1
Fifth stage
Dermatology
Lec-4
د
.
عمر
24/10/2015
Acne Vulgaris
Acne vulgaris is the most common cutaneous disorder.
It affects about 99% of teenagers in industrialized nations..
Patients can experience significant psychological morbidity and, rarely, mortality due to
suicide.
affects all races and ethnicities with equal significance.
Darker skinned patients at increased risk for developing post-inflammatory hyper-
pigmentation and keloids.
Definition
Acne vulgaris, more commonly referred to simply as acne, is a chronic inflammatory
disorder of the pilocebaceous unit.
Pathogenesis:
Increased sebum production (androgens).
Abnormal keratosis (androgens).
bacterial proliferation (Propionibacterium acnes).
inflammation.
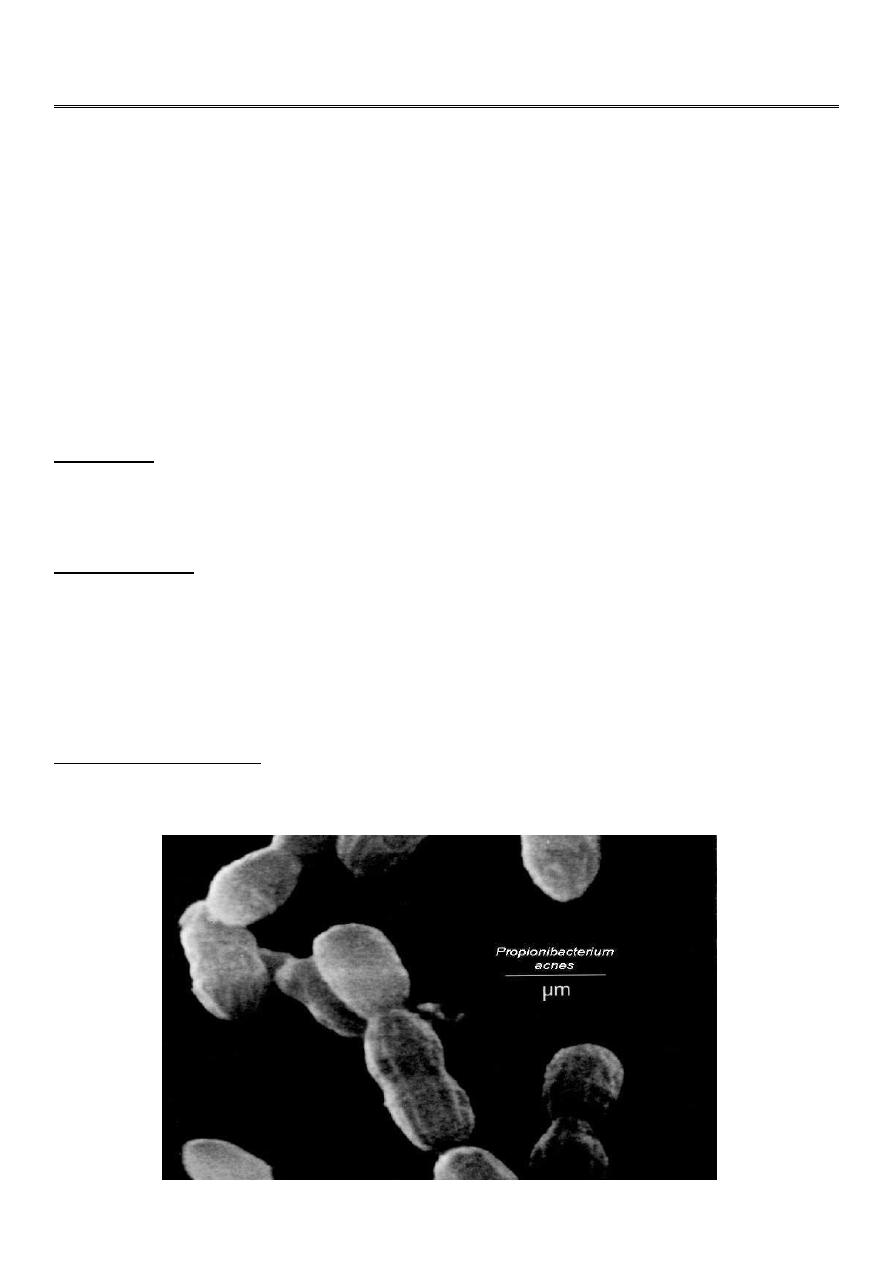
Propionibacterium Acne
Propionibacterium acnes is a gram-positive, non-motil rods relatively slow growing
typically aerotolerant anaerobic.
