
Chapter 4
Second week of
development
bilaminar germ disk
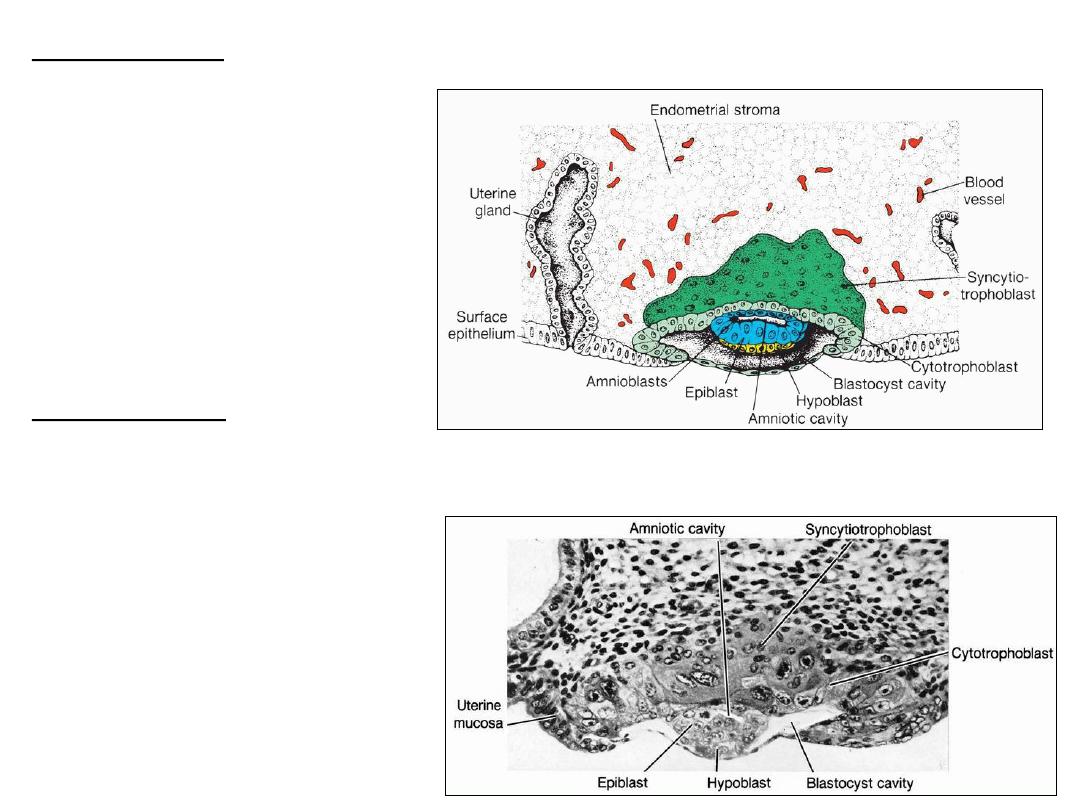
8-day human blastocyst
TROPHOBLAST:
1. Cytotrophoblast: inner,
mononucleated cells
2. Syncytiotrophoblast: outer
multinucleated zone
Cells in the cytotrophoblast
divide and migrate into the
syncytiotrophoblast.
EMBRYOBLAST:
1. Epiblast
2. Hypoblast
1. AMNIOTIC CAVITY: a small
cavity within the epiblast .
