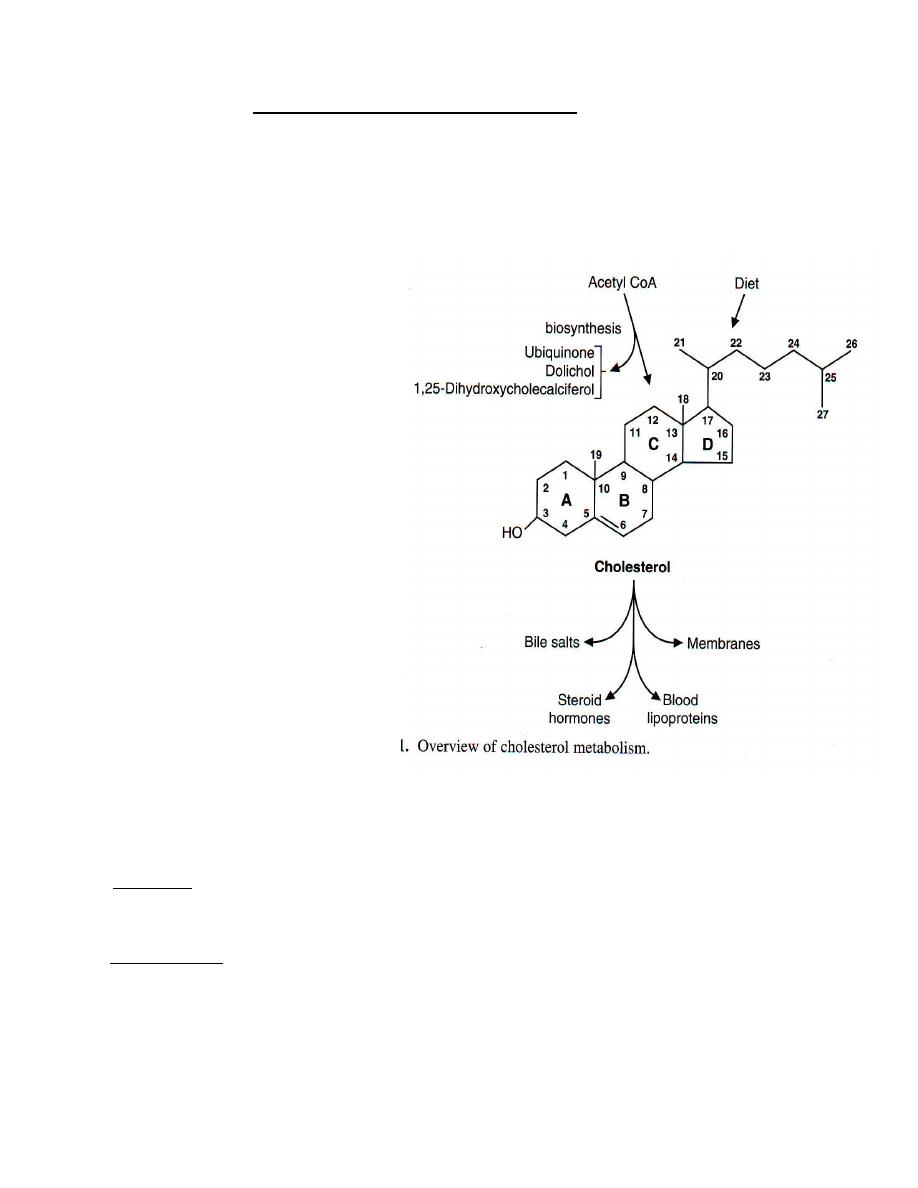
CHOLESTEROL & Bile Salts
● Cholesterol is the most common sterol in the body ; serves as :
1. a stabilizing component of cell membranes and
2. a precursor of the bile salts and steroid hormones ;
3. precursors of cholesterol are converted in the skin to cholecalciferol , the
active form of vitamin D .
● Cholesterol is present in tissues and in plasma either as free cholesterol( C )
or esterified cholesterol ( CE ) .
■ In tissues , the free cholesterol is mainly in the cell membranes and the
esterified cholesterol is the storage form inside the cells .
