29
Lecture 4 - Select Cases
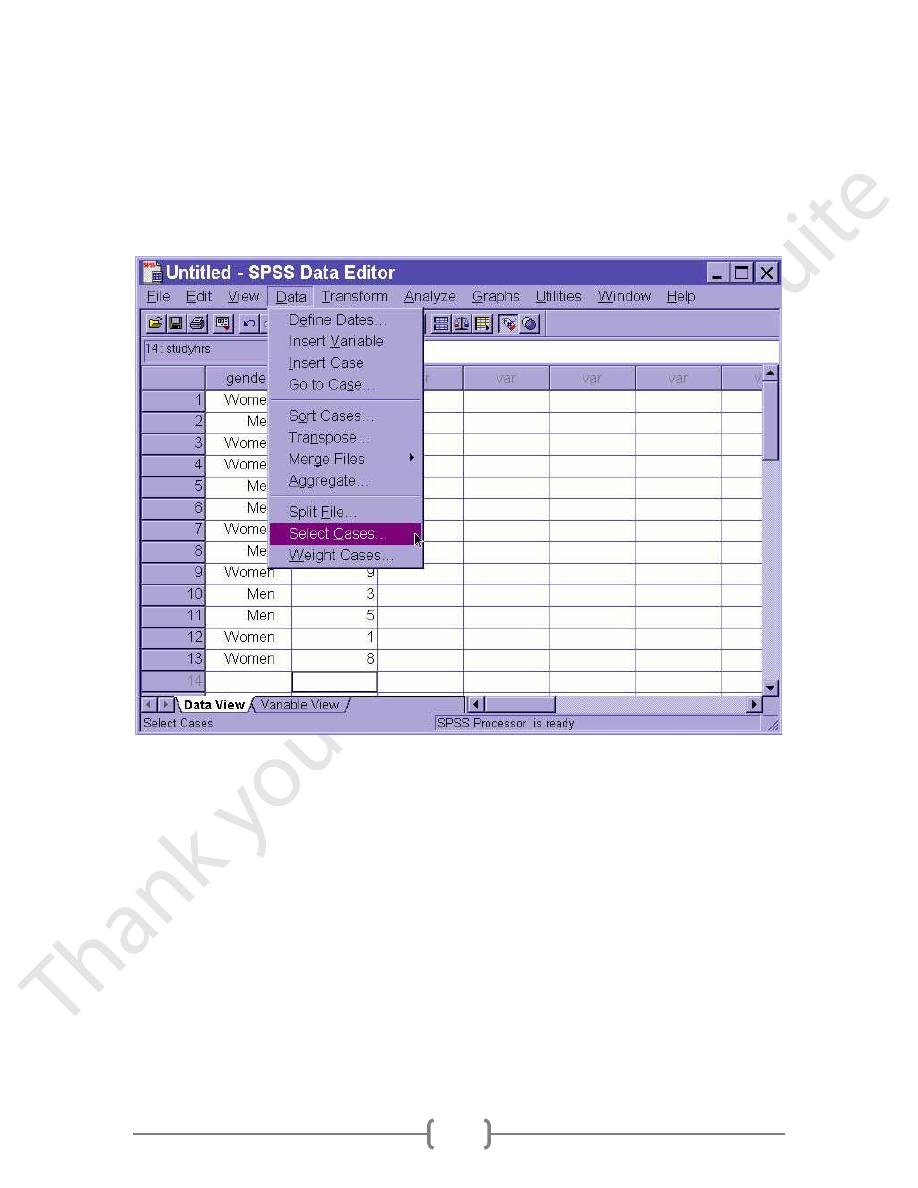
SPSS allows us to select part of the data set for further analysis, while excluding the
remaining cases from these analyses. The procedure is found by choosing Select from the
Data Menu.