2
Pathophysiology
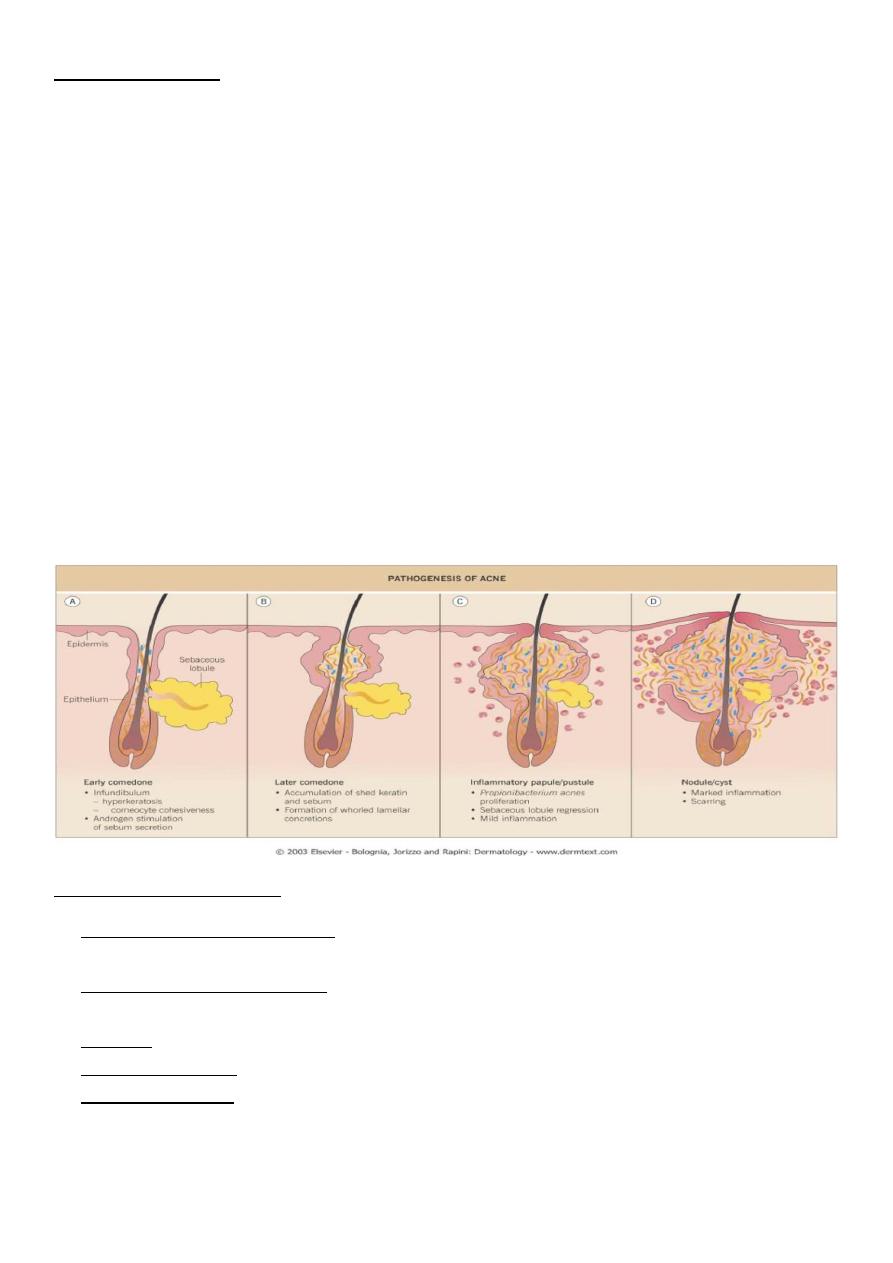
The initial step in the development of acne is the formation of the microcomedon:
Follicular keratinocytes that exhibit increased cohesiveness do not shed normally,
leading to retention and accumulation of sebum .
Androgens stimulate enlargement of sebaceous glands and increased sebum production,
and the abnormal keratinaceo-us material and sebum collect in the microcomedon .
This leads to a build-up of pressure, and whorled lamellar concretions develop. At this
stage, a non-inflammatory comedon may be seen clinically.
This micro-environment allows the proliferation of bacterium, which is part of the
normal flora of follicles. This gram-positive rod has low virulence but is capable of
metabolising triglycerides and releasing free fatty acids. This metabolism, as well as its
ability to activate complement, produces pro-inflammatory mediators, including
neutrophil chemo-attractants .
With increased pressure and recruitment of inflammatory mediators, the microcomedon
may rupture and release immunogenic keratin and sebum, thus stimulating an even
greater inflammatory response.