■
In the plasma , the greater part of cholesterol ( 75% ) is esterified and the
rest is free ; both are transported in the plasma in different lipoproteins ;
the highest proportion is found in LDL and transports cholesterol into
peripheral tissues .
● The enzymes that esterify cholesterol are :
(a) Lecithin –Cholesterol Acyl Transferase ( LCAT ) which is located in the
blood and esterifies cholesterol associated with the lipoprotein HDL ;
(b) Acyl: Cholesterol Acyl Transferase ( ACAT ) which is located in cells
( particularly cells that need to store cholesterol for the synthesis of
steroid hormones )
Sources of cholesterol :
● Cholesterol can be synthesized in the body ( endogenous , about 700 mg/day )
or obtained from the diet in foods of animal origin mainly meat and egg
(exogenous , about 300 mg/day ) .
BIOSYNTHESIS :
● Cholesterol is synthesized by a pathway that occur in most cells of the body but
to a greater extent in cells of the liver , intestine , adrenal cortex and gonads ;
Liver is responsible for 80% of endogenous synthesis .
● Enzymes involved in cholesterol synthesis are located in the cytoplasm and in
endoplasmic reticulum .
● All carbon atoms of cholesterol are derived from cytosolic acetyl CoA produced
mainly from dietary glucose or caloric excess of dietary protein .
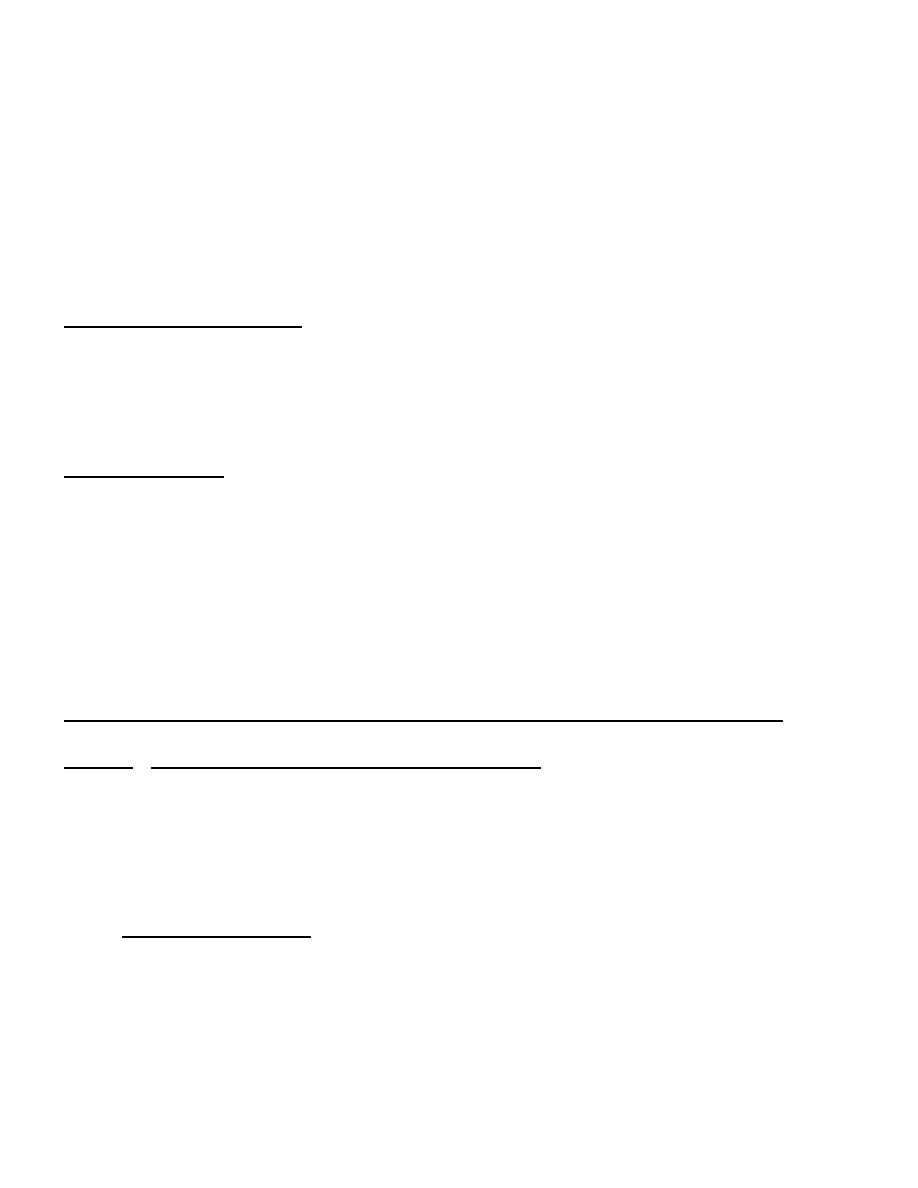
The pathway for the synthesis of cholesterol occurs in three phases
:
Phase I : Synthesis of
Mevalonate
from acetyl CoA : Include three reactions :
1. Two molecules of cytosolic acetyl CoA condense to form acetoacetyl CoA catalyzed
by cytoplasmic thiolase .
