476
CHAPTER 10
The Lower Limb
fractured by posterior displacement of the talus. The sustentac
popliteal surface of the femur, the posterior ligament of the
of the fossa is formed by the
floor
or
anterior wall
The
(Fig. 10.41)
above and the medial head of the gastrocnemius below
The semimembranosus and semitendinosus
Medially:
of the gastrocnemius and plantaris below (Fig. 10.41)
The biceps femoris above and the lateral head
Laterally:
nerve, connective tissue, and lymph nodes.
nerve of the thigh, the genicular branch of the obturator
mon peroneal and tibial nerves, the posterior cutaneous
the popliteal vessels, the small saphenous vein, the com
is most prominent when the knee joint is flexed. It contains
space situated at the back of the knee (Fig. 10.41). The fossa
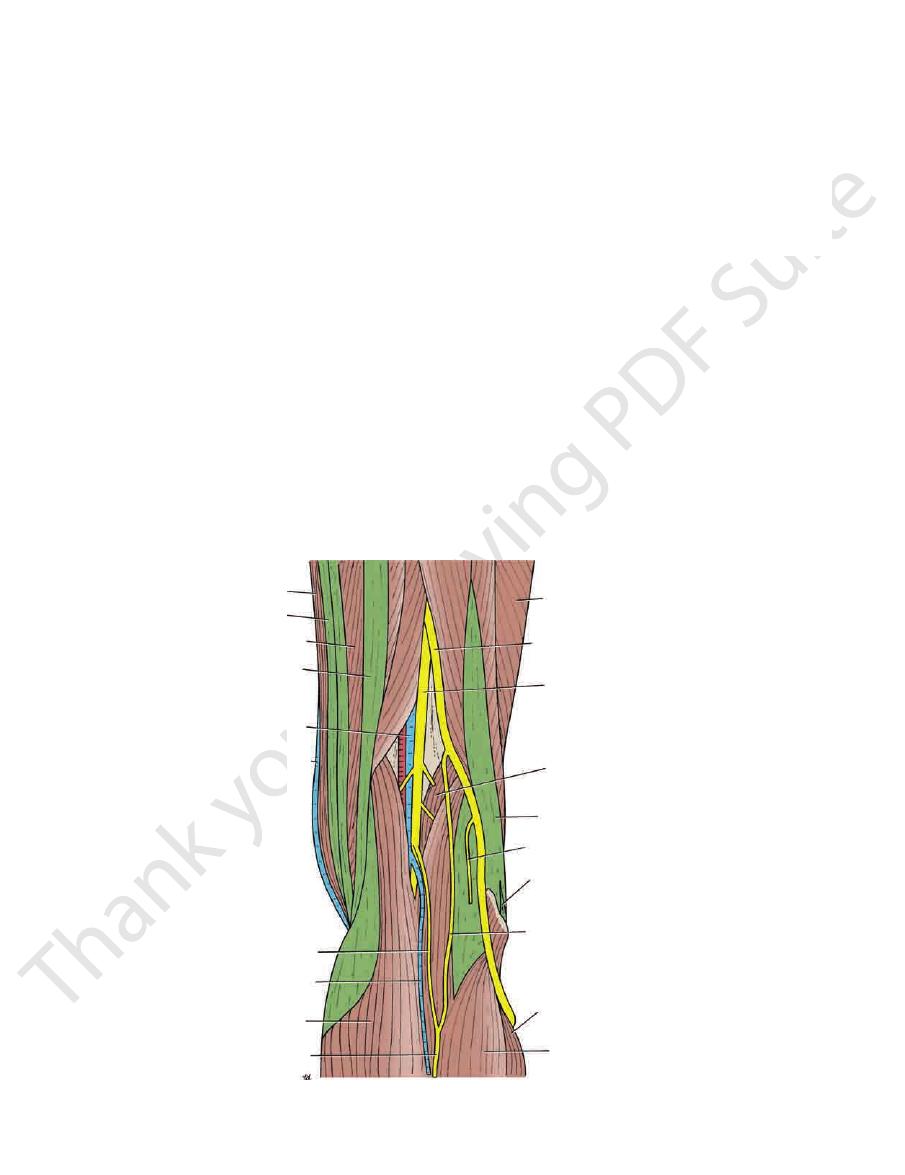
The popliteal fossa is a diamond-shaped intermuscular
ment occurs because of the attachment of the interosseous
nurses and hikers. It occurs most frequently in the distal third
gers and in soldiers after long marches; it can also occur in
-
ulum tali can be fractured by forced inversion of the foot.
