Fatty Acid Oxidation
● Fatty acid oxidation is the major source of energy for ATP synthesis
specially during fasting .
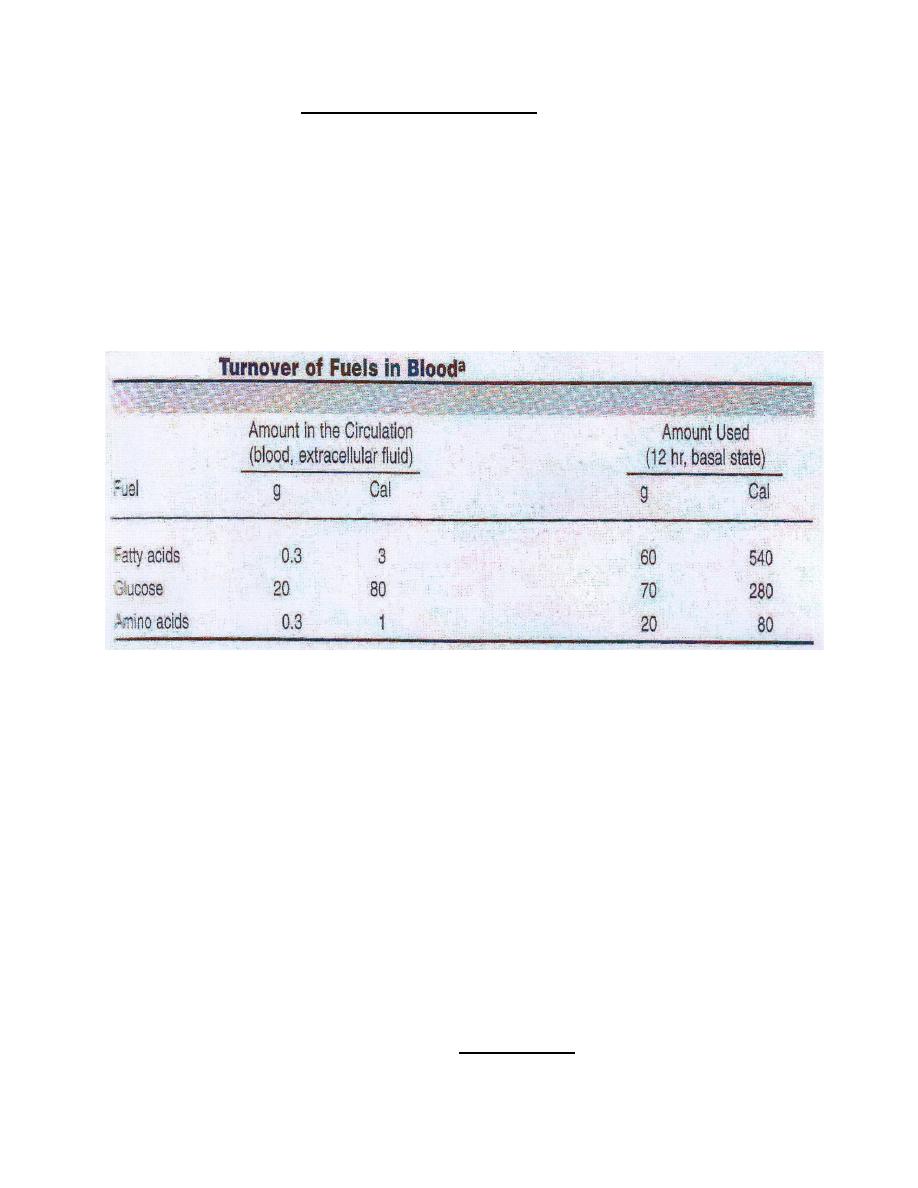
● The body oxidizes more fatty acids each day than any other fuel ; 540
calories are used in a 12-hour period in the basal state versus 280
calories of glucose or 80 calories of amino acids .
