Pontic design
Dr. Ahmed Jawadمعالجة اسنان\ خامس
د.احمذ م(3)
14\ 11\ 2016
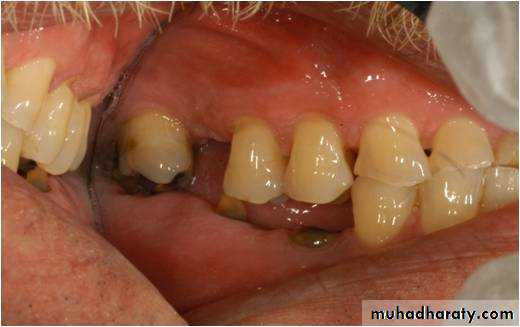
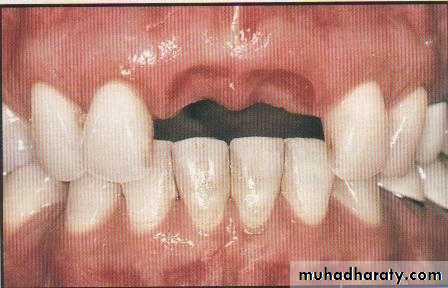
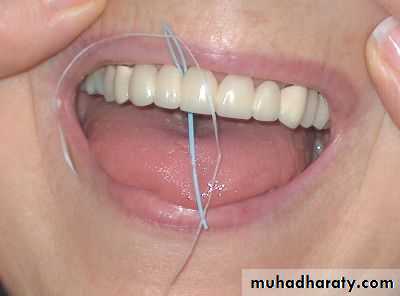
The pontic
Pontics are the artificial teeth in a fixed partial prosthesis, that replace the lost natural teeth ,and restore function and appearance.pontic
retainerRigid connector
2- Speech (phonetics)
A space created by the loss of tooth alters the pattern of airflow making normal speech difficult.
Pontic helps to restrict air passage through edentulous area to aid in the reestablishment of normal sounds
1-Mastication
the pontic provides hard surfaces against which food can be chewed by teeth in the opposing archFunctions of the Pontic
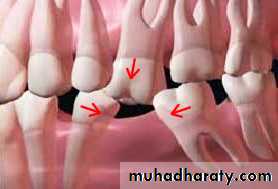
3 -Maintenance of tooth relationshipwhen missing teeth are not replaced, the teeth posterior to areas can move forward from their normal position , its also possible for teeth anterior to and opposing edentulous spaces to drift distally and occlusally into open area.
.
Pontics maintain the integrity of dental arches by preventing teeth that are adjacent to and opposing an edentulous area from moving out of their relationship.
4- Esthetics
Dental esthetics affects personal appearance , the presence of a full complement of teeth with a natural appearance is important to an individual's self image .-Pontics , fill in the empty spaces that would be observed during talking and smiling, provide support for lips and cheeks to allow normal facial form.
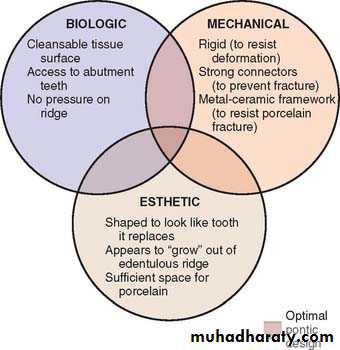
Considerations For A Successful Pontic Design
Biologic considerationsRidge Contact
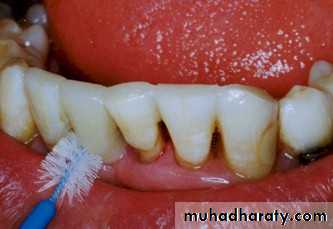
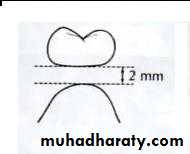
Area of contact with ridge should be small and convex.
• Oral hygiene considerations
Biologic considerations
Mechanical considerationsAvoid:
Improper choice of materials
Poor framework design
Poor tooth preparation
Poor occlusion
Esthetic considerations
Ideal Requirements of a Pontic• It should restore the function of the tooth it replaces.
• It should provide good aesthetics.
• It should be comfortable to the patient
• It should be biocompatible.
It should not impinge on the tissues or produce any kind of tissue reaction.
• It should permit effective oral hygiene. It should be easy to clean and easy to maintain.