2. BLASTOCYST CAVITY
Section of a 7.5-day human blastocyst
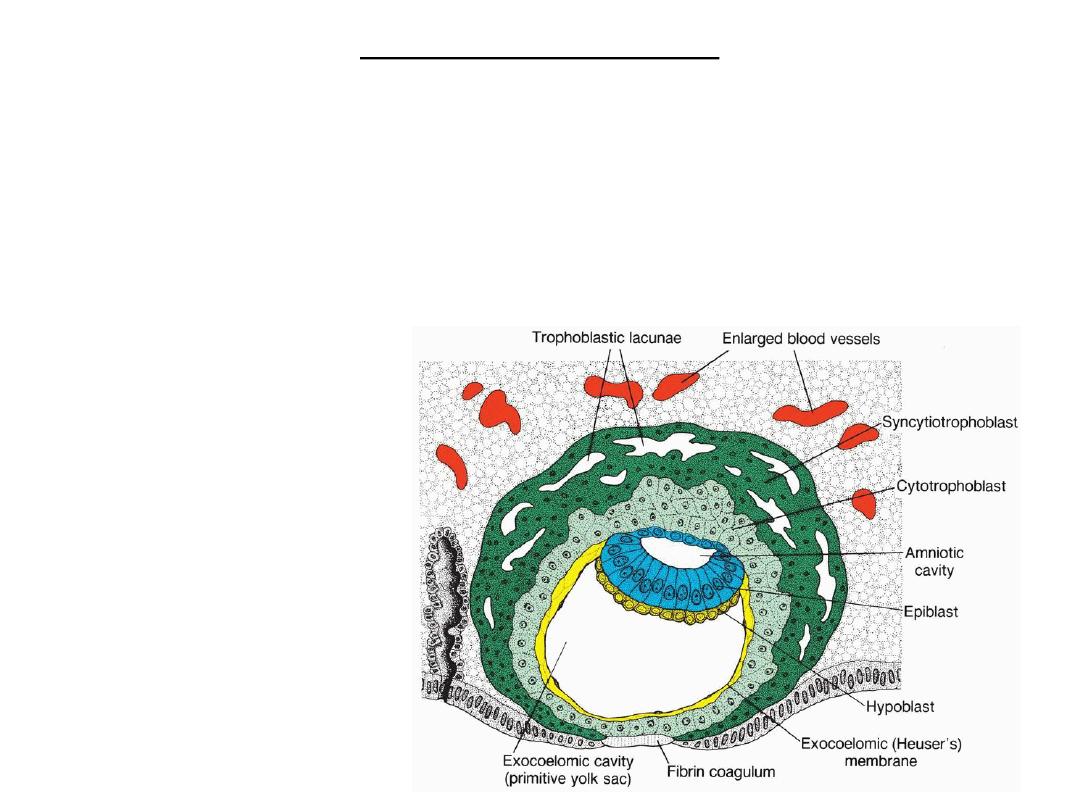
DAY 9 - LACUNAR STAGE
• Syncytiotrophoblast: lacunae.
• Primitive yolk sac (Exocoelomic cavity): Exocoelomic membrane (Hauser’s
membrane): originate from hypoblast, line cytotrophoblast.
• The bilaminar disc :epiblast cells & hypoblast cells.
• Endometrium: the penetration defect in the surface epithelium is closed by a
fibrin coagulum.
Human blastocyst at day 9
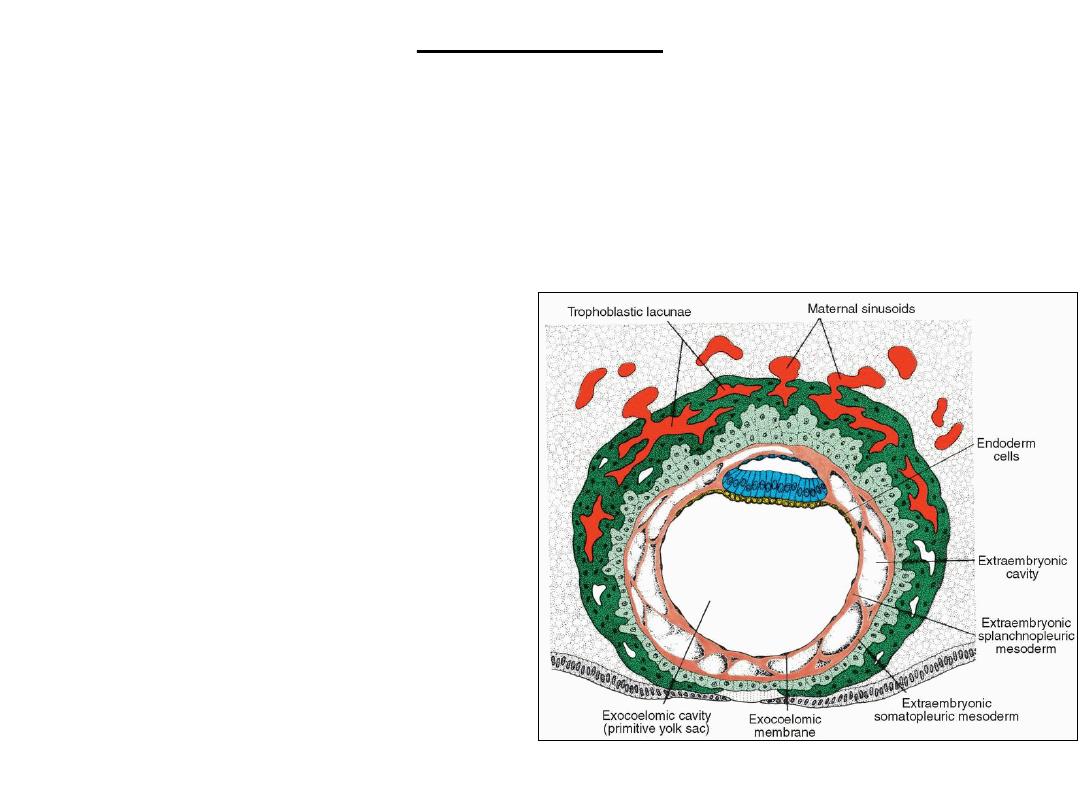
Day 11 and 12
