52
Lecture 6 - EMPLOY BOOLEAN OPERATORS
What are Boolean operators?
Boolean operators are expressions such as AND, OR, NEITHER, and NOR that allow
you to add multiple criteria to a query. They take their name from George Boole, the
mathematician who first used them.
If you had a T-shirt store with an Access database, for instance, and you wanted to find
out how many of your California customers had ordered blue T-shirts, you'd employ the
AND operator in your query:
customers from California
AND
who also bought blue T-shirts
If you wanted to see how many customers were from California (these California
customers could have bought T-shirts of any color),
and how many customers bought blue T-shirts (these blue T-shirt customers could be
from anywhere),
you'd employ the OR operator:
customers from California
OR
customers who bought blue T-shirts
Employ the OR operator
1.
Return to Design View.
2.
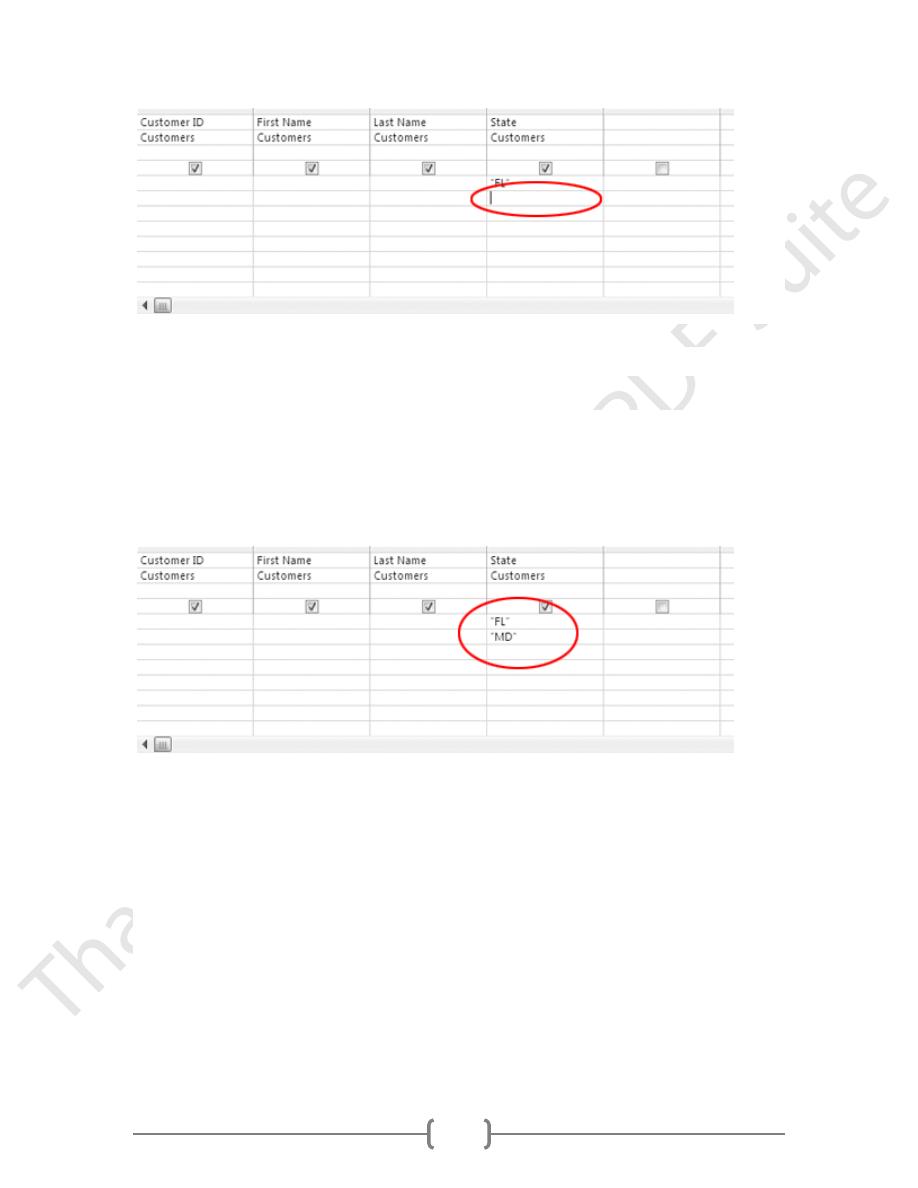
In the
State
field, click in the
or
row under the criterion
"FL"
.
53
3. Type:
MD
then press the
ENTER
key.
The design grid should look like this:
TIP: The two common Boolean operators are AND and OR. They're easily confused. If
you don't know which to use, ask yourself the purpose of the query:
Do I want to find customers with a state of both Florida AND Maryland?
No
—a customer can't be in two places at once.
Do I want to find customers with a state of either Florida OR Maryland?
That makes sense, so this query would use the OR operator.