2. Another molecule of acetyl CoA combine with acetoacetyl CoA to form
β-hydroxy-β-methyl glutaryl CoA ( HMG-CoA ) catalyzed by cytoplasmic
HMG-CoA synthase-II ( mitochondrial fraction of this enzyme is involved in the
synthesis of ketone bodies ) .
3. HMG-CoA is reduced to mevalonate using NADPH as reducing agent .This is
catalyzed by HMG-CoA reductase located in the endoplasmic reticulum .
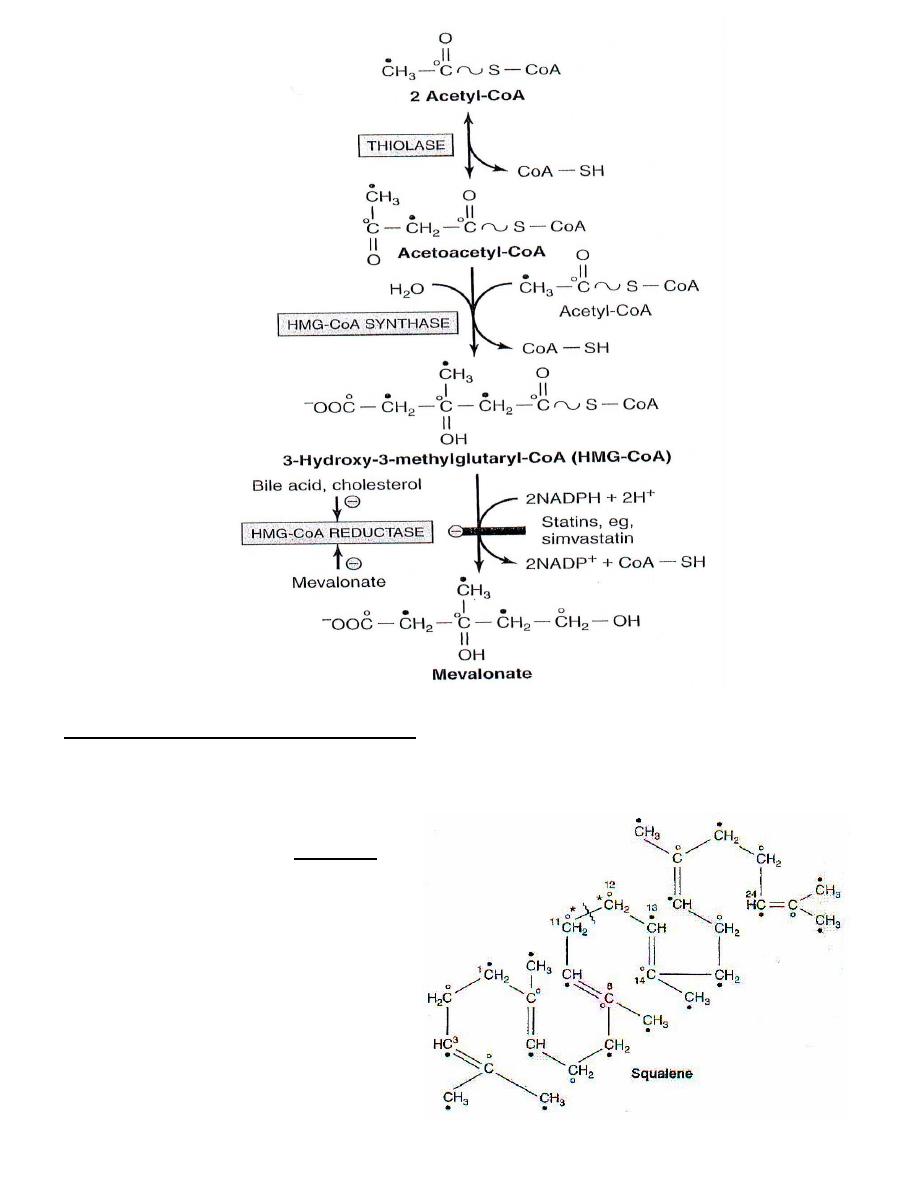
Phase II : Synthesis of squalene :
● Mevalonate is phosphorylated by ATP and subsequently decarboxylated &reduced
to produce 5-carbon isopentenyl pyrophosphate ( isoprene unit) .
