
394
CHAPTER 9
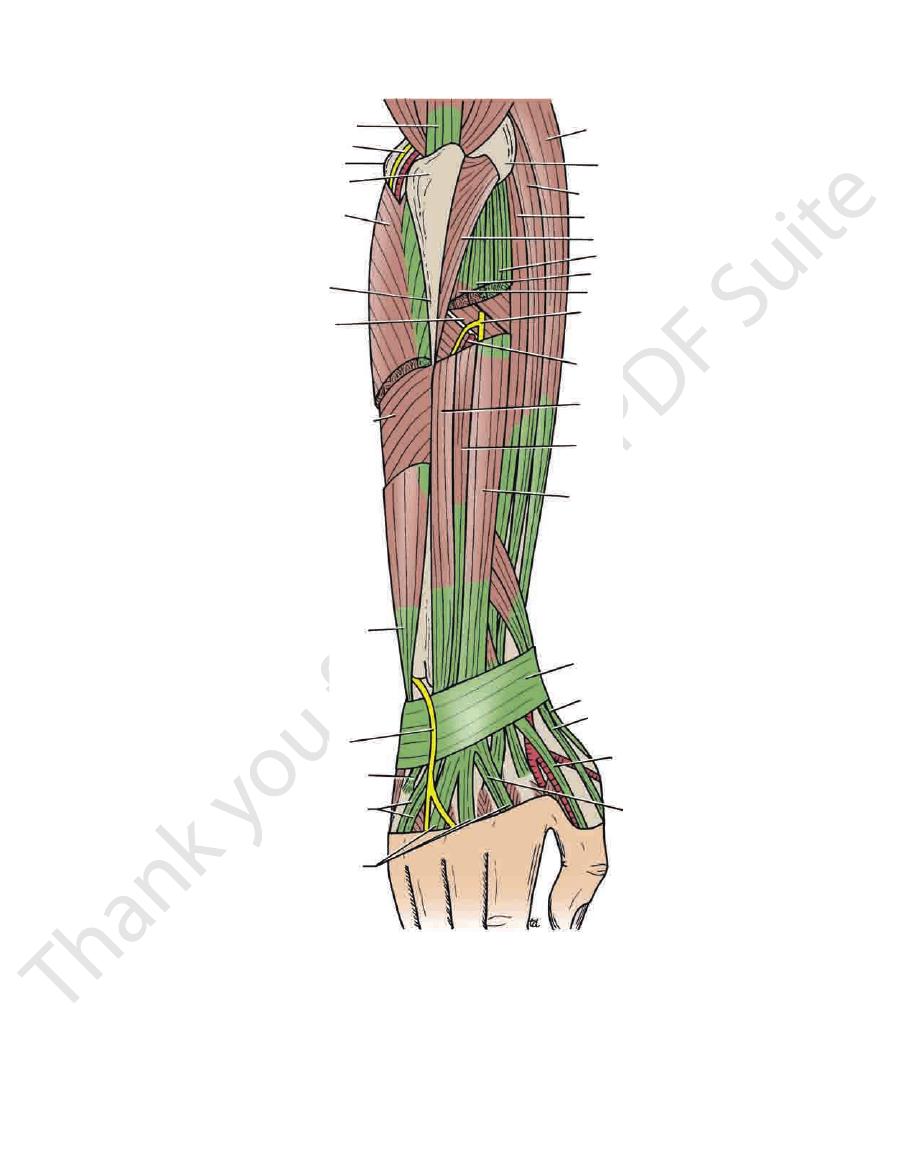
Palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve
aponeurosis
insertion into the flexor retinaculum and the palmar
(if present), passing to its
Palmaris longus tendon
Palmar cutaneous branch of the ulnar nerve
lies lateral to the ulnar nerve.
Ulnar artery
lies lateral to the pisiform bone.