We then have several "Select" options within the dialogue box that comes up so we can
tell SPSS which data to select and which to ignore. The select dialogue box looks like
this:
30
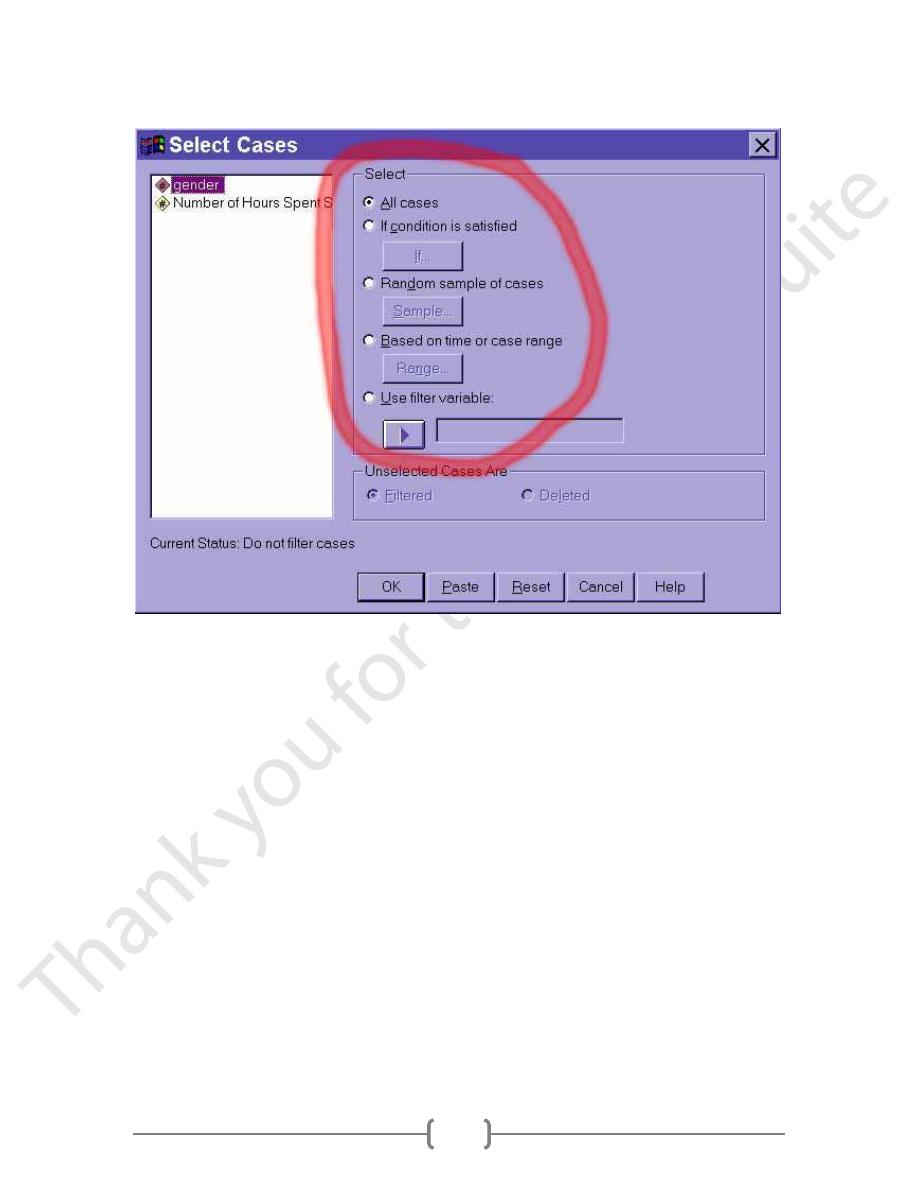
First, we have to specify how to select data and which data to retain for the analyses:
All cases
This option actually turns off any previous selection and uses all data in the file.
Click on this radio button and then click on the OK button.