● The isoprene units may condense to
form 30-carbon compound squalene as
follows :
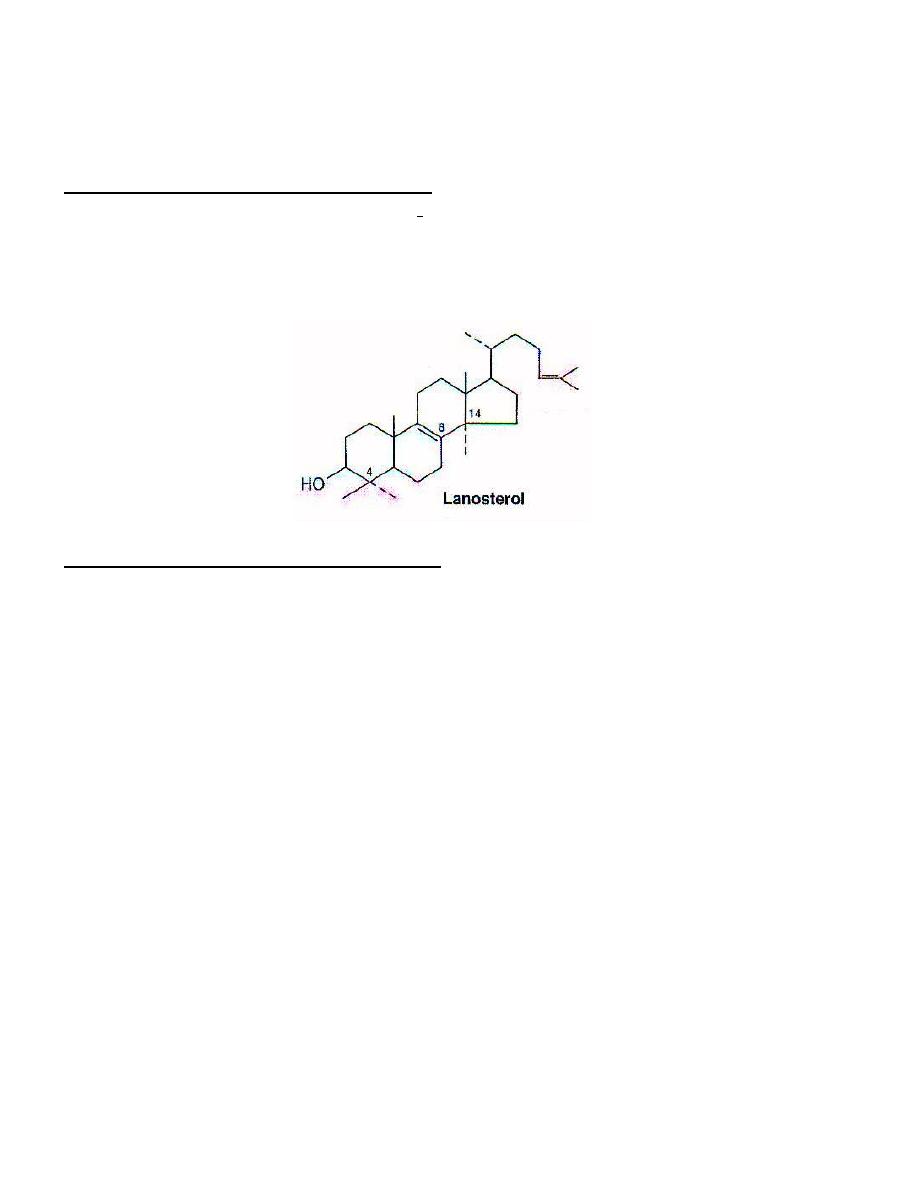
Phase III : Synthesis of cholesterol :
● Squalene cyclizes forming Lanosterol which contains the rings of the steroid nucleus .