54
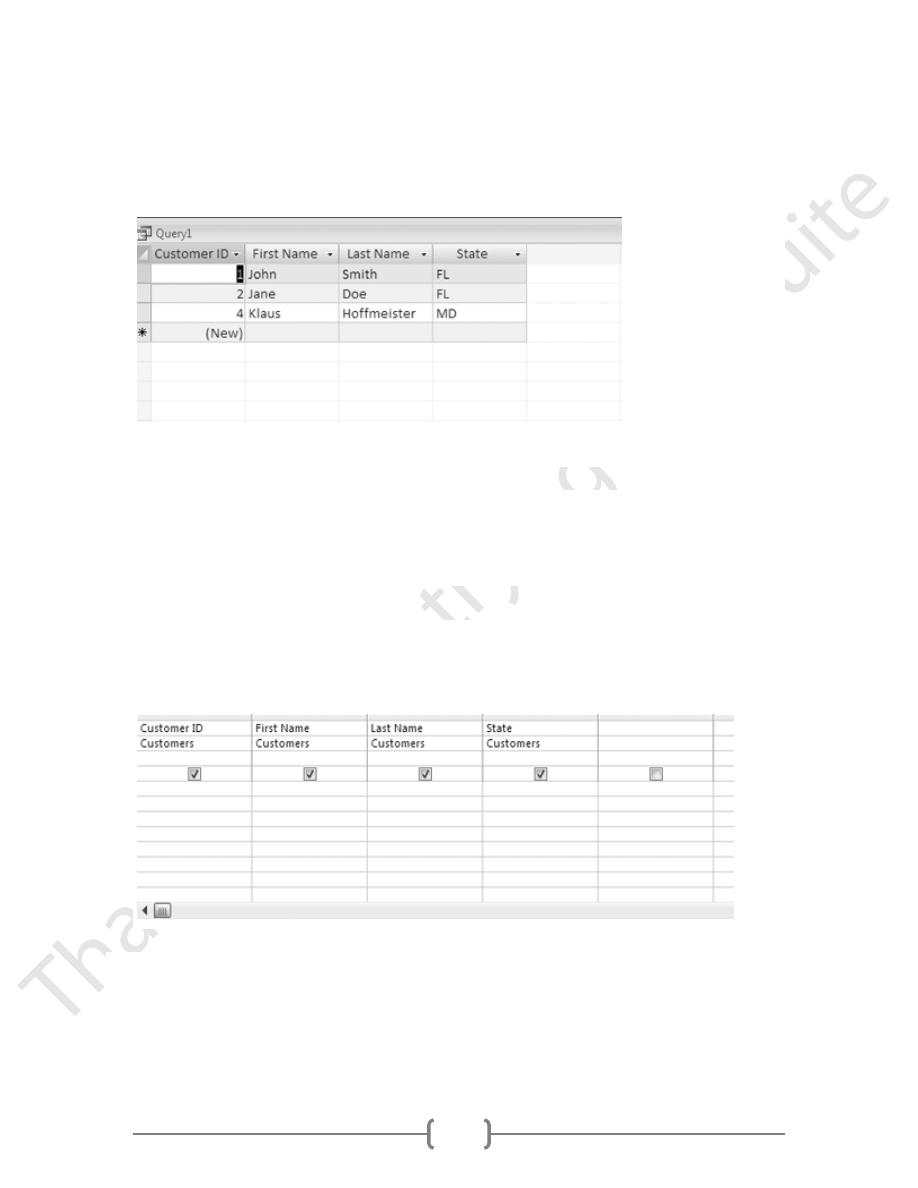
4. In the Ribbon, click Run.
The query results should look like this:
Employ the AND operator
1.
Return to Design View.
2.
Remove the query criteria from the
State
field.
(Highlight them, then press the
DELETE
key.)
The
Criteria
row in the design grid should be blank:
2.
In the First Name field, click in the Criteria row.
3.
Type:
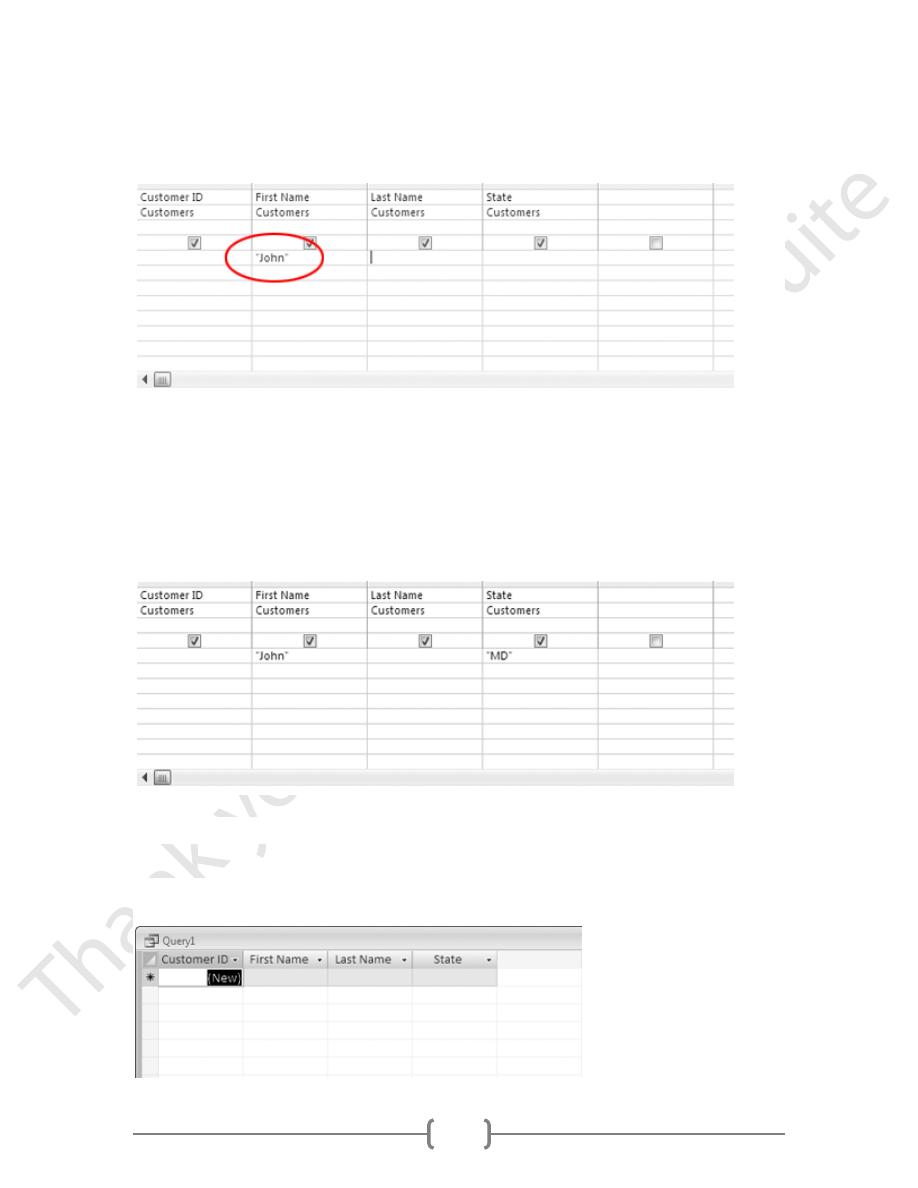
55
John
then press the ENTER key.