• Surface epithelium: completely closed.
• Trophoblastic lacunae: connection with maternal sinusoids uteroplacental
circulation.
• Extraembryonic mesoderm (originates from yolk sac), proliferates and fills the
space between the exocoelomic (yolk sac) cavity and the inner aspect of the
cytotrophoblast .
• The extraembryonic coelom
(chorionic cavity) forms within the
extraembryonic mesoderm.
• The extraembryonic
somatopleuric mesoderm:
covering the cytotrophoblast and
amnion.
• The extraembryonic
splanchnopleuric mesoderm:
covering the yolk sac.
• The decidua reaction: endometrial
cells are loaded with glycogen and
lipids; intercellular spaces are filled
with extra vasate, and the tissue is
edematous.
Human blastocyst at DAY 12
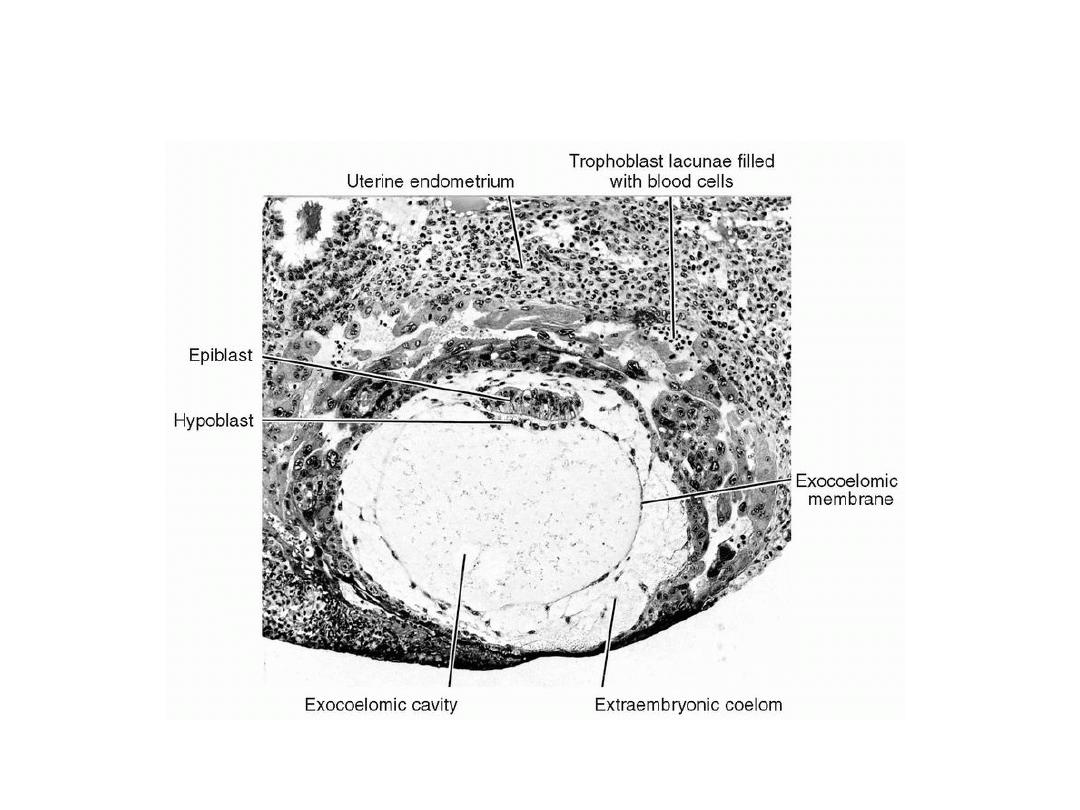
Fully implanted 12-day human blastocyst (_100). Note maternal blood cells in
the lacunae, the exocoelomic membrane lining the primitive yolk sac, and the
hypoblast and epiblast .
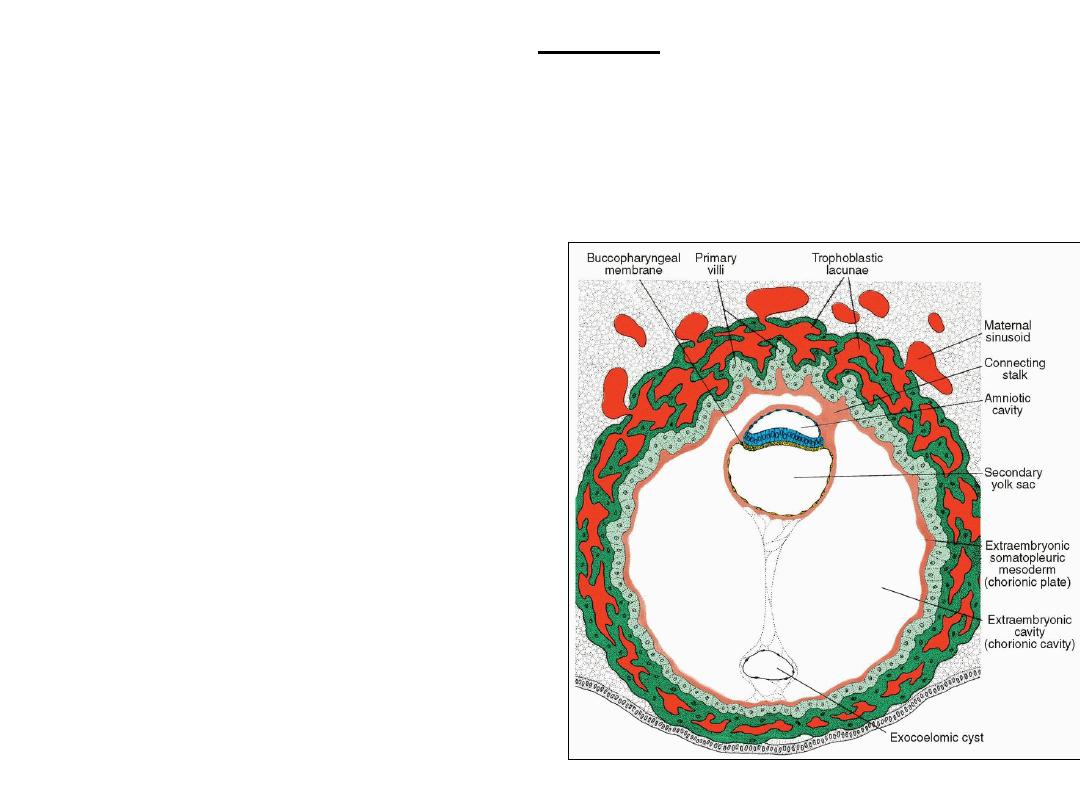
DAY 13
• Defect of endometrium healed.