● Lanosterol is modified in a series of steps to form cholesterol .
Lanosterol
────→
Zymosterol
────→
Desmosterol
───→
Cholesterol
Regulation of Cholesterol Synthesis :
● HMG-CoA reductase step is the rate-limiting and control point in the pathway of
cholesterol synthesis . This step is subject to regulation :
1. liver HMG-CoA reductase is activated when insulin is high and inactivated
when glucagon is high .
2. HMG-CoA reductase is inhibited by high levels of mevalonate
( feed-back regulation by immediate product ) .
3. Synthesis of HMG-CoA reductase is repressed by :
a – cholesterol ( final end product of synthesis ) .
b – influx of cholesterol into cells from LDL .
c – bile salts produced from cholesterol in liver .
4. Thyroid hormone ( T
3
) increase the activity of HMG-CoA reductase
5. Glucocorticoids ( cortisol ) decrease the activity of HMG-CoA reductase (end product
inhibition since glucocorticoids are synthesized from cholesterol .
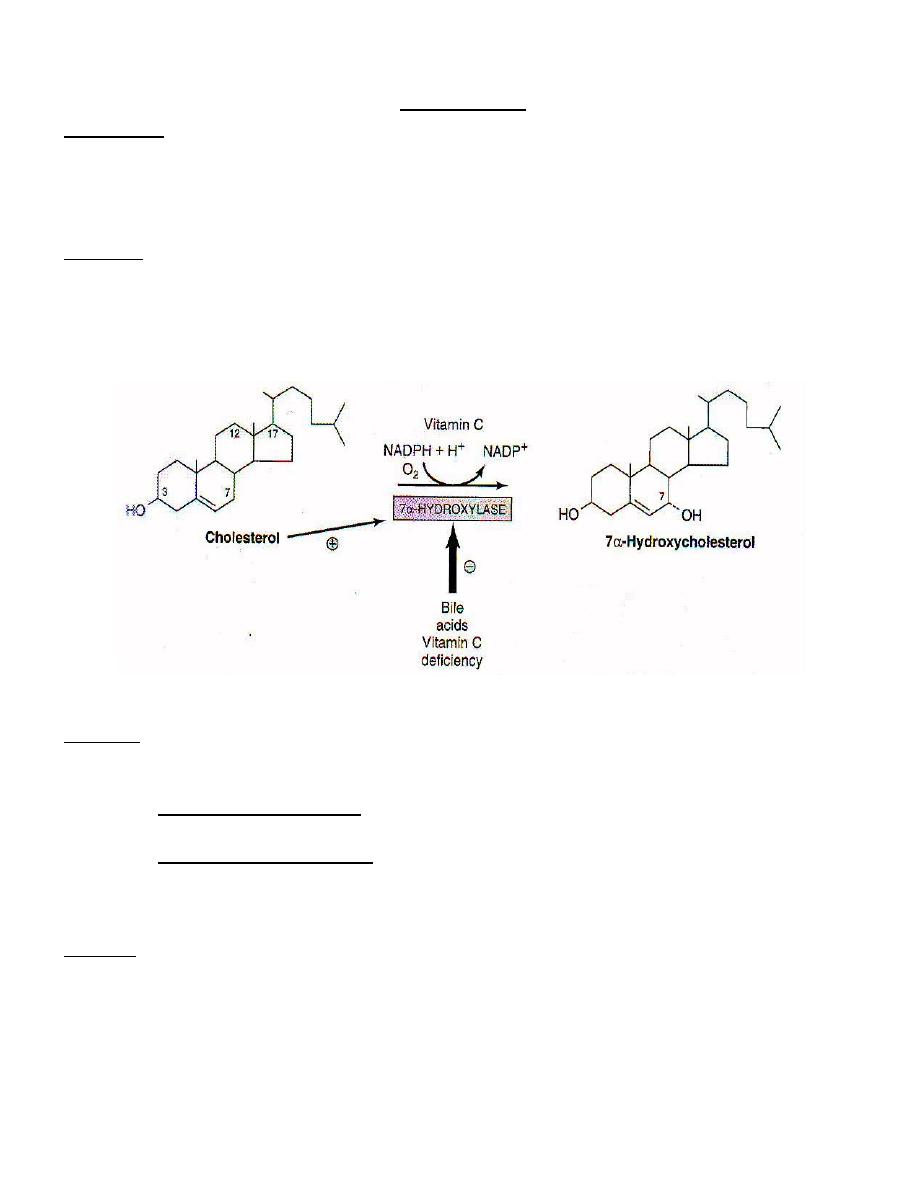
BILE SALTS
Synthesis :
● Bile salts are synthesized in the liver from cholesterol by reactions that hydroxylate
steroid nucleus and cleave the side chain .