If condition is satisfied
This option allows us to specify a rule based on values of variables; all cases that meet
the criteria are retained. After clicking on the radio button for this option, we click on the
"If..." button to bring up an additional dialogue box sp we can define the rule or rules for
including or excluding data:
31
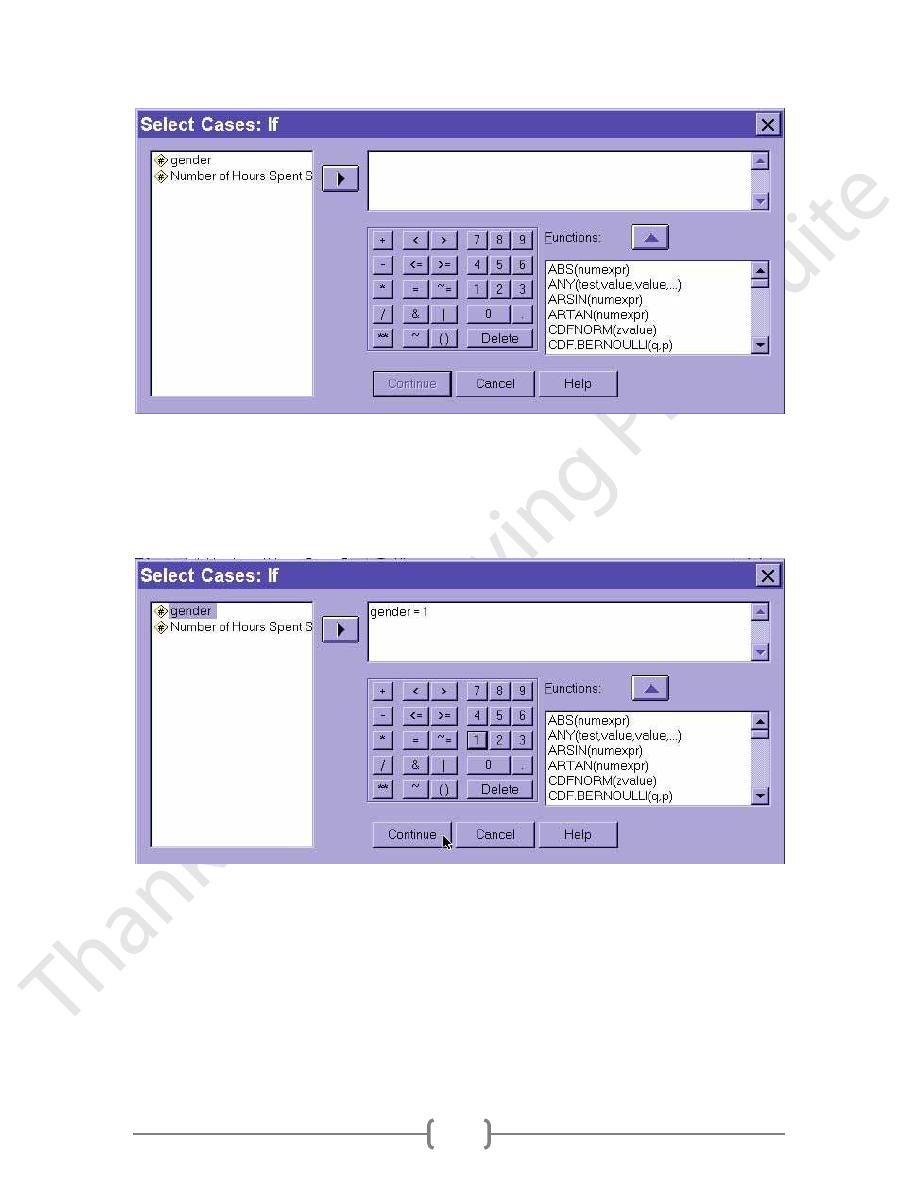
We want to specify a condition in the right box based on one or more variables listed in
the box to the left. Click on the HELP button for definitions of each of the "calculator"
buttons in this dialogue box. For instance, if we have a variable for gender coded as 1 for
women and 2 for men, we can select only the women for analysis by selecting