Ulnar nerve
inaculum but is included for the sake of completeness.)
bone. (This tendon does not actually cross the flexor ret
ending on the pisiform
Flexor carpi ulnaris tendon,
naculum from medial to lateral (Fig. 9.54):
The following structures pass superficial to the flexor reti
Wrist
structures as possible.
time, examine your own wrist and identify as many of the
identify the structures from medial to lateral. At the same
In a transverse section through the wrist (Fig. 9.54),
for injury.
joint. From a clinical standpoint, the wrist is a common site
the tendons, arteries, and nerves in the region of the wrist
a student have a sound knowledge of the arrangement of
Before learning the anatomy of the hand, it is essential that
The Region of the Wrist
to the wrist and carpal joints
Articular branches
pollicis longus, and the extensor indicis
pollicis longus, the extensor pollicis brevis, the extensor
digiti minimi, the extensor carpi ulnaris, the abductor
and the supinator, the extensor digitorum, the extensor
to the extensor carpi radialis brevis
Muscular branches
Branches
face of the wrist joint.
muscles (Fig. 9.65). It eventually reaches the posterior sur
in the interval between the superficial and deep groups of
posterior compartment of the forearm. The nerve descends
of the radius in the substance of the muscle to reach the
supinator and winds around the lateral aspect of the neck
the humerus in the cubital fossa (Fig. 9.61). It pierces the
from the radial nerve in front of the lateral epicondyle of
The deep branch arises
Deep Branch of the Radial Nerve
Forearm
Nerve of the Posterior Fascial Compartment of the
The Upper Limb
-
■
■
■
■
Structures on the Anterior Aspect of the
-
■
■
-
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
FIGURE 9.63
Insertions of long flexor and extensor tendons in the fingers. Insertions of the lumbrical and interossei muscles
pophalangeal joints and extending the interphalangeal joints.
are also shown. The uppermost figure illustrates the action of the lumbrical and interossei muscles in flexing the metacar-
extensor digitorum
interossei and lumbrical muscles
axis of rotation
flexor digitorum profundus
flexor digitorum superficialis
vincula brevia
vincula longa
dorsal extensor expansion
lumbrical
extensor
digitorum
interosseous
third metacarpal
extensor digitorum
third metacarpal
interosseous
flexor digitorum profundus
flexor digitorum superficialis
lumbrical
Basic Anatomy
synovial sheath.
the flexor retinaculum. The tendon is surrounded by a
going through a split in
Flexor carpi radialis tendon
surrounded by a synovial
Flexor pollicis longus tendon
Median nerve
both groups of tendons share a common synovial sheath.
