
Surface Anatomy
151
natomy
aphic
adiog
R
R
a
For a detailed discussion, see page 226.
natomy
face
s
uR
a
Surface Landmarks of the Abdominal
The xiphoid process is the thin cartilaginous lower part
Wall
Xiphoid Process
of the sternum. It is easily palpated in the depression where
of the umbilical cord in the fetus.
position. It is a puckered scar and is the site of attachment
The umbilicus lies in the linea alba and is inconstant in
median groove (see Figs. 4.11 and 4.12).
abdominal wall and is represented on the surface by a slight
fusion of the aponeuroses of the muscles of the anterior
and lies in the midline (see Fig. 4.3). It is formed by the
extends from the symphysis pubis to the xiphoid process
The linea alba is a vertically running fibrous band that
to enter the spermatic cord at the upper end of the scrotum.
emerges from the tail and ascends medial to the epididymis
The vas deferens
and a narrow lower end, the
body,
head,
(see Fig. 4.21). It has an enlarged upper end called the
epididymis
rior to the testis is an elongated structure, the
and not tethered to the skin or subcutaneous tissue. Poste
(see Fig. 4.21). The testis should therefore lie free
vaginalis
anterior, and medial surfaces by the two layers of the
on each side is a firm ovoid body surrounded on its lateral,
testis
along the line of fusion. The
scrotal raphe,
called the
is indicated by the presence of a dark line in the midline,
ered with sparse hairs. The bilateral origin of the scrotum
matic cords. The skin of the scrotum is wrinkled and is cov
testes, the epididymides, and the lower ends of the sper
The scrotum is a pouch of skin and fascia containing the
uterus.
difficult to palpate; it transmits the round ligament of the
In the female, the superficial inguinal ring is smaller and
(see Figs. 4.5 and 4.21).
vas deferens
terior part called the
and note the presence of a firm cordlike structure in its pos
upper part of the scrotum between the finger and thumb
scrotum (see Fig. 4.8). Palpate the spermatic cord in the
descending over or medial to the pubic tubercle into the
can be felt emerging from the ring and
spermatic cord
the scrotum with the tip of the little finger. The soft tubu
can be felt by invaginating the skin of the upper part of
4.8, and 4.12). In the adult male, the margins of the ring
above and medial to the pubic tubercle (see Figs. 4.2, 4.3,
aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle and is situated
The superficial inguinal ring is a triangular aperture in the
the pubic tubercle.
spine and curves downward and medially, to be attached to
4.11). It is attached laterally to the anterior superior iliac
rosis of the external oblique muscle (see Figs. 4.2, 4.6, and
groin. It is the rolled-under inferior margin of the aponeu
The inguinal ligament lies beneath a skin crease in the
tubercle (see Fig. 4.32).
superior surface of the pubic bones medial to the pubic
is the name given to the ridge on the
pubic crest
wall. The
midline at the lower extremity of the anterior abdominal
4.11). It is felt as a solid structure beneath the skin in the
the midline between the bodies of the pubic bones (see Fig.
The symphysis pubis is the cartilaginous joint that lies in
rior surface of the pubis (see Figs. 4.3, 4.12, and 4.32).
may be identified as a small protuberance along the supe
The pubic tubercle is an important surface landmark. It
Pubic Tubercle
the body of the 5th lumbar vertebra.
of the crest (see Fig. 4.12). The tubercle lies at the level of
iliac spine, the outer margin projects to form the tubercle
About 2 in. (5 cm) posterior to the anterior superior
4th lumbar vertebra.
