
Page 1 of 5
Q1)
In the table provided below, the results of a new diagnostic test for Cancer are
compared with the complete diagnostic package in current use in a random
sample representing the general population. What are the sensitivity,
specificity, accuracy, PPV and NPV of the new test. Would you recommend it
for screening purposes in the general population? Would you justify its use for
diagnosis of Cancer? For what purpose such test is good for?
Q2)
A physical examination was used to screen for breast Cancer in 2500 women
with biopsy proven adenocarcinoma of the breast and in 5000 age and race
matched control women. The results of the physical examination were positive
(i.e. a mass was palpated) in 1800 cases and 800 control women (who showed
no evidence of cancer at biopsy).
Q3)
A colon Cancer screening study is being conducted in a town. Individuals
aged 50 to 75 years will be screened with the hemoccult test, a stool sample is
tested for the presence of blood (RBCs under microscope). The hemoccult test
has a sensitivity of 70% and a specificity of 75%. If the prevalence of ca colon
in the population of 50-75 years of age in this town is 20/1000, What is the
PPV for this test? Interpret the value of PPV. Use a hypothetical sample of
5000.
Page 2 of 5
Q1)
In the table provided below, the results of a new diagnostic test for Cancer are
compared with the complete diagnostic package in current use in a random
sample representing the general population. What are the sensitivity,