to these, the tendons of the flexor digitorum profundus;
and, posterior
Flexor digitorum superficialis tendons
lum from medial to lateral (Fig. 9.54):
The following structures pass beneath the flexor retinacu
395
-
■
■
■
■
■
■
sheath
■
■
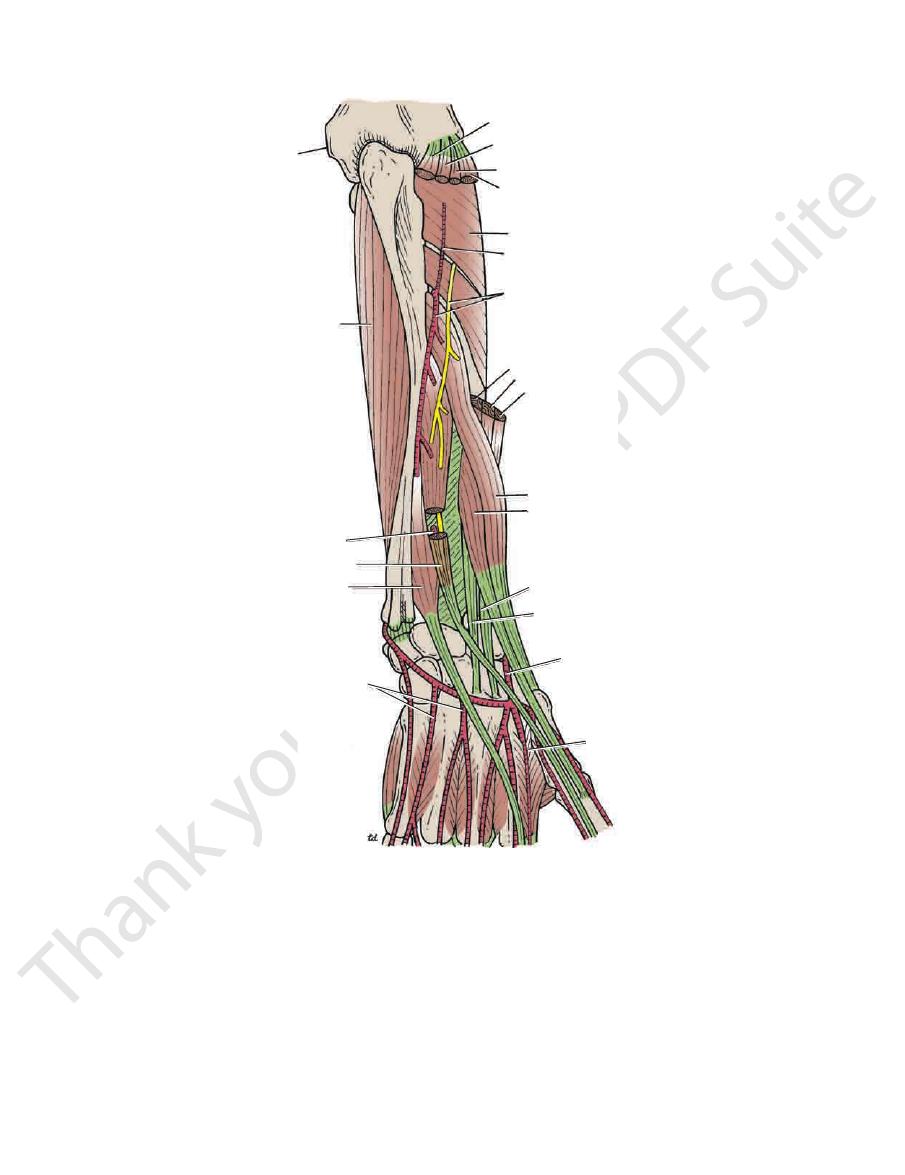
triceps
ulnar nerve
medial epicondyle
olecranon process
flexor carpi ulnaris
posterior subcutaneous
border of ulna
supinator
flexor digitorum profundus
flexor carpi ulnaris
posterior cutaneous branch
of ulnar nerve
extensor carpi ulnaris
extensor digiti minimi
extensor digitorum
extensor indicis
extensor pollicis longus
extensor pollicis brevis
abductor pollicis longus
extensor retinaculum
extensor digitorum
extensor digiti minimi
extensor carpi ulnaris
posterior interosseous artery
deep branch of radial nerve
extensor carpi ulnaris
extensor digiti minimi
extensor digitorum
anconeus
extensor carpi radialis brevis
extensor carpi radialis longus
lateral epicondyle
brachioradialis
FIGURE 9.64
Posterior view of the forearm. Parts of the extensor digitorum, extensor digiti minimi, and extensor carpi ulnaris
have been removed to show the deep branch of the radial nerve and the posterior interosseous artery.
396
CHAPTER 9
lateral part of the posterior surface of the radius.
share a common synovial sheath and are situated on the
extensor indicis tendons
Extensor digitorum
the distal radioulnar joint.
is situated posterior to
Extensor digiti minimi tendon
terior aspect of the head of the ulna
which grooves the pos
Extensor carpi ulnaris tendon,
ulum from medial to lateral (Fig. 9.54):
The following structures pass beneath the extensor retinac
Superficial branch of the radial nerve
Cephalic vein
Basilic vein
nerve
Dorsal (posterior) cutaneous branch of the ulnar
retinaculum from medial to lateral (Fig. 9.54):
The following structures pass superficial to the extensor
Wrist
The Upper Limb
Structures on the Posterior Aspect of the
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
-
■
■
-
■
■
■
■
and
medial epicondyle
flexor digitorum profundus
anterior interosseous artery
piercing interosseous membrane
extensor pollicis longus
extensor indicis
posterior metacarpal arteries
first dorsal interosseous
radial artery
extensor carpi radialis brevis
extensor carpi radialis longus
extensor pollicis brevis
abductor pollicis longus
brachioradialis
extensor carpi radialis longus
extensor carpi radialis brevis
deep branch of radial nerve and
posterior interosseous artery
interosseous recurrent artery
supinator
extensor digitorum
extensor digiti minimi
extensor carpi ulnaris
anconeus
FIGURE 9.65
Posterior view of the forearm. The superficial muscles have been removed to display the deep structures.

