
Techniques for
local anasthesia in
dentistry
Dr.Mohamed Rhael Ali
2016 - 2017
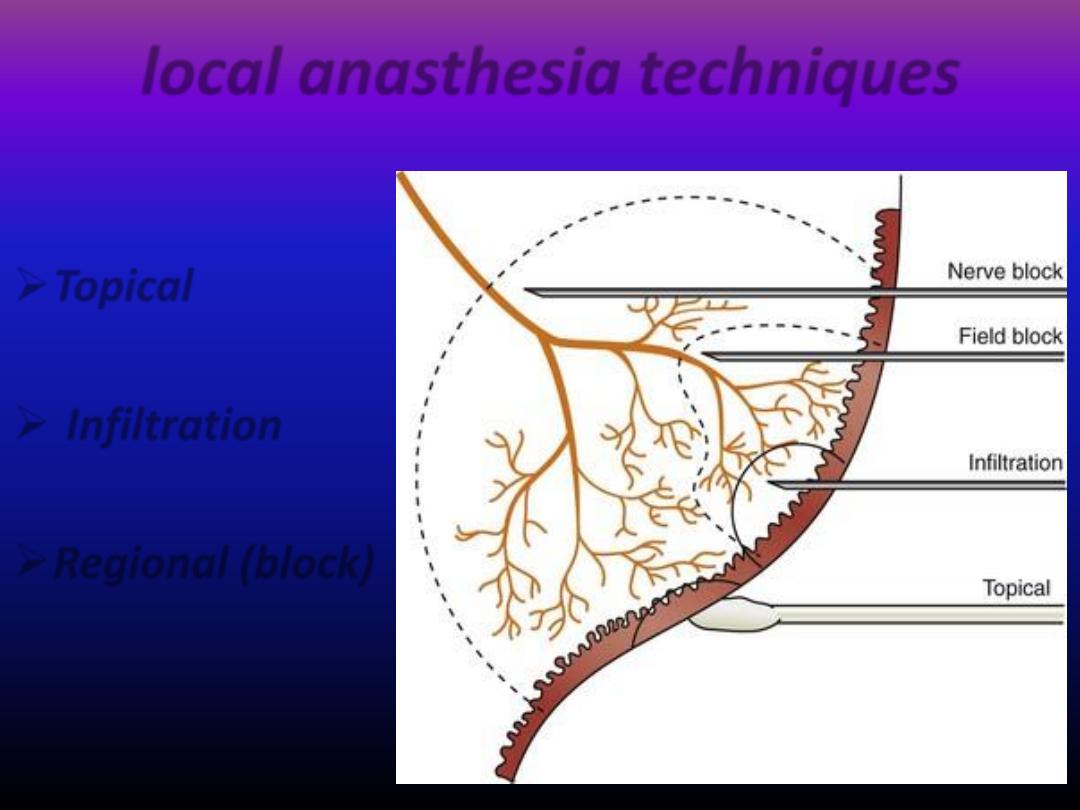
local anasthesia techniques
Topical
Infiltration
Regional (block)

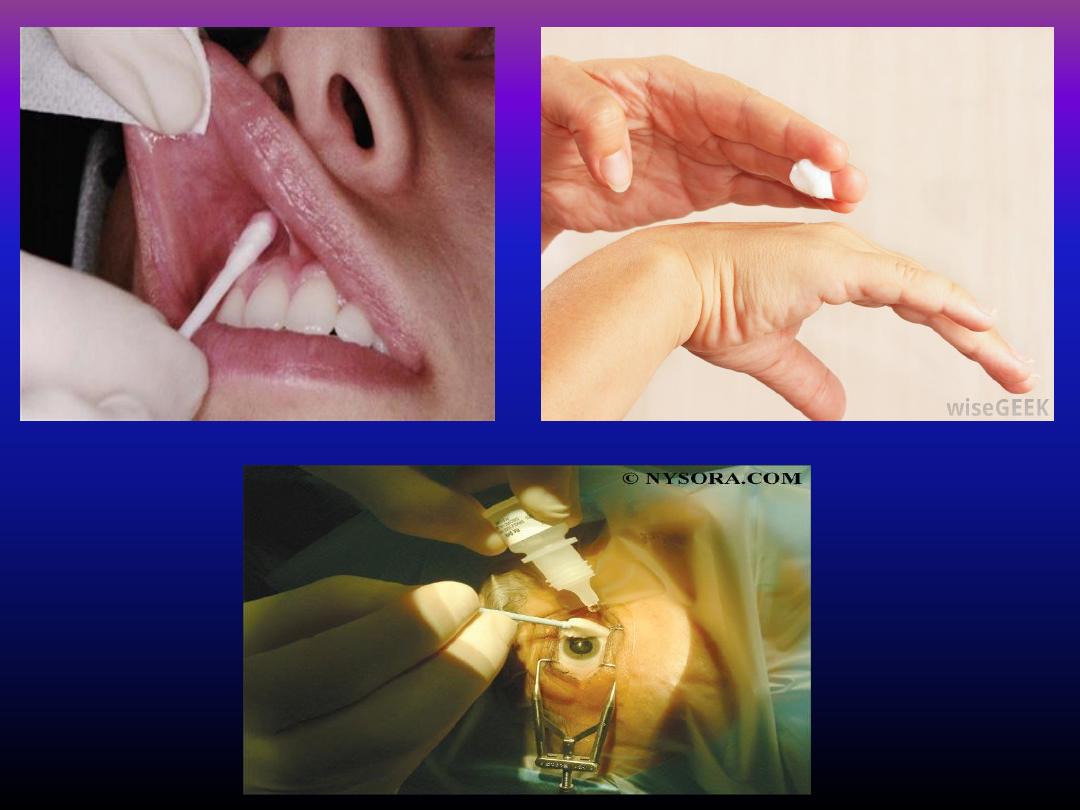
Topical ( surface )
anasthesia
• Obtained by application of anasthetic agent to skin
or mucosa to anasthetize superfacial nerve ending
• Its used mainly prior to injection
• Sprays containing appropriate local anasthesia
mostly suitable prior to injection due to its rapid
onset time

Topical ( surface ) anasthesia

• Mainly used spray LA consist from
10% lidocaine
hydrochloride .
• The onset of time about
1 minute
and the duration about
10 min .
• Ointment 5% lidocaine
hydrochloride can be used for the
same purpose but it
take 3-4 minutes
to produce surface
anasthesia .
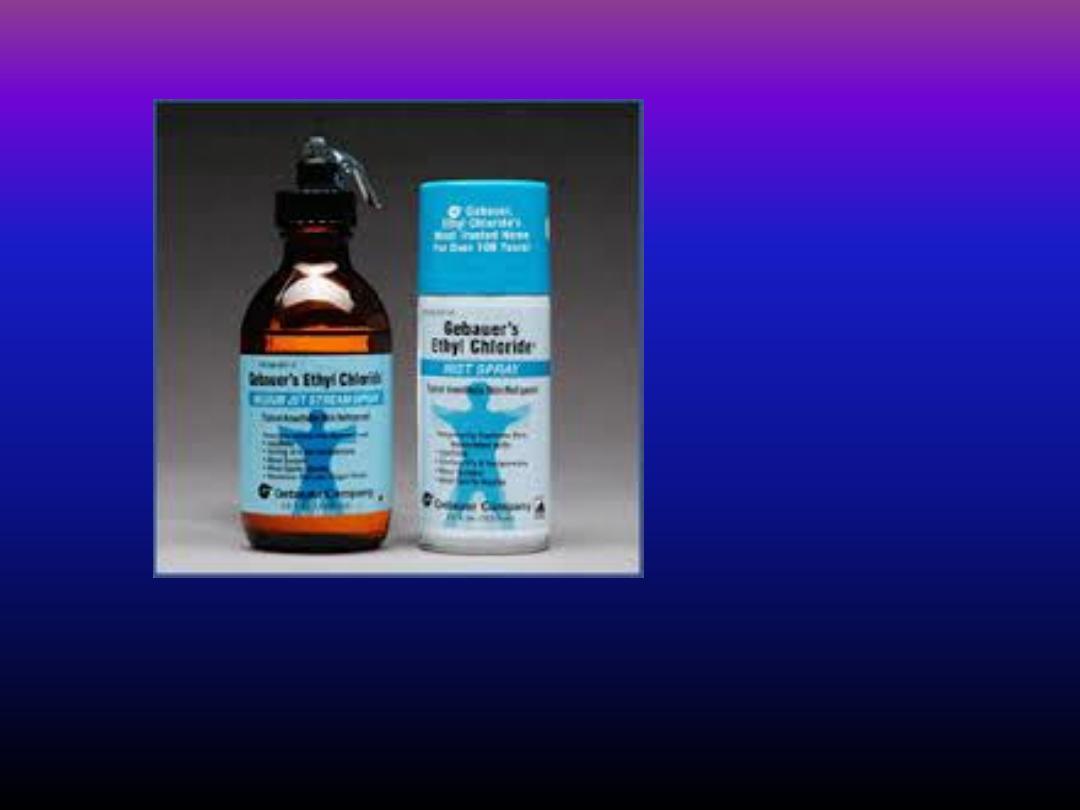
• Ethyl chloride spray
can be used to produce rapid surface
anasthesia by refrigeration , this technique used mainly
prior to incision of drainage of pus .
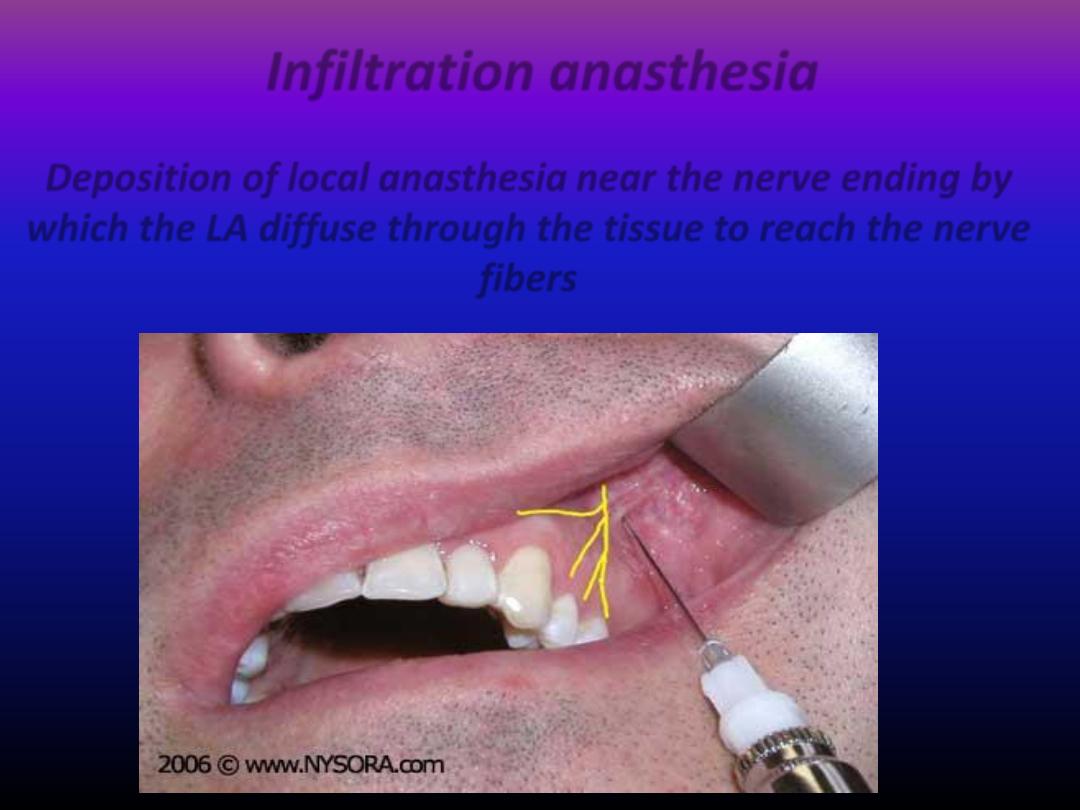
Infiltration anasthesia
Deposition of local anasthesia near the nerve ending by
which the LA diffuse through the tissue to reach the nerve
fibers