Clinical Manifestations
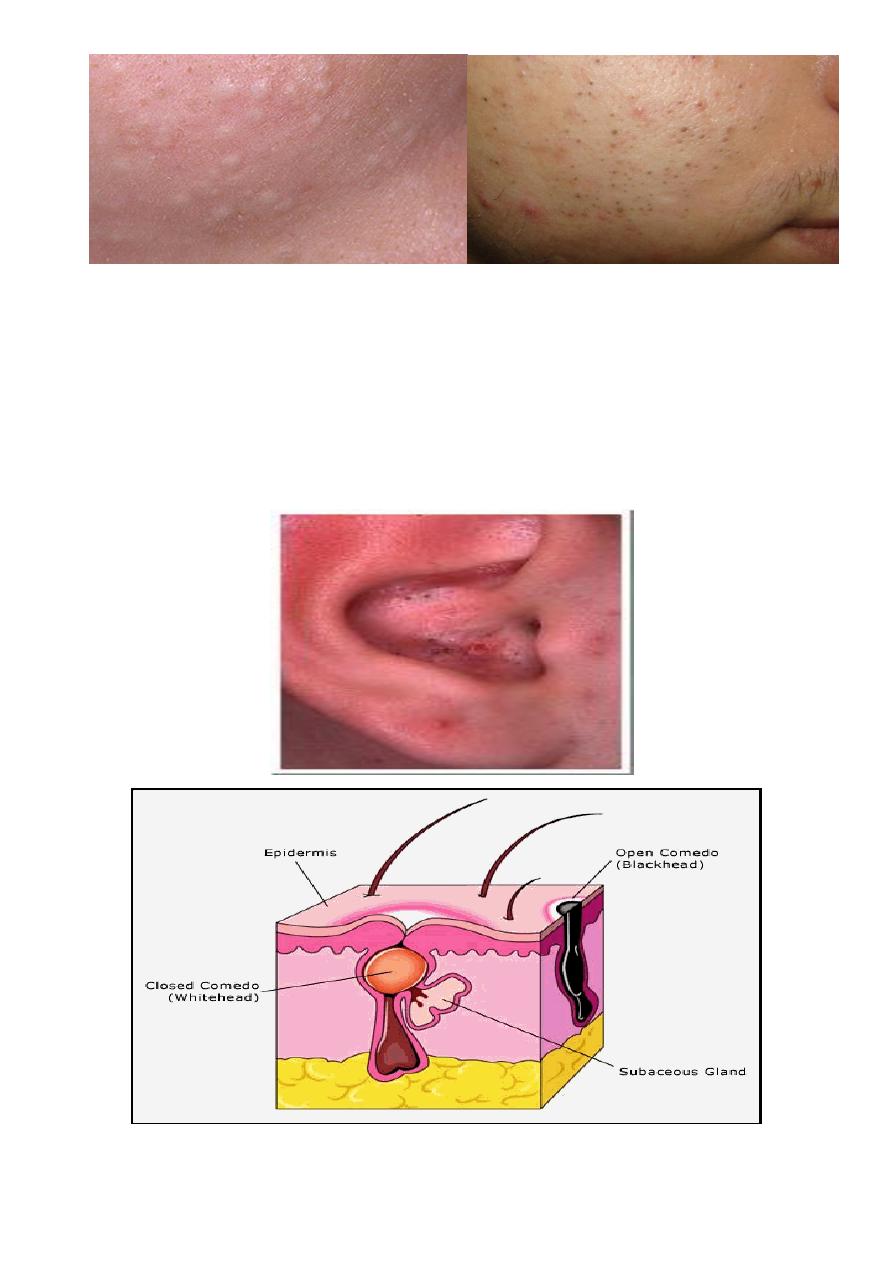
Closed comedone (whitehead) - a clogged follicle. Whiteheads usually appear on the
skin as small, round, white bumps.
Open comedone (blackhead) - a plugged follicle that opens and turns dark at the surface
of the skin. Blackheads do not indicate the presence of dirt.
Papules - inflamed lesions that appear as small, pink bumps on the skin.
Pustules (pimples) - inflamed pus filled lesions that are red at the base.
Cysts and nodules - large, inflamed, pus filled lesions deep under the skin that can cause
pain and scarring.
3
Open comedones (blackhead)
when follicular orifice is opened and distended
Melanin + packed
keratinocytes + oxidized
lipids dark colour

4
Whitehead and blackheads
Local symptoms
:
include pain , tenderness.
Systemic symptoms :
most often absent .