specificity, accuracy, PPV and NPV of the new test. Would you recommend it
for screening purposes in the general population? Would you justify its use for
diagnosis of Cancer? For what purpose such test is good for?
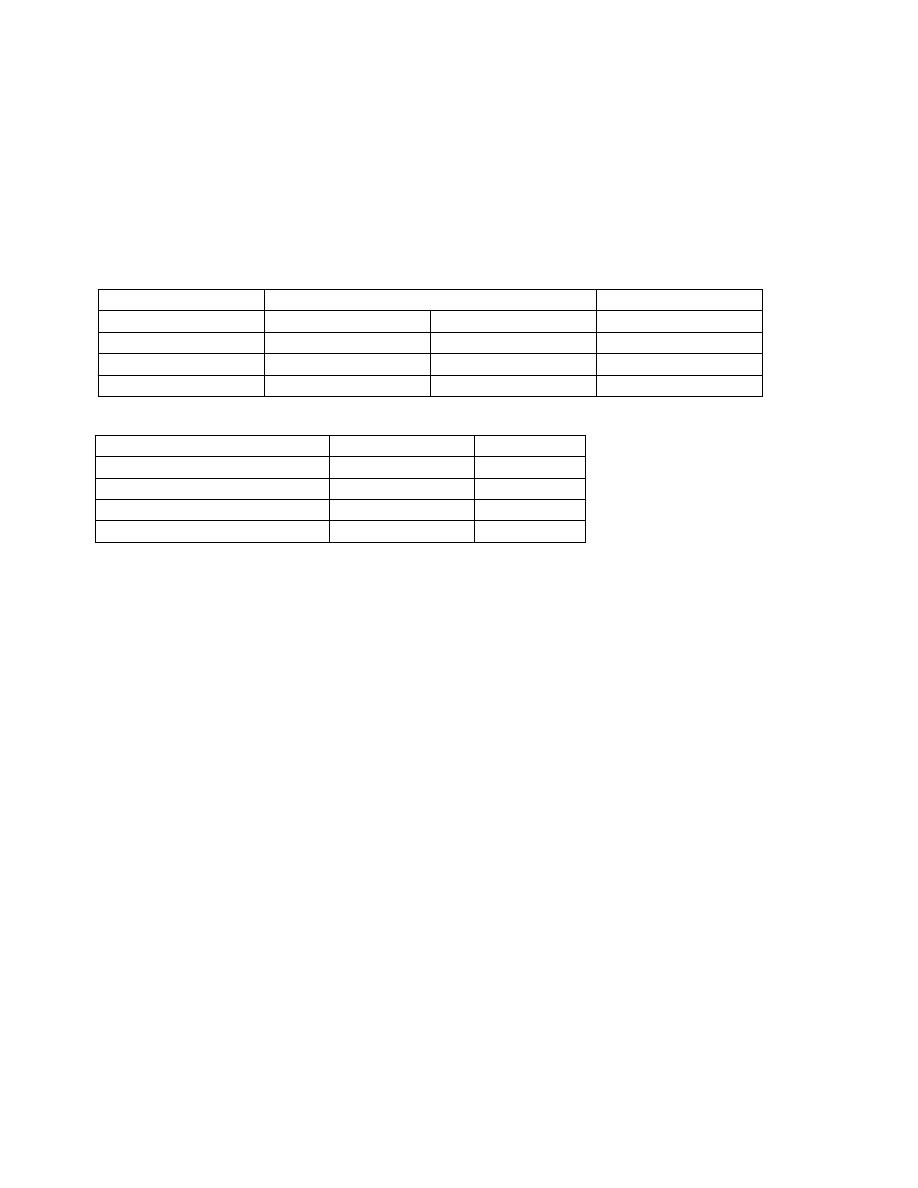
Complete diagnosis (true disease status)
New test
Ca Present
Ca absent
Total
+ve
9
1000
1009
-ve
1
9000
9001
Total
10
10000
10010
Sensitivity =
(9/10)x100
=90%
Specificity =
(9000/10000)x100 =90%
Prevalence (pretest probability)= (10/10010)x100000 =99.9/100,000
PPV =
(9/1009)x100
=0.9%
NPV =
(9000/9001)x100
=99.99%
I would not recommend it for screening purposes although the test is fairly
sensitive (90%) because the prevalence of the diseases in general population is very
low (99.9 per 100000) resulting in very low PPV (1% only), therefore only 1 in every
100 possible case is really Ca resulting in unnecessary anxiety on the part of false
positive Ca cases.
I would not justify its use for establishing the diagnosis of Ca since its PPV is
very low (1% only)
The test is suitable to exclude a possible diagnosis of Ca in subjects with no
other reason to suspect a Ca in them (like in screening) since its NPV is almost
perfect (100%).
Page 3 of 5
Q2)
A physical examination was used to screen for breast Cancer in 2500 women
with biopsy proven adenocarcinoma of the breast and in 5000 age and race
matched control women. The results of the physical examination were positive
(i.e. a mass was palpated) in 1800 cases and 800 control women (who showed
