Unit 2: Protozoa
17
Lecture 7 - Phylum ciliophora
Balantidium coli
Subphylum : Ciliophora
Class : Ciliata
Disease : called Balantidiasis or Balantidial dysentery
Have a cosmopolitan distribution in ahogs and a common
parasite of several species of Monkeys. In man is found in
warm climates.
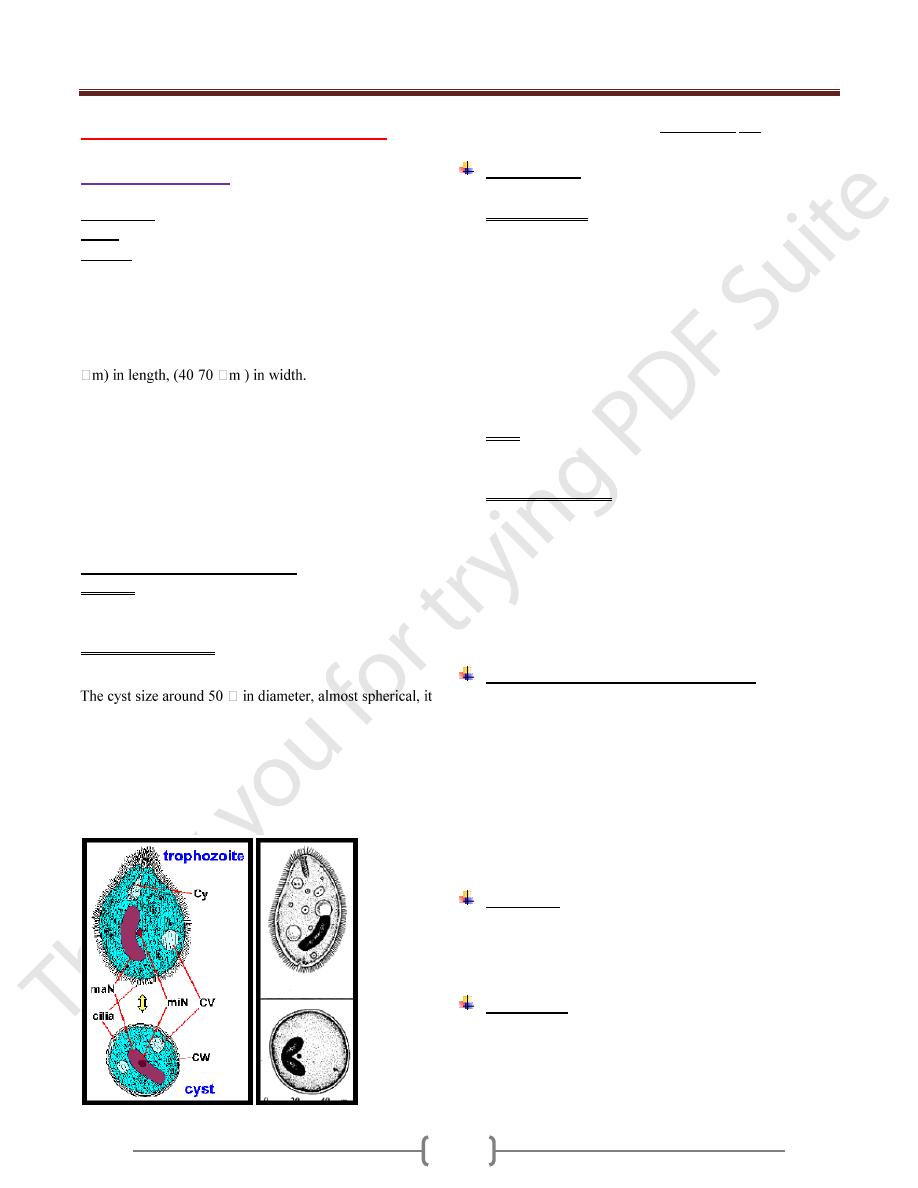
2 stages occur in the life cycle, trophozoite or vegetative
& cyst stage. The trophozoite is ovoidal in shape (50-100
-
Anterior somewhat conical anteriorly and rounded
posteriorly, cilia present all around the body of the
microorganism. Anteriorly has funnel-shape called
peristome leading to Cytostome (mouth of the cell) and
posteriorly Cytopyge (anus of the cell). It has 2 nuclei,
large one Macronucleus (kidney shaped) & small one
Micronucleus. Also it has 2 contractile vacuoles which
called pulsating vacuoles, those disappeared in old cyst.
Two types of multiplication:
1) A sexual, micronucleus divides mitotically and
Macronucleus divides amititically followed by the
division of cytoplasm result in 2 organisms.
2) Conjugation (sexual), has been observed in B. coli but
not essential for its propagation.
has no cilia (double outline wall). Although the markings
on the cell remain 2 nuclei, 2 Pulsating vacuoles, although
they disappeared in the old cyst. Invasion by motility &
cytolyticenzyme.
Loalized to large intestines, rarely seen in Extra intestinal.
Ulcer:wide mouth. May cause diarrhea or dysentery.
Trophozoite & cyst stage of Balantidium coli
Morphology
The organism has 2 stages, trophozoite and cyst.
The trophozoite is the largest of the protozoa that
parasitized man .It is ovoid covered with short cilia, the
organism exhibited rotary boring motility (size 50-100
µm in length by 40-70 µm in width).The anterior end is
conical and the posterior end is rounded .Near the anterior
end of the body, there is funnel –shaped peristome, which
leads into the cytostome.A minute cytopyge is situated at
the opposite end (anal opening).Two large contractile
vacuoles present in the cytoplasm. Also there is two
nuclei, micronucleus (small, spherical) lies adjacent to
kidney –shaped macronucleus.
Cyst: ovoid or spherical (43-56 µm in diameter) and it’s
the transfer stage, a double protective cyst wall surrounds
the organism; the cilia disappear.
The natural habitat of B.coli is the caecal and sigmoid-
rectal region of hogs, man is an incidental host.
In the trophozoite, asexual reproduction consists of
transverse binary fission in which the micronucleus first
divides mitotically, then the macronucleus amitotically
followed by the cytoplasm resulting in two daughter
organisms. Also conjugation has been observed in B.coli
but it is not essential for its propagation.
Pathogenesis and symptomatology:
B.coli penetrates the mucosal layer with extensive
submucosal destruction and causing ulceration. The
parasite may move through the muscularis mucosa into
the submucosa, where it spread radially causing rapid
destruction of the tissue. Unlike E.histolytica, it rarely
invades the muscular coat and extraintestinal infection is
very rare. The symptoms in balantidiasis vary from
fulminating dysentery or acute diarrhea to an
asymptomatic carrier state.
Diagnosis
Examination of stool for the presence of trophozoite and
cyst stage.Multible samples may be required to determine
the presence or absence of the parasite.
Treatment
1- Diiodohydroxyquin.
2- Tetracycline.
3- Metronidazole.
