183
Is a special type of connective tissue ,which adipose cells (adipocytes) predominates.
In men of normal weight ,represents 15-20% of the body weight
In women of normal weight ,it represents 20-25% of body weight.
Adipose Tissue is :
the largest repository of energy in the body (in the form of triglyceride ).
a very efficient storage tissue .
sensitive to both nervous & hormonal stimuli .
Subcutaneous layers of adipose tissue help to shape the surface of the body , it acts as
shock absorbers ,chiefly in the soles & palms
fills up space between other tissues & keep some organs in place .
Secretes various type of molecules that may be carried by the blood to influence distant organs.
There are two types of adipose tissue
Unilocular (common,or yellow) adipose T. Multilocular (brown) adipose T.
.
Unilocular adipose tissue
The color varies from white to dark yellow due to the presence of carotenoids dissolved in fat
droplets of the cells.
It is found in adult throughout the human body except for the eyelids ,the scrotum and the
entire of external ear except for the lobules .
Age and sex determine the distribution and density of adipose tissue .
Its distribution is regulated by sex hormones and adrenocortical hormones
The shape of cells are spherical to polyhedral ,they appear as a thin of cytoplasm surrounding
the vacuole left by the dissolved lipid droplet .
Unilocular adipose t. is subdivided into incomplete lobules by a partition of connective
tissue containing a rich vascular bed and network of nerves.
Reticular fibers supports fat cells and binds them together.
The functions of unilocular Adipose Tissue.
Adipose cell can synthesize fatty acids from glucose, a process accelerated by insulin.
Insulin also stimulates the uptake of glucose into the adipose cells and increases the
synthesis of lipoprotein Lipase
Leptin: Is a protein made of 164 amino acid ,that produced by adipose cells .it
participates in the regulation of adipose tissue in the body .
It acts in the hypothalamus to decrease food intake and increase energy consumption.

184
Histogenesis of Unilocular Adipose tissue
Mesenchymale tissue give rise to lipoblasts ,which
have appearance of fibroblasts but are able to
accumulate fat in their cytoplasm .The fat
accumulate at week 30 of gestation .After birth, the
development of new adipose cells is common
around small blood vessels ,where undifferentiated
mesenchym cells are found
It is believed during only a finite postnatal period ,
nutritional and other influences can result in an
increase in the number of adipocytes, after that Do
not increase in number
Medical application
In adults may result from an excessive accumulation of fat in unilocular
:
Obesity
tissue , that become larger than usual (hypertrophic obesity )
An increase in the number of adipocytes cause hyperplastic obesity