no evidence of cancer at biopsy).
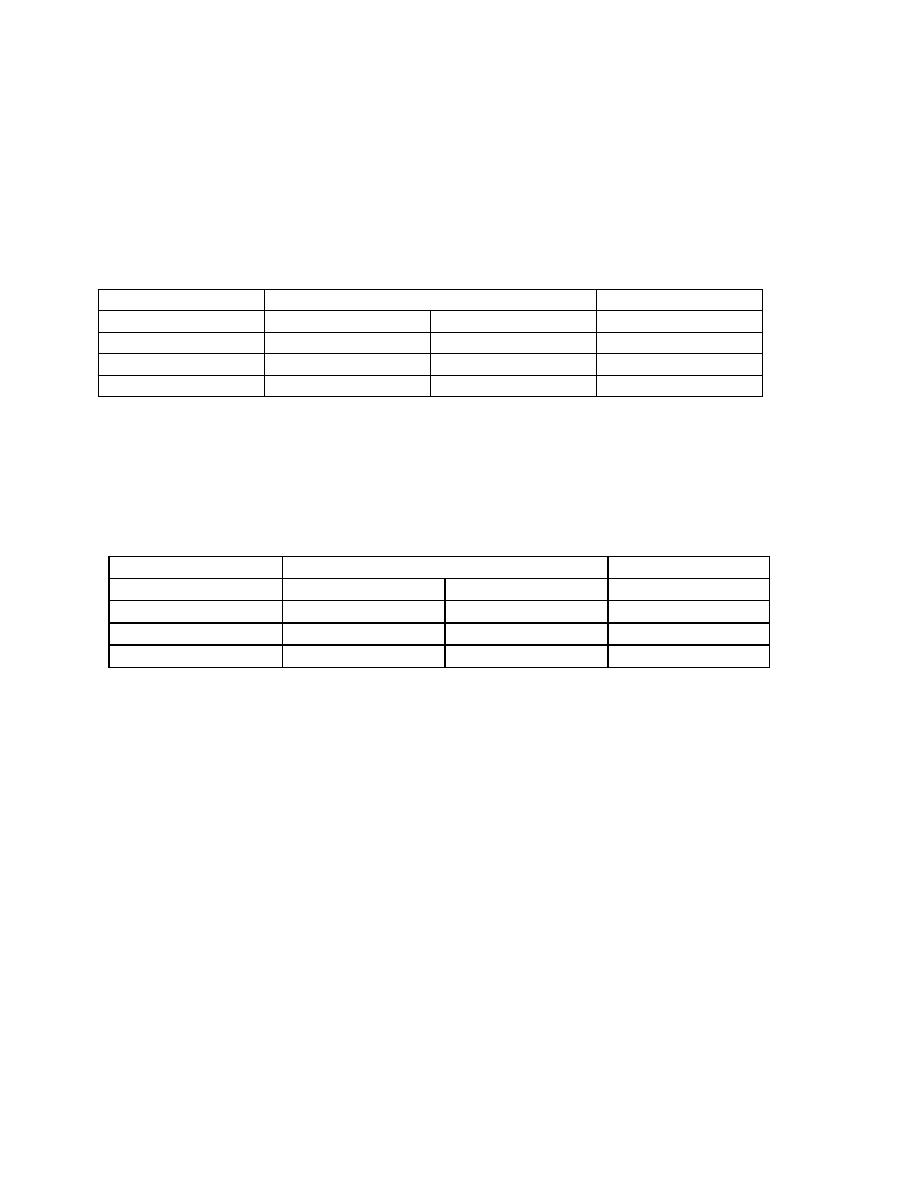
biopsy proven adenocarcinoma of the breast
Physical examination
Ca Present
Ca absent
Total
+ve
-ve
Total
2500
5000
7500
What are the sensitivity, specificity, proportion of false positive and false
negative test, accuracy, PPV and NPV of physical examination when used to predict
Ca breast? What is the pretest probability of breast Ca in the present example?
biopsy proven adenocarcinoma of the breast
Physical examination
Ca Present
Ca absent
Total
+ve
1800
800
2600
-ve
700
4200
4900
Total
2500
5000
7500
Sensitivity =
(1800/2500)x100
=72%
Specificity =
(4200/5000)x100
=84%
Prevalence (pretest probability)= (2500/7500)x100
=33.3%
PPV =
(1800/2600)x100
=69.2%
NPV =
(700/4900)x100
=85.71%
Proportion of false positive=
100-specificity = 100-84 =16%
Proportion of false negative=
100-sensitivity = 100-72 =28%
Page 4 of 5
Q3)
A colon Cancer screening study is being conducted in a town. Individuals
aged 50 to 75 years will be screened with the hemoccult test, a stool sample is
tested for the presence of blood (RBCs under microscope). The hemoccult test
has a sensitivity of 70% and a specificity of 75%. If the prevalence of ca colon
in the population of 50-75 years of age in this town is 2/1000, What is the
PPV for this test? Interpret the value of PPV. Use a hypothetical sample of
5000.
Prevalence = Total diseased / Total sample examined = 2/1000 = 0.002
Sensitivity = T+/total diseased = 0.70
Specificity = T- / total disease free = 0.75.
