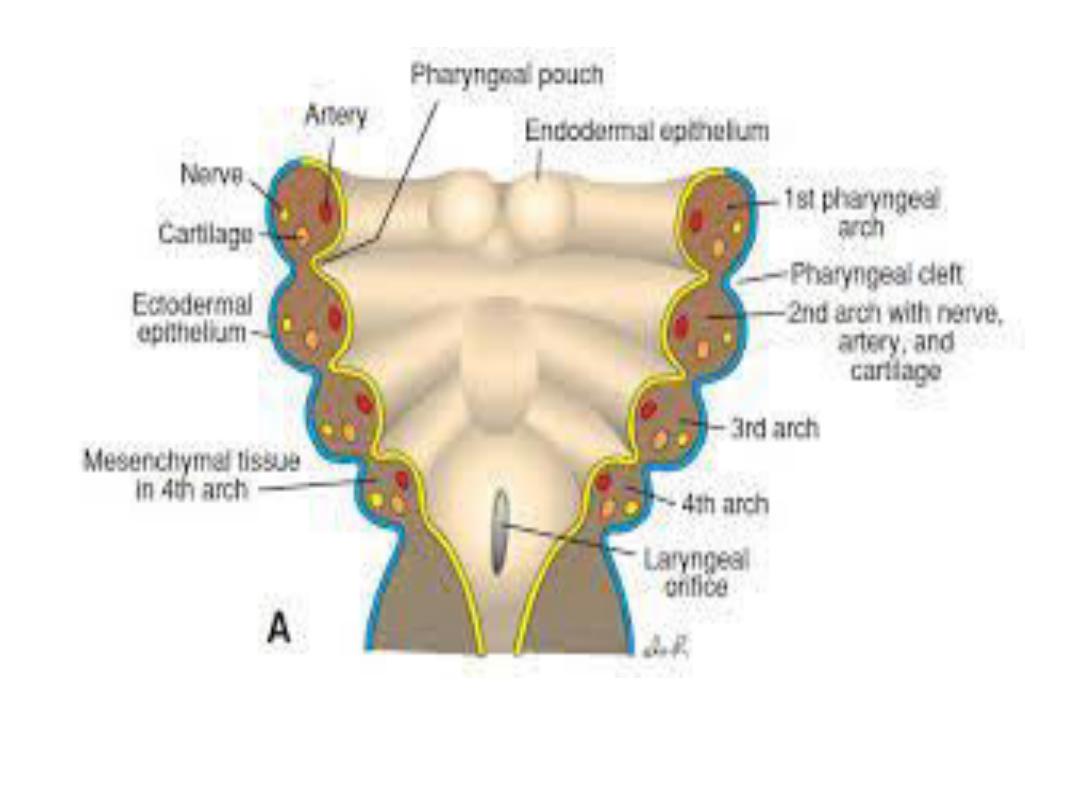
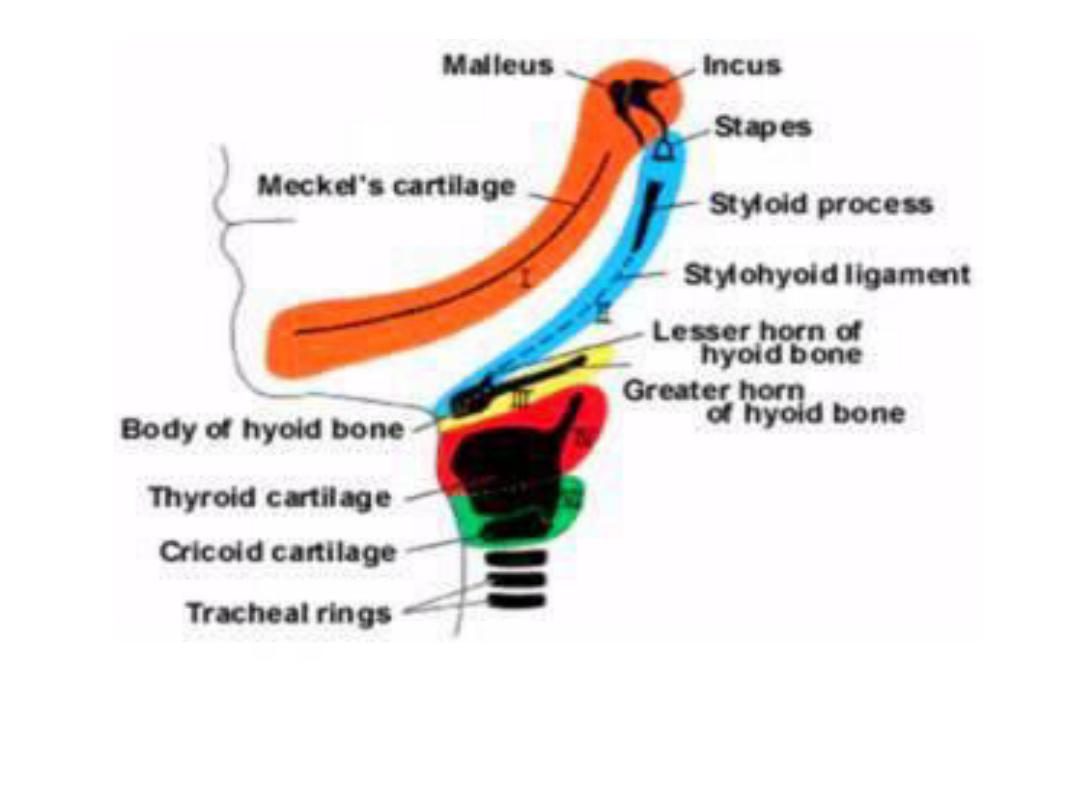
Pharyngeal arches
Consisting of bars of mesenchymal tissue
separated by pharyngeal pouches &clefts give the
head & neck their typical appearance in ^ 4
th
week.
Each arch contains its own artery, cranial nerve,
muscle element & cartilage bar or skeletal
element.
Endoderm of pharyngeal pouches gives rise to a
no. of endocrine glands & part of middle ear. In
subsequent order ^ pouches give rise to
(a) Middle ear cavity & auditory tube (pouch1)