Subdivided in to several techniques :
a. Submucosal injection
LA solusion deposited just beneath the mucous
membrane , its suitable for soft tissue anasthetization
but
not effective for pulp anasthetization
Infiltration anasthesia
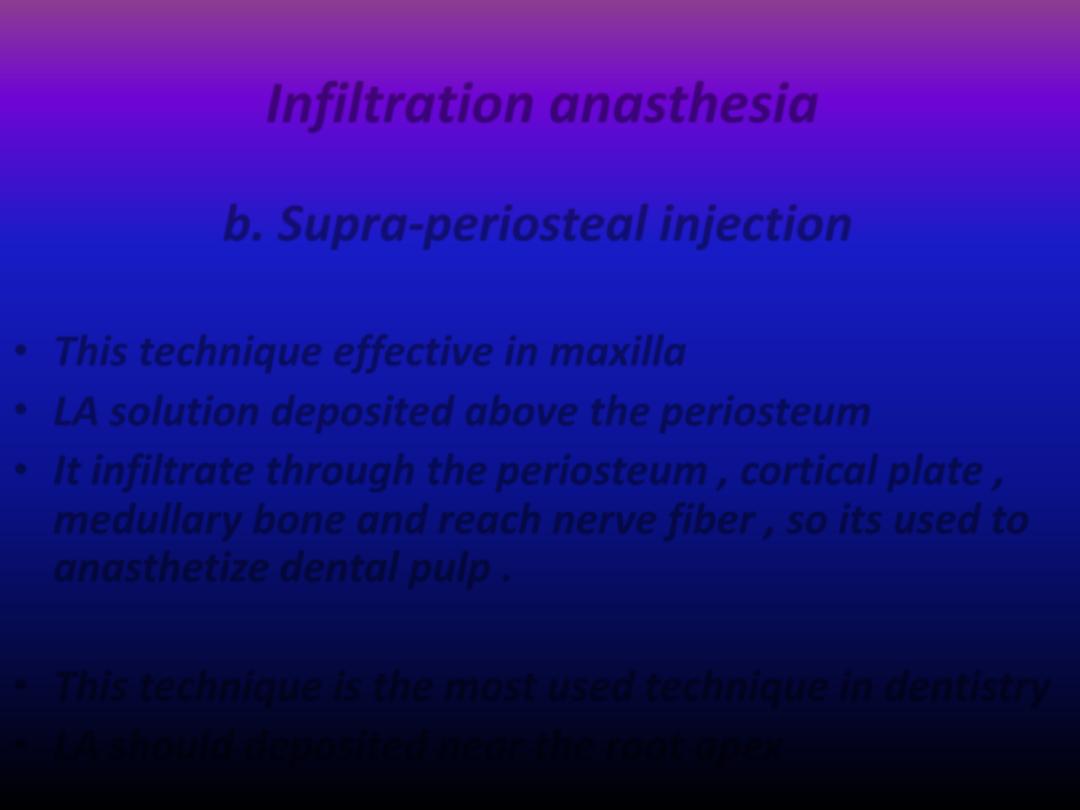
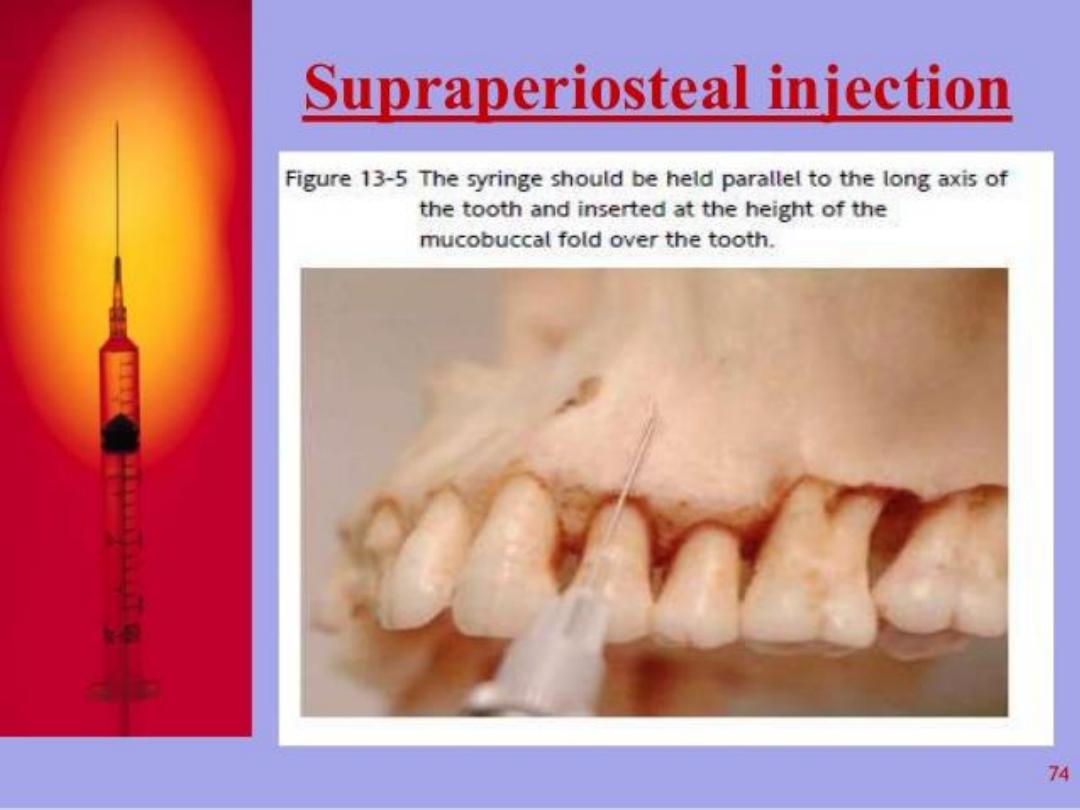
b. Supra-periosteal injection
• This technique effective in maxilla
• LA solution deposited above the periosteum
• It infiltrate through the periosteum , cortical plate ,
medullary bone and reach nerve fiber , so its used to
anasthetize dental pulp .
• This technique is the most used technique in dentistry
• LA should deposited near the root apex
Infiltration anasthesia