• Increased blood flow into lacunar spaces Bleeding at implntation site
confused with menstrual bleeding (at day 28) inacuracy of EDD.
• Primary villi: cytotrophoblast columns
covered by syncytiotrophoblast.
• Secondary (definitive) yolk sac (originate from
hypoblast cells) forms within exocoelomoic
cavity.
• Exocoelomic cysts: remnants of exocoelomic
cavity.
• Chorionic (extraembryonic) cavity : enlarged.
• Chorionic plate: mesoderm lining chorionic
cavity (and cytotrophoblast).
• The extraembryonic somatopleuric
mesoderm: lining of the cytotrophoblast and
amnion.
• The extraembryonic splanchnopleuric
mesoderm: mesoderm covering the yolk sac.
• The only place where extraembryonic
mesoderm traverses the chorionic cavity is in
the connecting stalk (that will become the
umbilical cord with development of blood
vessels ).
Human blastocyst at Day 13
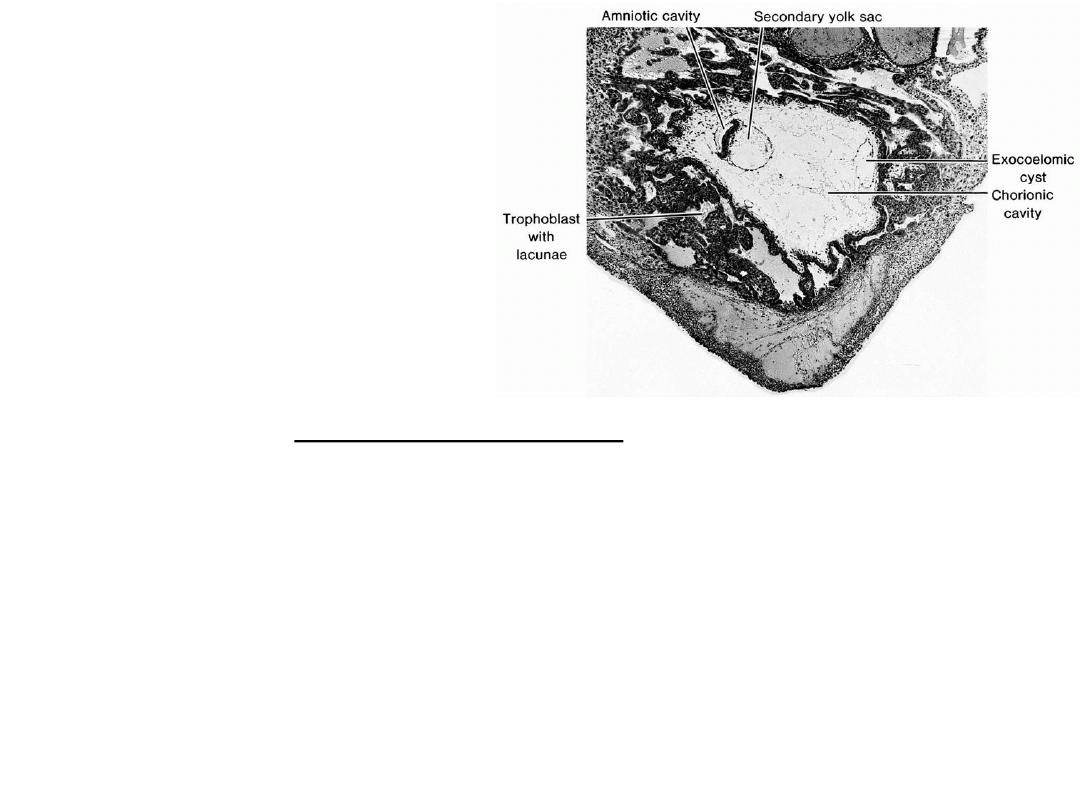
Section through the implantation
site of a 13-day embryo. Note the
amniotic cavity, yolk sac, and
exocoelomic cyst in the chorionic
cavity. Most of the lacunae are filled
with blood .