Fractures of the Metatarsal Bones
The base of the 5th metatarsal can be fractured during forced
inversion of the foot, at which time the tendon of insertion of the
peroneus brevis muscle pulls off the base of the metatarsal.
Stress fracture of a metatarsal bone is common in jog-
of the 2nd, 3rd, or 4th metatarsal bone. Minimal displace-
muscles.
Popliteal Fossa
-
Boundaries
■
■
■
■
knee joint, and the popliteus muscle (Figs. 10.41 and 10.42).
on page 487.
are described in the section on the back of the leg,
plantaris
gastrocnemius
the back of the thigh, on page 465. The
muscles are described in the section on
semitendinosus
semimembranosus,
biceps femoris,
The
deep fascia of the thigh.
is formed by skin, superficial fascia, and the
roof
The
the
and the
and
sartorius
gracilis
semimembranosus
semitendinosus
popliteal vein
great saphenous vein
sural nerve
small saphenous vein
medial head of
gastrocnemius
sural nerve
lateral head of
gastrocnemius
soleus
sural communicating branch
of common peroneal nerve
lateral ligament
lateral cutaneous nerve of calf
biceps femoris
plantaris
tibial nerve
common peroneal nerve
vastus lateralis
FIGURE 10.41
Boundaries and contents of the right popliteal fossa.
Basic Anatomy
477
biceps femoris
short head
articular branch of
plantaris
anterior tibial arte
peroneal artery
flexor digitorum longus
tibialis posterior
oblique popliteal
genicular artery
popliteal surface
(posterior division)
popliteal artery
popliteal vein
tibialis posterior
posterior tibial artery
tibial nerve
opening in
adductor magnus
adductor magnus
obturator nerve
of femur
semimembranosus
capsule of knee joint
ligament
medial collateral ligament
popliteus
peroneus longus
tibial nerve
ry
soleus
nerve to popliteus
lateral collateral ligament
common peroneal nerve
common peroneal nerve
long head
sciatic nerve
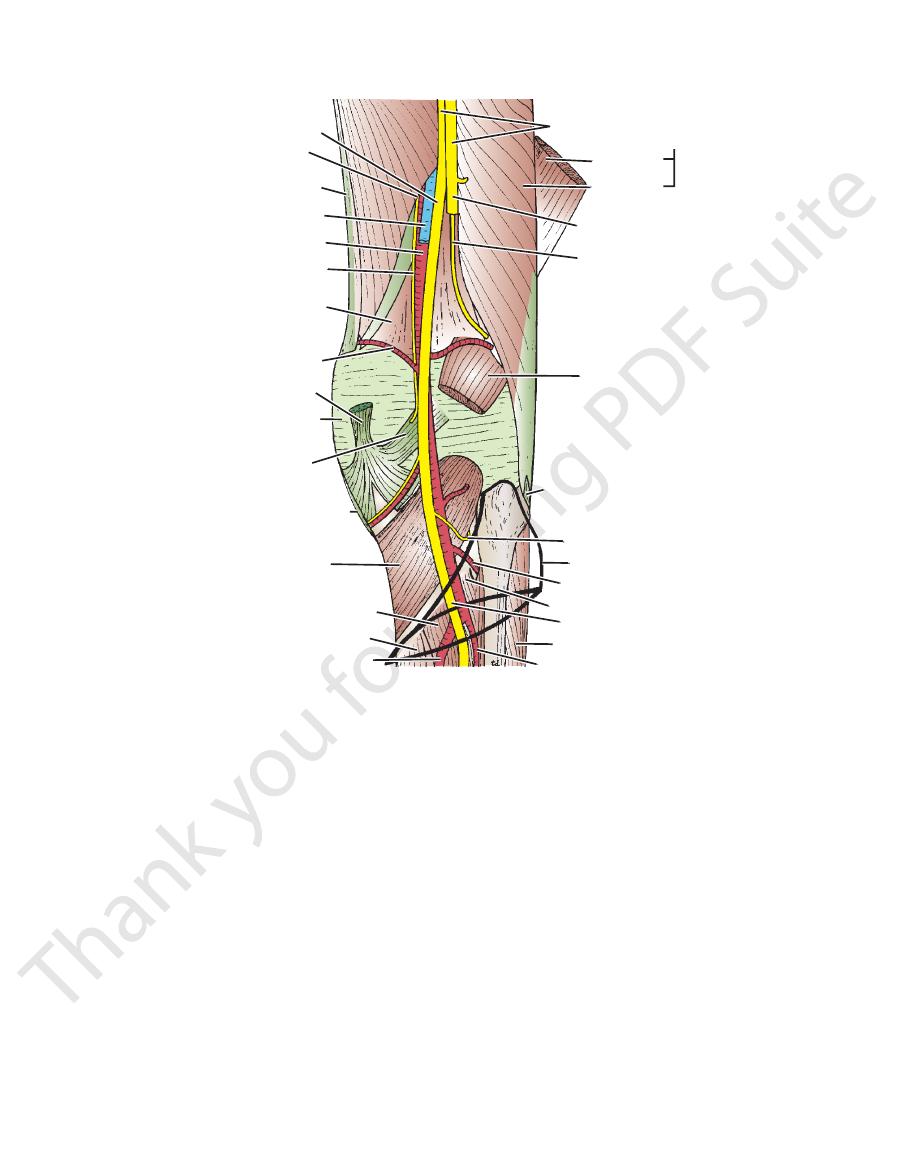
FIGURE 10.42
Deep structures in the right popliteal fossa. The proximal end of the soleus muscle is shown in outline only.
to the knee.
branches
articular
muscular branches
The popliteal artery has
Branches
cia, and skin (Figs. 10.41 and 10.42)