1
ST
Step : an oxygen atom is added to carbon-7 of cholesterol forming an 7α-hydroxy
cholesterol ; this is catalyzed by the enzyme 7α–hydroxylase which is the
rate-limiting step ; the enzyme activity is decreased by high levels of bile salts
(feedback inhibition ) & activated by vitamin C .
2
nd
Step : the double bond (between carbons 5& 6) is reduced and two different sets of
bile salts are produced :
Dihydroxy set ( Diols ) produces the chenocholic acid series .
Trihydroxy set ( Triols ) forming the cholic acid series
of bile salts . Cholic acid is the major bile acid .
3
rd
Step : three carbons are removed ( as propionate derivative ) from the side chain
by an oxidation reaction so the side chain becomes carboxylated .
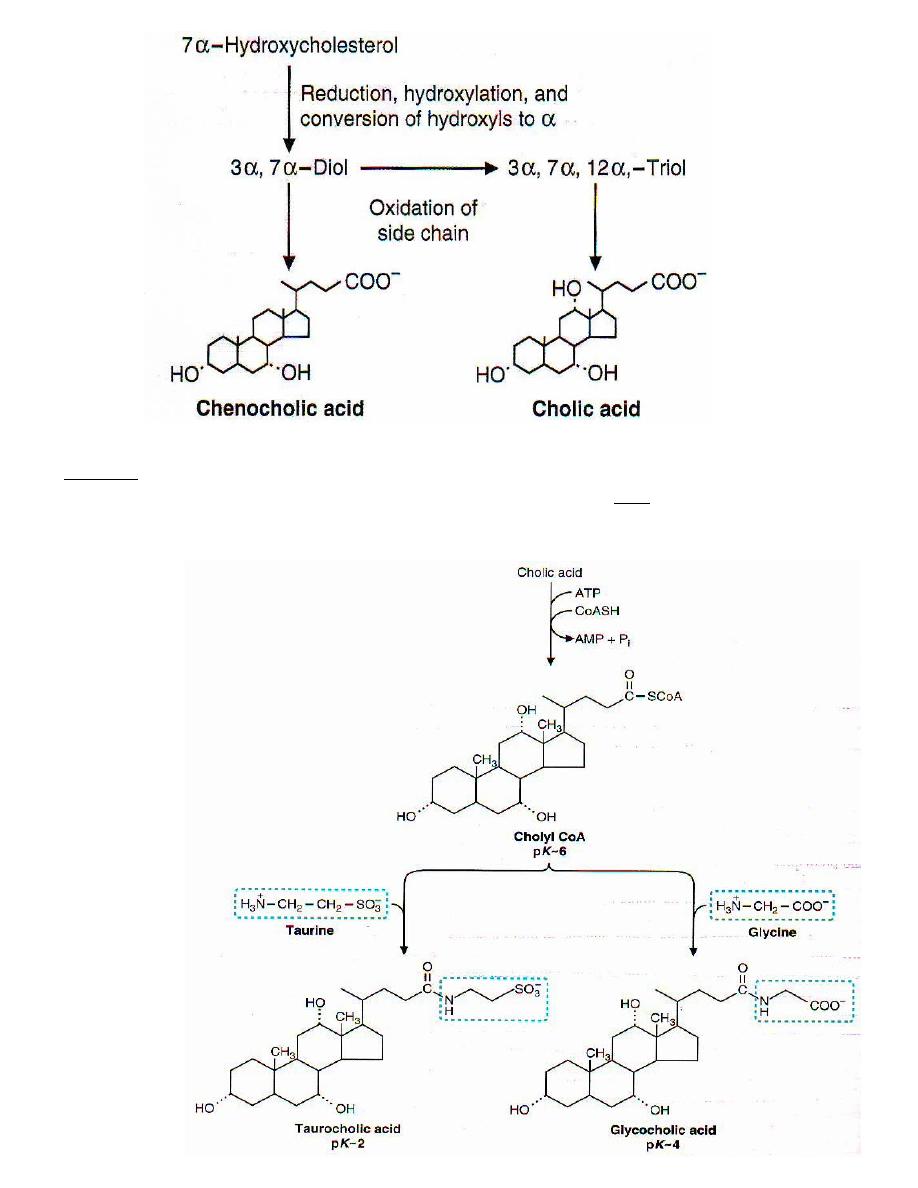
4
th
Step : the carboxyl group is activated by reacting with coenzyme A (ATP required)
producing the CoA-derivative of bile acids which can then react with either
glycine or taurine forming conjugated bile acids , for example : cholic acid
conjugated with glycine to form glycocholic acid .
● The bile acids and their conjugates produced in the liver are secreted into the bile ;
stored in the gallbladder and released into the intestine during a meal .
● Conjugation of bile acids with Glycine or Taurine decreases the pK value of the bile
acids .
● In the alkaline bile and in the intestinal lumen which normally have a pH = 6 , most
of the bile acids & their conjugates are ionized so that can bind cations and are
termed "primary bile salts " having better detergent action .