4.
In the State field, type:
MD
in the Criteria row
then press the ENTER key.
5. In the Ribbon, click Run.
The query results should look like this:
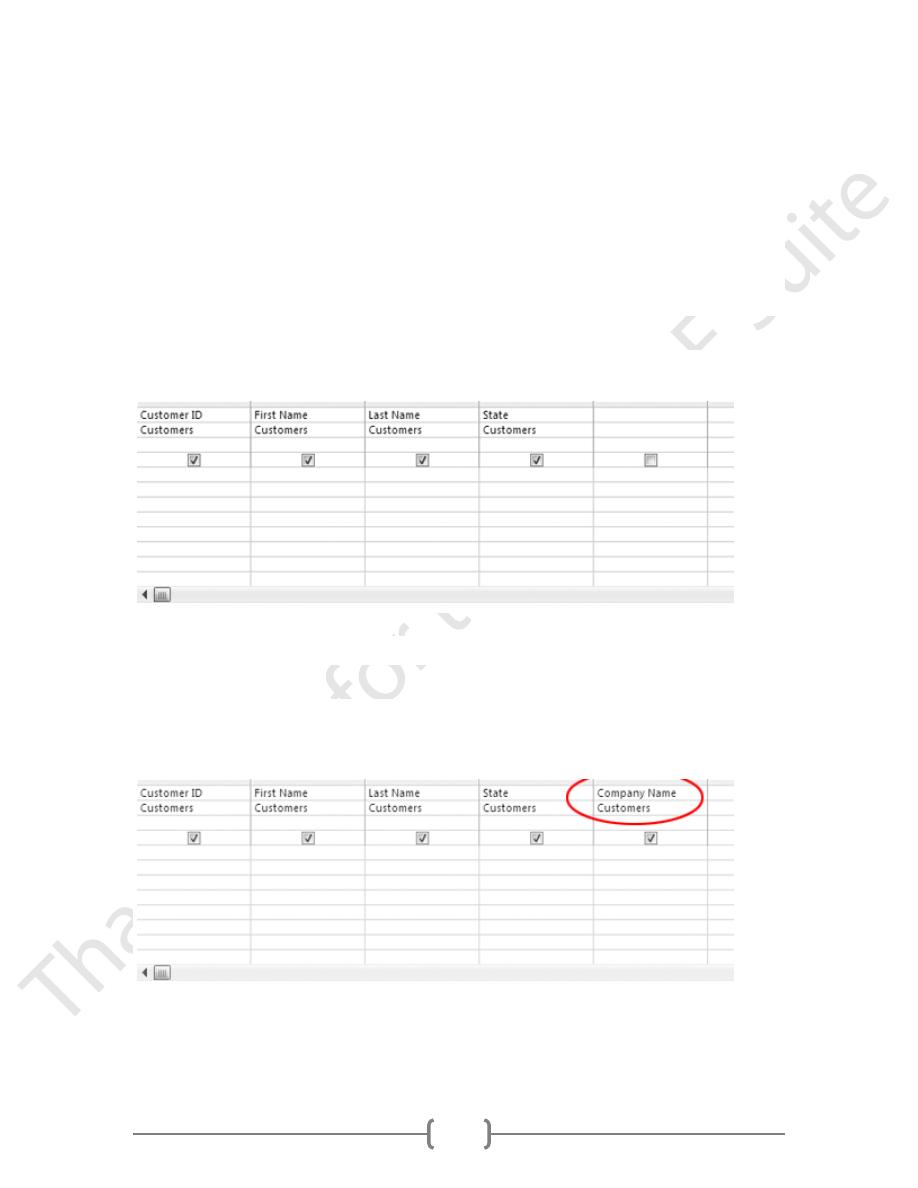
56
No records were returned, because there's no one in the table whose first name is John
AND lives in Maryland.