Classification
Comedonal acne: only comedons .
Mild acne : less than 20 pustules .
Moderate to sever acne : more than 20 pustules .
Treatment
Antibiotics:
Topical antibiotics (clindamycin and erythromycin) , and
systemic antibiotics used in the treatment of acne vulgaris are directed
at Propionibacterium acne:
Minocycline.
Doxycycline (50 t0 200 mg / day for 3 months)
Tetracycline.
Lymecycline.
Retinoid:
These agents decrease the cohesiveness of abnormal hyperproliferative keratinocytes.
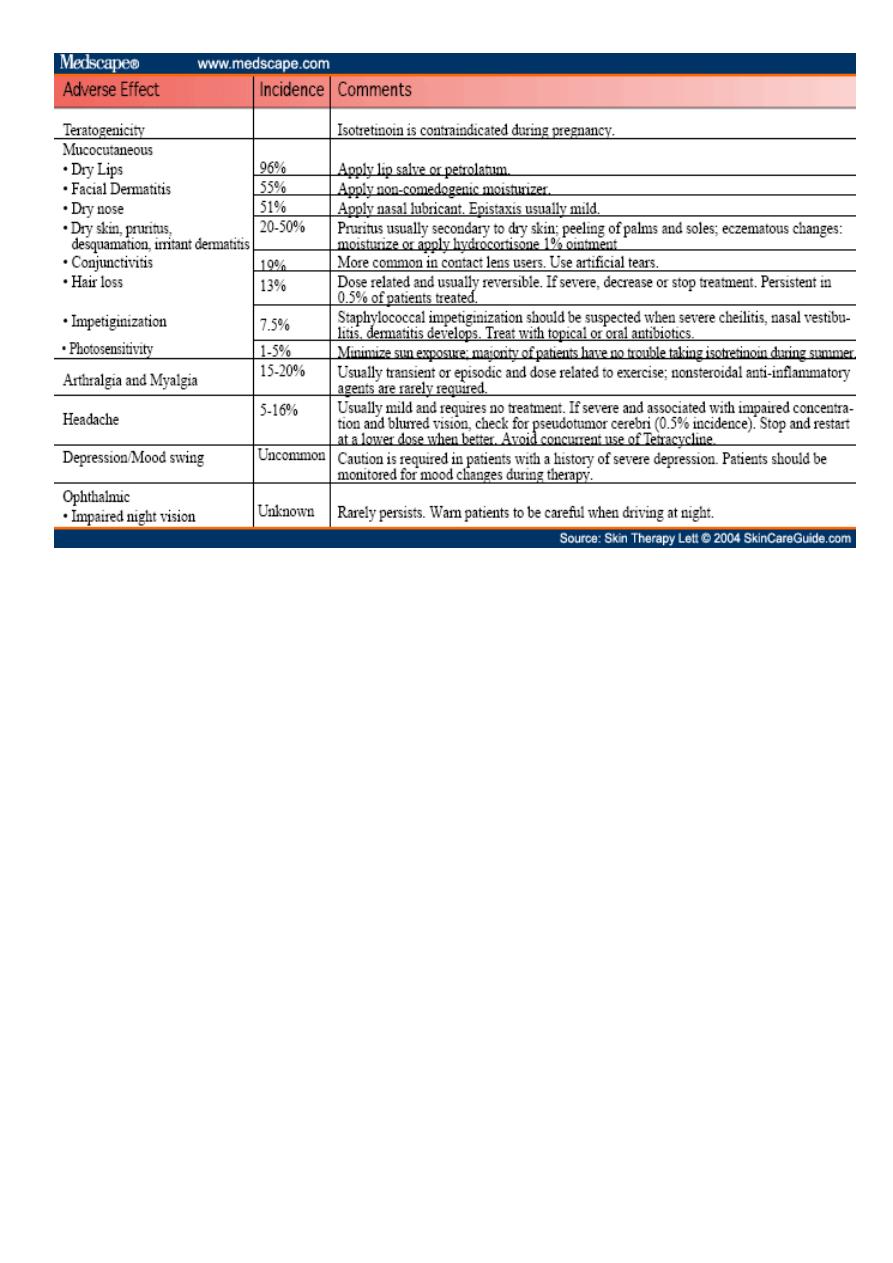
Isotretinoin (systemic) 0.5 - 1 mg over 4 to 6 months
Indications:
1-failure of traditional therapy.
2-Sever acne.
3-Nodule cystic acne.
4-Excessive facial oiliness.
5-Patient who scar.
6-Severly depressed patient.
Tretinoin (topical) cream (0.025%, 0.05%, 0.1%).
5
