
Fifth stage
Dermatology
Lec. 5
د. منار
17/11/2016
Exogenous eczema
Exogenous (Environmental)
1. Contact dermatitis:
• Allergic
• Irritant
2. Photodermatitis.
• Phototoxic
• Photoallergic
3. Infective dermatitis
Contact Dermatitis
• An exogenous substance (solid, liquid, gas) When contact with the skin cause an
inflammatory skin reaction
• The substance act as irritants or allergens
• The contact dermatitis may cause acute, subacute or chronic dermatitis.
• Very common problem
• E.g. leather–shoe dermatitis
• Nickel–earlobes, neck, wrist, periumblical
• History of contact with some chemical substance is very important
Irritant Contact Dermatitis:
Irritation of the skin is the most common cause of contact dermatitis, it accounts more
than 80% of all cases.
Causes
• The epidermis is a thin cellular barrier with an outer layer composed of dead
cells in a water-protein-lipid matrix.
• Any process that damages any component of this barrier will compromises its
function and a non- immunological eczematous response may result.
• Strong irritants cause an acute reaction after brief contact and the diagnosis is
usually obvious.
• Weak irritants may need prolonged exposure, sometime over years, to cause
dermatitis.
• There is a wide range of individual susceptibility to develop irritant contact
dermatitis which include; those with dry, fair skin and past or present atopic
dermatitis double the risk of irritant hand eczema.
• Contact dermatitis may occur as an occupational disease.
• Site of exposure gives a clue about the causative substance; such as hair dies,
make up, detergents, perfumes, clothes, shoes, jewelleries...Etc.
• People liable for contact dermatitis are house wives, doctors, barbers, building
workers...Etc.
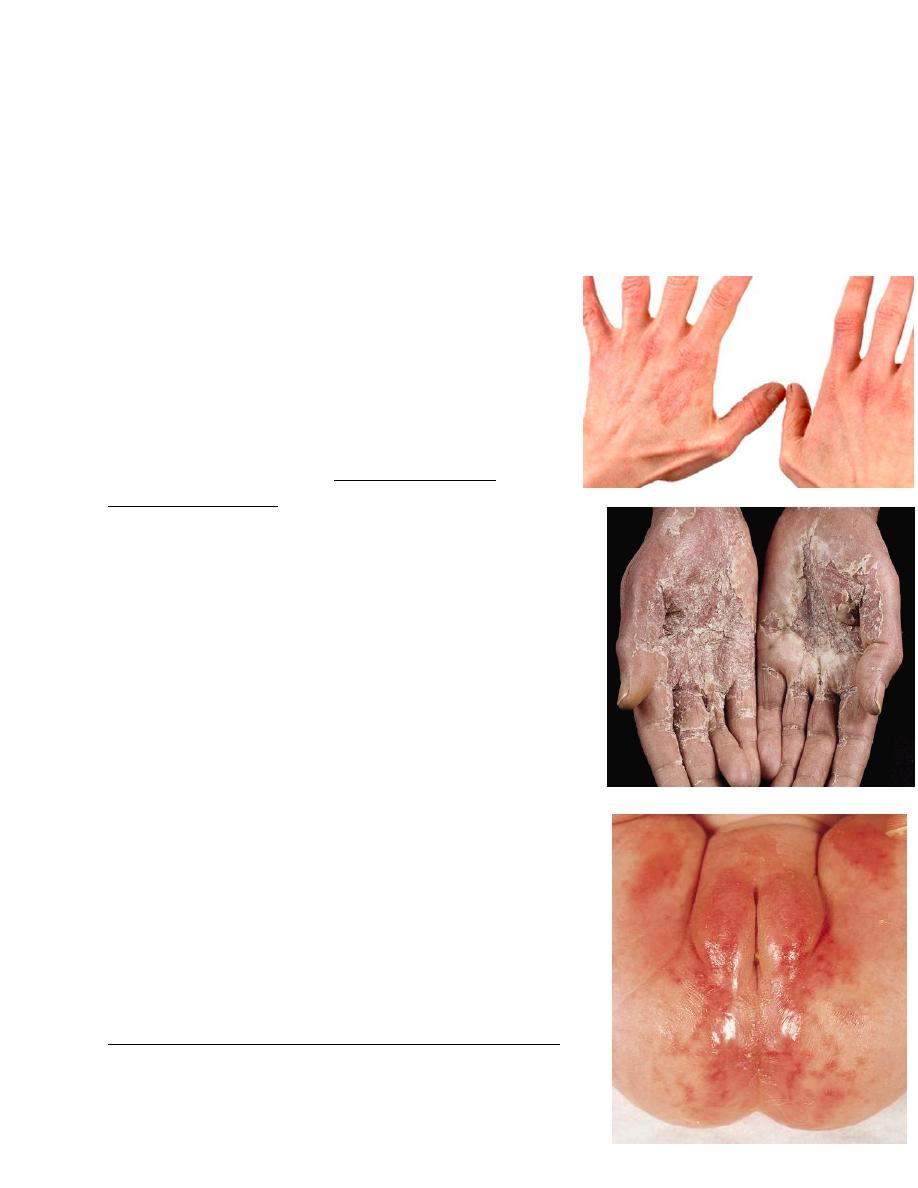
Housewife's dermatitis
• This results from repeated exposures to toxic or
subtoxic concentrations of offending agents (alkaline
detergents).
• Repeated rubbing of the skin, prolonged soaking in
water, fasters the evolution of dermatitis.
• Present in form of itching, dyness, roughness,
scaliness & fissuring.
• Mx ??
Cement Contact Dermatitis
• Is the hand eczema seen in bricklayers.
• In these persons, hand eczema is usually a combination
of chronic irritant contact dermatitis (alkaline medium of
cement, sand, rubbing) and allergic (chromate).
• Rx: (same rx) with stopping exposure or using gloves.
Napkin (Diaper) Dermatitis
• This is a primary irritant effect of body fluids on the skin.