c. Sub-periosteal injection
• Here the LA solution deposited between the periosteum
and the cortical plate .
• Its painful technique because periosteum tense and
firmly attached to the cortical bone plate
Infiltration anasthesia
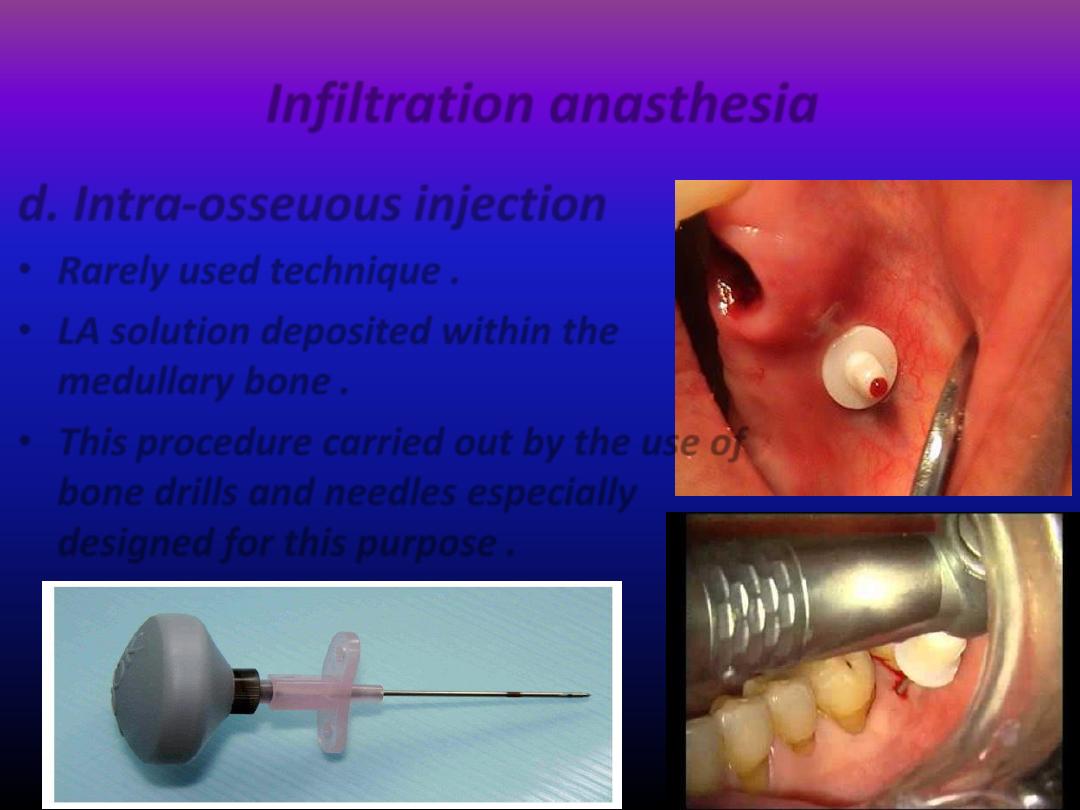
Infiltration anasthesia
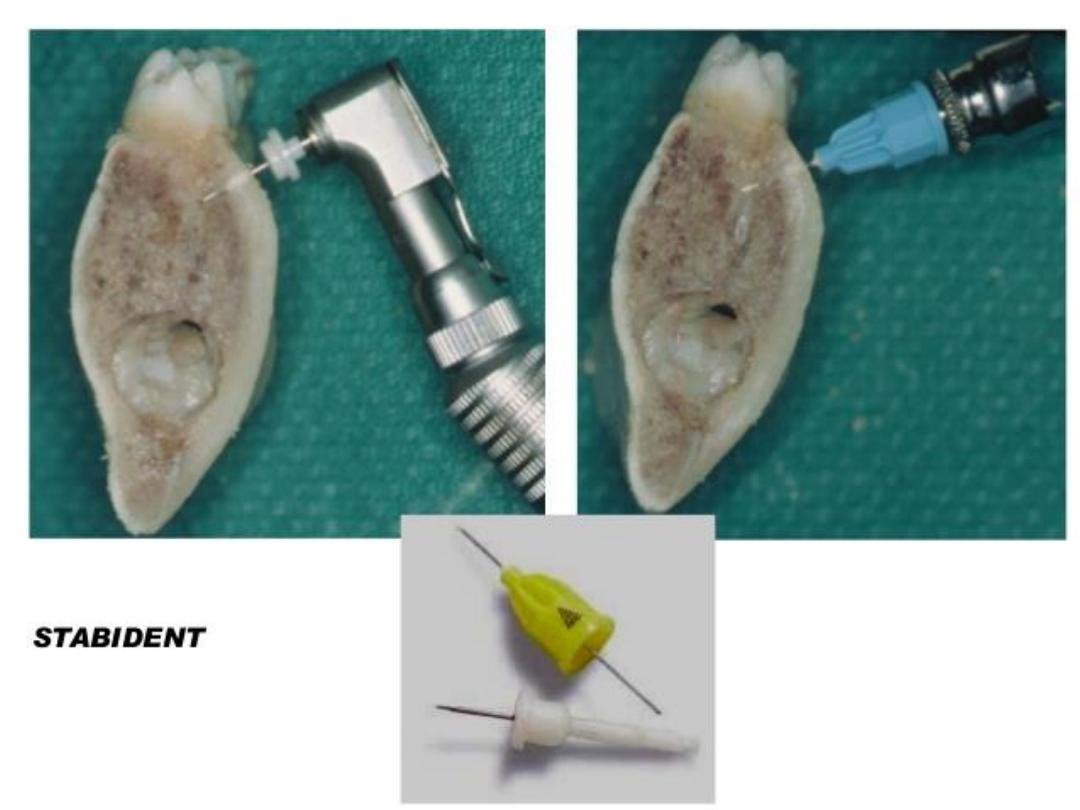
d. Intra-osseuous injection
• Rarely used technique .
• LA solution deposited within the
medullary bone .
• This procedure carried out by the use of
bone drills and needles especially
designed for this purpose .
Regional anasthesia (block)
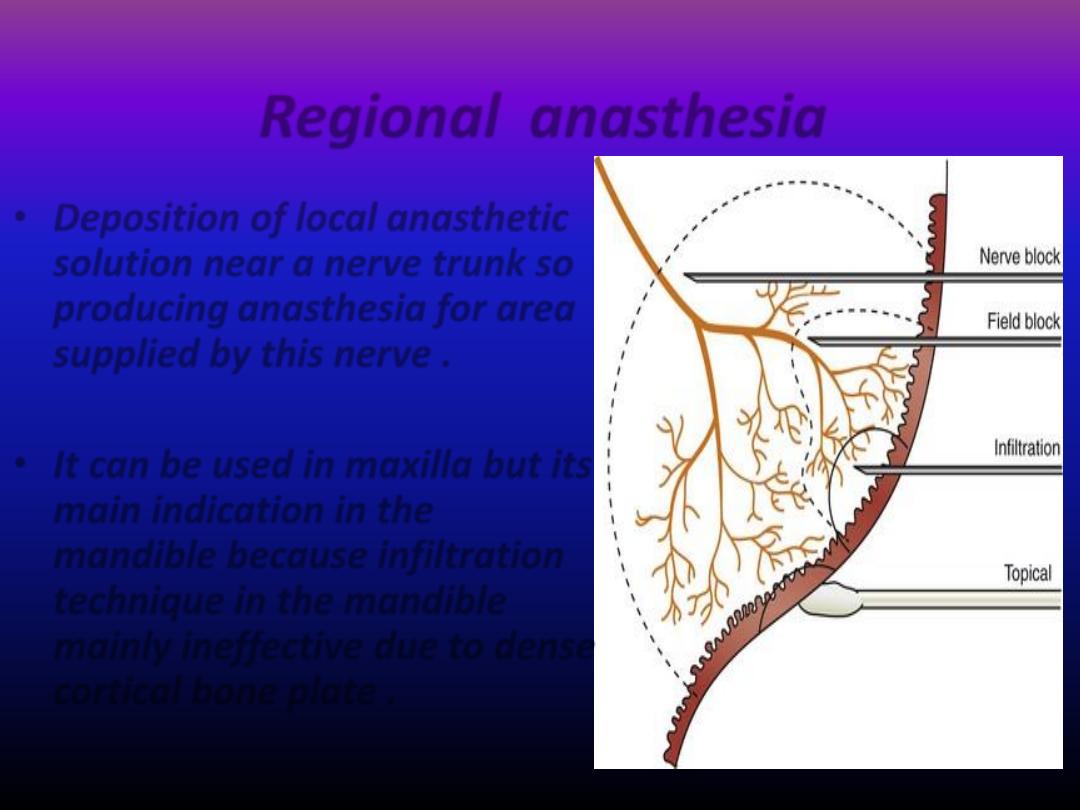
Regional anasthesia
• Deposition of local anasthetic
solution near a nerve trunk so
producing anasthesia for area
supplied by this nerve .
• It can be used in maxilla but its
main indication in the
mandible because infiltration
technique in the mandible
mainly ineffective due to dense
cortical bone plate .
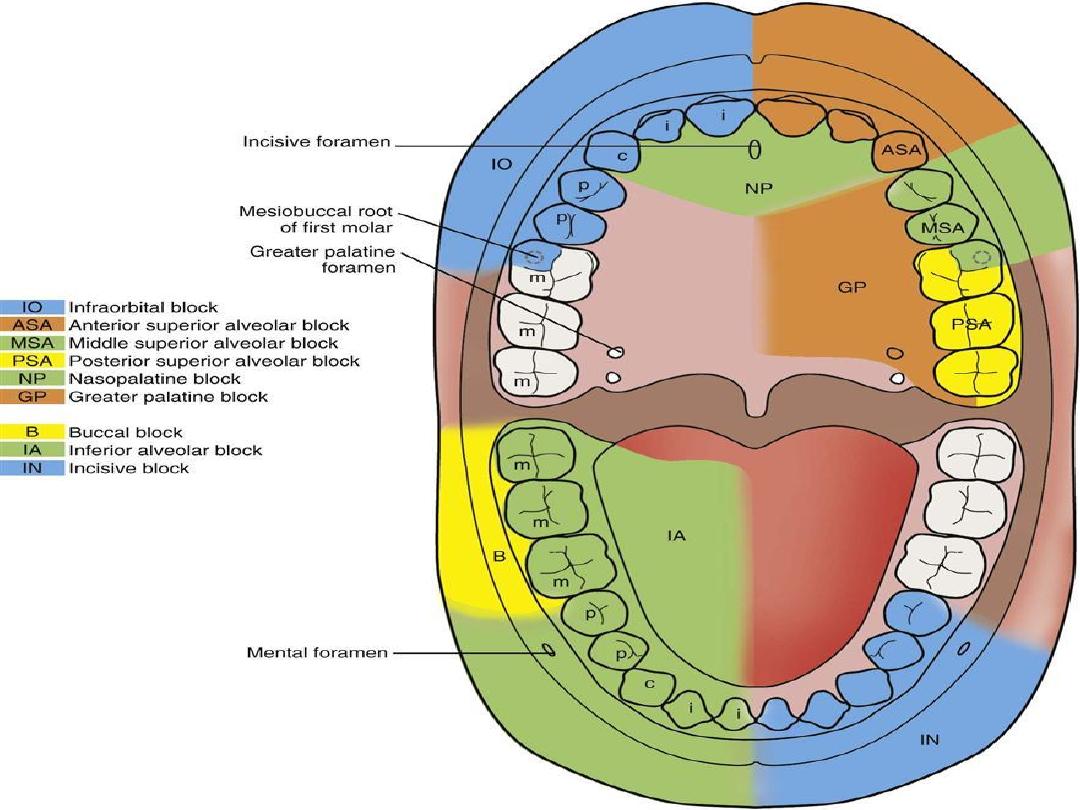
local anasthesia in maxilla