"gender=1" as shown below:
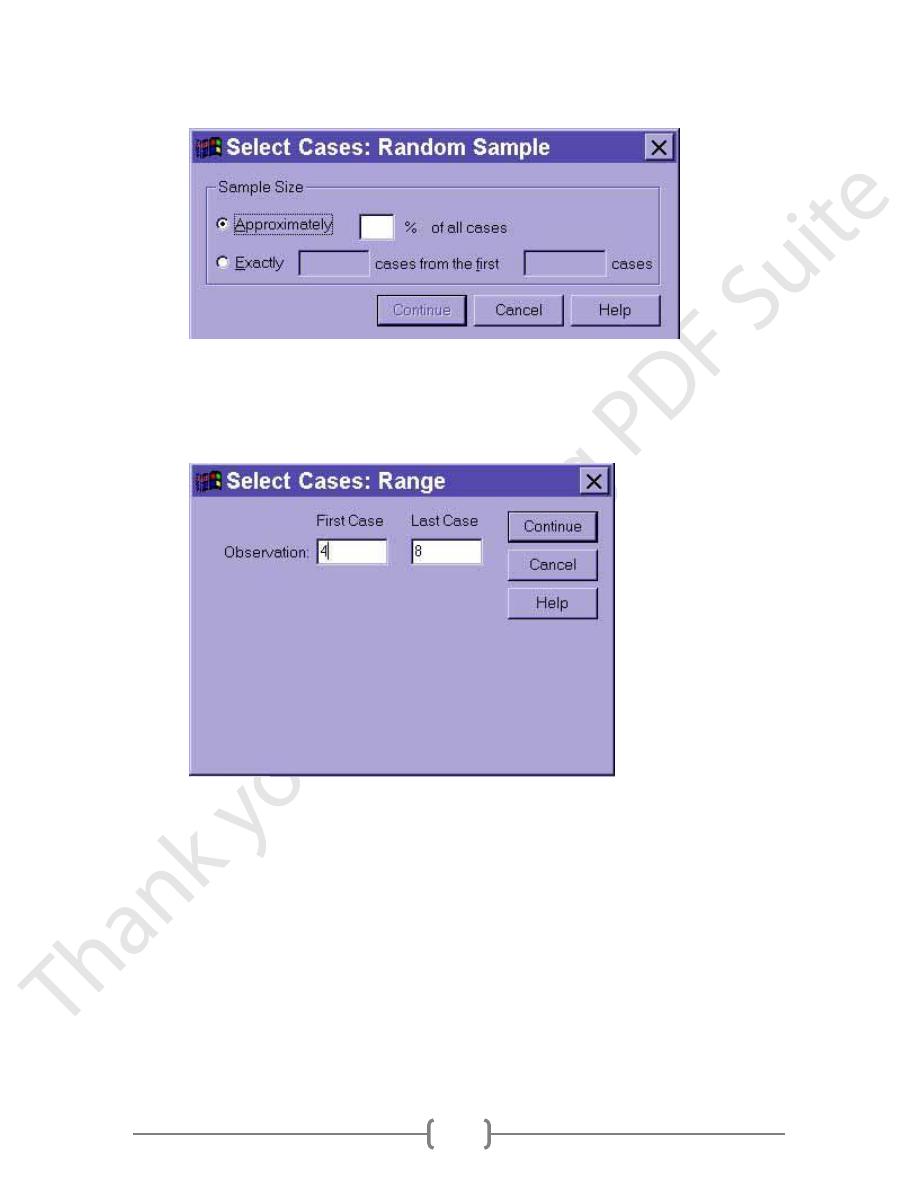
Random sample of cases
This option allows us to select a specified proportion of the cases or a fixed
number of cases at random. After selecting the corresponding radio button, we
click on the "Sample" button to bring up a dialogue box that allows us to specify
either an approximate percentage of cases or to sample an exact number of cases
at random.
32
Based on time or case range
This option allows us to specify a range of cases based on the internal case
number. Thus, by typing in "4" and "8", we can select only cases 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8.