The eruption is essentially confined to the area in contact
with the diaper.
• It is very common in infancy (but could affect old people
who use diapers).
• Caused by contact with urine & faeces (bacteria in the
last split urea (in urine) to ammonia which is very irritant.
• The area (especially convex areas) is mildly to intensely
erythematous, macerated ± papules, vesicles& ulcers.

Rx.
• Avoid using occlusive diapers
• Keep the area clean &dry
• Using abarrier cream such as zinc oxide
• Use mild topical steiod along with topical antifungal
DDx:
1- Candidiasis which often accompany it.
2- Seborrhoeic dermatitis.
3- Tinea cruris.
4- Bacterial infections
5- Inverted psoriasis.
Investigation ICD:
Patch test with irritants is not helpful and may be misleading.
So diagnosis mainly by history of contact with substance plus the lesion of eczema
Treatment of contact dermatitis in general
• Prevention is better than cure, because irritant eczema once started, it can
persist for long time even after the contacts has ceased and despite the
vigorous use of emollients and topical steroid.
• Management is based upon avoidance of the irritants responsible for the
condition which is often not possible and the best is to reduce the exposure by
the use of protective gloves and clothing, and barrier vasaline
• Washing facilities at work should be good.
• Dirty hands should not be cleaned by harsh solvents.
• Topical steroid and in severe cases systemic steroid.
Allergic contact dermatitis:
It is a delayed (type IV) hypersensitivity reaction characterized by:
• Its specific to one chemical and its close relatives.
• After allergy has been established, all area of the skin will react to the allergens.
• Sensitization persists indefinitely.
• Desensitization is not possible.
Comparison between irritant & allergic and contact dermatitis:
Characteristic
points
Irritant CD
Allergic CD
1
People at risk
Every one
Genetically predisposed
2
Mechanism
Non- immunological
Delayed hypersensitivity (type-
IV) reaction
3
No. of exposure
Few to many
(sensitization )
No need for previous exposure
4
Nature of
substance
Organic solvent, soap &
detergent
Low molecular weight hapten
e.g. Nickel, fragrance, hair dye
5
No. of compound
Many
Few
6
Concentration of
substance
Usually high
May be very low
7
Distribution
Localized
May spread beyond area of
contact
8
Onset
Gradual
Rapid
9
Investigation
Non
Patch test
10 Avoidance
Decreasing exposure is
useful.
