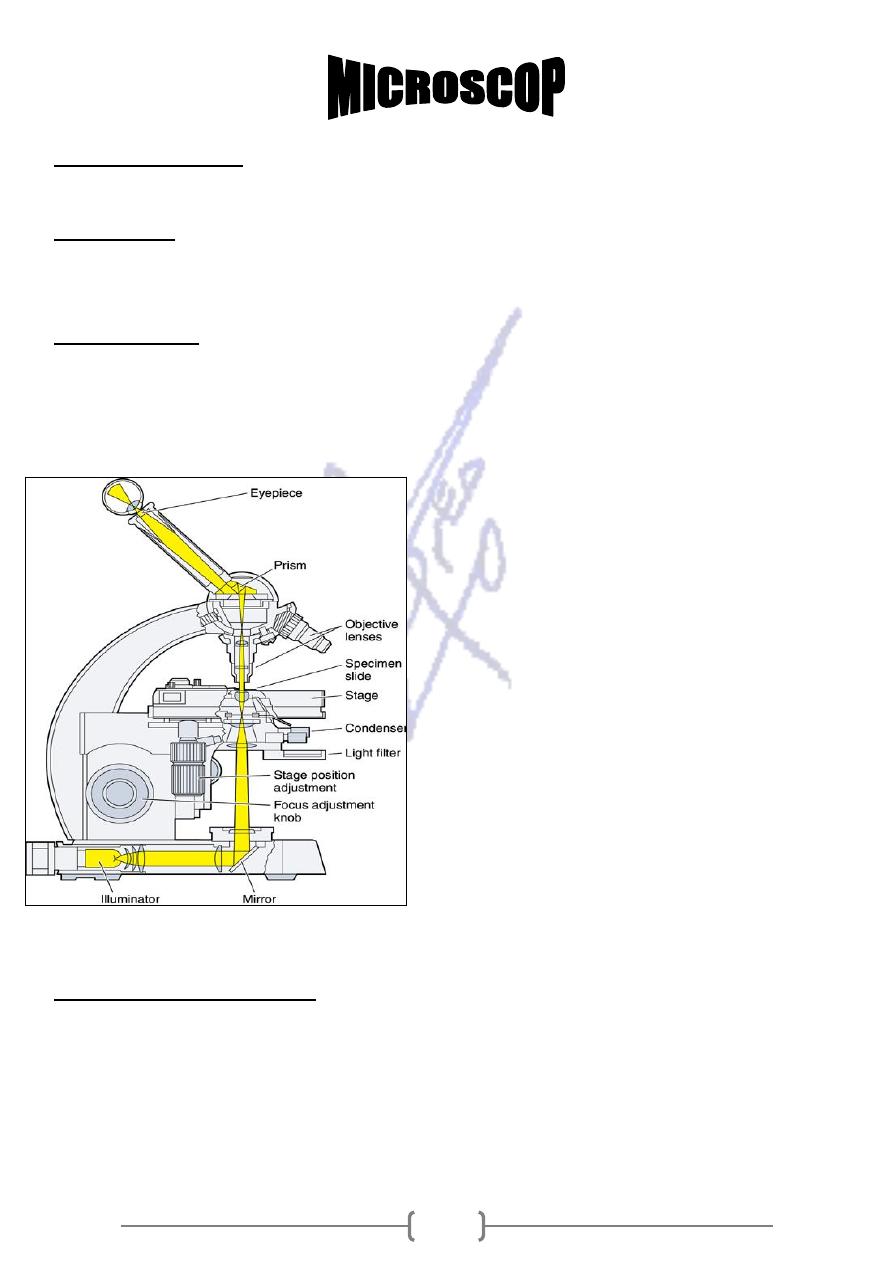
7
,in which light ray passing through a specimen are brought into focus
Light Microscope
-
1
by a set of glass lenses and resulting image is then viewed by the human eye .
is the ratio of the size of the images seen with the microscope to actual size
Magnification
of the object a
* L.M. can magnify them hundreds of thousands of tim
show fine detail, defined as the minimum
the ability of a microscope to
:
power
Resolving
distance between two points at which they can be seen as separate images .It depends on
the quality of the lenses and the wavelength of the illumination light .As the wavelength
decrease, the resolution increases.
* The wavelength of L.M. ranging from 400nm-
700nm.
* Nanometer (nm)=10
-9
m
* Micrometer(µm)=10
-6
m
* Millimeter(mm)=.001 (10
-3
) m
* Centimeter (cm)=.01(10
-2
)m
* In L.M. used organic compounds that
specifically stain different cell structure,
which enabled the biologist to discover
the organelles * Phase contrast: some
internal structures can be seen in
unstained living cells
Fluorescence microscope :
* Are used to detect the location of the specific molecules that absorb light energy of
one wavelength and then release some of that energy as light of longer wavelength.