(Fig. 4.49). Its highest point lies opposite the body of the
posterior superior iliac spine
and 4.12) and behind at the
(see Figs. 4.11
anterior superior iliac spine
in front at the
The iliac crest can be felt along its entire length and ends
rib may be short and difficult to palpate.
lies opposite the body of the 3rd lumbar vertebra. The 12th
gin reaches its lowest level at the 10th costal cartilage, which
by the cartilages of the 11th and 12th ribs. The costal mar
8th, 9th, and 10th ribs (see Figs. 4.11 and 4.12) and behind
racic wall and is formed in front by the cartilages of the 7th,
The costal margin is the curved lower margin of the tho
thoracic vertebra.
of the sternum, and it lies opposite the body of the ninth
is identified by feeling the lower edge of the body
junction
xiphisternal
abdominal wall (see Figs. 4.11 and 4.12). The
the costal margins meet in the upper part of the anterior
Costal Margin
-
-
Iliac Crest
-
Symphysis Pubis
Inguinal Ligament
-
Superficial Inguinal Ring
-
lar
-
Scrotum
-
-
tunica
-
a
tail.
Linea Alba
Umbilicus

152
CHAPTeR 4
4th lumbar vertebra. This is commonly used as a sur
on the iliac crests and lies on the level of the body of the
The intercristal plane passes across the highest points
vertebra.
(see Fig. 4.12). This plane lies at the level of the 3rd lumbar
costal margin on each side—that is, the 10th costal cartilage
The horizontal subcostal plane joins the lowest point of the
hila of the kidneys.
duodenojejunal junction, the neck of the pancreas, and the
This plane passes through the pylorus of the stomach, the
It lies at the level of the body of the 1st lumbar vertebra.
(linea semilunaris) crosses the costal margin (see Fig. 4.12).
point where the lateral margin of the rectus abdominis
of the ninth costal cartilages on the two sides—that is, the
The horizontal transpyloric plane passes through the tips
Transpyloric Plane
symphysis pubis.
point between the anterior superior iliac spine and the
Each vertical line (right and left) passes through the mid
Vertical Lines
cedures.
diseased structures or the performing of abdominal pro
monly used to facilitate the description of the location of
Vertical lines and horizontal planes (see Fig. 4.12) are com
stand out.
the rectus abdominis muscles so that their lateral edges
using the arms. To accomplish this, the patient contracts
on the back and raise the shoulders off the couch without
accentuate the semilunar lines, the patient is asked to lie
of the ninth costal cartilage (see Figs. 4.11 and 4.12). To
abdominis muscle and crosses the costal margin at the tip
The linea semilunaris is the lateral edge of the rectus
halfway between the two (see Fig. 4.11).
level of the tip of the xiphoid process, at the umbilicus, and
als, they can be palpated as transverse depressions at the
across the rectus abdominis muscle. In muscular individu
The tendinous intersections are three in number and run
Tendinous Intersections of the Rectus
the arms.
the shoulders while in the supine position without using
they can be made prominent by asking the patient to raise
alba (see Fig. 4.11) and run vertically in the abdominal wall;
The rectus abdominis muscles lie on either side of the linea
The Abdomen: Part I—The Abdominal Wall
Rectus Abdominis
Abdominis
-
Linea Semilunaris
Abdominal Lines and Planes
-
-
-
Subcostal Plane
Intercristal Plane
-
face
erforming a lumbar spinal tap (see
landmark when p
may just be felt (see Fig. 4.48).