0.002 = Total diseased / 5000
Total diseased = 5000 x 0.002 = 10
0.70 = T+/10
T+ = 0.70x10=7
0.75 = T- / (5000-10)
T- = 0.75 x 4990 = 3743
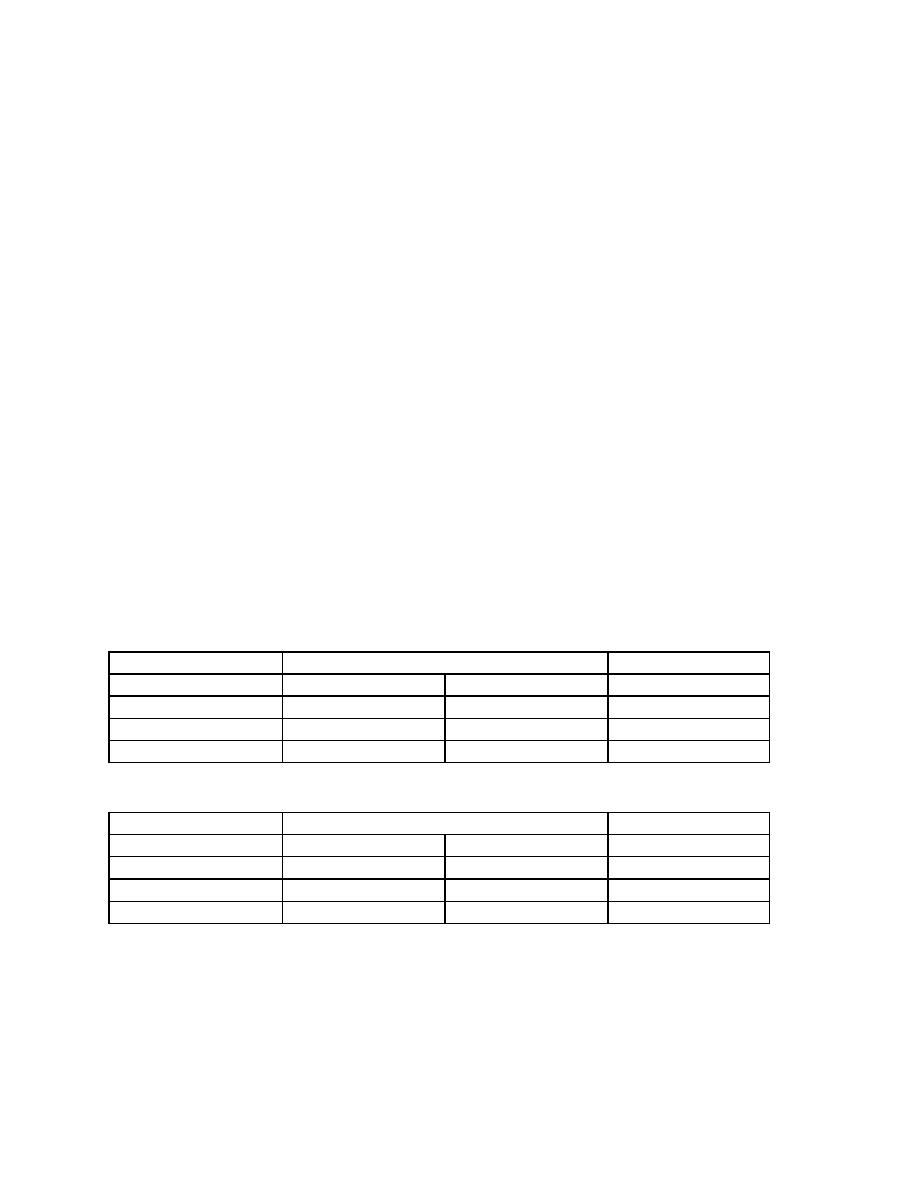
Final diagnosis of Ca colon
hemoccult test
Ca Present
Ca absent
Total
+ve
T+
F+
-ve
F-
T-
Total
Total diseased
Total disease free
5000
Final diagnosis of Ca colon
hemoccult test
Ca Present
Ca absent
Total
+ve
7
1247
1254
-ve
3
3743
3746
Total
10
4990
5000
PPV = (7/1254)x100 =0.6%
The PPV is very low. The test is of no use in establishing the diagnosis of Ca
colon, since the confidence in its positive value is less than 1%.