• It should preserve underlying mucosa and bone.
•It should not produce any ulceration in the mucosa.
•It should not produce resorption of the residual alveolar ridge.
Factors Affecting the Design of a pontic• Space available for the placement of the pontic.
• The contour of the residual alveolar ridge.
• Amount of occlusal load that is anticipated for that patient.
General Design Considerations for a Pontic
Gingival surface:(1) the gingival surface of the pontic should be preferably finished using ceramic for better tissue response.
(2) the tissue contact of the gingival surface should be minimal to prevent adverse tissue reaction.
• Occlusal surface
• The size of the occlusal table can be reduced to decrease the amount of force centred on the abutment.• The functional cusps of the occlusal surface of the pontic should not be reduced, to preserve a stable vertical dimension. The functional cusp is the load-bearing cusp of the tooth.
• In the maxillary teeth the buccal cusps provide
Aesthetics. In the lower teeth the lingual cusps
Aid to protect the tongue.
• Proximal surface
• Vertical clearance should be sufficient to permit physiologic contour of the pontic and allow space for the interproximal tissues.
• Interproximal embrasures should be left open to permit easy cleaning.
• Buccal and lingual surfaces.They are designed based on the aesthetic, functional and hygienic requirements, the embrasures are wider lingually than facially.
Classification of pontic based on Mucosal Contact
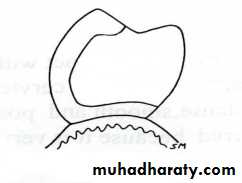
Saddle ponticRidge lap pontics
Modified ridge lap pontic
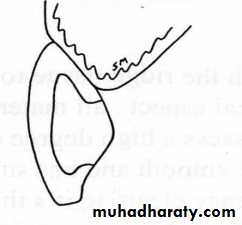
Ovate pontics
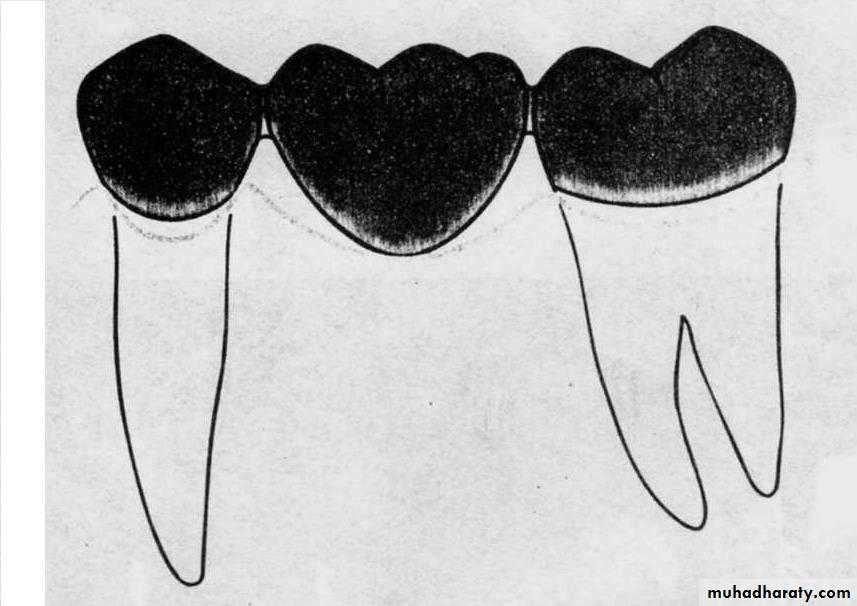
Conical pontic, or heart shape
Spheroidal and modified spheroidal pontics
Sanitary or hygienic pontics
• form• disadvantages
• advantages
• Recommended
• Location
• Pontic designs
• Poor esthetics
• Good access for hygiene
• Posterior
• mandible
• Sanitary
• (hygienic)
• Not amenable to oral hygyeine
• Esthetics
• Not recommended
• saddle or ridge-lap
• Moderately easy to clean
• Good esthetics
• Anterior teeth and premolars , some maxillary molars
• Modified ridge-lap
• Poor esthetics
• Good access for oral hygiene
• Molars without esthetics requirements
• Conical
• Egg or heart shaped
• Requires surgical preparation
• Superior esthetics negligible food entrapment easy to clean
• Maxillary incisor and premolars
• Ovate