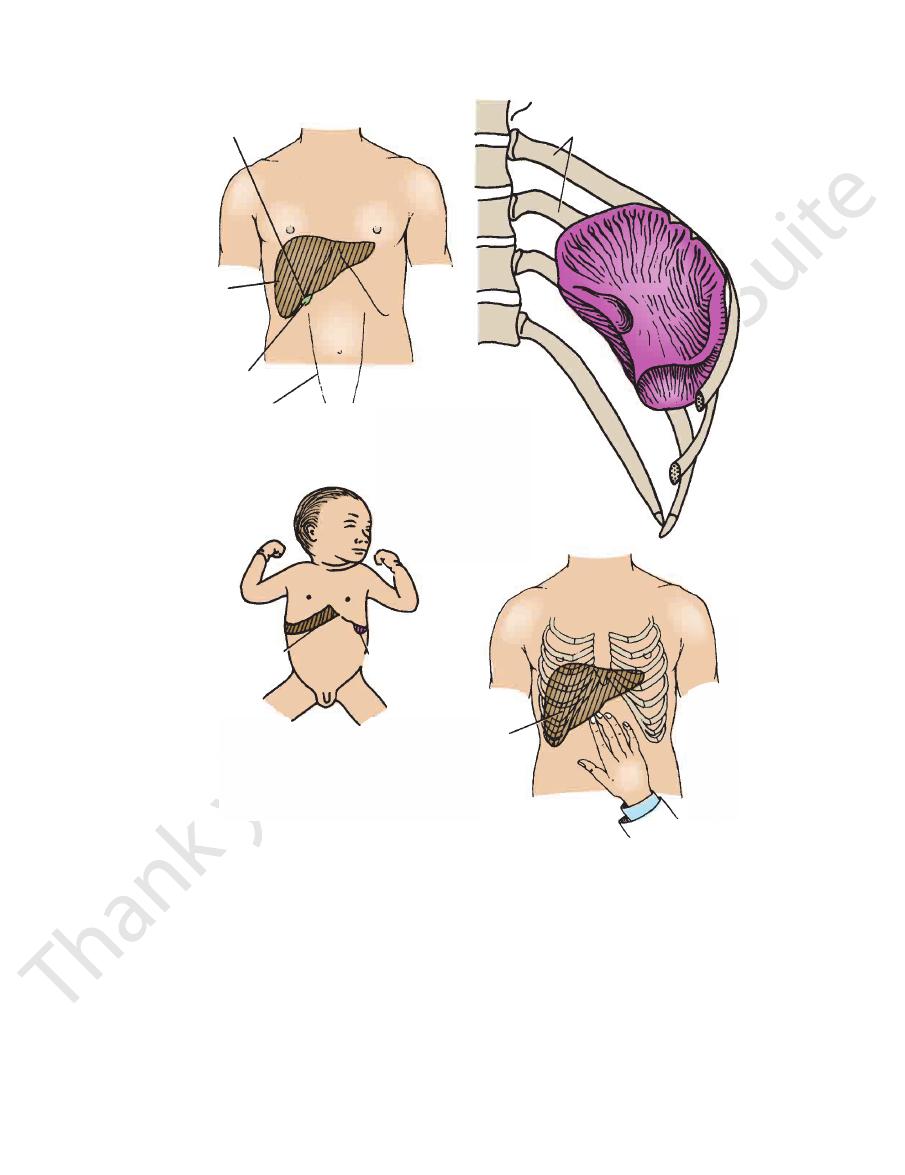
midaxillary line. In infants, the lower pole of the spleen
adult it does not normally project forward in front of the
Its long axis corresponds to that of the 10th rib, and in the
under cover of the 9th, 10th, and 11th ribs (see Fig. 4.48).
The spleen is situated in the left upper quadrant and lies
margin (see Fig. 4.48).
of the right rectus abdominis muscle crosses the costal
right ninth costal cartilage—that is, where the lateral edge
The fundus of the gallbladder lies opposite the tip of the
contracts and pushes down the liver.
ily felt when the patient inspires deeply and the diaphragm
felt a fingerbreadth below the costal margin. It is most eas
palpable. In a thin adult, the lower edge of the liver may be
developed right rectus abdominis muscle, the liver is not
gin (see Fig. 4.48). In the adult who is obese or has a well-
extends one or two fingerbreadths below the costal mar
about the end of the third year, the lower margin of the liver
its bulk lies on the right side (Fig. 4.48). In infants, until
The liver lies under cover of the lower ribs, and most of
surface markings are of clinical value.
The following organs are more or less fixed, and their
of viscera.
and respiration have a profound influence on the position
variations in the same person at different times. Posture
abdominal viscera show individual variations as well as
It must be emphasized that the positions of most of the
Viscera
umbilicus and the area around the umbilicus, respectively.
indicate the area below the xiphoid process and above the
are loosely used to
periumbilical
epigastrium
terms
upper right, upper left, lower right, and lower left. The
sect at the umbilicus (see Fig. 4.12). The quadrants are the
rants by using a vertical and a horizontal line that inter
It is common practice to divide the abdomen into quad
lumbar vertebra.
the iliac crests (see Fig. 4.12) and lies at the level of the 5th
The horizontal intertubercular plane joins the tubercles on
page 704).