The popliteal vein and the tibial nerve, fas
Posteriorly:
joint, and the popliteus muscle (Fig. 10.42)
The popliteal surface of the femur, the knee
Anteriorly:
dividing into anterior and posterior tibial arteries.
at the level of the lower border of the popliteus muscle by
as a continuation of the femoral artery (Fig. 10.42). It ends
liteal fossa through the opening in the adductor magnus,
The popliteal artery is deeply placed and enters the pop
ment of flexion of the knee.
it also pulls the cartilage backward at the commence
joint.” Because of its attachment to the lateral meniscus,
action is sometimes referred to as “unlocking the knee
action slackens the ligaments of the knee joint; this
ment of flexion of the extended knee, and its rotatory
on the tibia. The latter action occurs at the commence
the foot is on the ground, lateral rotation of the femur
Medial rotation of the tibia on the femur or, if
Action:
Tibial nerve.
Nerve supply:
the joint to pass to its insertion.
the lower part of the posterior surface of the capsule of
from the lateral ligament of the joint. It emerges through
knee joint, and its tendon separates the lateral meniscus
the soleal line. The muscle arises within the capsule of the
are attached to the posterior surface of the tibia, above
The fibers pass downward and medially and
Insertion:
the lateral semilunar cartilage (Figs. 10.42 and 10.43).
the femur by a rounded tendon and by a few fibers from
From the lateral surface of the lateral condyle of
Origin:
the knee joint and will be described in detail.
The popliteus muscle plays a key role in the movements of
Popliteus Muscle
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
-
-
Popliteal Artery
-
Relations
■
■
■
■
-
and
478
CHAPTER 10
The Lower Limb
insertion of semimembranosus
contribution to popliteus fascia
tibial nerve
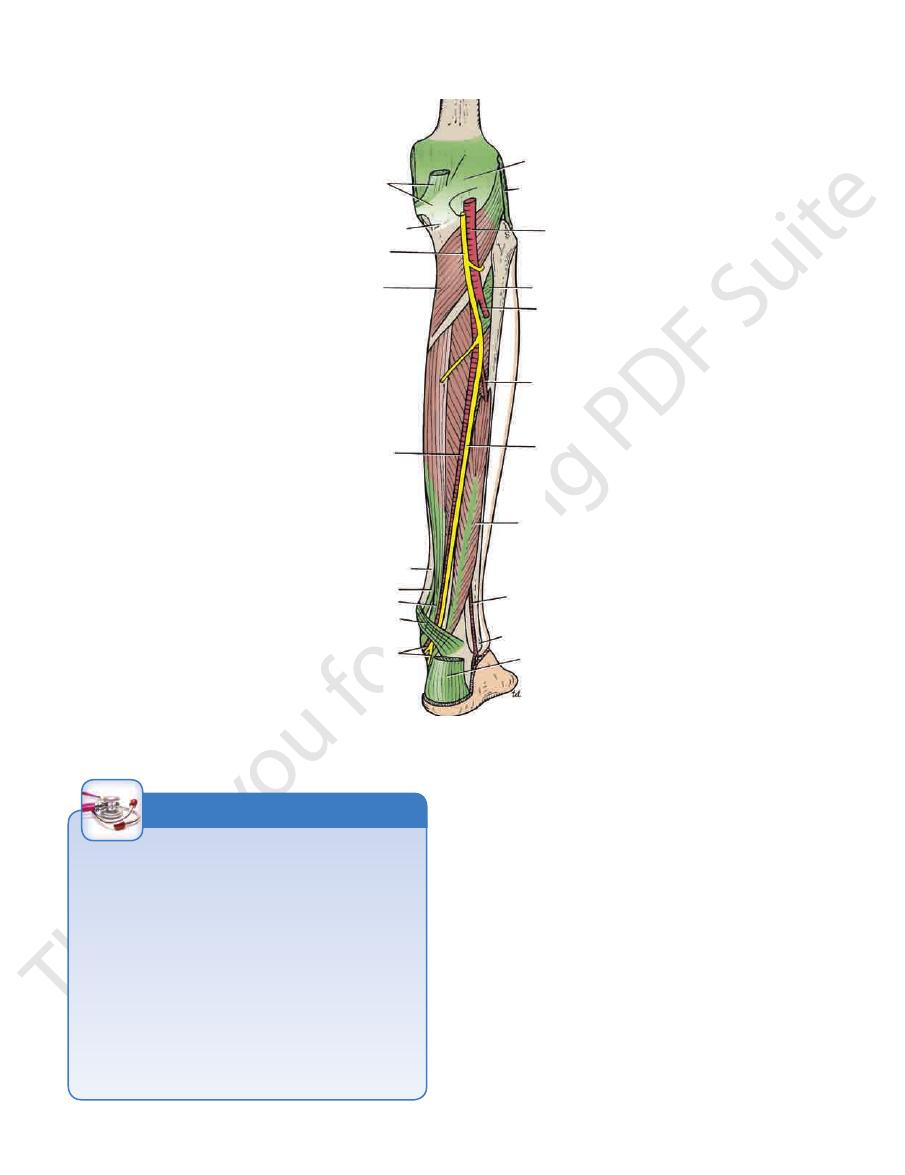
popliteus
posterior tibial artery
tibia
tibialis posterior
flexor digitorum longus
flexor retinaculum
plantar nerves and arteries
tendo calcaneus
lateral malleolus
peroneal artery
flexor hallucis longus
tibial nerve