Unilocular adi. can generate very common benign tumors called Lipomas .Malignant
Liposarcoms) .
derived tumors (
–
adipocyte
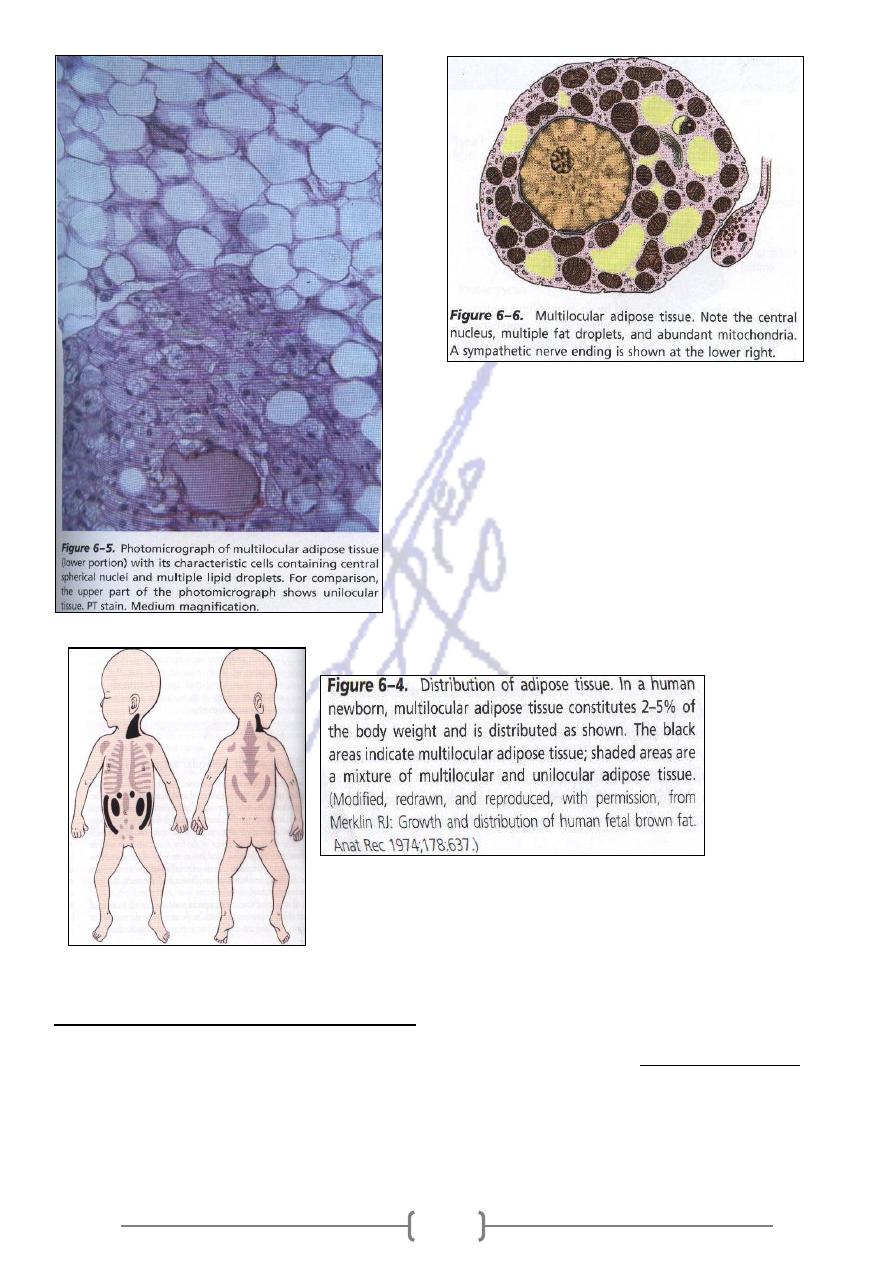
brown) adipose tissue
ultilocular (
M
od capillaries and the numerous
blo
The color is due to both the large number of
mitochondria in the cells
It has a more limited distribution in the body .It is called (hibernating gland).
In the human embryo and new born ,this tissue is encountered in several areas and
remain restricted to these location after birth .
It is important in the first month of postnatal life ,when it produces heat and protects the
newborn against cold .It reduced in adulthood
Cells are polygonal & smaller than cells of unilocular cells ,their cytoplasm contains a
great number of lipid droplets of various size The tissues are subdivided by partitions of
connective tissue into lobule.
Cells of these tissue receive direct (Sympathetic innervations), While in Uniloculare nerve
endings are found mainly in the walls of blood vessels; only few adipocytes are directly
innervated.
There is no formation of multilocular adipose tissue after births
185
functions of multilocular adipose tissue
The
Thermogenin
called
Produce heat ,because the mitochondria in cells of this tissue have protein
in their inner membrane .This protein permits the backflow of protons wormed blood circulates
throughout the body ,heating the body& carrying fatty acids not metabolized in adipose tissue .

186
Histogenesis of multilocular adipose tissue
Multilocular adipose tissue develops differently from unilocular tissue The mesenchymal cells
that constitute this tissue resemble epithelium before they accumulate fat .
Multilocular Adipose Tissue
Unilocular Adipose Tissue
The color is due to both the large number of
blood capillaries and the numerous
mitochondria in the cells
The color varies from white to dark yellow due
to the presence of carotenoids dissolved in fat
droplets of the cells.
It has a more limited distribution in the body
.It is called (hibernating gland).
In the human embryo and new born ,this
tissue is encountered in several areas and
remain restricted to these location after birth
It is found in adult throughout the human body
except for the eyelids ,the scrotum and the
entire of external ear except for the lobules .
Cells are polygonal & smaller than cells of
unilocular cells ,their cytoplasm contains a
great number of lipid droplets of various size
The tissues are subdivided by partitions of
connective tissue into lobule.
The shape of cells are spherical to polyhedral
,they appear as a thin Of cytoplasm
surrounding the vacuole left by the dissolved
lipid droplet .
Cells of these tissue receive direct
(Sympathetic innervations )
in Uniloculare nerve endings are found mainly
in the walls of blood vessels; only few
adipocytes are directly innervated.
