
The Thigh (Front)
Lab Session 4
Dr. Hayder Jalil Al-Assam
MBChB (Iraq), MRes Anatomy (UK)
: dr_hayder_anatomy@yahoo.com
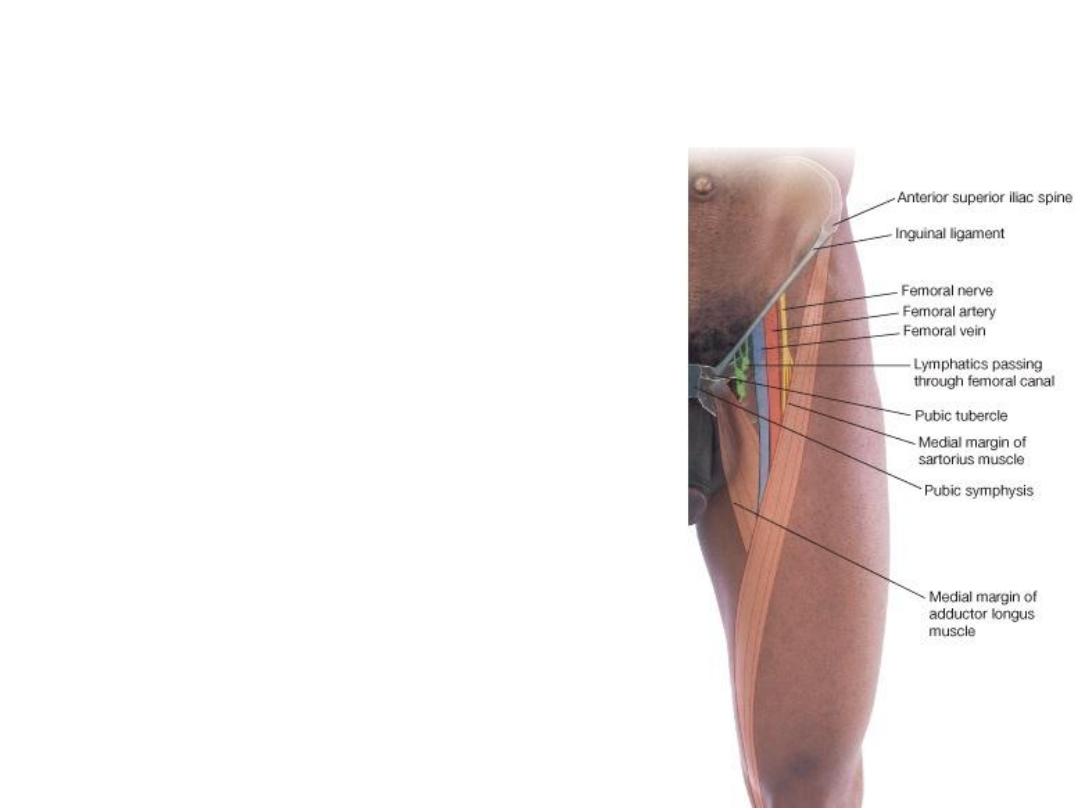
Femoral Triangle
• Its boundaries are:
• Superiorly: The inguinal ligament
• Laterally: The sartorius muscle
• Medially: The adductor longus muscle
• Its floor is formed from lateral to medial
by the iliopsoas, the pectineus, and the
adductor longus.
• Its roof is formed by the skin and fasciae
of the thigh.