CLINICAL CORRELATES
hCG
• The syncytiotrophoblast is responsible for hormone production including human
chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
• By the end of the second week, quantities of this hormone are sufficient to be
detected by radioimmunoassays, which serve as the basis for pregnancy testing.
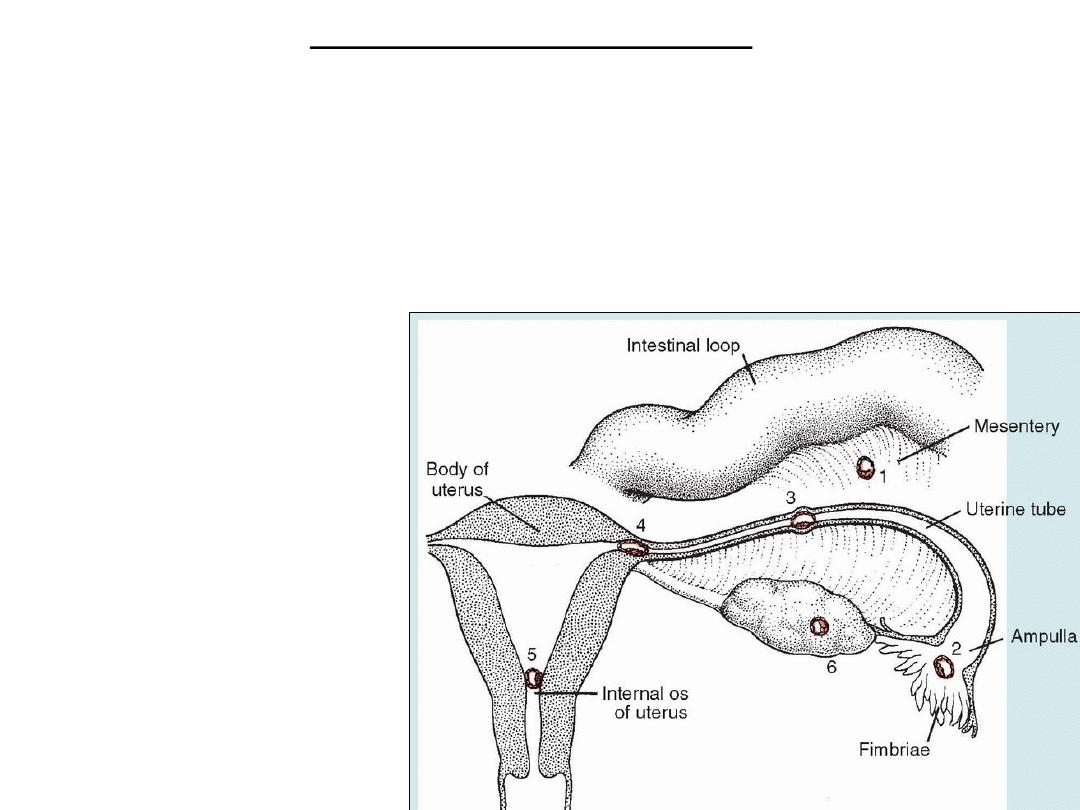
Abnormal implantation sites
• Normally, the human blastocyst implants along the anterior or posterior
wall of the body of the uterus.
• Placenta previa: blastocyst implants close to the internal os of the cervix
later in development the placenta bridges the opening severe, even life-
threatening bleeding in the second part of pregnancy and during delivery
EXTRAUTERINE (ECTOPIC)
PREGNANCY
• Rectouterine cavity [pouch
of Douglas]
• Ampullary region of uterine
tube
• Tubal implantation
• Ovarian implantation.