● During fasting , adipose triglycerides (stored fat) are mobilized by a
process known as Lipolysis ; triglycerides are hydrolyzed by the enzyme
hormone–sensitive lipase into free fatty acids & glycerol which are
released into the blood . The hormones glucagon , epinephrine & ACTH
activate this enzyme while it is inhibited by insulin . Thus , lipolysis is
accelerated during starvation and in uncontrolled diabetes mellitus .
● The fatty acids released during fasting spare glucose for use by brain and
other glucose-dependent tissues .
● Fatty acid oxidation is aerobic process and are oxidized mainly in
mitochondria by a process known as β-oxidation (major pathjway) . This
process generates acetyl CoA and energy (ATP) ; oxidation of the acetyl

CoA in the TCA cycle produces additional ATP .
● The liver during fasting , only partially oxidize most of the fatty acids into
acetyl CoA to obtain energy ; much of the acetyl CoA is then converted
within the mitochondria to the ketone bodies which are released into the
blood .
■ ơ–oxidation of saturated fatty acids
: involves 3 steps :
I.
Activation :
● Fatty acids must be activated before they can be oxidized ; they
are activated by ATP in two step reaction catalyzed by the enzyme
thiokinase to form fatty acyl CoA ; two ATP are consumed in the
activation process .
II. Transport into mitochondria ( Carnitine cycle ) :
● Activated long chain fatty acids ( Acyl CoA ) require Carnitine
to be transported into mitochondria for oxidation .
● The enzyme carnitine acyltransferase-I ( CAT-I ) present on the
outer surface of the mitochondrial membrane , transfers
acyl group of activated fatty acids (acyl CoA) to carnitine forming
acyl carnitine .
● Translocase ( a mitochondrial membrane protein ) carry the
acyl carnitine across the inner membrane into the matrix .
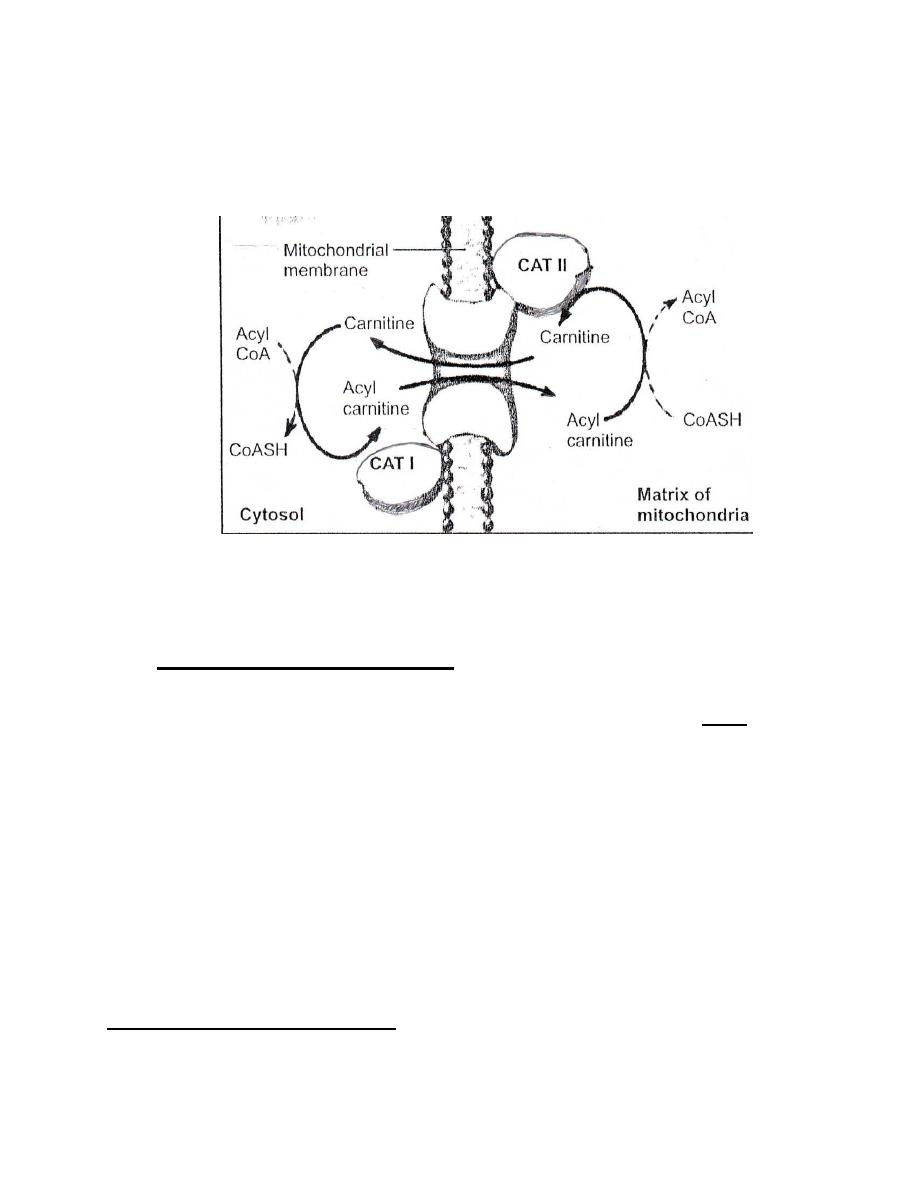
● carnitine acyltransferase-II ( CAT-II ) present in the matrix
transfers the acyl group from acyl carnitine
and acyl CoA
is reformed ; carnitine returns to the cytosol by the
same translocase .
-
Carnitine cycle -
III. Reactions of
ơ–oxidation :
● Beta oxidation involves repeated rounds ( spirals ) of four