(b) Stroma of palatine tonsil (pouch 2 )

(c) Inferior parathyroid glands & thymus
(pouch3).
(d) Superior parathyroid glands &
ultimobranchial body (pouch 4 &5).
Pharyngeal clefts give rise to only one
structure, the external auditory meatus.
The thyroid gland originates from an epithelial
proliferation in the floor of tongue & descends
to its level in front of the tracheal rings in the
course of development

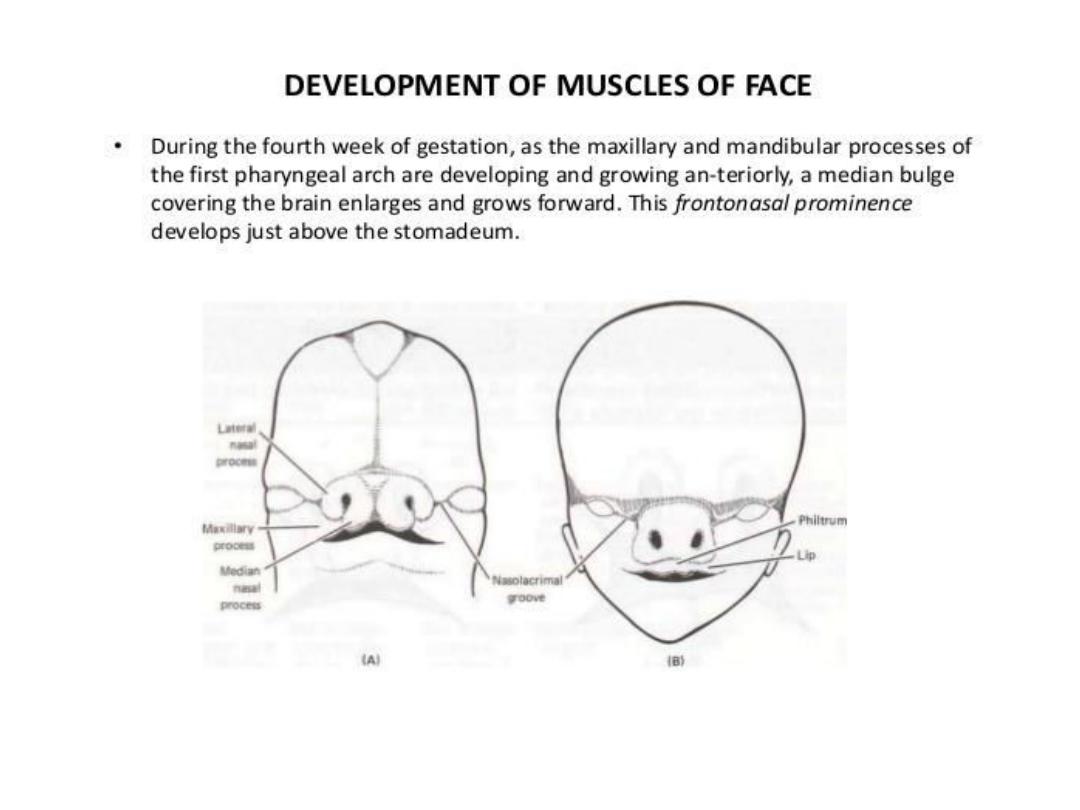
• The paired maxillary & mandibular prominence are
the 1
st
prominences of ^ facial region.