Employ a Wild Card character
1.
Return to Design View.
2.
Remove all query criteria from all fields.
The design grid should be blank:
3. Add the
Company Name
field to the query:
Drag it from the field list in the
Customers
table and drop it in the blank field to
the right of the
State
field.
4.
In the Company Name field, click in the Criteria row.
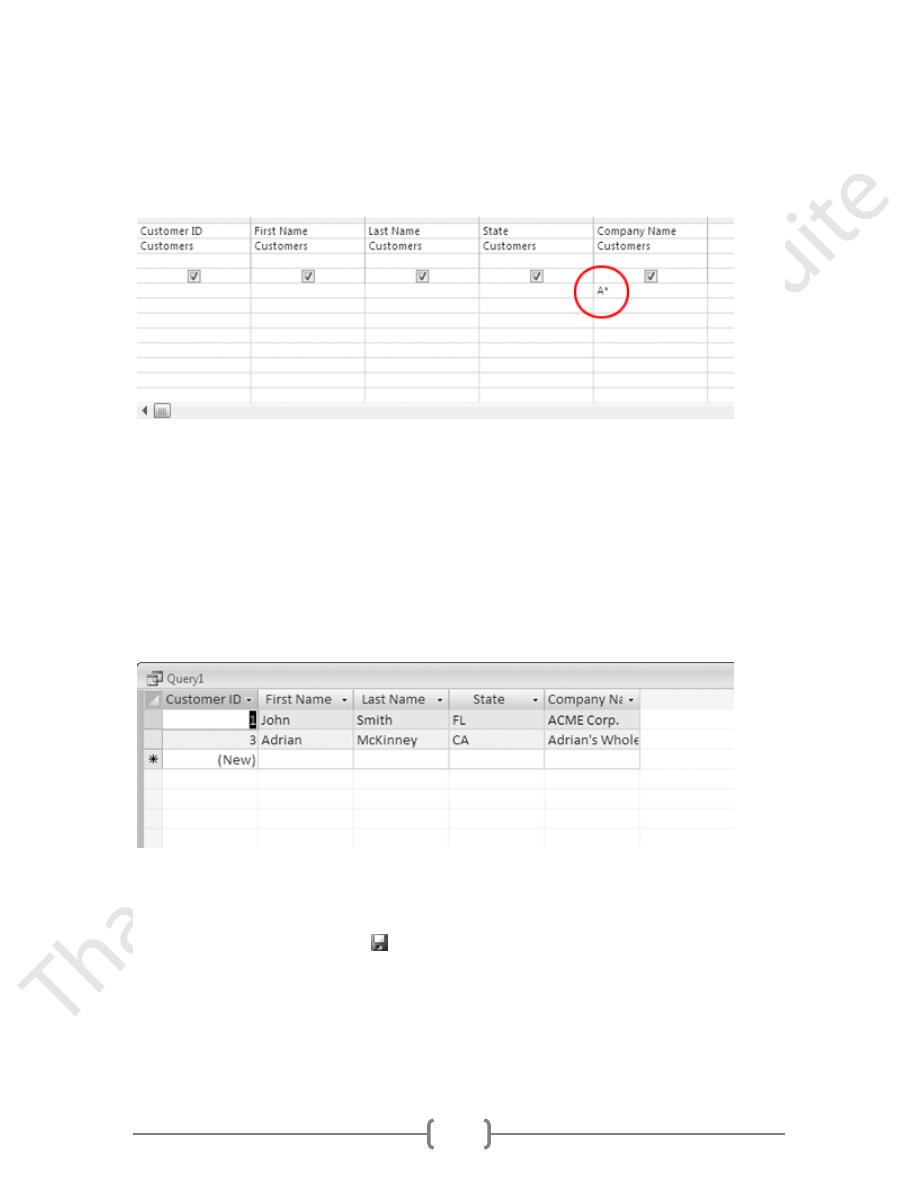
57
5.
Type:
A*
then press the ENTER key.
TIP: An asterisk (*) stands for any character or combination of characters. For instance,
Ap* would match Ape, Aptitude, Apparent, etc.
6.
In the Ribbon, click Run.
The query results should look like this:
The query shows all companies whose names begin with A.
7.
In the Title Bar, click the
icon.