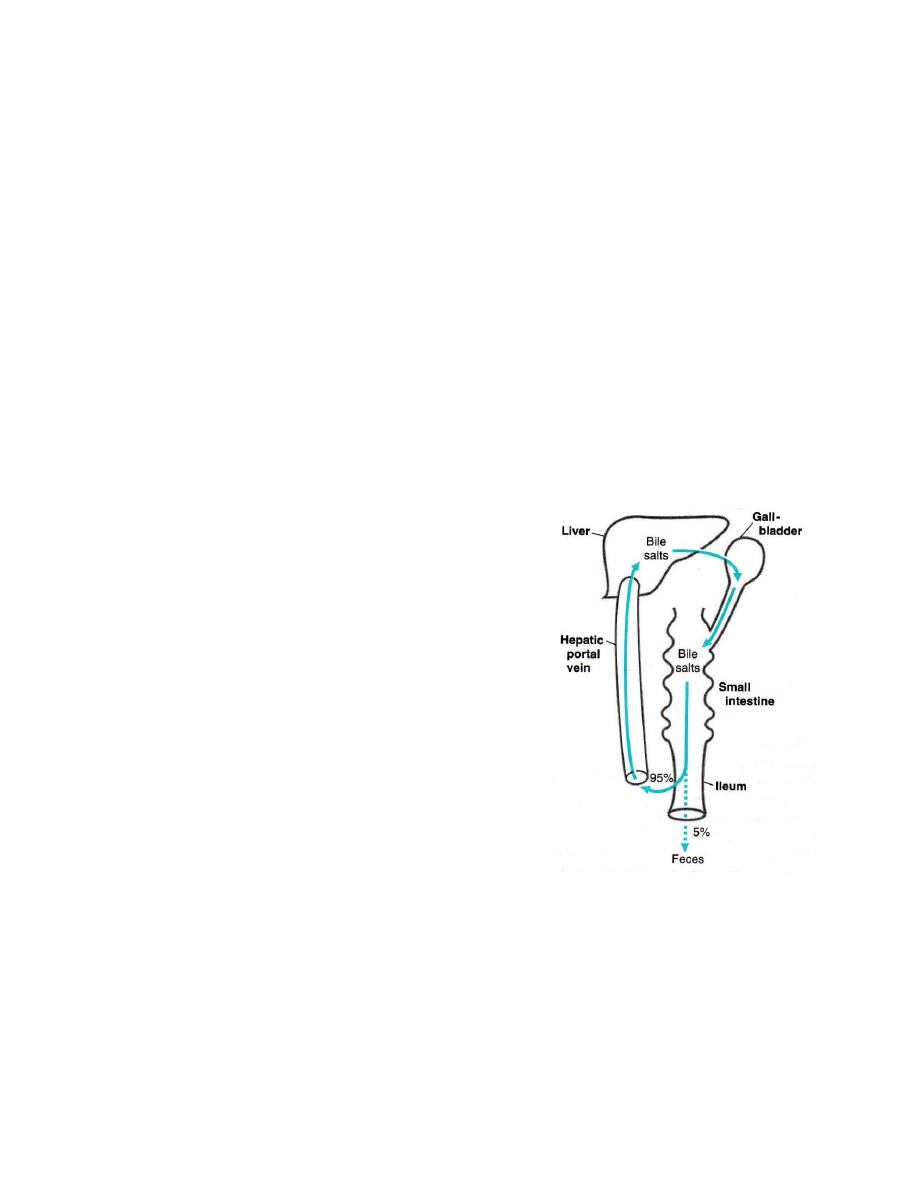
● Greater than 95% of the bile salts are reabsorbed in the ileum and return to the liver
via the enterohepatic circulation and re-secreted into the bile . Less than 5% of the
bile salts entering the gut are excreted in the feces every digestive cycle .
● Intestinal bacteria deconjugate and dehydroxylate the bile salts removing the glycine
and taurine residues and the hydroxyl group at position 7 . These bile salts are termed
"secondary bile salts " ; are less soluble and less reabsorbed from the intestinal
lumen than the primary bile salts so their major fate is excretion .
● Bile salts regulate cholesterol level in the body . Bile salts serve as a major route for
removal of the steroid nucleus and thus of cholesterol from the body . Bile salts form
molecular complex with cholesterol and keep cholesterol soluble in solution thus
facilitate cholesterol excretion .
● In the intestine , part of the excreted cholesterol is reabsorbed and returns to liver .

Clinical Aspects :
Serum cholesterol levels :
In normal persons , cholesterol level varies from 150 to 200 mg/dl . It should be below
200 mg/dl ( desired level ) . Concentrations between 200 – 220 are considered
borderline ; between 220 – 240 mg/dl considered as elevated ( low risk ) ; and above
240 mg/dl has definite risk for heart attack ( high risk ) .
Regulation of body cholesterol level :
● The concentration of cholesterol in tissues and body fluids is decided by a balance
between the rate of synthesis and the rate of metabolism ( metabolism include steroid