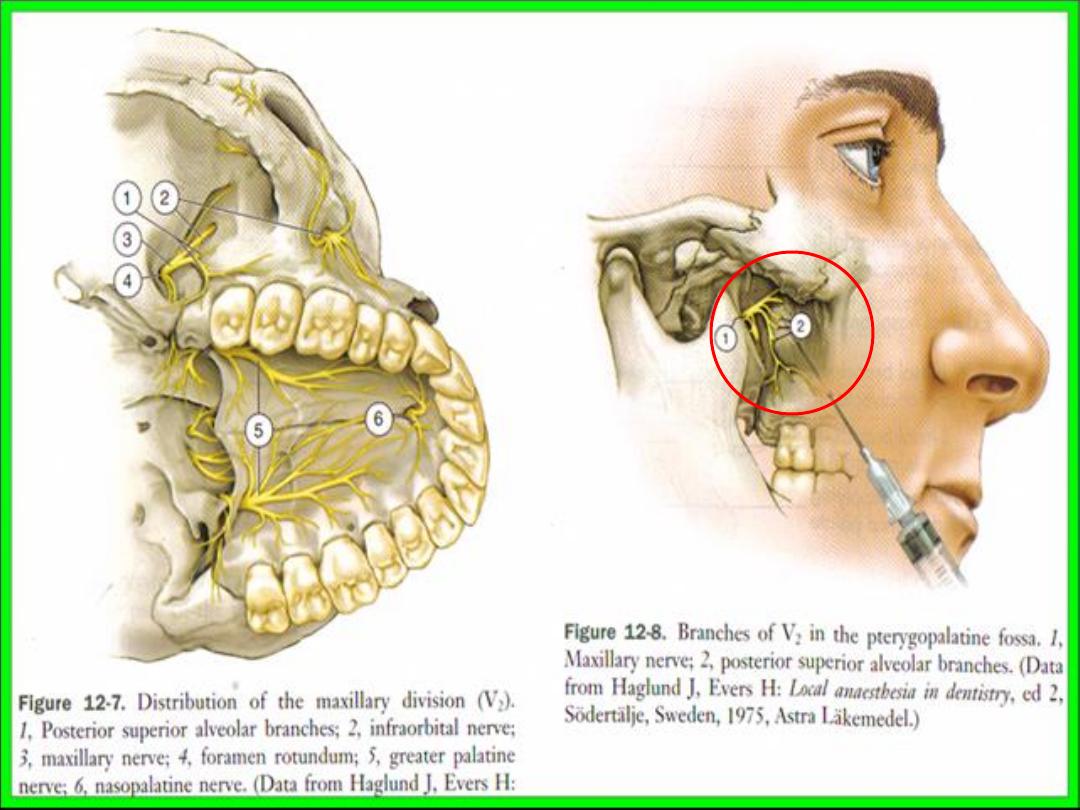
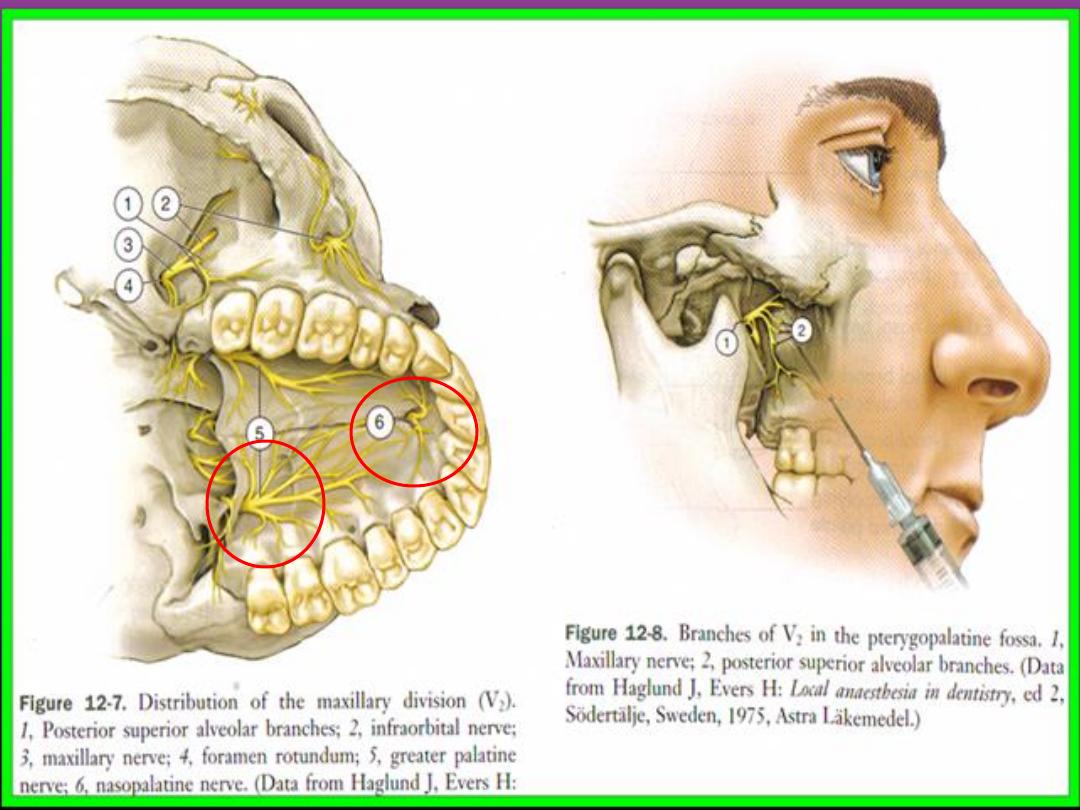
Anasthesia of upper molars teeth
• The pulp of all upper molars innervated by
branches from superior posterior alveolar nerve
(except the mesiobuccal root of first molar )
• Theses nerves also responsible for innervation of
periosteum and buccal gingiva in molars region .
• Deposition of anasthesia close to the nerve after it
leaves its bony canal will produce regional
anasthesia but its rarely used because it carries a
risk of damage to the pterygoid venous plexus
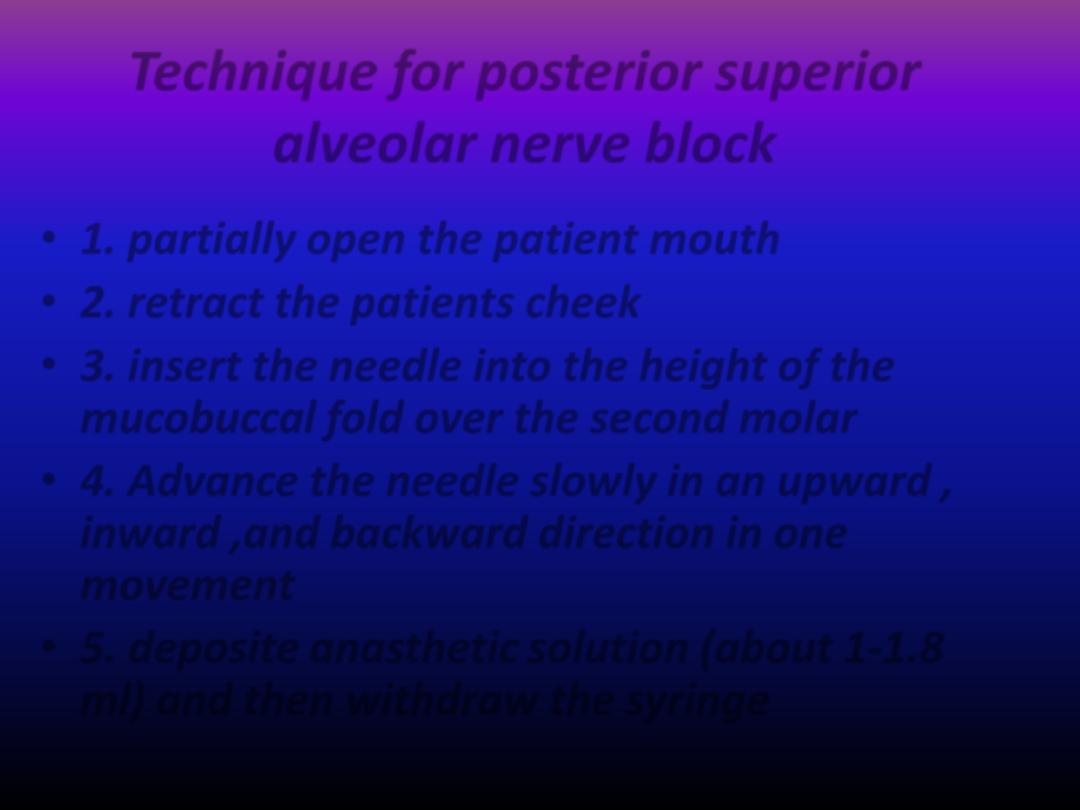
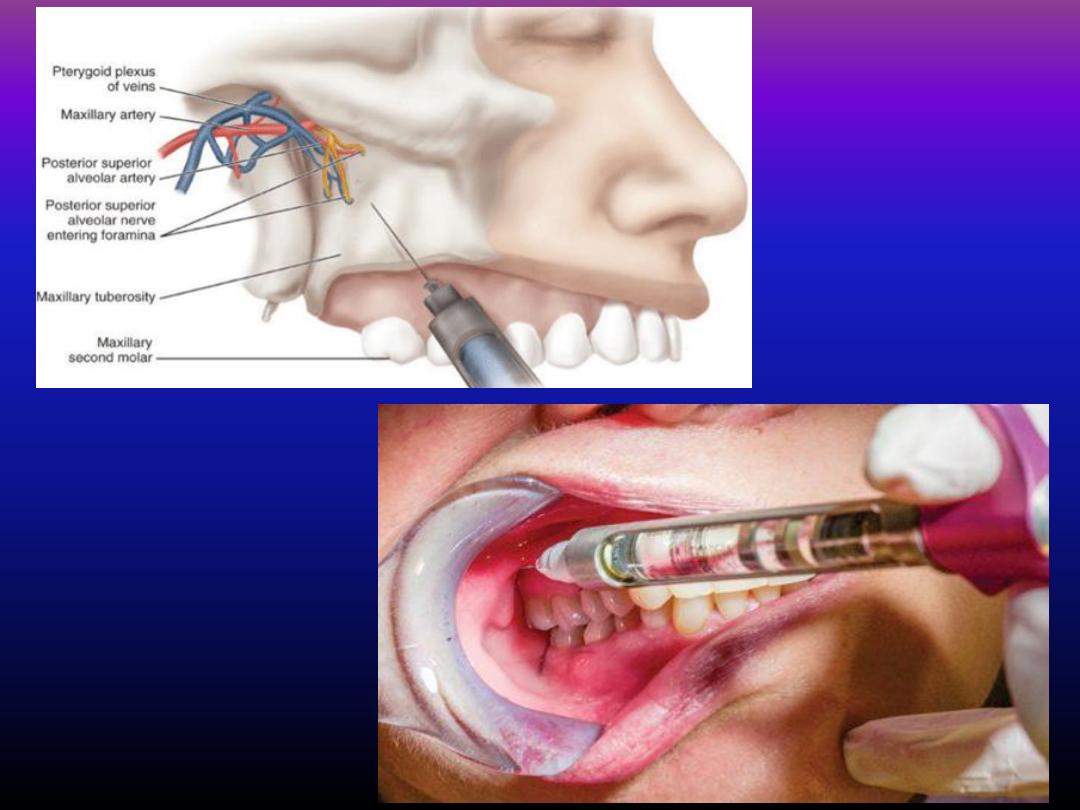
Technique for posterior superior
alveolar nerve block
• 1. partially open the patient mouth
• 2. retract the patients cheek
• 3. insert the needle into the height of the
mucobuccal fold over the second molar
• 4. Advance the needle slowly in an upward ,
inward ,and backward direction in one
movement
• 5. deposite anasthetic solution (about 1-1.8
ml) and then withdraw the syringe
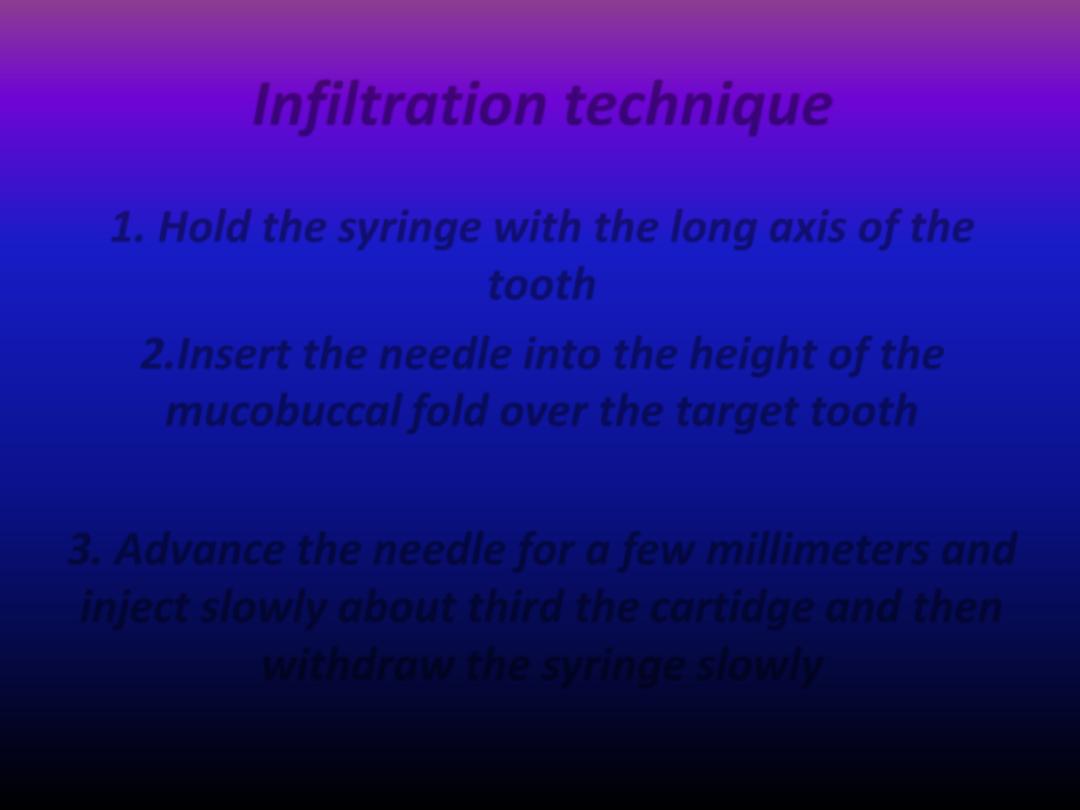
Infiltration technique
1. Hold the syringe with the long axis of the
tooth
2.Insert the needle into the height of the
mucobuccal fold over the target tooth
3. Advance the needle for a few millimeters and
inject slowly about third the cartidge and then
withdraw the syringe slowly