8. When the Save As window appears, type:
Companies that begin with A
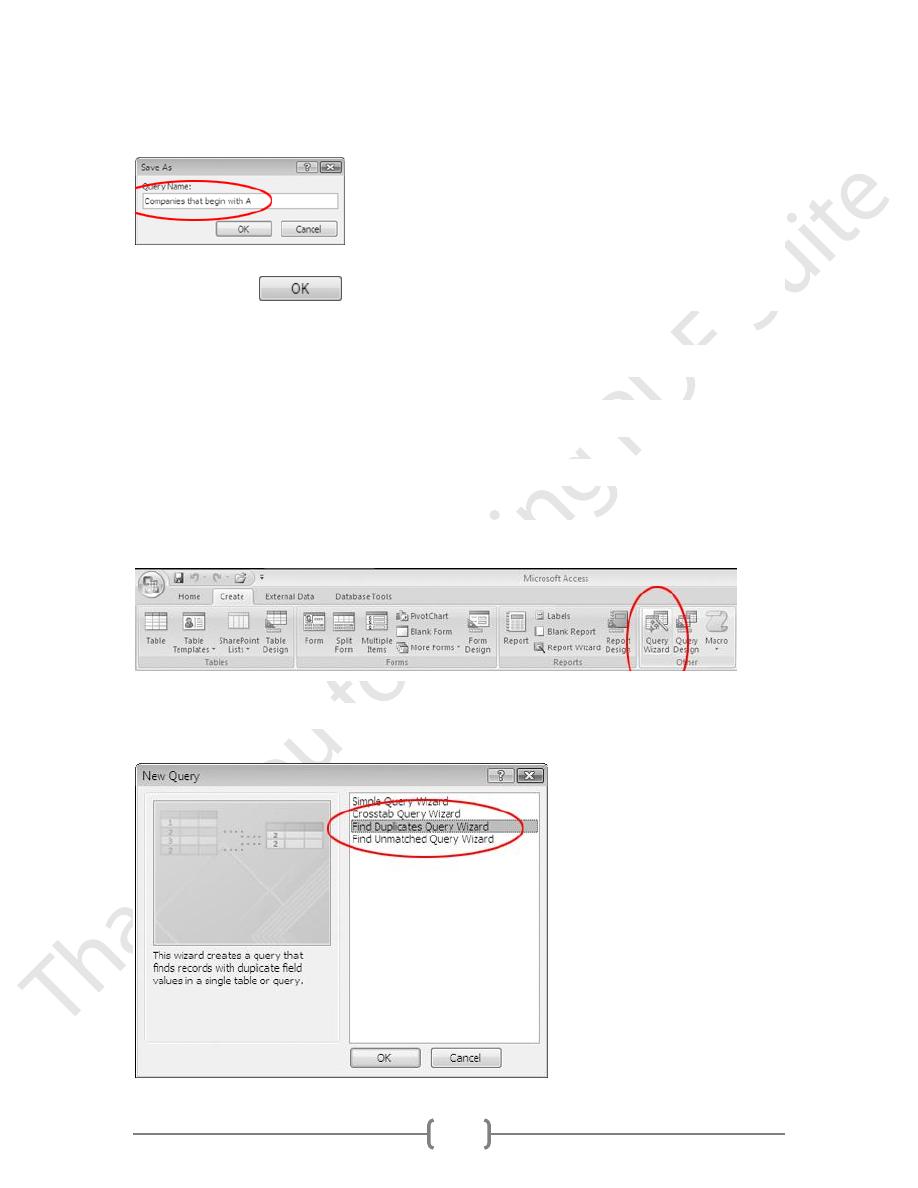
58
in the Query Name box.
9.
Click the
button.
10.
Close the query window.
FIND DUPLICATE RECORDS
1. Click the Create tab.
In the Ribbon, click Query Wizard.