• Later, medial & lateral nasal prominences form
around ^ nasal placodes on the frontonasal
prominence. All of these structures are important,
since they determine, through fusion & specialized
growth, ^ size & integrity of ^ mandible, upper lip,
palate and noise.
• Formation of upper lip occurs by fusion of ^ two
maxillary prominence with the two medial nasal
prominences.
• The intermaxillary segment is formed by merging of
the two medial nasal prominences in the midline.

• This segment is composed of
(a)^ philtrum
(b) ^ upper jaw component, which carries ^ 4
incisor teeth.
(c) ^ palatal component, which forms the triangular
primary palate.
• The nose is derived from (a) ^ frontonasal
prominences, which forms the bridge. (b) ^
medial nasal prominences which provide ^ crest
&tip; & (c) ^ lateral nasal prominences, which
form the alae.

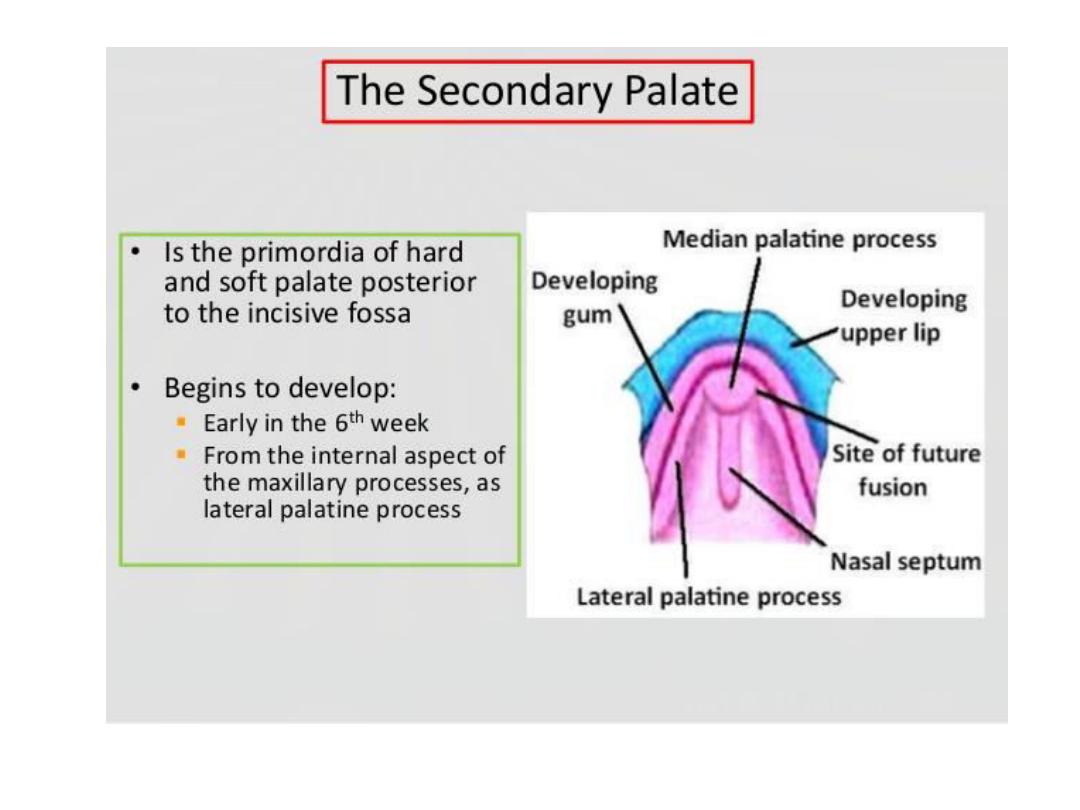
• Fusion of the palatal shelves, which form from ^
maxillary prominences, creates ^ hard & soft
palate.