Use filter variable
This option uses a special variable type (a filter variable that has values of 1 or 0
only: the cases with a 1 are included, and the cases with 0 on the filter variable are
excluded.
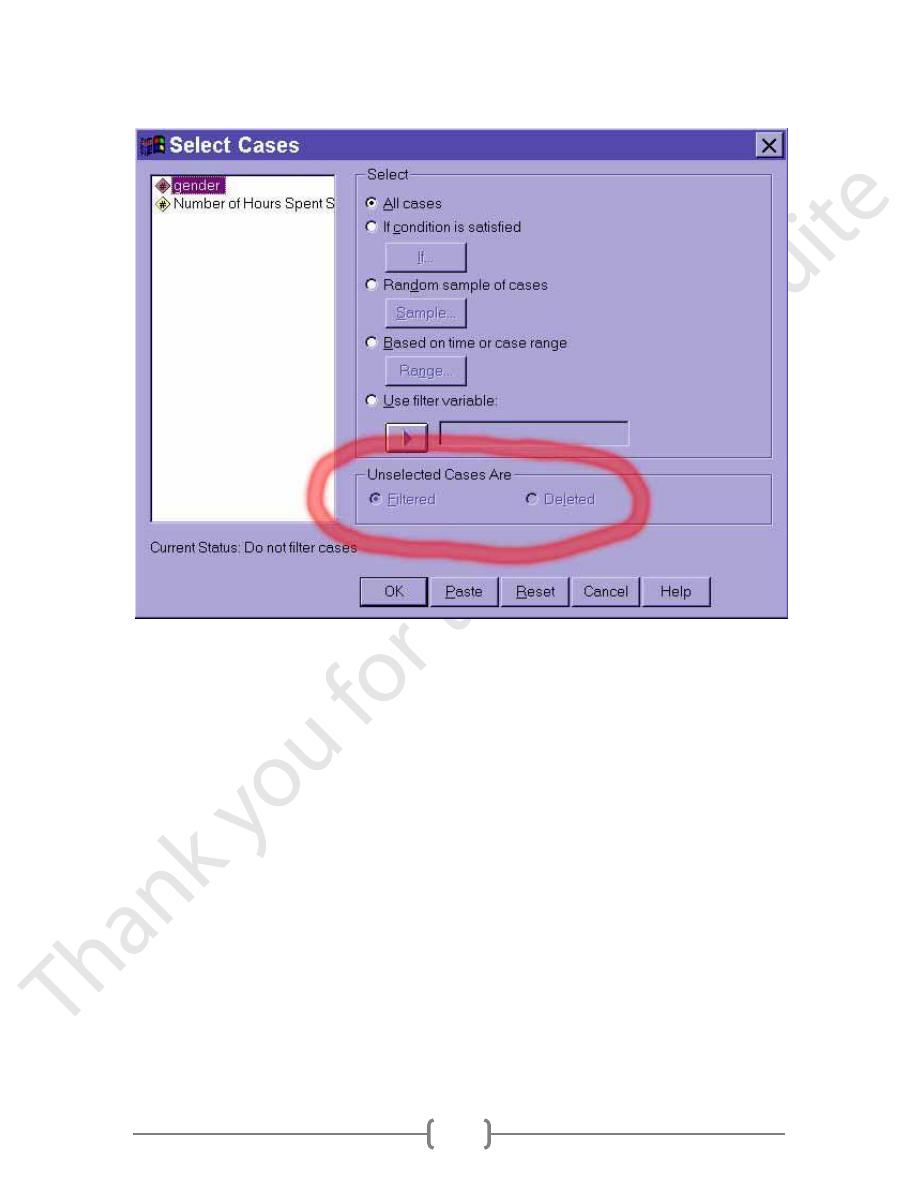
We also have to tell SPSS what to do with the unselected data. SPSS can either filter it or
delete it. If we choose to delete the unselected data, those cases not meeting the criteria
specified above will be deleted and cannot be recovered! If we choose to filter the
unselected data, then the data will not be deleted, but SPSS will ignore the data in any
and all analyses until the filter is "turned off" by selecting the All cases option described
above. This filtering option, therefore, is far safer than the deleting option.