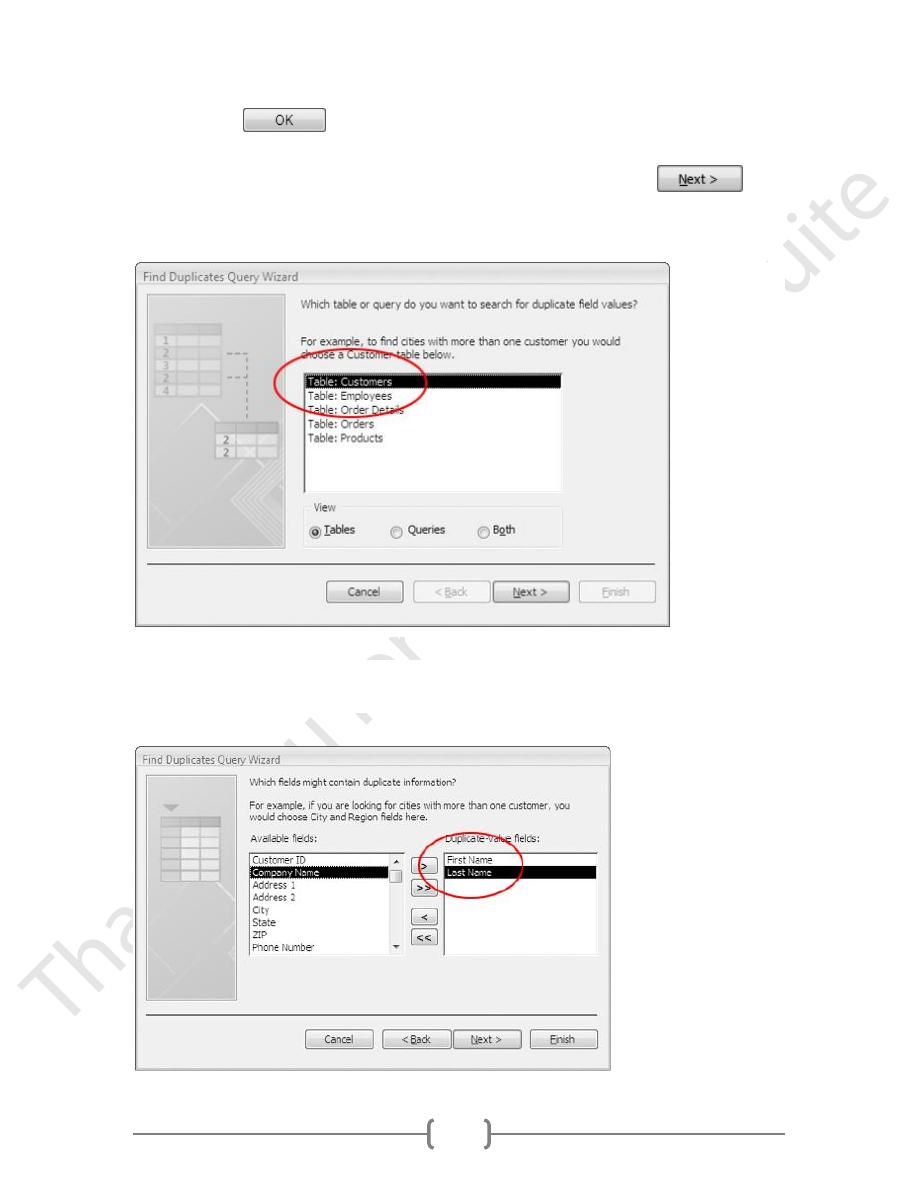
2. When the New Query window appears, click Find Duplicates Query Wizard.
59
Then click the
button.
4. When the next screen appears, click Table: Customers, then click the
button.
5. When the next screen appears, double-click First Name, then Last Name to add the
fields to the query:
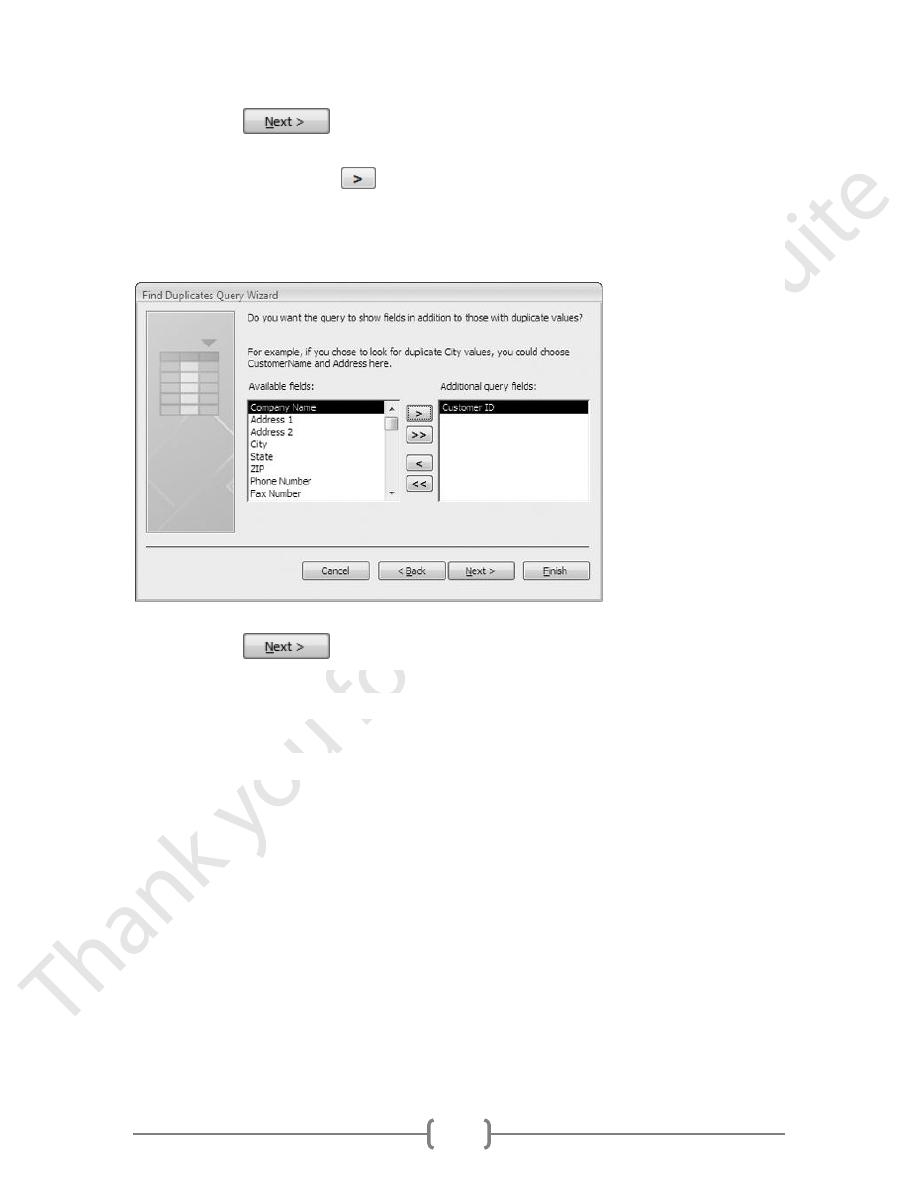
60
Then click the
button.
6. In the next screen, click the
button.
The screen should look like this:
Then click the
button.
7. When the final screen appears, type:
Find Duplicate Customers in the name box.