• A series of cleft deformities may result from partial
or incomplete fusion of these mesenchymal tissues
which may be caused by hereditary factors and
drugs ex. (diphenylhydantoin).
• The adult form of the face is influenced by
development of paranasal sinuses, nasal conchae,
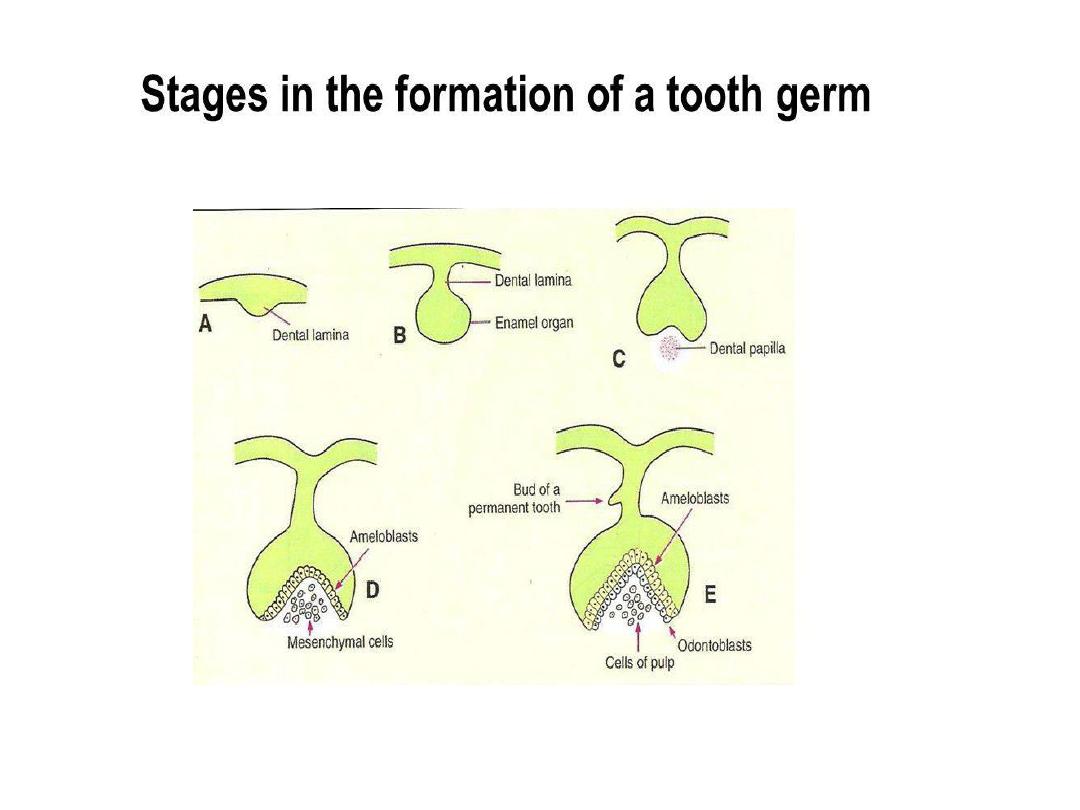
& teeth. Teeth develop from epithelial-
mesenchymal interactions between oral epithelium
& neural crest- derived mesenchyme.

• Enamel is made by ameloblasts. It lies on a thick
layer of dentin produced by odontoblasts, a
neural crest derivative.
• Cementum is formed by cementoblasts, another
mesenchymal derivative found in the root of ^
tooth.
• The 1
st
teeth (deciduous teeth or milk teeth)
appear 6-24 months after birth. And the
definitive or permanent teeth, which supplant
the milk teeth are formed during 3
rd
month of
development.