In block technique the whole region supplied by
superior posterior alveolar nerve will be
anasthetize while in infiltration technique a
limited area of specific target tooth will be
anasthetized

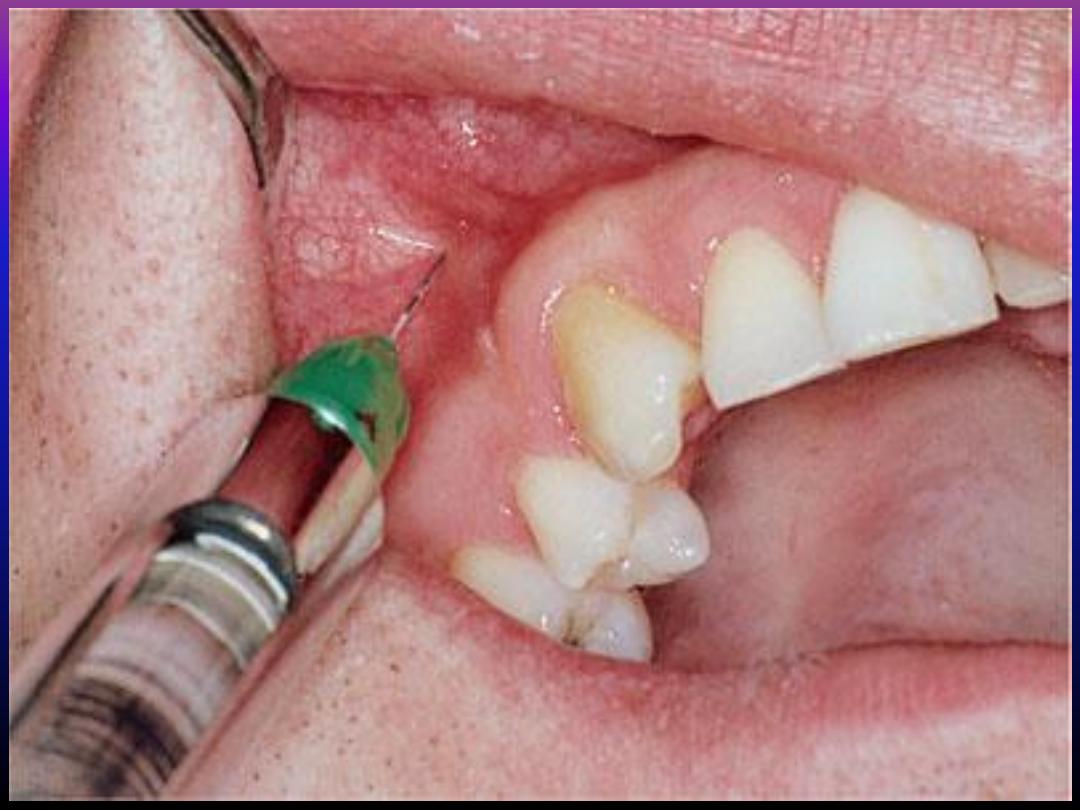
Anasthesia for upper premolar teeth
• The mesiobuccal root of the upper first molar
and both premolars and buccal supporting
tissue and mucoperiosteum related to them
all are
innervated by middle superior alveolar
nerve .
• So infiltration technique to this nerve will be
sufficient to anasthetize all these structures .

Anasthesia for upper anterior teeth
The upper anterior teeth and its supporting
tissues and mucoperiosteum related to them
are innervated via anterior superior dental
nerve so infiltration technique will be sufficient
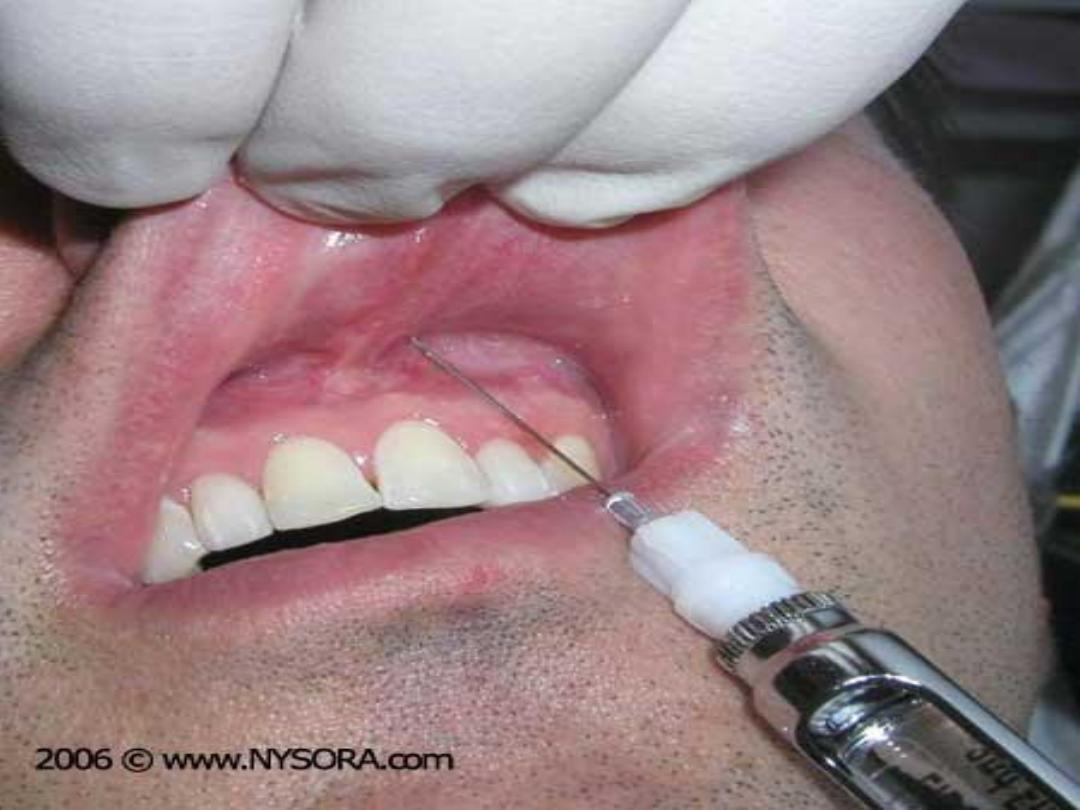

Note :
In conservative treatment the pulp only needed
to be anasthetized while in tooth extraction the
pulp , bone ,periosteum and the gingiva (labial
and palatal ) should be anasthetized