Intertubercular Plane
Abdominal Quadrants
-
-
and
Surface Landmarks of the Abdominal
Liver
-
-
Gallbladder
Spleen
Surface Anatomy
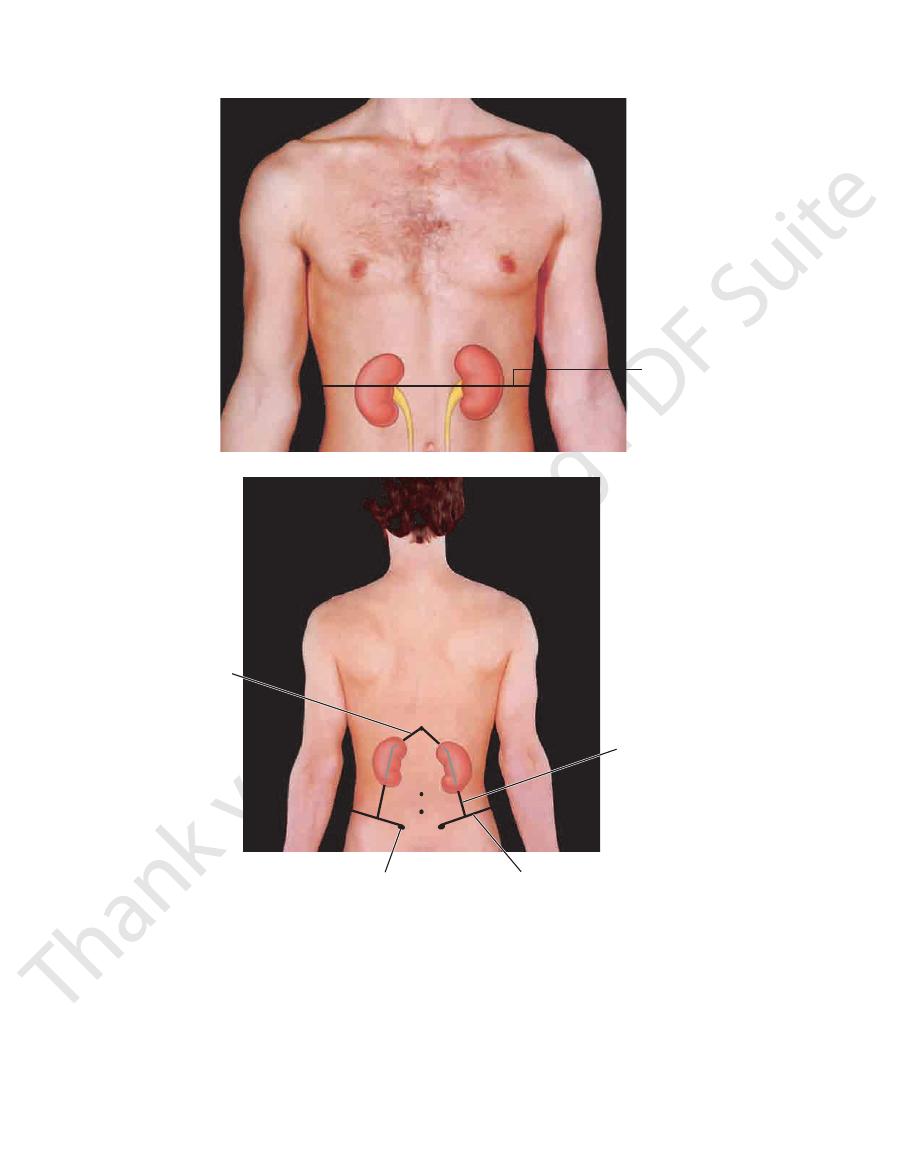
kidneys extend from the 12th thoracic spine to the 3rd lum
breadths from the midline (see Fig. 4.49). On the back, the
kidney lies on the transpyloric plane, about three finger
On the anterior abdominal wall, the hilum of each
ney, which is higher than the right kidney, is not palpable.