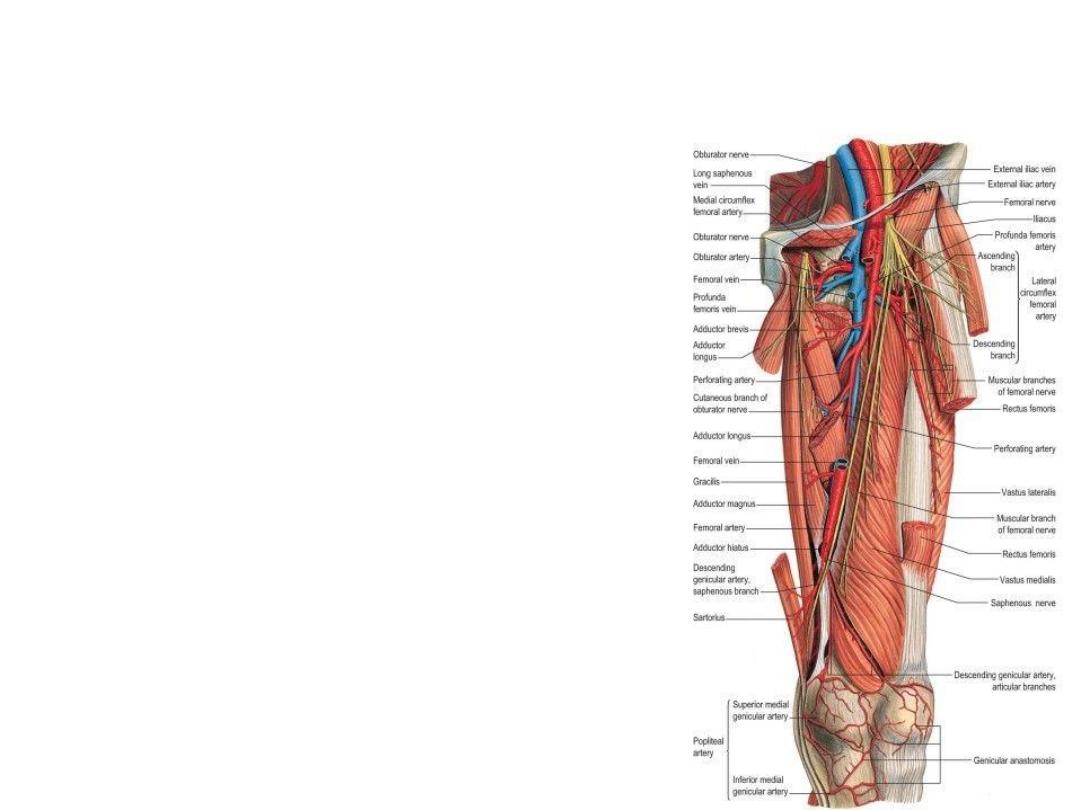
Adductor (Sub-sartorial) Canal
• The adductor canal is an intermuscular cleft
situated beneath the sartorius muscle
• In cross section it is triangular, having:
1.
The anteromedial wall is formed by the
sartorius muscle and fascia.
2.
The posterior wall is formed by the
adductor longus and magnus.
3.
The lateral wall is formed by the vastus
medialis.
• Contents: Femoral artery & vein, deep lymph
vessels, saphenous nerve, nerve to the
vastus medialis & obturator nerve.
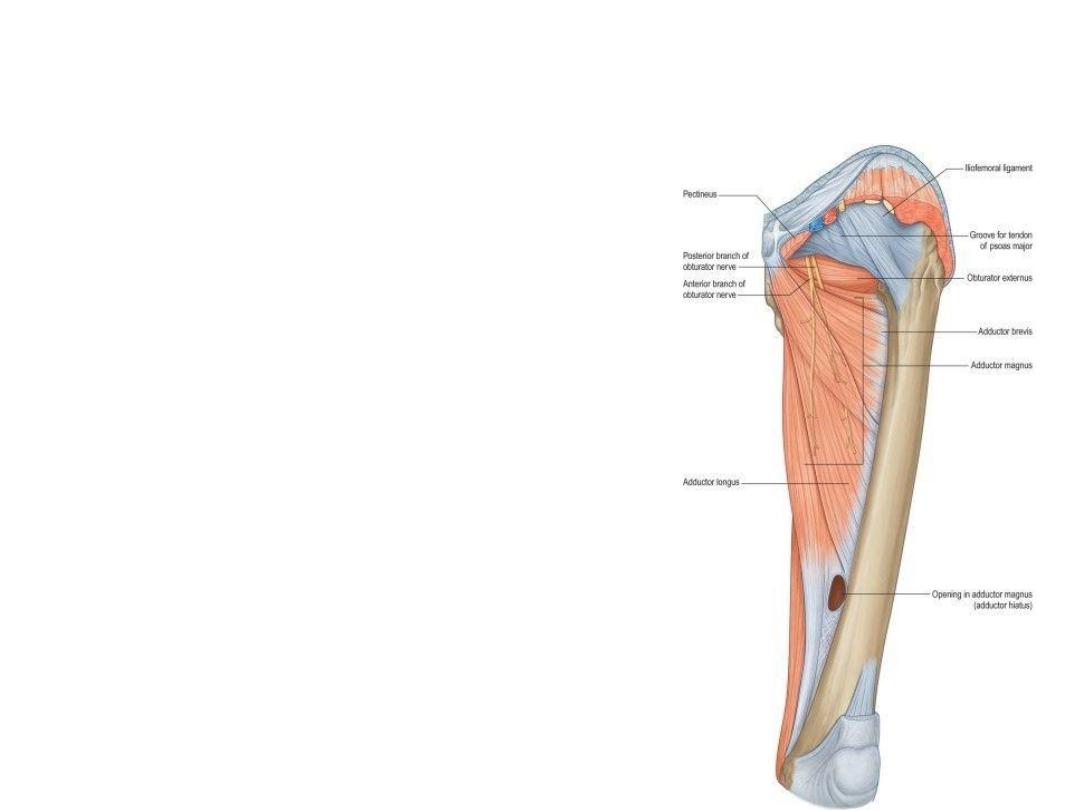