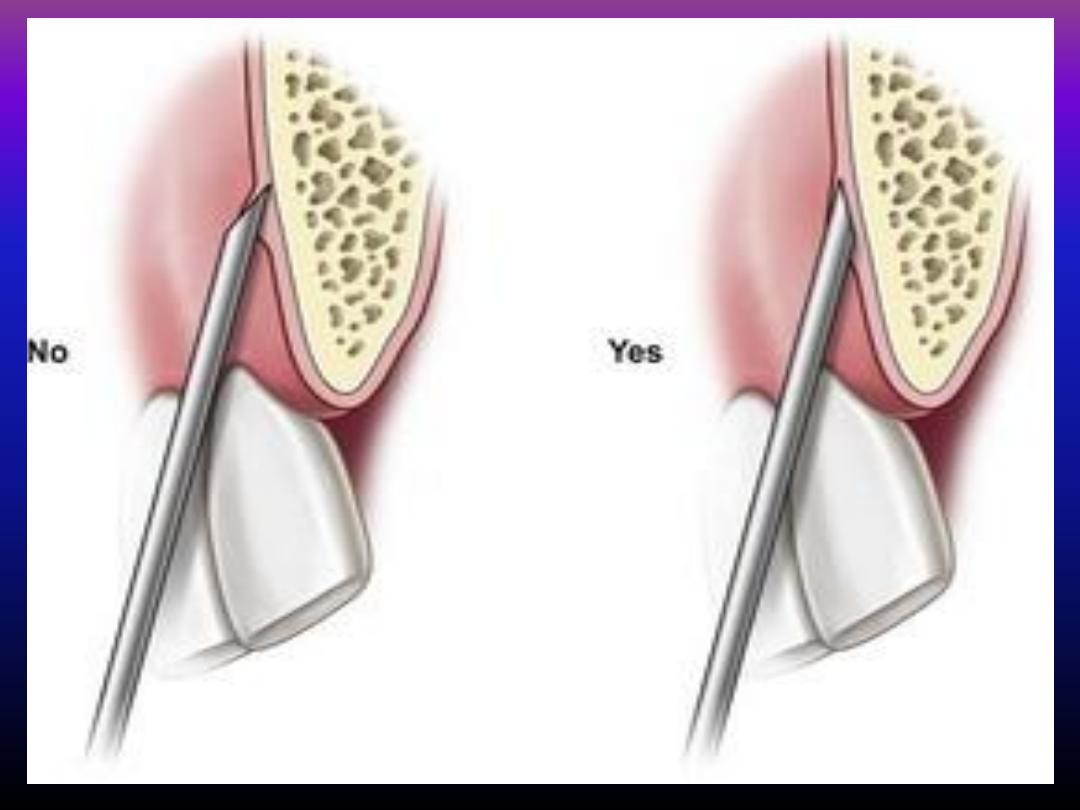
Anasthesia for palatal mucosa
Palatal mucosa are tense and closely attached
to the underlying bone so :
• Injection will need great pressure
• Injection usually painful . pain can be reduced by
inserting the needle with the bevel facing the bone
and as near as possible at right angle to the vault of
the palat

Palatal anasthesia can be achieved by block injection:
to the
greater palatine nerve
in the posterior part of hard palat
distal to the second molar about 1 cm toward the midline
and
nasopalatine block
in the anterior part of hard palat
(incisive foramen) in the midline of the palate ,about 1 cm
posterior to the maxillary central incisor.
Or
by infiltration :
in which the solution is deposited in the
palatal tissue adjacent to the target tooth .
Anasthesia for palatal mucosa
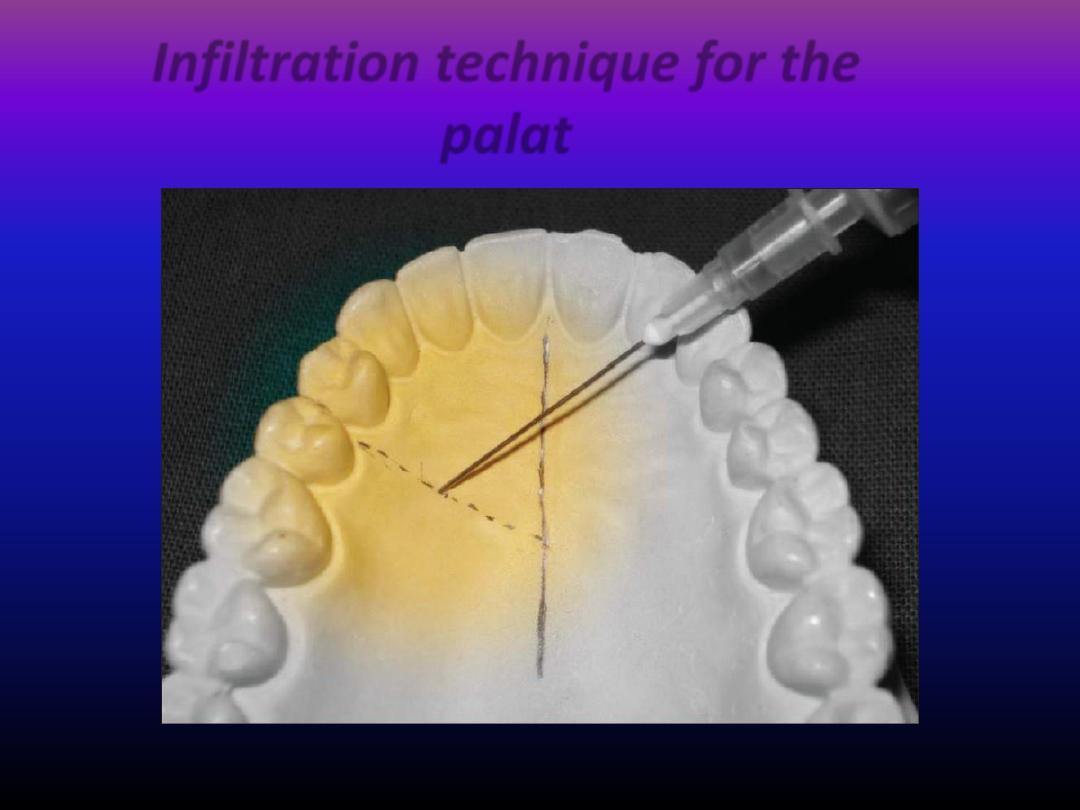
Infiltration technique for the
palat
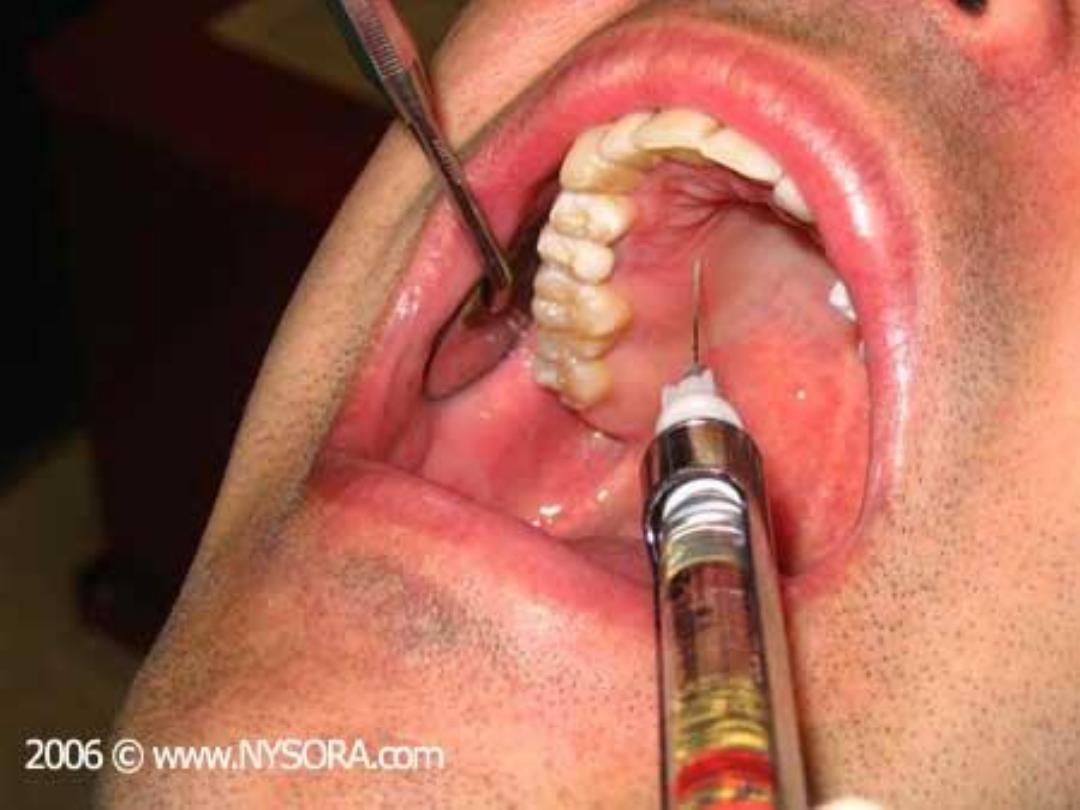