Page 5 of 5
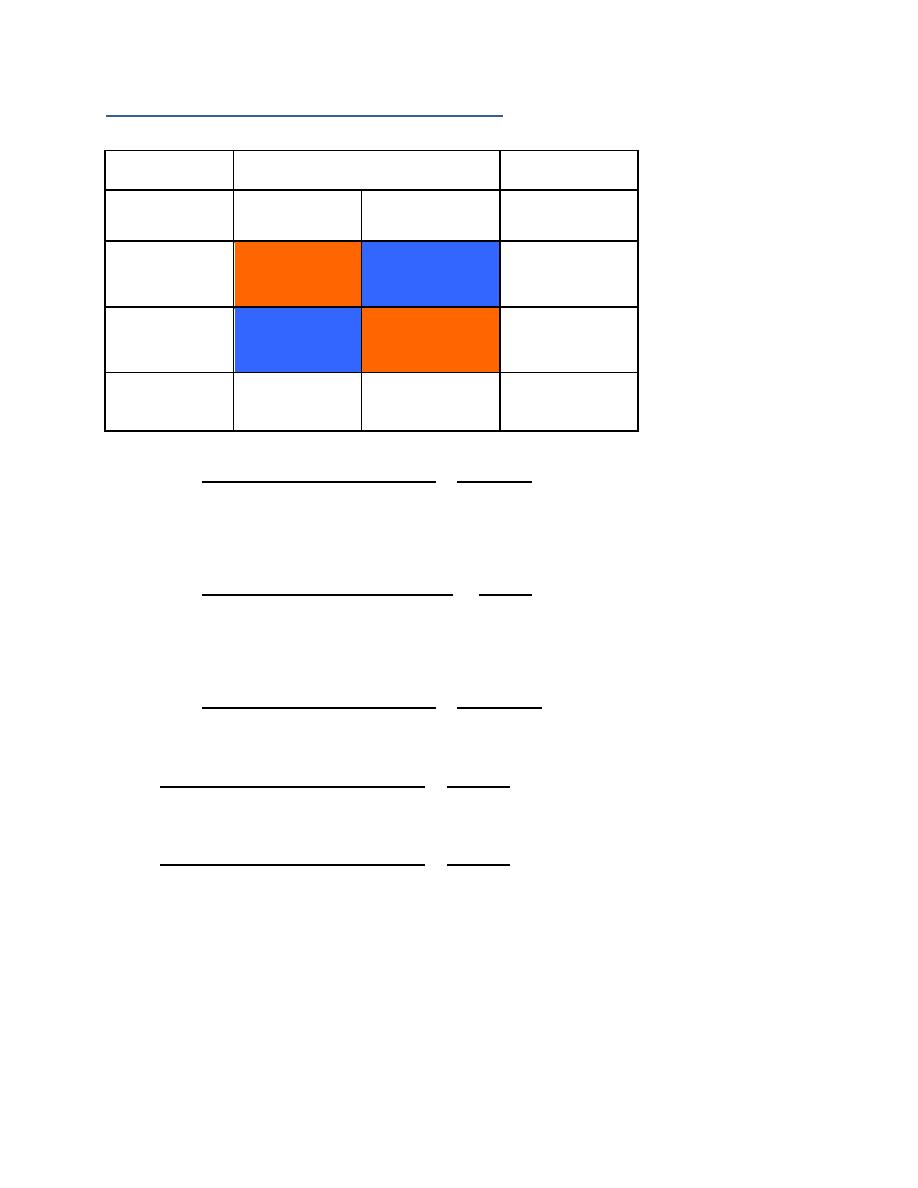
Formula used in calculations
Disease status
Test results
Disease
positive
Disease
free
Total
+ve
(A)
True +ve test
(B)
False +ve test
Total positive test
results
-ve
(C)
False –ve test
(D)
True -ve test
Total negative
test results
Total
Total cases
(disease)
Total non-cases
(disease free)
Total sample
Sensitivity
=
Number of true positives
=
A
Number of diseased people
A+C
Proportion of false negative = 1-sensitivity or 100-sensitivity%
Specificity
=
Number of true negative
=
D
Number of disease free people
B+D
Proportion of false positive = 1-specificity or 100-specificity%
Accuracy =
Number of true +ve and -ve
=
A+D
Total sample size
A+B+C+D
PPV =
Number of true positive
=
A
Number of all positive test results
A+B
NPV =
Number of true negative
=
D
Number of all negative test results
C+D