Medial fascial Compartment of the
thigh
• Gracilis
• Adductor Longus
• Adductor Brevis
• Adductor Magnus
• Obturator Externus
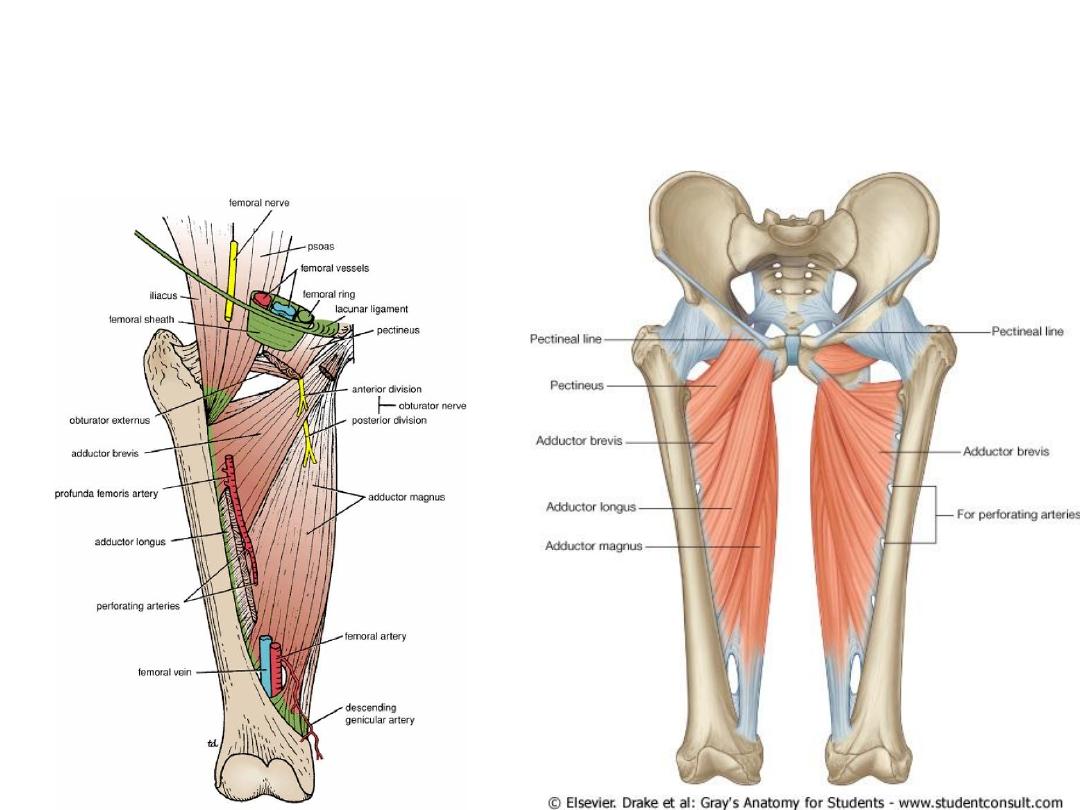
Medial fascial Compartment of the
thigh
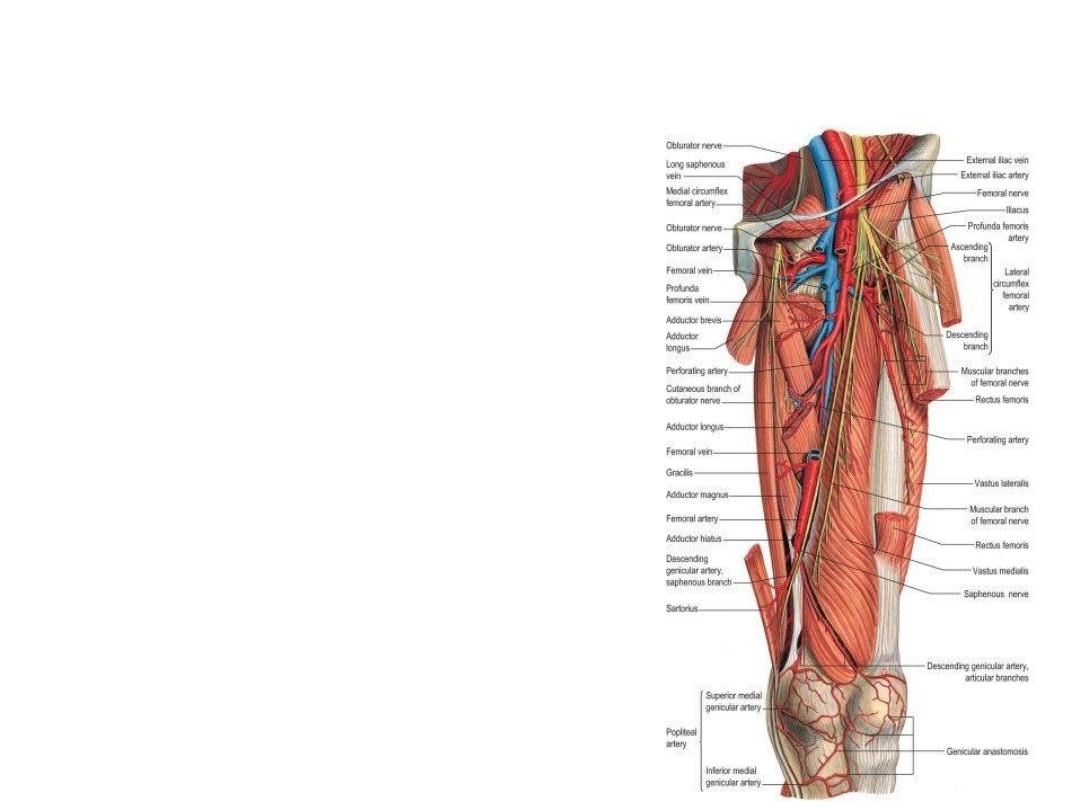
Blood Supply of medial thigh compartment
• Profunda Femoris artery & vein
• Obturator artery & vein
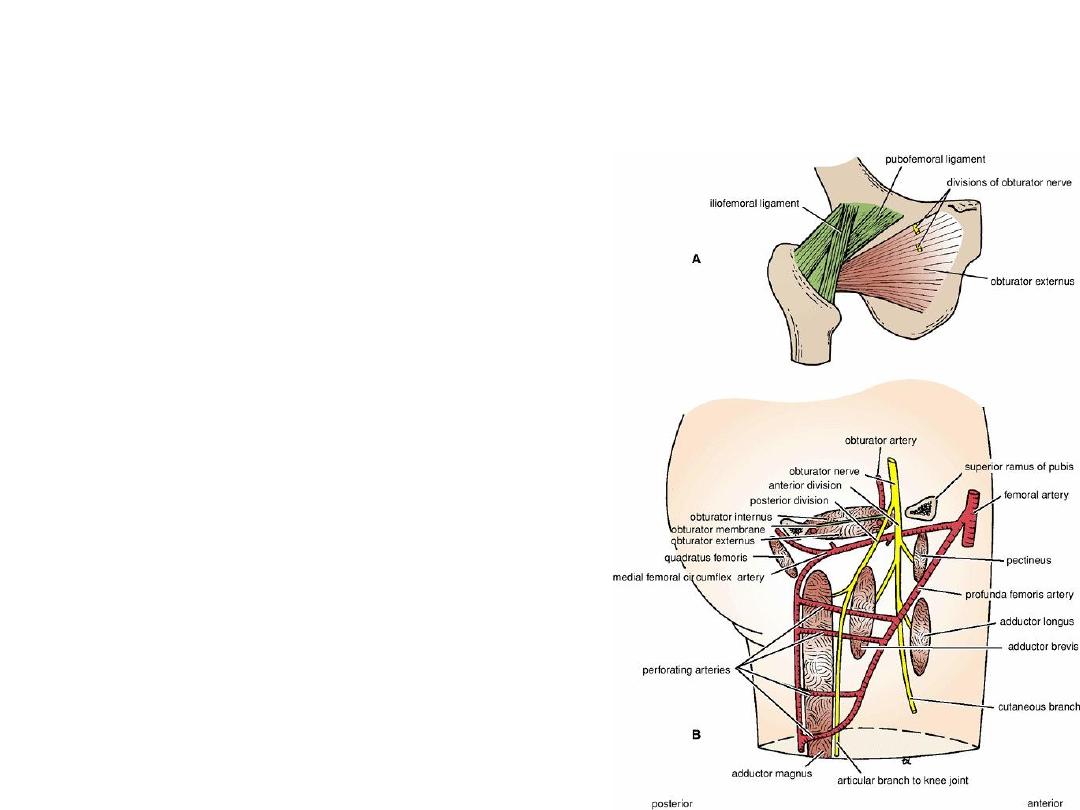
Nerve Supply of the medial fascial
compartment
• Branch from the lumbar plexus (L2, 3, and 4) and
emerges on the medial border of the psoas
muscle within the abdomen.
• It runs forward on the lateral wall of the pelvis to
reach the upper part of the obturator foramen
(see Fig. 6-12), where it divides into anterior and
posterior divisions (Fig. 10-27).
• Branches
1.
The anterior division
(muscular branches to the gracilis, adductor brevis,
and adductor longus, and occasionally to the
pectineus)
(Articular branches to the hip joint and terminates as
a small nerve that supplies the femoral artery)
2. The posterior division
(muscular branches to the obturator externus, to the
adductor part of the adductor magnus, and
occasionally to the adductor brevis)

Thank You