Infra - orbital block injection
Rarely used because infiltration technique so effective in
maxilla .
Usually indicated when numerous extration or extensive
surgery are to be done in maxillary anterior teeth .
Also indicated when infiltration technique precluded by
presence of infection at the injection site .
This technique provide ansthesia for centrals, lateral
incisors,canine , premolars and supporting structures .
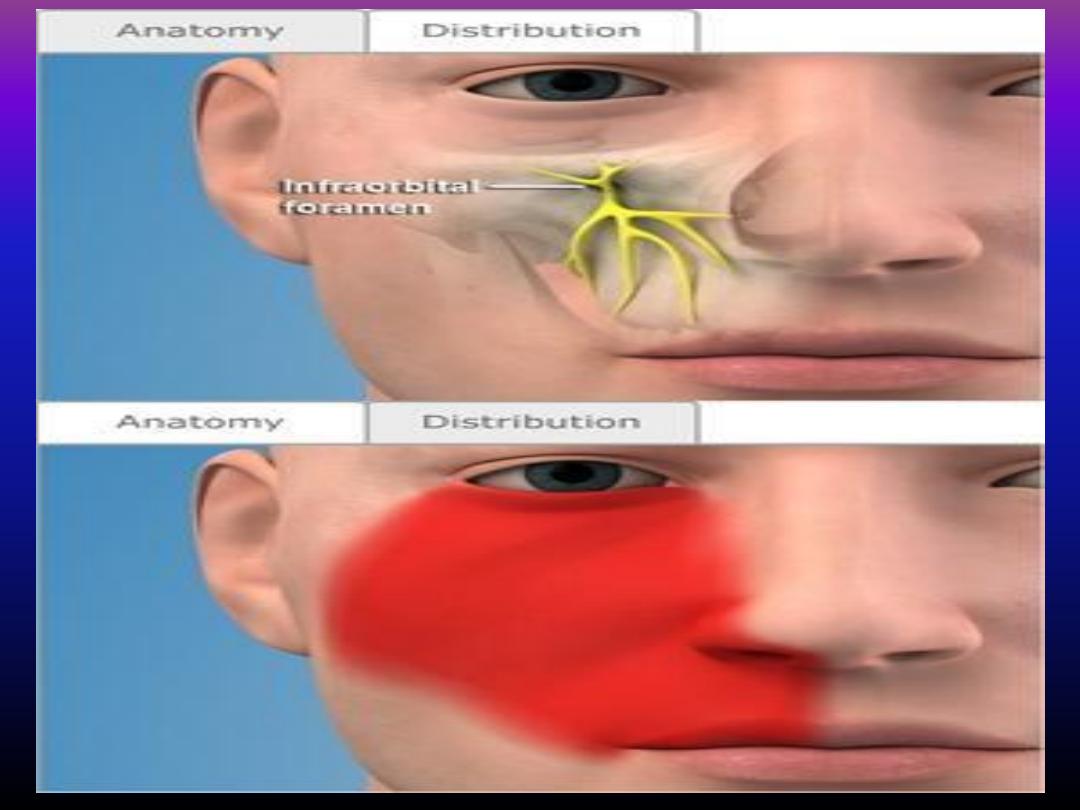
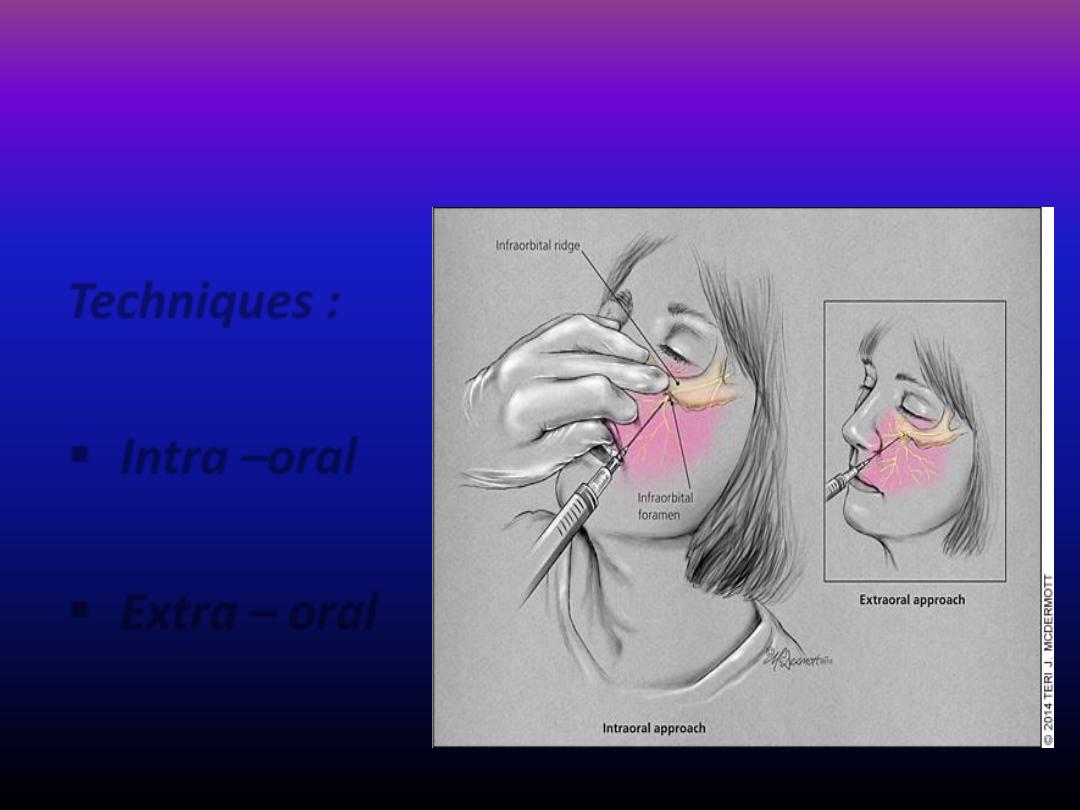
Techniques :
Intra –oral
Extra – oral
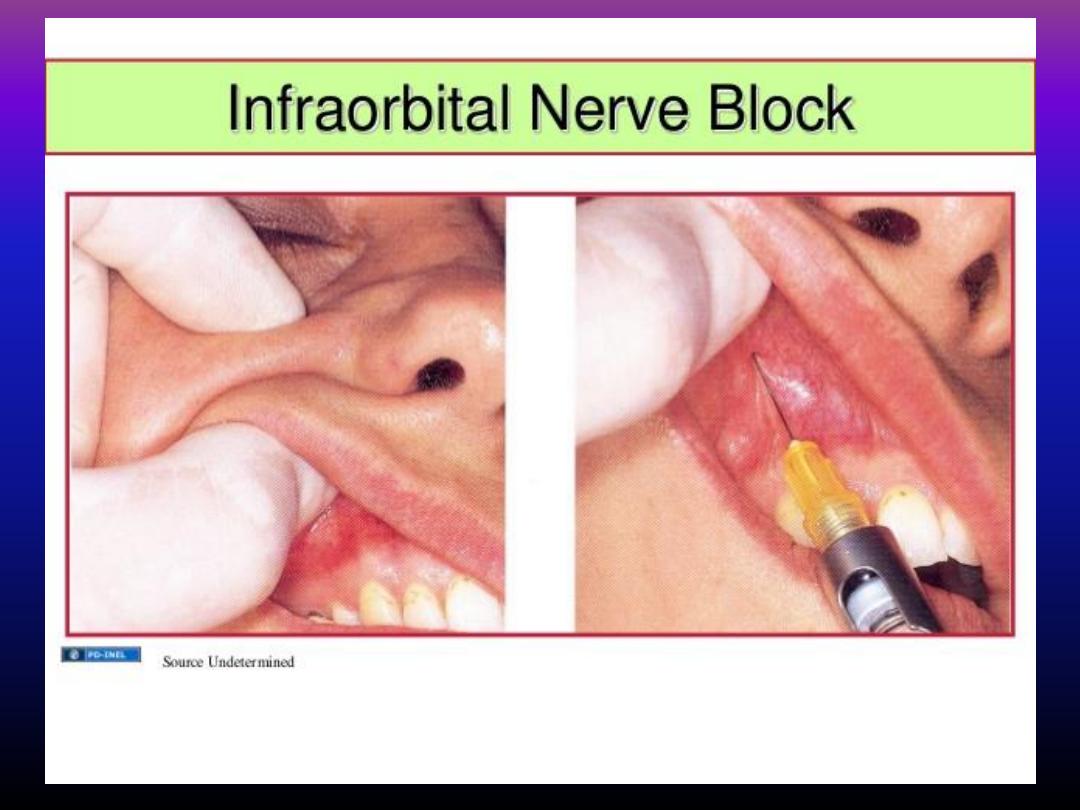
Infra - orbital block injection

Intra-oral approach :
• Most popular technique .
• Infra-orbital ridge palpated and the infraorbital notch
determined .
• Infrorbital foramen lie directly below below this notch
• lip reflectd and long needle inserted in to a depth
about 1.5-2 cm
in to the mucous membrane over
second premolar .
• About I ml of LA given
Infra - orbital block injection
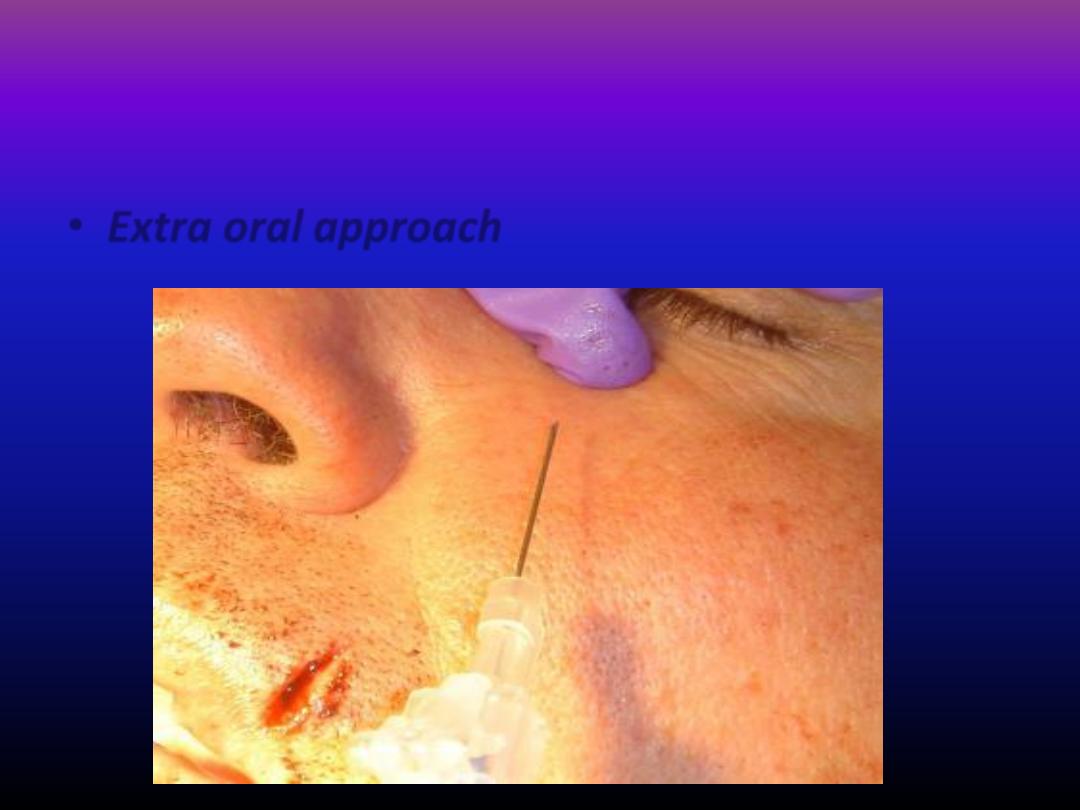
• Extra oral approach
Infra - orbital block injection

Anasthesia of the upper deciduous
teeth
• Infiltration technique highly effective because
the labio-buccal bone plate are thin and
perforated by numerous vascular canals .
• Care should be taken to estimate the length
of roots and depth of injecion.