piratory movement of the diaphragm. The normal left kid
about 1 in. (2.5 cm) in a vertical direction during full res
poorly developed abdominal muscles. Each kidney moves
region at the end of deep inspiration in a person with
and the lower pole can be palpated in the right lumbar
kidney (because of the bulk of the right lobe of the liver),
The right kidney lies at a slightly lower level than the left
the body and tail lie above and to the left.
lies below and to the right, the neck lies on the plane, and
The pancreas lies across the transpyloric plane. The head
153
Pancreas
Kidneys
-
-
-
-
bar spine, and the hili are opposite the 1st lumbar
ebra
vert
(see Fig. 4.49).
tip of 9th
costal cartilage
liver
fundus of
gallbladder
linea semilunaris
margin of liver
lower pole of spleen
liver
ribs
9
10
11
12
FIGURE 4.48
Surface markings of the fundus of the gallbladder, spleen, and liver. In a young child, the lower margin of the
may just be felt at the end of deep inspiration.
normal liver and the lower pole of the normal spleen can be palpated. In a thin adult, the lower margin of the normal liver
154
CHAPTeR 4
fingerbreadths to the right of the midline.
The duodenum lies on the transpyloric plane about four
in the umbilical region or below.
has an extremely variable position
greater curvature
The
line joining the cardioesophageal junction and the pylorus.
lies on a curved
lesser curvature
right of the midline. The
lies on the transpyloric plane just to the
pylorus
The
10th thoracic vertebra).
(the esophagus pierces the diaphragm at the level of the
breadths below and to the left of the xiphisternal junction
lies about three finger
cardioesophageal junction
The
The Abdomen: Part I—The Abdominal Wall
Stomach
-
Duodenum (First Part)
transpyloric
plane
L1
A
posterior supe rior
T12
L3
L4
lateral margin of
erector spinae muscle
iliac crest
iliac spine
12th rib
B
FIGURE 4.49
Surface anatomy of the kidneys on the posterior abdominal wall.
hilum of each kidney to the transpyloric plane.
Surface anatomy of the kidneys and ureters on the anterior abdominal wall. Note the relationship of the
A.
B.

Surface Anatomy
anterior superior iliac spine and the symphysis pubis.
oral artery. It can be located at a point halfway between the
the inguinal ligament to become continuous with the fem
The pulsations of this artery can be felt as it passes under
of the midline.
the upper part of the anterior abdominal wall just to the left
The pulsations of the aorta can be easily palpated through
the 4th lumbar vertebra—that is, on the intercristal plane.
below into the right and left common iliac arteries opposite
The aorta lies in the midline of the abdomen and bifurcates
above the symphysis pubis (see page 260).
through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall
The full bladder and pregnant uterus can be palpated
and can be palpated through the anterior abdominal wall.
ing colon has a smaller diameter than the ascending colon
become continuous with the sigmoid colon. The descend
left lower quadrant, it curves medially and downward to
tal margin on the lateral side of the left vertical line. In the
The descending colon extends downward from the left cos
position is variable.
concavity directed upward. Because it has a mesentery, its
pying the umbilical region. It arches downward with its
The transverse colon extends across the abdomen, occu
Transverse Colon
the anterior abdominal wall.
under the right costal margin. It can be palpated through
the lateral side of the right vertical line and disappears
The ascending colon extends upward from the cecum on
appendix is variable.
(McBurney’s point). The position of the free end of the
joining the anterior superior iliac spine to the umbilicus
the appendix is situated one third of the way up the line,
The appendix lies in the right lower quadrant. The base of
nal wall.
percussed. It can be palpated through the anterior abdomi
often distended with gas and gives a resonant sound when
The cecum is situated in the right lower quadrant. It is
155
Cecum
-
Appendix
Ascending Colon
-
Descending Colon
-
-
Urinary Bladder and Pregnant Uterus
Aorta
External Iliac Artery
-
www.thePoint.lww.com/Snell9e.
Clinical Cases
and
Review Questions
are available online at