peroneal artery
anterior tibial artery
interosseous membrane
popliteal artery
lateral collateral ligament
oblique popliteal ligament
FIGURE 10.43
Deep structures in the posterior aspect of the right leg.
Popliteal Aneurysm
should be distinguished from a Baker’s cyst, which is centrally
ing found in the popliteal space. It is made tense by extending
tendon of adductor magnus at the opening of the adductor
The pulsations of the wall of the femoral artery against the
magnus are thought to contribute to the cause of popliteal
aneurysms.
Semimembranosus Bursa Swelling
Semimembranosus bursa swelling is the most common swell-
the knee joint and becomes flaccid when the joint is flexed. It
located and arises as a pathologic (osteoarthritis) diverticu-
lum of the synovial membrane through a hole in the back of the
capsule of the knee joint.
C L I N I C A L N O T E S
Popliteal Vein
vein is described on page 487.
muscle to end in the popliteal vein. The origin of this
and passes between the two heads of the gastrocnemius
which perforates the deep fascia
Small saphenous vein,
popliteal artery.
Veins that correspond to branches given off by the
The tributaries of the popliteal vein are as follows:
Tributaries
ing in the adductor magnus to become the femoral vein.
eral side (Figs. 10.41 and 10.42). It passes through the open
behind the popliteal artery so that it comes to lie on its lat
the popliteal artery. As it ascends through the fossa, it crosses
lower border of the popliteus muscle on the medial side of
comitantes of the anterior and posterior tibial arteries at the
The popliteal vein is formed by the junction of the venae
-
-
■
■
■
■

Basic Anatomy
the knee joint is a profuse anastomosis of small branches
which occurs during extreme flexion of the knee, around
To compensate for the narrowing of the popliteal artery,
479
Arterial Anastomosis Around
the Knee Joint
of the femoral artery with muscular and articular branches
ris muscle, which arises high up in the popliteal fossa
branch to the short head of the biceps femo
Muscular
the skin on the lateral side of the back of the leg (Figs.