& bile salt synthesis plus excretion ) .
● The rate of cholesterol synthesis is determined by the amount of cholesterol in diet :
■ Synthesis is increased if cholesterol in diet is low .
■ Hepatic synthesis is inhibited by high levels of cholesterol in diet .
● Overall , the amount of cholesterol that is added daily to the body pool which is about
1000 mg/day ( synthesis plus diet ) is balanced by an equal amount of cholesterol
excreted in the bile either as unchanged free cholesterol or as bile salts since the
amount utilized for steroid synthesis is small .
Raised blood cholesterol level :
1. Diabetes mellitus : there is increased lipolysis and subsequent increased formation
of very low density lipoprotein ( VLDL ) rich in cholesterol .
2. Nicotine , caffeine and emotional stress : all cause enhanced lipolysis .
3. Bile duct obstruction .
4. liver diseases : impaired synthesis of bile .
5. Hereditary .
6. Hypothyroidism ( T
3
increases HDL receptors on liver cells ) .
Cholelithiasis :
● A defect in the rate of synthesis of bile salts ( as in liver diseases) or if the molecular
complex between the bile salts and cholesterol is broken down within the gallbladder
( as in infectious process ) then the cholesterol tend to precipitate forming cholesterol
stones ( cholelithiasis ) .
Hypolipidimic drugs :
● HMG-CoA reductase step is the target for the statins drugs ( e.g. Pravastin ) . These
drugs inhibit the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase and lower blood cholesterol .
*********************************