33
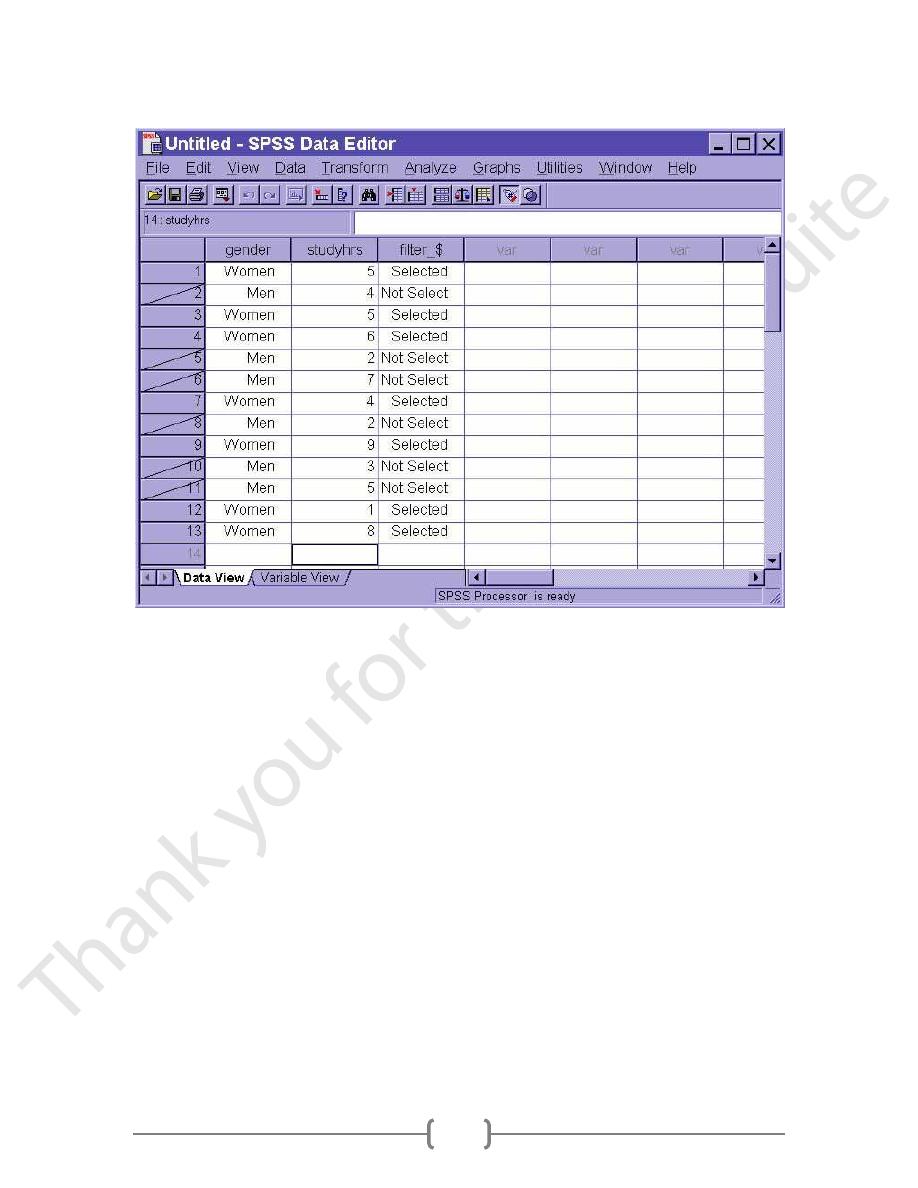
After we have selected one of the radio buttons for the selection method and after we
have selected one of the radio buttons for handling unselected data, clicking on the OK
button will perform the selection. If we have chosen to filter unselected data, cases that
are not being used with have a slash through the case number
34