supplies
lateral cutaneous nerve of the calf
nerve. The
10.16 and 10.41) runs downward and joins the sural
(Figs.
sural communicating branch
The
Cutaneous:
Branches
is subcutaneous and can easily be rolled against the bone.
nerve lies on the lateral aspect of the neck of the fibula, it
neal nerve and the deep peroneal nerve (Fig. 10.44). As the
divides into two terminal branches: the superficial pero
neck of the bone, pierces the peroneus longus muscle, and
behind the head of the fibula, winds laterally around the
lateral head of the gastrocnemius muscle. It then passes
(Fig. 10.42). It leaves the fossa by crossing superficially the
closely following the medial border of the biceps muscle
of the thigh. It runs downward through the popliteal fossa,
467), the common peroneal nerve arises in the lower third
The smaller terminal branch of the sciatic nerve (see page
branches supply the knee joint.
Articular
mius and the plantaris, soleus, and popliteus (Figs. 10.41
branches supply both heads of the gastrocne
Muscular
border of the foot and the lateral side of the little toe.
malleolus and is distributed to the skin along the lateral
panies the small saphenous vein behind the lateral
the calf and the back of the leg. The sural nerve accom
branches arise from the sural nerve to supply the skin of
peroneal nerve (Figs. 10.41 and 10.17). Numerous small
branch of the common
sural communicating
by the
heads of the gastrocnemius muscle and is usually joined
descends between the two
sural nerve
The
Cutaneous:
Branches
course is described on page 489.
of the leg by passing beneath the soleus muscle. Its further
out its course. The nerve enters the posterior compartment
liteal vein lies between the nerve and the artery through
and finally medial to it (Figs. 10.41 and 10.42). The pop
the lateral side of the popliteal artery, then posterior to it,
It runs downward through the popliteal fossa, lying first on
467), the tibial nerve arises in the lower third of the thigh.
The larger terminal branch of the sciatic nerve (see page
Tibial Nerve
and posterior tibial arteries.
and from deep lymph vessels accompanying the anterior
popliteal fossa. They also receive lymph from the knee joint
and leg; these accompany the small saphenous vein into the
superficial lymph vessels from the lateral side of the foot
tive tissue of the popliteal fossa (Fig. 10.4). They receive
About six lymph nodes are embedded in the fatty connec
Popliteal Lymph Nodes
and posterior tibial arteries.
of the popliteal artery and with branches of the anterior
-
-
-
■
■
-
■
■
-
and 10.42).
■
■
Common Peroneal Nerve
-
■
■
10.1 and 10.41).
■
■
-
(Fig. 10.42).
branches to the knee joint.
Articular
■
■
is exposed to direct trauma or is involved in fractures of the
Common Peroneal Nerve Injury
The common peroneal nerve is extremely vulnerable to
injury as it winds around the neck of the fibula. At this site, it
upper part of the fibula. Injury to the common peroneal nerve
causes footdrop.
C L I N I C A L N O T E S
Posterior Cutaneous Nerve of the Thigh
as pulleys.
the long tendons around the ankle joint in position and act
The retinacula are thickenings of the deep fascia that keep
(see Figs. 10.44 and 10.45).
together and provides attachment for neighboring muscles
The interosseous membrane binds the tibia and fibula
having its own muscles, blood supply, and nerve supply.
three compartments—anterior, lateral, and posterior—each
together with the interosseous membrane, divide the leg into
pass from its deep aspect to be attached to the fibula. These,
borders of the tibia (Fig. 10.45). Two intermuscular septa
it is attached to the periosteum on the anterior and medial
with the deep fascia of the thigh. Below the tibial condyles,
The deep fascia surrounds the leg and is continuous above
10.42). The nerve terminates by supplying the knee joint.
passing through the opening in the adductor magnus (Fig.
465. It leaves the subsartorial canal with the femoral artery by
in the medial compartment of the thigh is described on page
The course of the posterior division of the obturator nerve
over the popliteal fossa (Fig. 10.1).
described on page 465. It terminates by supplying the skin
through the gluteal region and the back of the thigh is
The course of the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh
Obturator Nerve
Fascial Compartments of the Leg
Interosseous Membrane
Retinacula of the Ankle