Total avoidance of causative agent
is necessary.
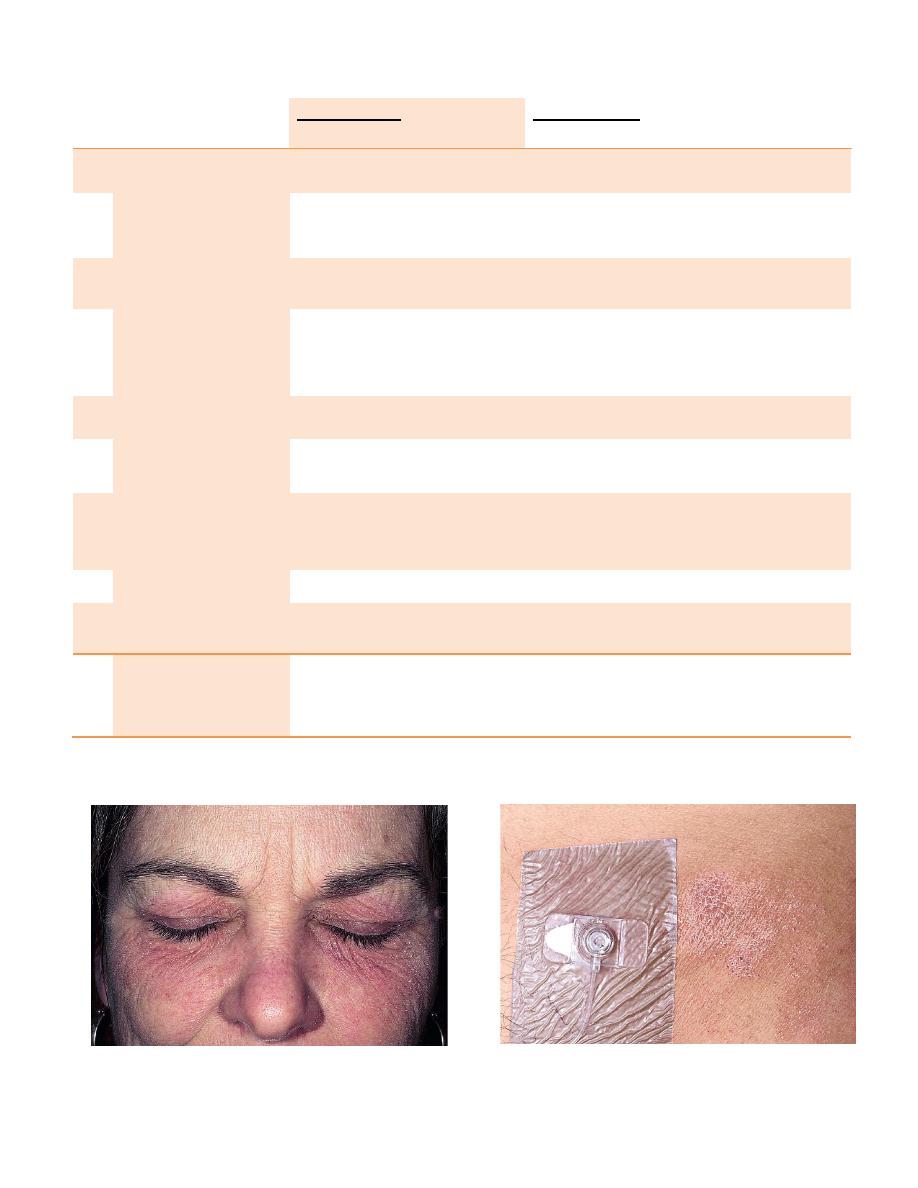
Eye (cosmetic allergy) Allergic contact dermatitis
Adhesives allergy
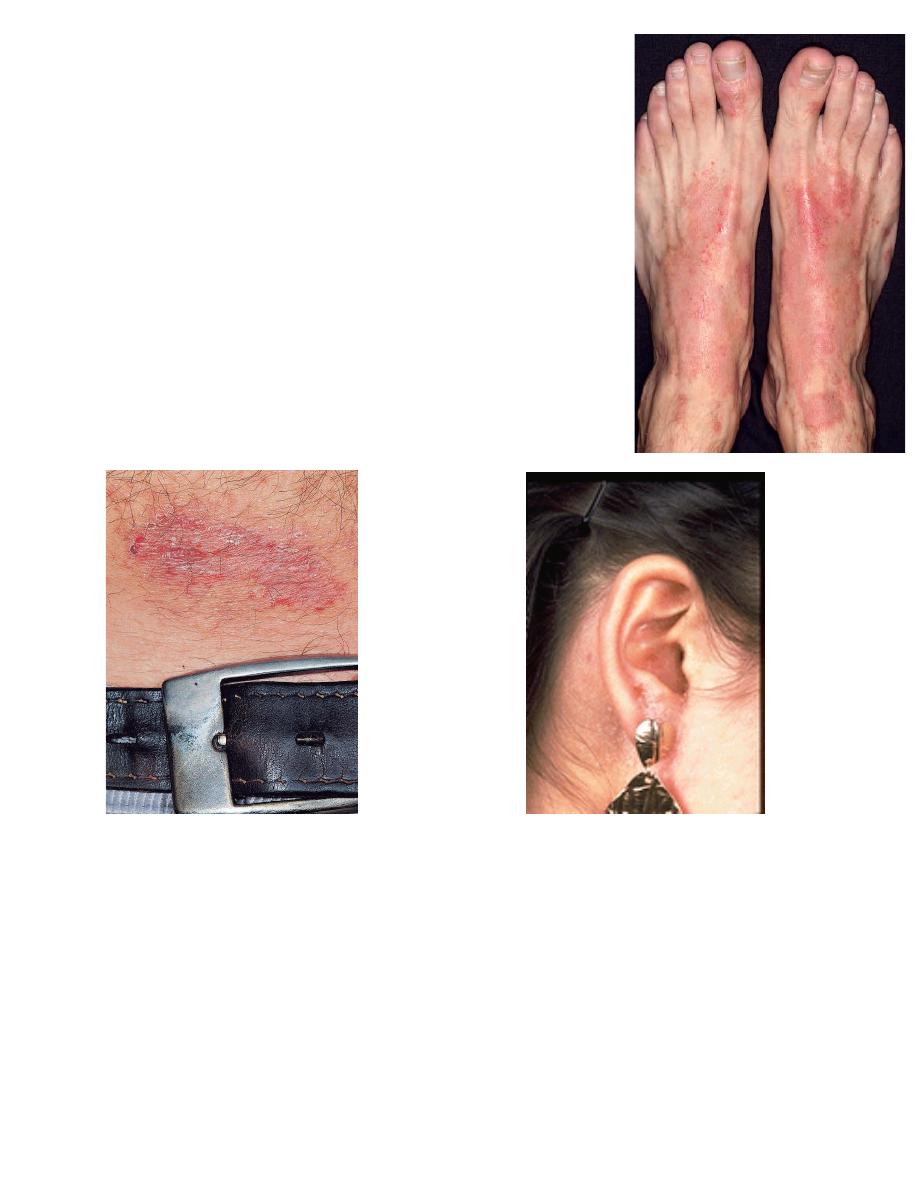
Shoe allergy:
• More on the dorsum
• The interdigital spaces are spared, in contrast to tinea pedis.
• Inflammation is usually bilateral, but unilateral involvement
does not preclude the diagnosis of allergy.
• The thick skin of the soles is more resistant to allergens
Investigation:
Patch test
• Used to detect the causative agents in ACD
• Application of known allergens to the back of & left under
occlusion to be seen after 48 & 96 hrs.
• A positive patch test shows erythema and papules, as well
as possibly vesicles.
Nickel ACD
Treatment:
• Avoid completely the offending allergen.
• Symptomatic treatment of eczematous reaction by topical steroid.
• Systemic steroid is used in severe cases.