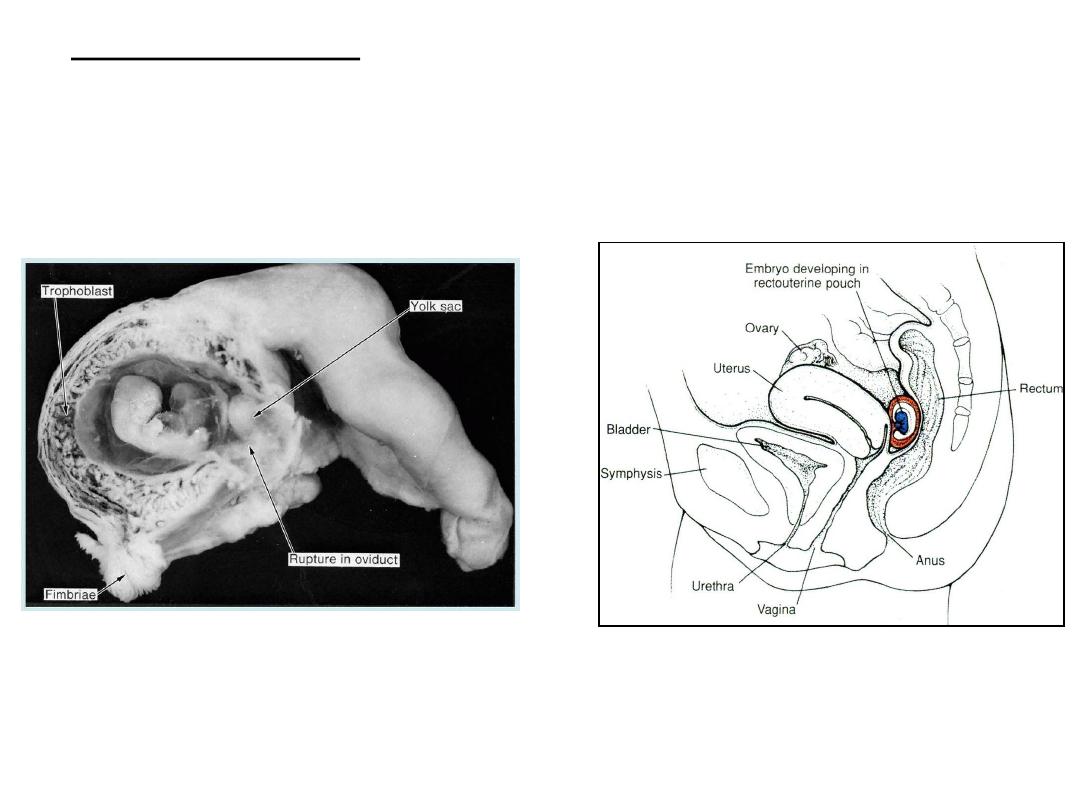
Midline section of bladder, uterus,
and rectum shows an abdominal
pregnancy in the rectouterine
(Douglas) pouch .
• In most ectopic pregnancies the embryo dies about the second month
of gestation and may result in sever hemorrhaging in the mother.
Tubal pregnancy
Embryo is approximately 2
months old and is about to
escape through a rupture in
the tubal wall
.
Hydatidiform mole
• Trophoblast develops but no embryonic tissue is present.
• Moles secrete high levels of human chorionic gonadotropin, hCG, and may
produce benign or malignant (invasive mole, choriocarcinoma) tumors.
• Genetic analysis of hydatidiform moles :
1.
Although cells of moles are diploid, the entire genome is paternal. Thus, most
moles arise from fertilization of an oocyte lacking a nucleus followed by
duplication of the male chromosomes to restore the diploid number.
2.
Paternal genes regulate most of the development of the trophoblast, because
in moles this tissue differentiates even in the absence of a female pronucleus.
3.
Genomic imprinting.
WEEK OF TWOS
• The second week of development is the week of twos:
• The trophoblast: the cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast.
• The embryoblast: the epiblast and hypoblast.
• The extraembryonic mesoderm: the somatopleure and splanchnopleure.
• Two cavities, the amniotic and yolk sac cavities.
