Fifth stage
MedicineLec-1
د.فاخر
30/10/2016
Introduction to Rheumatological DiseasesMajor Symptoms In Joint Disorders:
Pain
Stiffness
Joint swelling
Functional impairments
Systemic manifestations
Extr-articular features
Peri-articular symptoms
Pain
There may be :
Pain (arthralgia).
Inflammation (arthritis) - redness, warmth, and swelling
There may be:
Only a single joint involved (mono-articular).
Multiple joints involved.
The pain may occur :
Only with use, suggesting a mechanical problem (eg, osteoarthritis, tendinitis).
At rest, suggesting inflammation (eg,rheumatoid arthritis crystal disease, septic arthritis).
Joint pain may arise from:
Structures within the joint (intra-articular):
Sources of pain within the joint include:
The joint capsule
periosteum
Ligaments
subchondral bone
and synovium
but not the articular cartilage, which lacks nerve endings
The quantity or severity of rheumatic pain
varies widely from patient to patient and from time to time in any one patient. Except under extremely aggravating circumstances, it is general chronology of a rheumatic pain syndrome often helps to suggest a precise diagnosis; however, rheumatic pain in general may begin insidiously or abruptly and persist for only a few days or indefinitely. With definitive diagnosis in mind, the time and nature of onset and subsequent overall disease behavior should be determined.It is less severe than ischemic, neuropathic, or visceral pain .
Stiffness
Stiffness is a perceived sensation of tightness when attempting to move joints after a period of inactivity.
It typically subsides over time.
Its duration may serve to distinguish inflammatory from non-inflammatory forms of joint disease.
With inflammatory arthritis, the stiffness is present upon waking and typically lasts 30-60 minutes or longer.
With noninflammatory arthritis, stiffness is experienced briefly (eg, 15 min) upon waking in the morning or following periods of inactivity.
Swelling
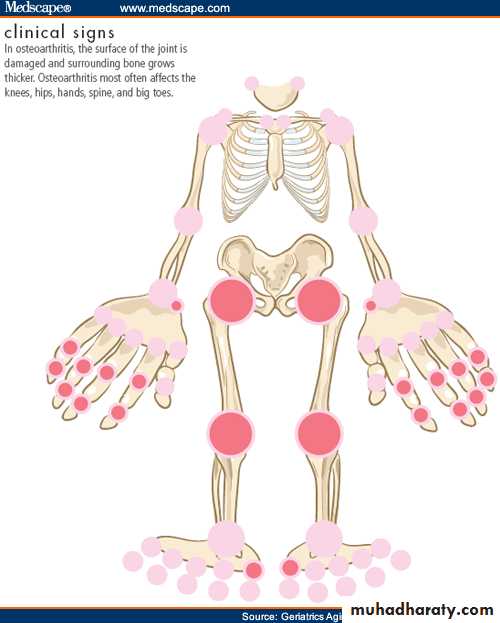
With inflammatory arthritis, joint swelling is related to synovial hypertrophy, synovial effusion, and/or inflammation of periarticular structures. The degree of swelling often varies over time.With noninflammatory arthritis, the formation of osteophytes leads to bony swelling. Patients may report gnarled fingers or knobby knees. Mild degrees of soft tissue swelling do occur and are related to synovial cysts, thickening, or effusions.
Limitation of motion
Loss of joint motion may be due tostructural damage
inflammation
contracture of surrounding soft tissues.
Patients may report restrictions on their activities of daily living, such as
fastening a bra
cutting toenails
climbing stairs
or combing hair.
Weakness
Muscle strength is often diminished around an arthritic joint as a result of disuse atrophy.
Weakness with pain suggests a musculoskeletal cause (eg, arthritis, tendonitis) rather than a pure myopathic or neurogenic cause.
Manifestations include decreased grip strength, difficulty rising from a chair or climbing stairs, and the sensation that a leg is "giving way."
Examination of the joint:
RednessHotness
Tenderness
Limitation of movement
Loss of function
RA sign and symptoms:
Joint inflammationSwelling
Loss of function
Pain
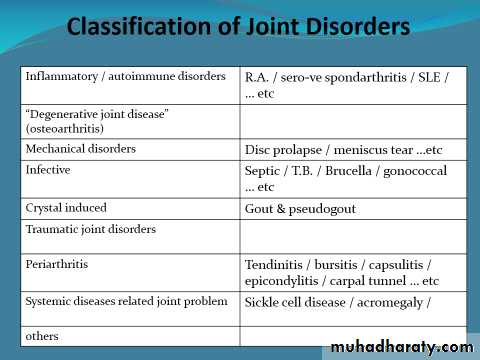
Classification
Polyarthritis : more than 4 joints .Oligoarthritis : 2-4 joints .
Monoarthritis : one joint .
Chronic polyarthritis : more than 2 months .