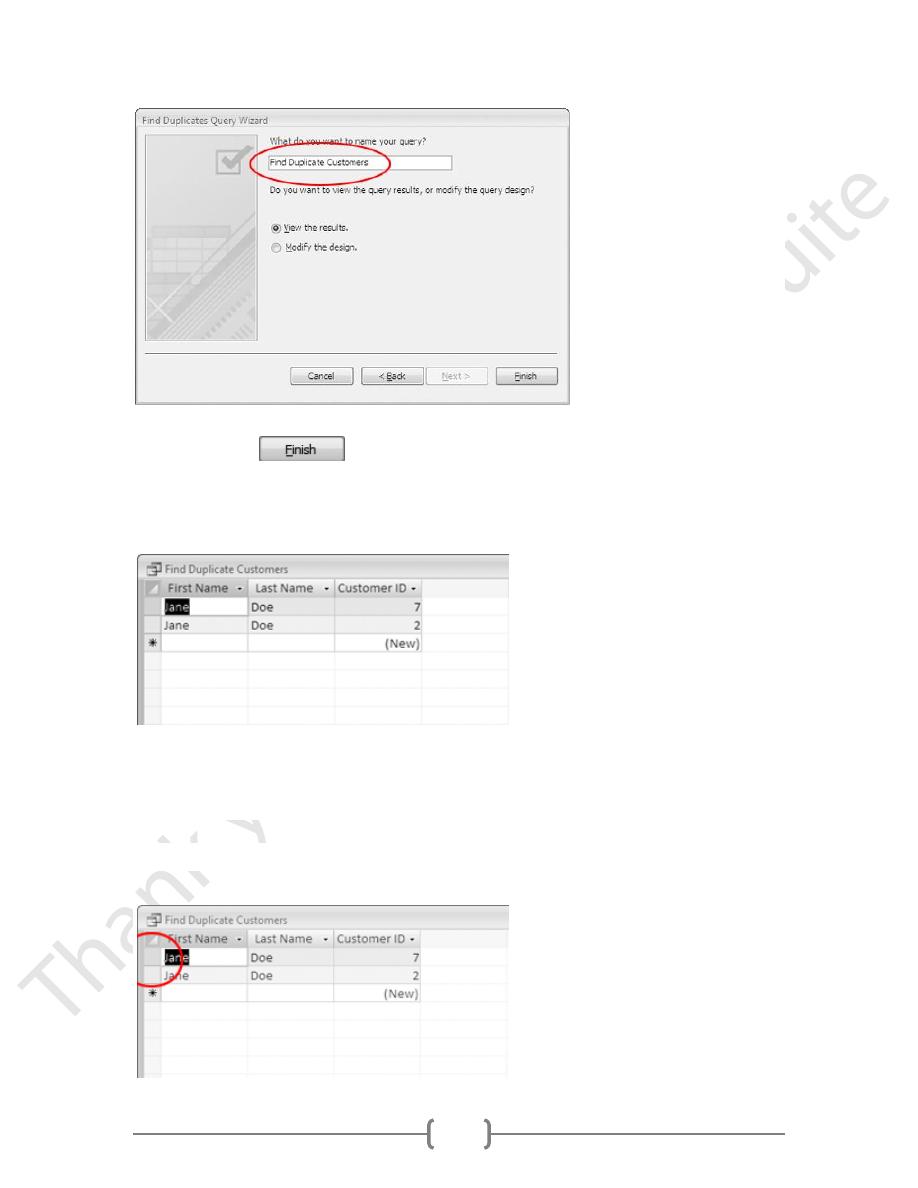
61
8.
Click the
button.
The query should run, and look like this:
There are two identical entries for Jane Doe in the database.
Remove duplicates
1. Click the row selector button for the Jane Doe record with the Customer ID of
7
.
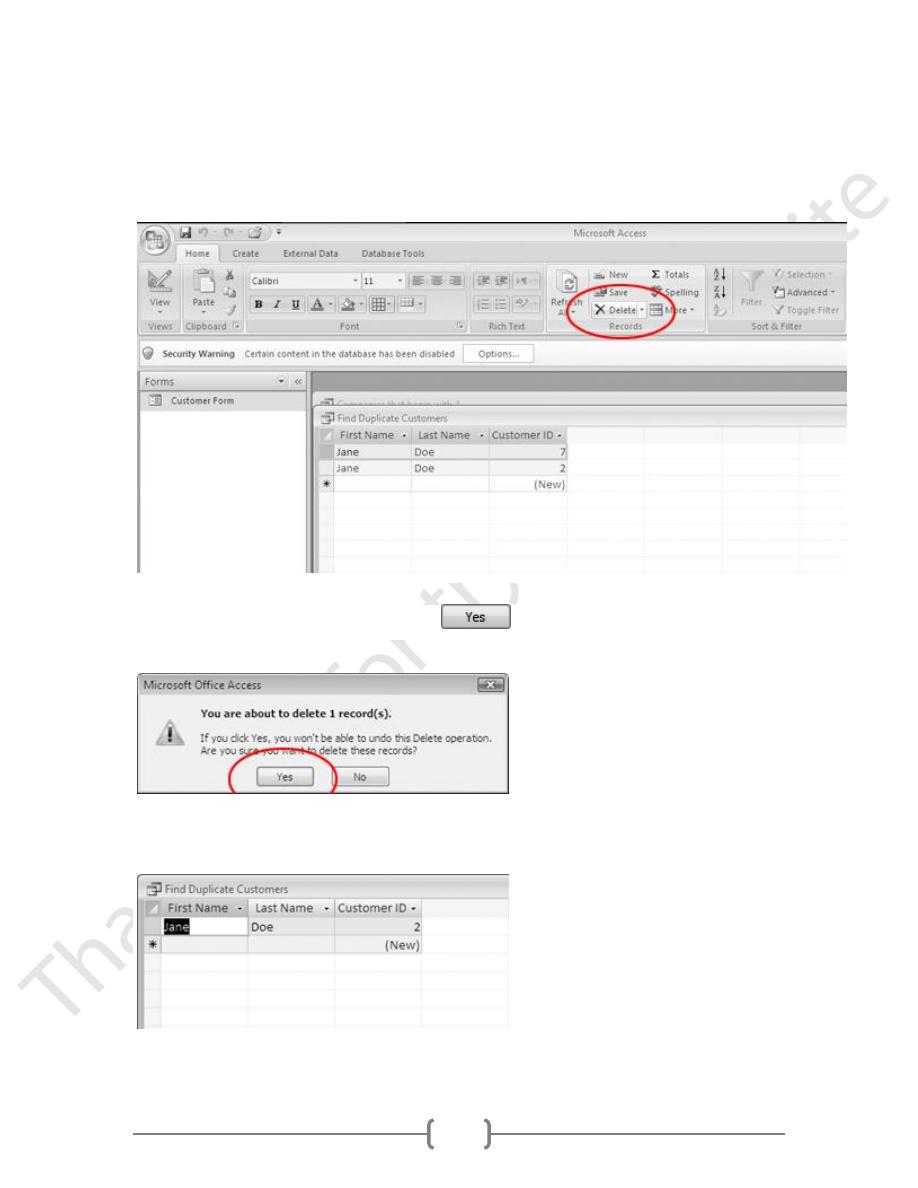
62
2. Click the
Home
tab.