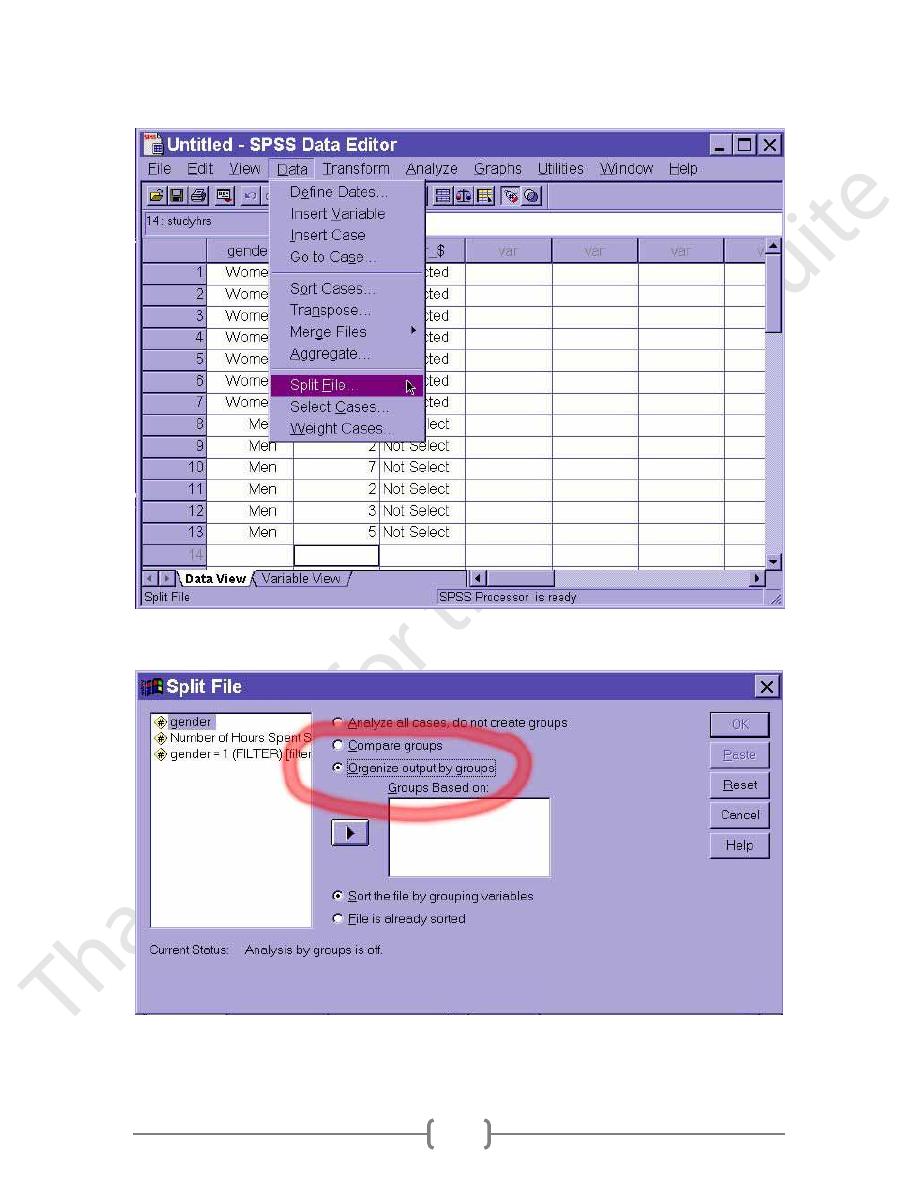
Split File
The split file option from the Data menu works similarly to the select option. The
difference, though, is that we use the split function to repeat the same analyses, separatel,
on multiple groups. For instance, if we want to compute descriptive statistics of men and
women separately, we would select the split option from the Data menu.