Acute , recent … within 2 or “few” months .
“Early” R.A : ? Few months to 2 years .
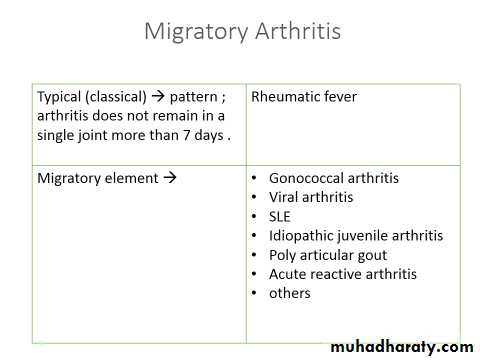
Migratory arthritis :
Typical non additive.
Additive.
Monoarthritis
Causes :
Acute bacterial arthritis (septic , brucella ….).
Acute gout.
Pseudogout.
Monoarticular onset of chronic inflammtory joint disease such as reactive arthritis , rheumatoid arthritis and chronic juvenile arthritis.
Traumatic arthritis.
Hemophilic joint.
Polyarthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis and other immune related disorders such as juvenile rheumatoid arthritis , spondylarthropathies , systemic lupus and other connective tissue diseases .
Generalized osteoarthritis .
Pseudogout .
Sarcoidosis .
CLINICAL FEATURES COMMON TO SEROPOSITIVE ARTHRITIS (RA):
Morning stiffness (> 1 hour)Arthritis of three or more joint areas
Arthritis of hand joints
Symmetrical arthritis
Rheumatoid nodules
Rheumatoid factor seropositive (rheumatoid factor positive )
Radiological changes
Duration of 6 weeks or more
CLINICAL FEATURES COMMON TO SERONEGATIVE SPONDARTHRITIS
Asymmetrical inflammatory oligoarthritis (lower > upper limb)Sacroiliitis
inflammatory spondylitis
Inflammatory enthesitis
Absence of nodules and other extra-articular features of RA
Male predominance in A.S. & in Re A
Association with HLA-B27
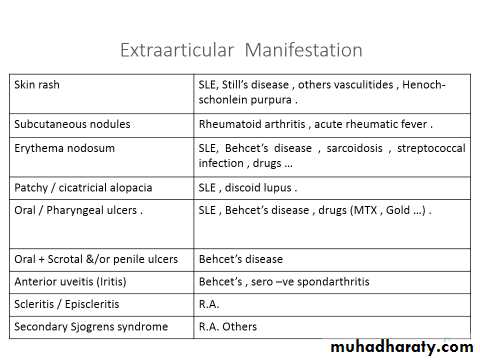
Mucosal surface inflammation-conjunctivitis, buccal ulceration, urethritis, prostatitis, bowel ulceration' Pustular skin lesions, nail dystrophy
Anterior uveitis
Aortic root fibrosis (aortic incompetence, conduction defects)
Erythema nodosum
Special Joints Features
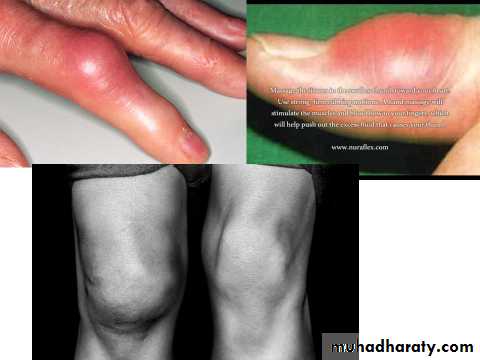
Red overlying skin :
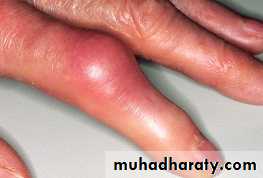
Acute gout .
Septic arthritis .
Skin infection .
Flare of Heberden’s nodules .
Systemic Manifestation
Such as fever , weight loss , reduced appetite and general weakness .
Mild to moderate severity systemic features can occur in most causes of polyarthritis but not polyarticular O.A.
Severe systemic features :
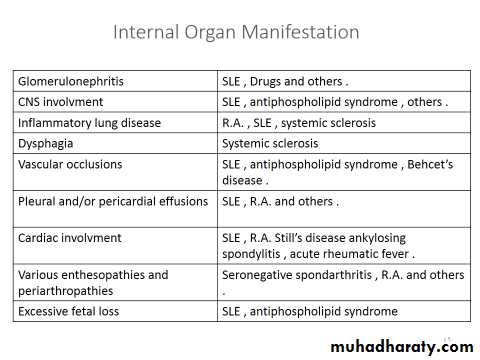
Arthritis of infective disorders e.g infective endocarditis .
Acute reactive arthritis .
Bacterial arthritis (about 10-19% polyarthritis) .
Still’s disease .
SLE .