In the Ribbon, click
Delete
.
3. When the alert window appears, click the
button.
The query results should now look like this:
Record number 7 is removed from the database.
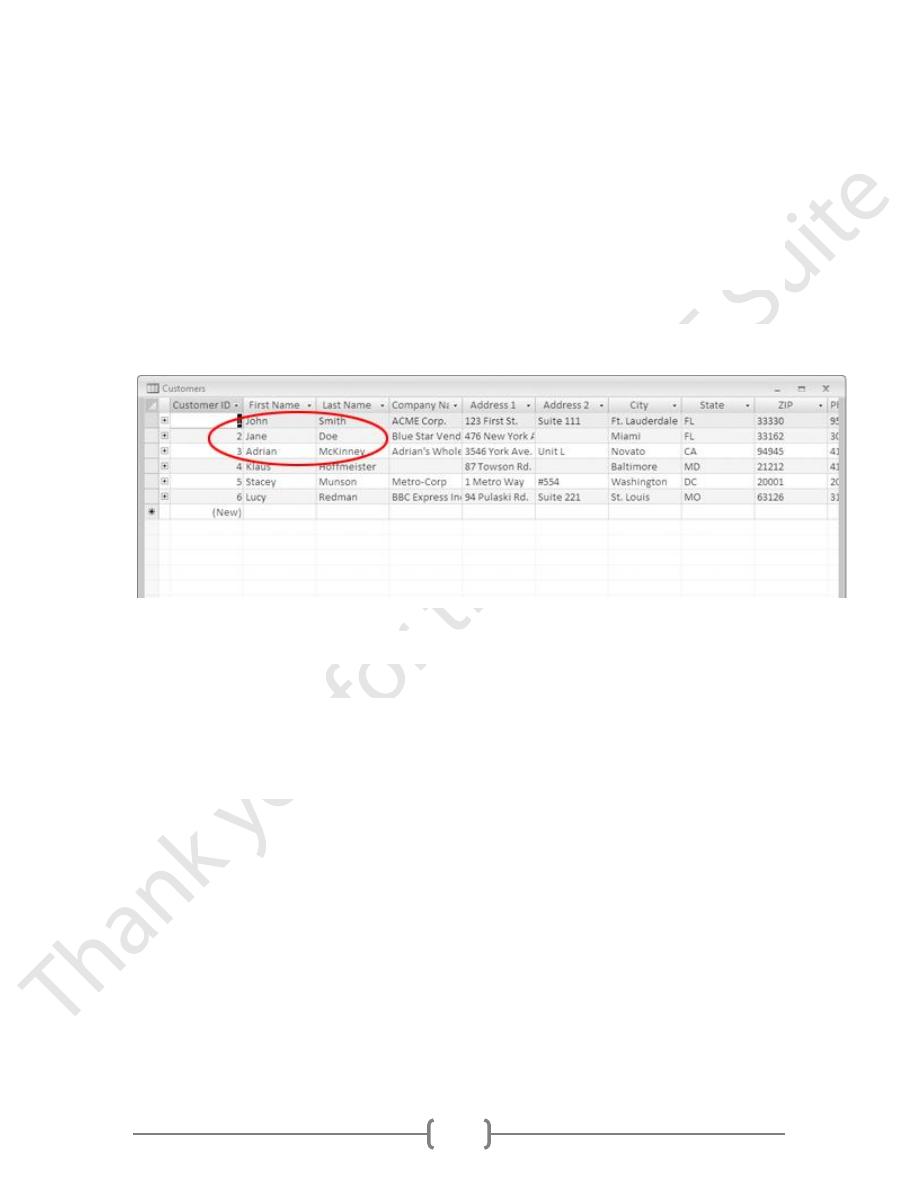
63
TIP: Deleting a record from a query also deletes it from the table it was stored in.
Verify results
1.
Close the window.
2.
Open the
Customers
table.
It should now look like this, with only one record for Jane Doe:
3.
Close the
Customers
table.

