Lectures in Veterinary Anesthesia
Muneer S. Al-BadranyVeterinary Anesthesia
By
Prof. Dr. Muneer S. Al-Badrany
Lectures in Veterinary AnesthesiaMuneer S. Al-Badrany
A state of unconsciousness produced by a process of controlled reversible drug-induced intoxication of the central nervous system
Anesthesia:
Lectures in Veterinary Anesthesia
Muneer S. Al-BadranyTypes of anesthesia
Local analgesiaRegional analgesia
Surface application
Intra and subdermal infiltrationField analgesia
Perineural injection
Spinal block
Subararchnoid
epiduralPosterior
InteriorInhalation
General anesthesiaParental
Lectures in Veterinary AnesthesiaMuneer S. Al-Badrany
Analgesia : it is state which has temporarily abolishes awareness of pain
Narcosis: It sleep like action due to moderate depression of CNS, thus all anesthetic agent are narcotic but not many narcotic are anesthetic agents
Hypnosis : Mild depressions of CNS, a state which produce sleep, and unconsciousness
Sedative : is a narcotic agent which is used to calm a nervous, vicious or excited animals. `
Pain?
An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage.””Pain is always subjective
Lectures in Veterinary Anesthesia
Muneer S. Al-BadranyBalance Anesthesia: A state of analgesia, muscle relaxant and Narcosis usually produce by combination more than one drugs
Narcosis
Analgesia
Muscle Relaxant
Lectures in Veterinary Anesthesia
Muneer S. Al-Badrany
General considerations in the selections of Anesthetic
1- Animals2- Nature of operation
Inspection before anaesthesia
Check animals before startingDo not anaesthetise sick animals, they are unsuitable
Animal should be fasting
How to fast before anaesthesia ?
