
Citric Acid Cycle / Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle {TCA} /
Krebs Cycle
DR. AWS HASSAN
2
ND
LECTURE
● The cycle is a sequence of reactions taking place in the mitochondria in which
the acetyl moiety of Acetyl-CoA (derived from carbohydrates , lipids & proteins)
is oxidized to CO
2
& H
2
O and in which reduced coenzymes are produced .
The reduced coenzymes are then re-oxidized in the electron transport chain
to generate ATP .
Reactions of TCA cycle :
1 . Condensation of acetyl-CoA with oxaloacetate forming Citrate catalyzed by the
enzyme citrate synthase .
2 . Isomerization of Citrate to Isocitrate .
3 . Isocitrate undergo oxidative decarboxylation to
α
-ketoglutarate by the enzyme
isocitrate dehydrogenase which is NAD
+
-linked . One molecule of NADH is
produced and one molecule of CO
2
is released .
4 . Second oxidat
ive decarboxylation converts α-Ketoglutarate to high-energy
compound succinyl-CoA . One molecule of CO
2
is released and one molecule
of NADH is produced .
5 . Succinyl-CoA is converted to Succinate by the enzyme Succinate
thiokinase . GDP is phosphorylated to GTP .
GTP is equivalent to ATP .
6 . Succinate is oxidized to Fumarate by FAD-linked Succinate dehydrogenase . One
molecule of FADH
2
is formed .
7 . Fumarate is hydrated by the enzyme Fumarase to form L
–malate .
8 . Regeneration of oxaloacetate
: the cycle is completed by the oxidation of malate to
Oxaloacetate by NAD
+
-linked malate dehydrogenase . One molecule of NADH is
produced .
Energy production by the TCA cycle
*
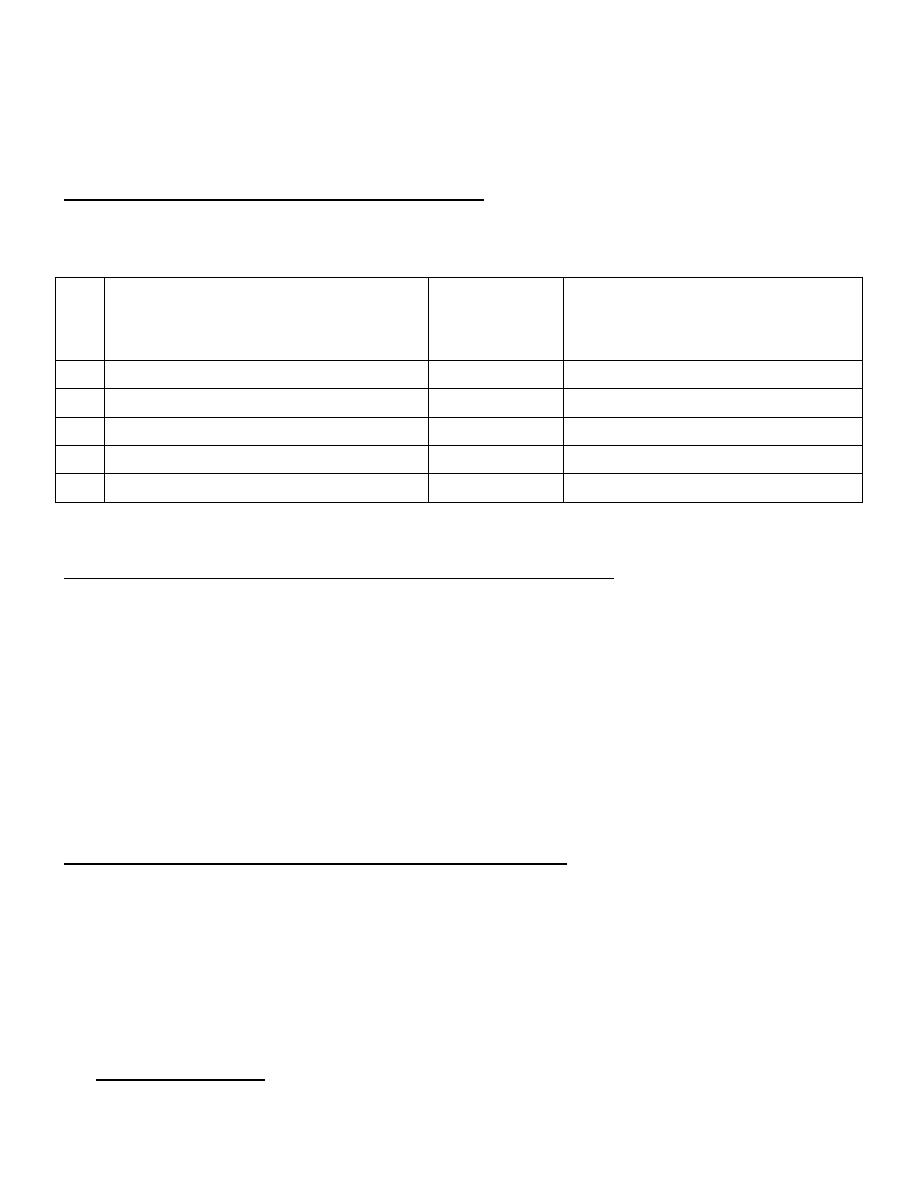
Number of ATP molecules generated by TCA Cycle per molecule of Glucose :
Enzyme/step
Source
Number of ATP gained
or used
3.
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
2 NADH
6 ATP ( gained )
4.
α-
Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase 2 NADH
6 ATP ( gained )
5.
Succinate thiokinase
2 GTP
2 ATP ( gained )
6.
Succinate dehydrogenase
2 FADH
2
4 ATP ( gained )
8.
Malate dehydrogenase
2 NADH
6 ATP ( gained )
Total = 24 ATP generated per molecule of glucose
ATP formation in the aerobic metabolism of glucose
1.
Glycolysis reactions to Pyruvate = 8 molecules of ATP gained
2.
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase step :
Two molecules of NADH produced = 6 molecules of ATP generated
3.
Citric Acid Cycle = 24 molecules of ATP generated
Total ATP per molecule of glucose under aerobic condition = 8+6+24 = 38 ATP
Metabolic Purposes ( Importance ) of TCA cycle
1.
Citric acid cycle is the major energy-producing pathway in the body . The cycle
is the common pathway for the aerobic oxidation of carbohydrates , lipids , and
proteins to generate energy ( ATP ) .
2.
The citric acid cycle is amphibolic in nature ; it functions in both oxidative
pathway (catabolism) and synthetic pathway ( anabolism) ; TCA cycle acts
as link between catabolic and anabolic pathways .
Catabolic function
■ Glucose and fatty acids are metabolized to acetyl-CoA which enters the cycle

and oxidized .
■ Amino acids are metabolized to acetyl-CoA or to intermediates of the cycle .
Anabolic function
■ Some of the intermediates of the cycle act as the starting point for the synthesis
of the compounds needed by the living cells . Ex: Synthesis of :
Heme from succinyl-CoA ,
3.
Reactions of the TCA cycle are utilized in the fasting state for the production of
glucose from non
– carbohydrate sources ( Gluconeogenesis ) .
4. Reactions of TCA cycle are also used to synthesize amino acids or to convert one
amino acid to another ; ex:
Regulation of citric acid cycle
The cycle is regulated by the need of the cell for ATP :
When the concentration of ATP is high (when the cell has an adequate energy
supply ) , the electron transport chain slows down and NADH builds up .
NADH & ATP inhibit all the enzymes catalyzing the reactions of
the cycle that generate NADH ( specially isocitrate dehydrogenase ) resulting
in slowing of the cycle .