* Computer, laser and photo detectors are new techniques for viewing cells to
produce three dimensional views.
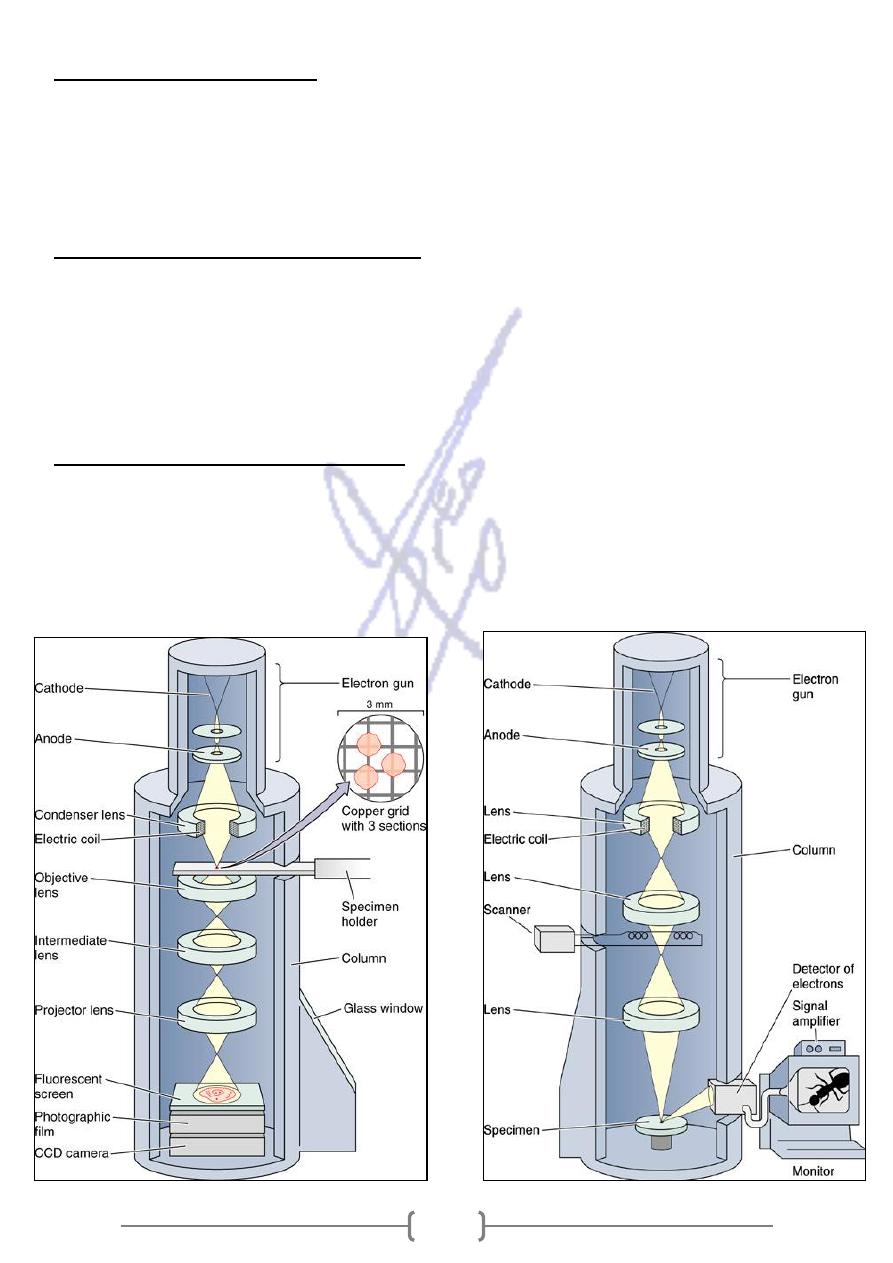
8
Electron Microscope (E.M)
* Use in 1950 to study the fine details or the functions of ultra-structure (the fine
detail of a cell).
* The (E.M.) can magnify 250,000 times or more .Electron wave have very short
wavelength (0.1-0.2nm).
Transmission electron microscope (T.E.M.)
* The specimen is embedded in plastic and then cut into extraordinarily thin section
(50-100nm thick)
* A section placed on small metal grid .The electron beam passes through the
specimen and then falls through the specimen and then falls onto photographic
plate or a fluorescent screen that works much like a television screen .
Scanning Electron microscope .(S.E.M.)
* The specimen is coated with thin film of gold are some other metal .The S.E.M.
provides information about the shape and external features of the specimen that
cannot be obtained with T.E.M. , by give a three dimensional picture of the surface .
* The S.E.M. image is viewed on a type of television.