Basic Anatomy
which crosses in front of the
branch of the median nerve,
palmar cutaneous
9.38 and 9.55) is derived from the
supply to the skin of the palm (Figs.
sensory nerve
The
so improve the grip of the palm in holding a rounded object.
rugate the skin at the base of the hypothenar eminence and
superficial branch of the ulnar nerve. Its function is to cor
and is inserted into the skin of the palm. It is supplied by the
arises from the flexor retinaculum and palmar aponeurosis
(Fig. 9.55) is a small muscle that
palmaris brevis
The
the site of joints. Sweat glands are present in large numbers.
sites of skin movement, which are not necessarily placed at
fibrous bands. The skin shows many flexure creases at the
bound down to the underlying deep fascia by numerous
The skin of the palm of the hand is thick and hairless. It is
pollicis brevis (Fig. 9.65).
the tendons of the abductor pollicis longus and extensor
between the lateral collateral ligament of the wrist joint and
The radial artery reaches the back of the hand by passing
extends above and below the retinaculum.
compartment is provided with a synovial sheath, which
that contain the tendons of the extensor muscles. Each
underlying radius and ulna and form six compartments
Beneath the extensor retinaculum, fibrous septa pass to the
common compartment.
have separate synovial sheaths but share a
vis tendons
extensor pollicis bre
Abductor pollicis longus
lateral part of the posterior surface of the radius.
share a common synovial sheath and are situated on the
brevis tendons
Extensor carpi radialis longus
medial side of the dorsal tubercle of the radius.
winds around the
Extensor pollicis longus tendon
397
■
■
■
■
and
■
■
and the
-
The Palm of the Hand
Skin
-
Muscles of the Posterior Fascial Compartment of the Forearm
T A B L E 9 . 8
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Nerve Roots
a
Action
Extensor carpi
radialis brevis
Lateral epicondyle of
humerus
Posterior surface
of base of third
metacarpal bone
Deep branch of
radial nerve
C7, 8
Extends and abducts
hand at wrist joint
Extensor
digitorum
Lateral epicondyle of
humerus
Middle and distal
phalanges of
medial four
fingers
Deep branch of
radial nerve
C7, 8
Extends fingers and hand
(see text for details)
Extensor digiti
minimi
Lateral epicondyle of
humerus
Extensor expansion
of little finger
Deep branch of
radial nerve
C7, 8
Extends metacarpal
phalangeal joint of little
finger
Extensor carpi
ulnaris
Lateral epicondyle of
humerus
Base of 5th
metacarpal bone
Deep branch of
radial nerve
C7, 8
Extends and adducts
hand at wrist joint
Anconeus
Lateral epicondyle of
humerus
Lateral surface
of olecranon
process of ulna
Radial nerve
C7, 8; T1
Extends elbow joint
Supinator
Lateral epicondyle of
humerus, anular
ligament of proximal
radioulnar joint, and
ulna
Neck and shaft of
radius
Deep branch of
radial nerve
C5, 6
Supination of forearm
Abductor pollicis
longus
Posterior surface of
shafts of radius and
ulna
Base of first
metacarpal bone
Deep branch of
radial nerve
C7, 8
Abducts and extends
thumb
Extensor pollicis
brevis
Posterior surface of
shaft of radius
Base of proximal
phalanx of thumb
Deep branch of
radial nerve
C7, 8
Extends
metacarpophalangeal
joints of thumb
Extensor pollicis
longus
Posterior surface of
shaft of ulna
Base of distal
phalanx of thumb
Deep branch of
radial nerve
C7, 8
Extends distal phalanx of
thumb
Extensor indicis
Posterior surface of
shaft of ulna
Extensor expansion
of index finger
Deep branch of
radial nerve
C7, 8
Extends
metacarpophalangeal
joint of index finger
a
The predominant nerve root supply is indicated by boldface type.