Take away food - not waterthe smaller species, the faster metabolism, the shorter fasting
Lectures in Veterinary Anesthesia
Muneer S. Al-Badrany
Examination patient before general anesthesia
HistoryPhysical Examinations
Heart disease
Respiratory diseaseAnemia
Hypoprotenemia
Renal diseaseLectures in Veterinary Anesthesia
Muneer S. Al-BadranyPreparation of the patient
Food and waterFluid & electrolytes
Hameoglobin level
Lectures in Veterinary Anesthesia
Muneer S. Al-BadranyIntroduction to general anesthesia:
G. A is a state of unconsciousness produced by a process of controlled reversible intoxication of central nervous systemAn anesthetic agent may be defined as a substance which produce loss of consciousness in controllable matter.
General anesthesia may be
Volatile or gaseous substances
Introduce upper respiratory Blood BrainElimination of inhalation anesthetics
Water-soluble non-volatile compound
i.v., i.m, orally, per rectum, intraperitoneal,Lectures in Veterinary Anesthesia
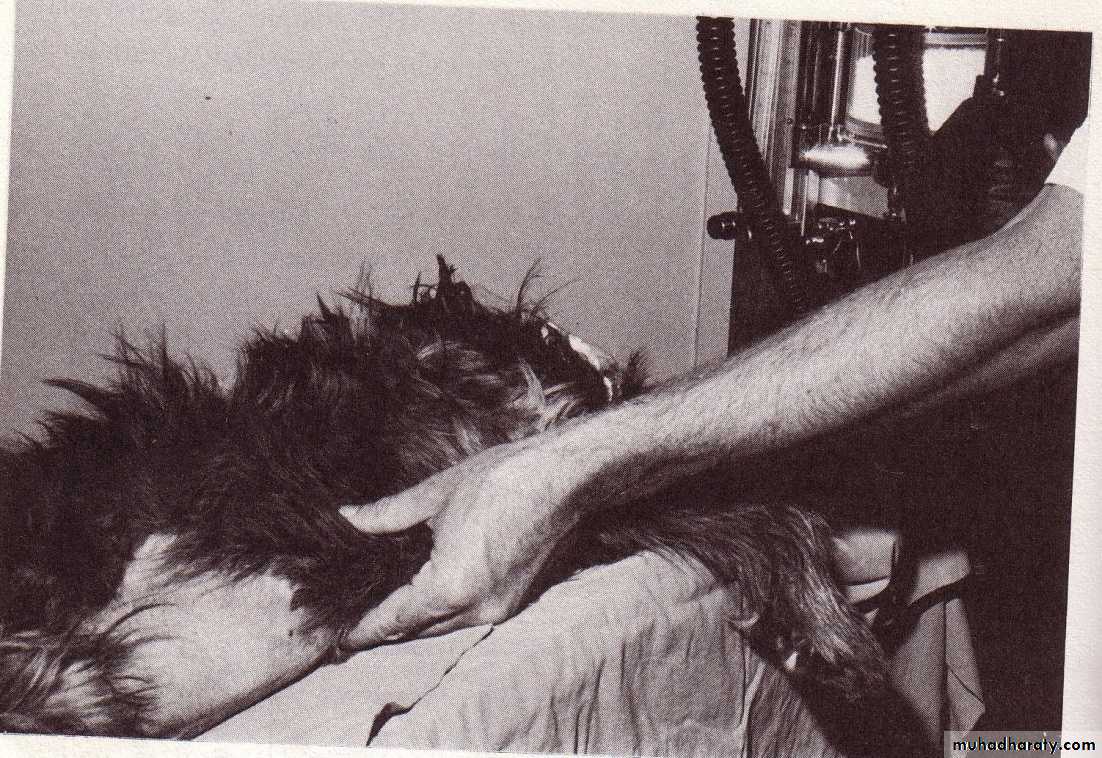
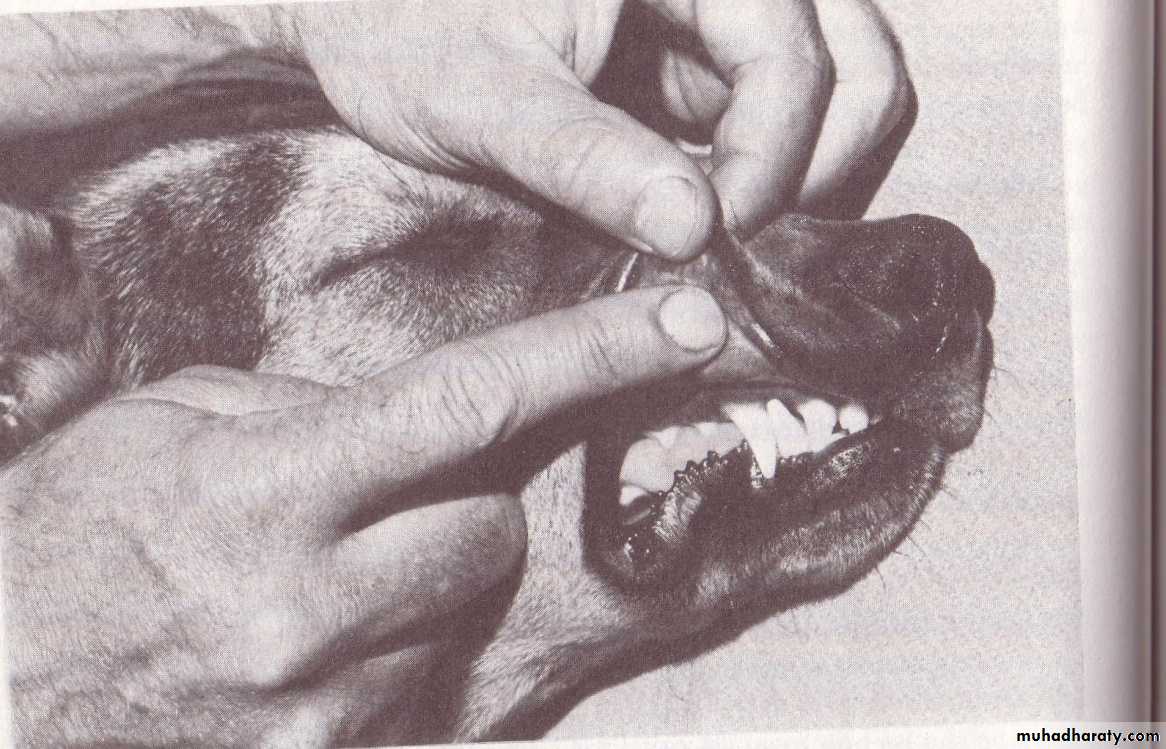
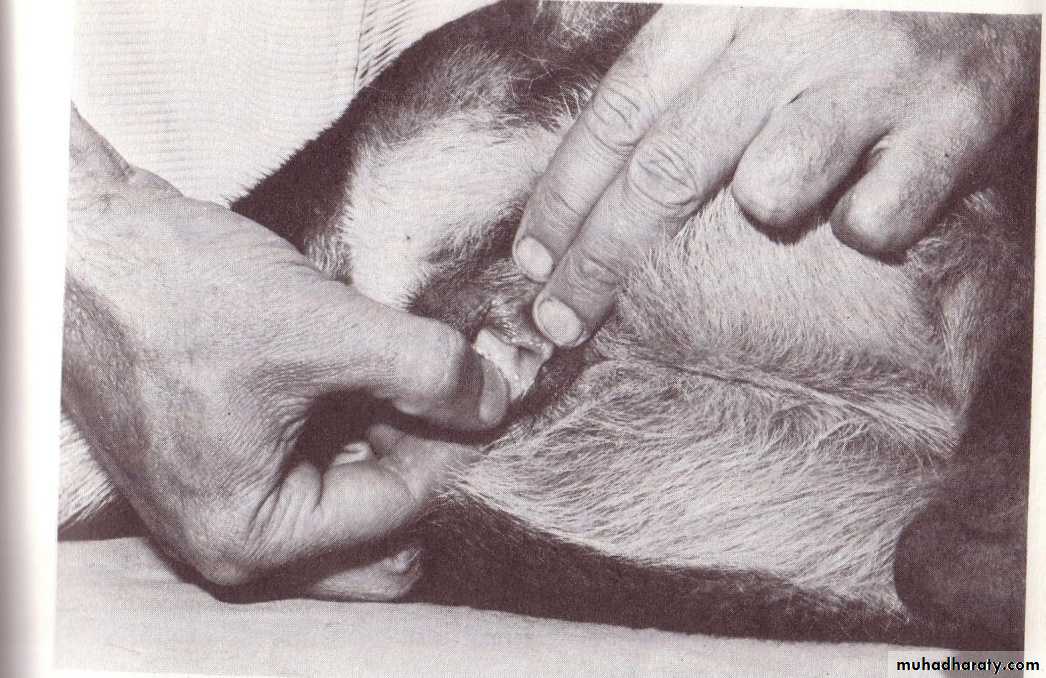
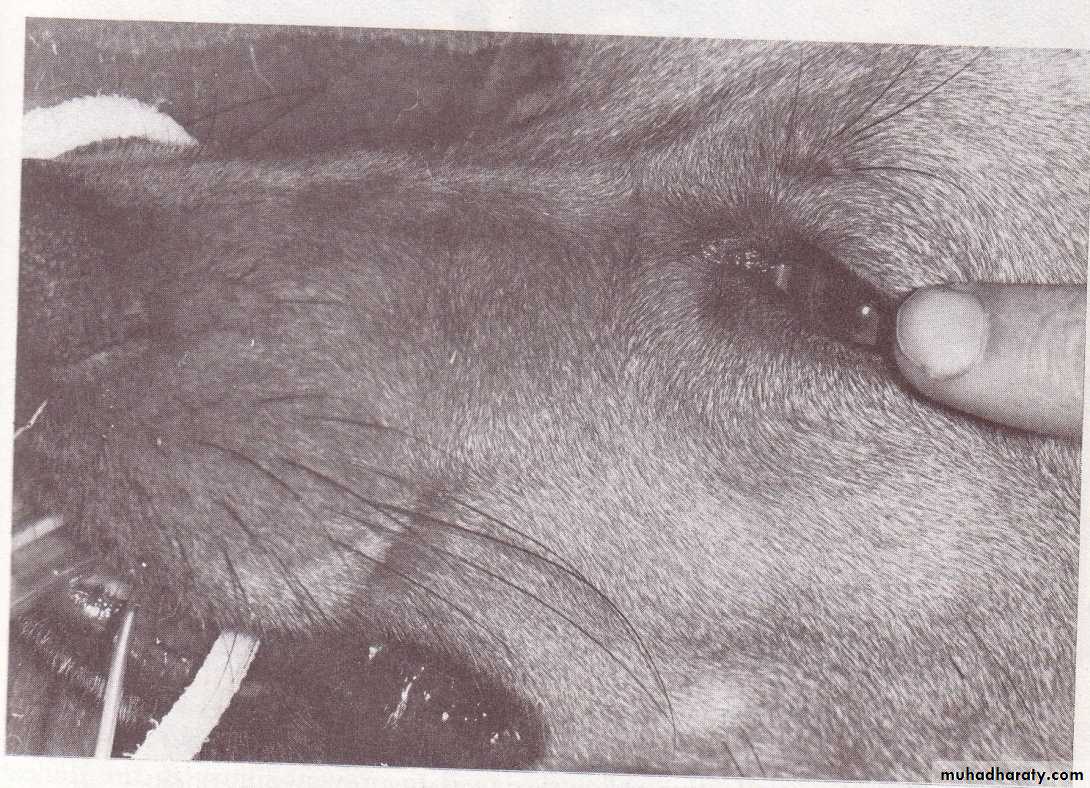
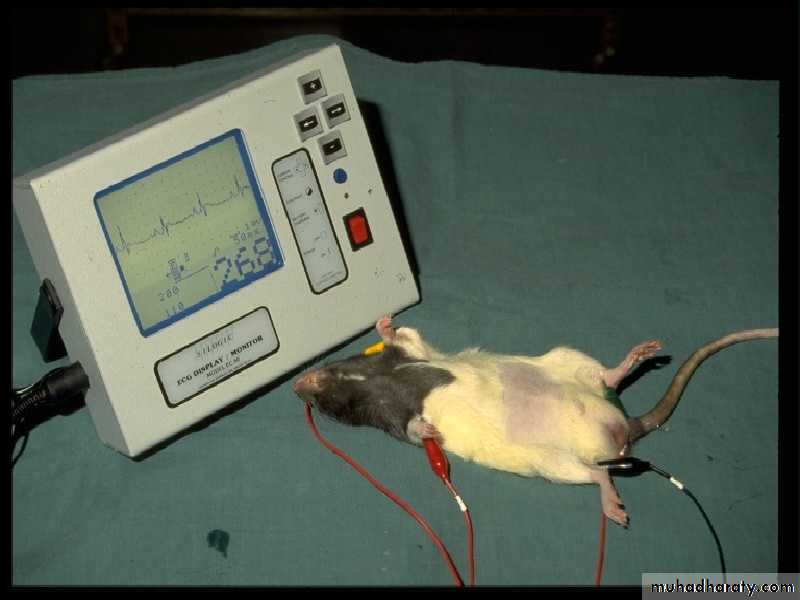
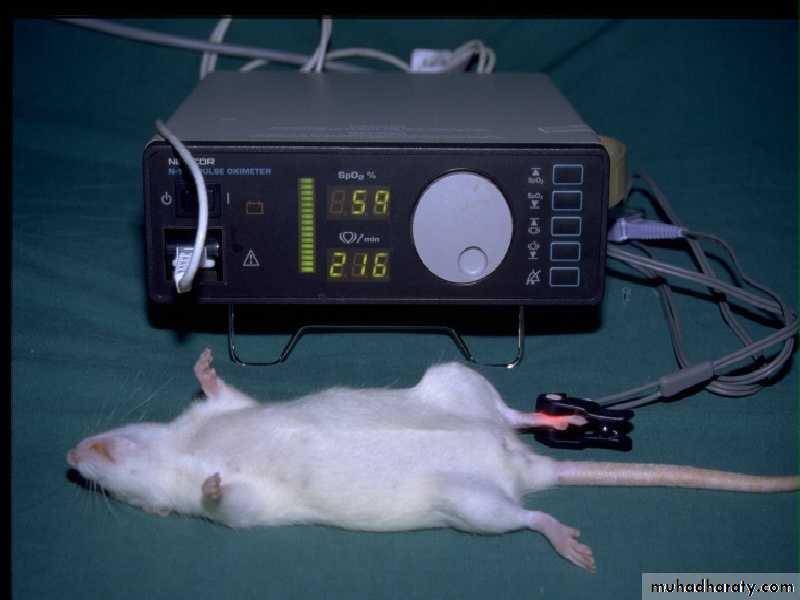
Muneer S. Al-BadranyPATIENT MONITORING AND CLINICAL MEASUREMENT MONITORING
Monitoring Central Nervous SystemMonitoring respiratory rate and Cardiovascular function
Gas analyzer
Monitoring the Circulation
Heart Rate MonitorsStethoscope
ECG
Arterial Blood Pressure
Central Venous Pressure
Cardiac Out Put Measurement
Monitoring Respiratory System
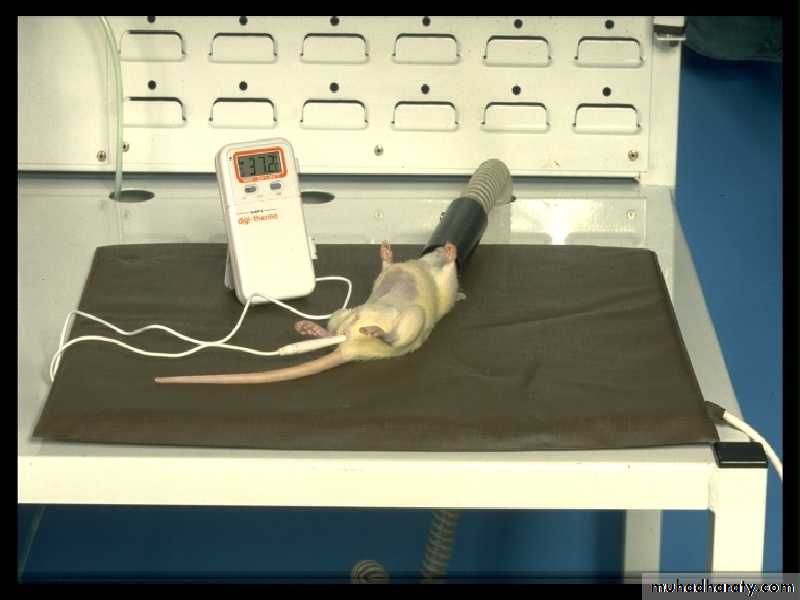
Monitoring Body Temperature
Lectures in Veterinary Anesthesia