35
Then, we would click on the radio button for "Organize output by groups":
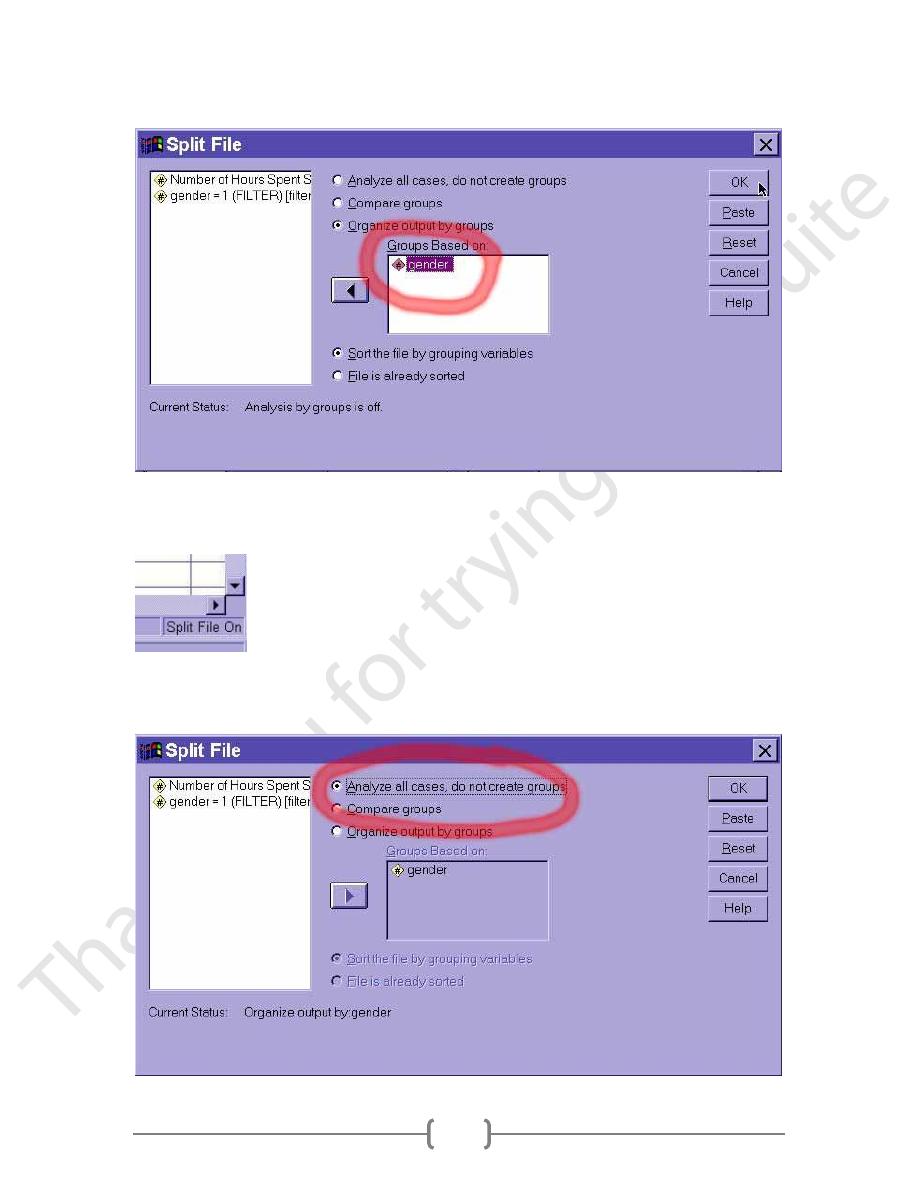
Then, we would select the gender variable in the left field and click the right arrow to
move it to the right field:
36
After clicking on the OK button, we would see the "Split file on" message in the lower
right-hand corner of the SPSS data window
Finally, any further analyses we run will be run separately for men and for women until
we turn off the split file option by selecting "Analyze all cases -- do not split groups":