metabolic reaction steps . In each round of four reactions , two
carbons are removed from the carboxyl end
and released as acetyl CoA .
.
● The acetyl CoA molecules produced during β-oxidation may enter
the citric acid cycle and oxidized completely to generate ATP .
● ơ–oxidation is so named since the pathway involves oxidation of
the
β-carbon (carbon 3) of the fatty acid chain to a keto group .
1
st
reaction : first oxidation :
● One molecule of FADH
2
produced .

2
nd
reaction : hydration :
3
rd
reaction : second oxidation :
One molecule of NADH is produced .
4
th
reaction : cleavage :
The enzyme thiolase breaks the bond between
Ơ- & ơ- carbons . The
products are acetyl CoA and a fatty acyl CoA which is two carbon
shorter than the original fatty acid .


ENERGETICS :
ATP generated from beta-oxidation of Palmitic acid ( C-16 ) :
● One molecule of Palmitic acid which has 16 carbons is cleaved in 7 rounds
of β-oxidation producing 7 FADH
2
,7 NADH and 8 acetyl CoA .
7 FADH
2
X 2 = 14 ATP
7 NADH X 3 = 21 ATP
8 acetyl CoA X 12 = 96 ATP
.
● One molecule of palmitic acid , therefore , generates a total of 131 ATP .
● Activation of one molecule of palmitic acid require 2 high energy bond
equivalent of 2 ATP .
● Therefore , the net energy yield from complete oxidation of one molecule of
palmitic acid is equal to 131
– 2 = 129 ATP .
Fat versus Carbohydrate :
A second advantage for the body to store excess energy as fat rather than
as glycogen is that more energy is obtained from fat oxidation than from
carbohydrate ( glucose) oxidation . This is so as follows:
● Sum of two molecules of glucose contain same number of carbon atoms
as one molecule of Lauric acid (12carbons) .
● β –oxidation of one molecule of lauric acid produces 6 molecules of
acetyl CoA in 5 rounds and will generate a net of 95 ATP :
5 FADH
2
X 2 = 10 ATP
5 NADH X 3 = 15 ATP
6 acetyl CoA X 12 = 72 ATP
Total ATP generated = 97 ATP
2 ATP used in activation
Net yield = 97
– 2 = 95 ATP .
● On the other hand , oxidation of one molecule of glucose generates 38
ATP(glycolysis +TCA) .
● Oxidation of two molecules of glucose generates 72 ATP .
● Therefore , body gets less ATP from glucose than from fat .
0


********************************