local ansthesia in mandible

local ansthesia in mandible
• Infiltration techniques are of limited value
due to the dense cortical bone of mandible
• Block technique for inferior alveolar nerve is
the preffered technique
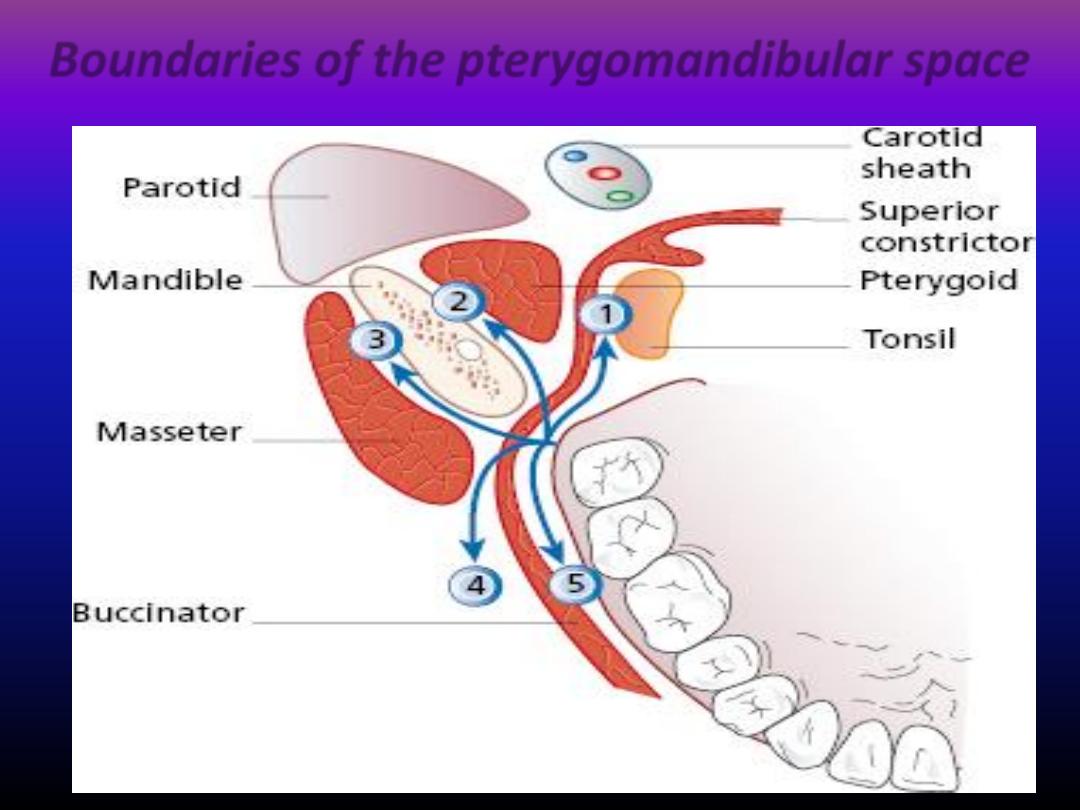
Boundaries of the pterygomandibular space
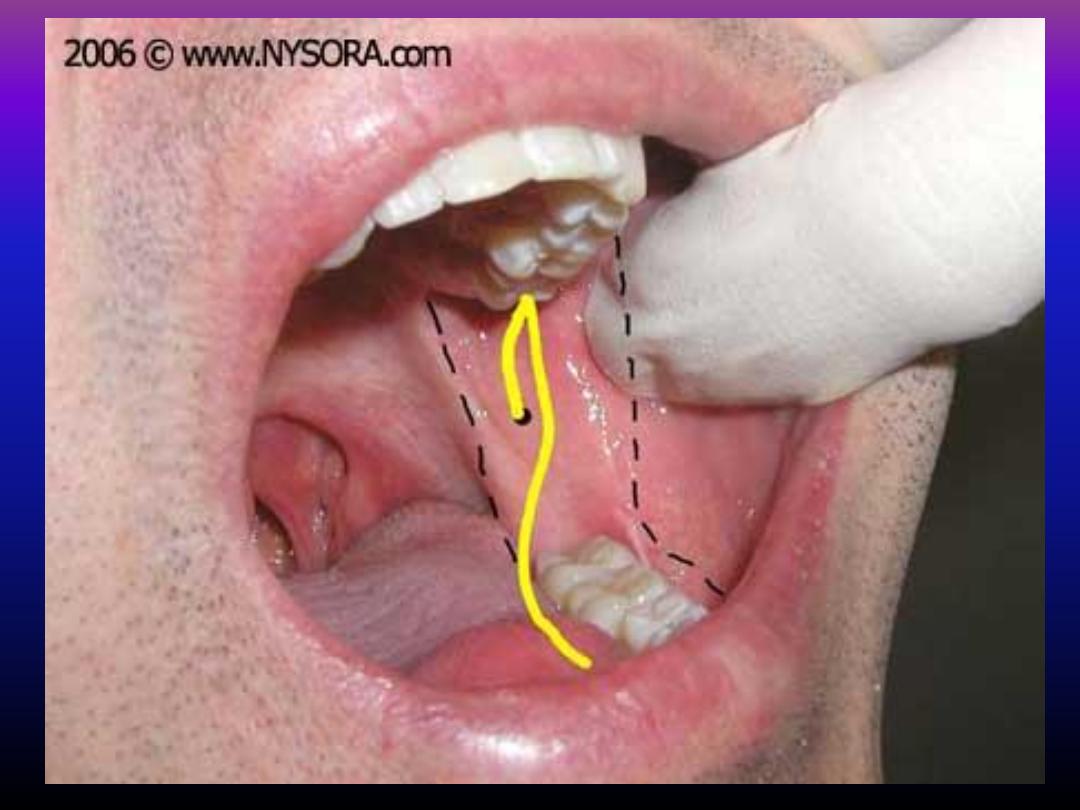
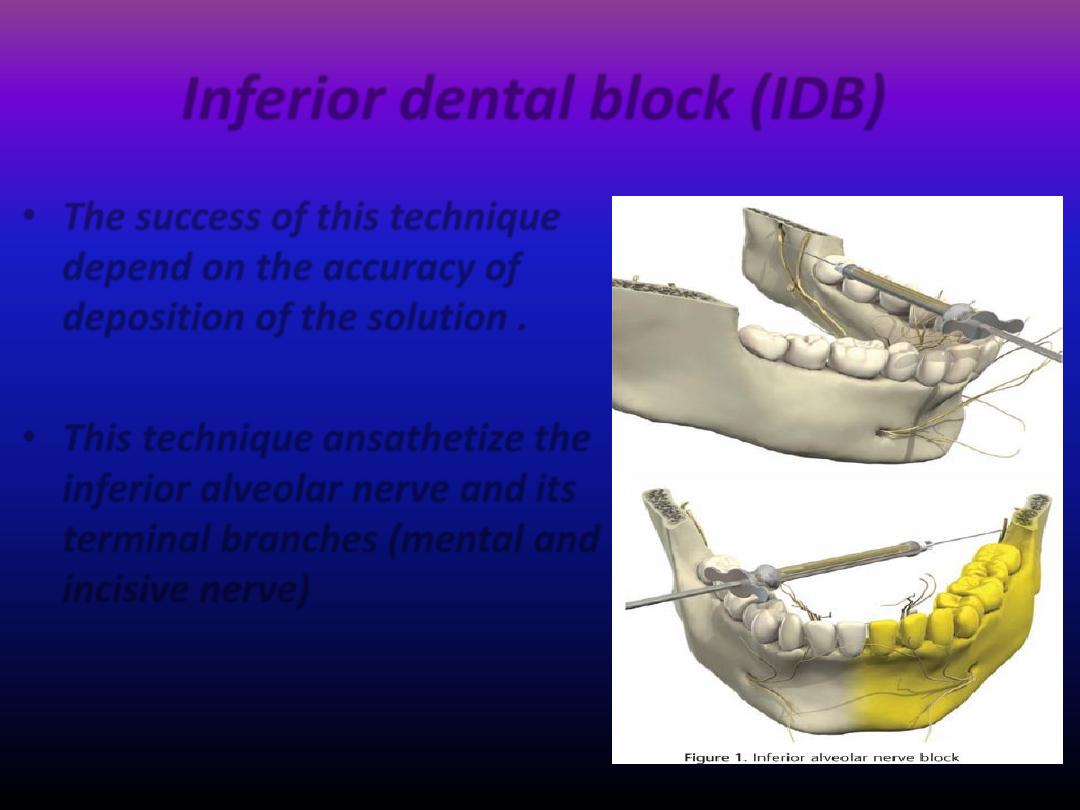
Inferior dental block (IDB)
• The success of this technique
depend on the accuracy of
deposition of the solution .
• This technique ansathetize the
inferior alveolar nerve and its
terminal branches (mental and
incisive nerve)
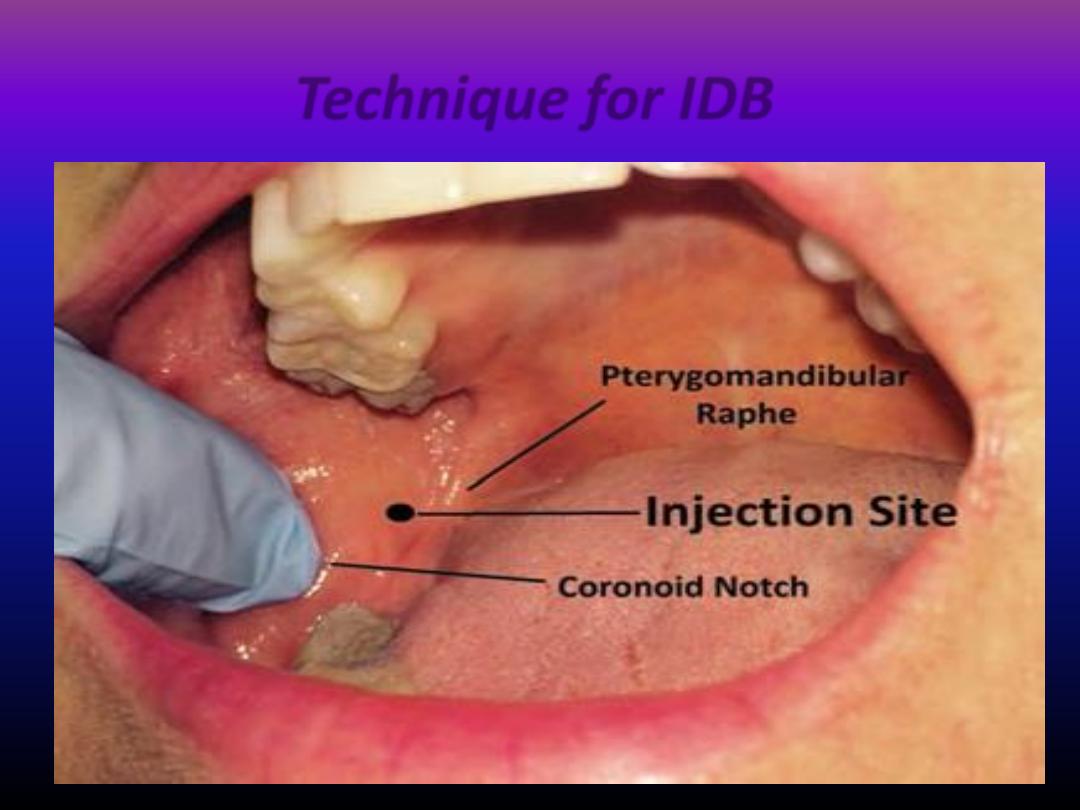
Technique for IDB
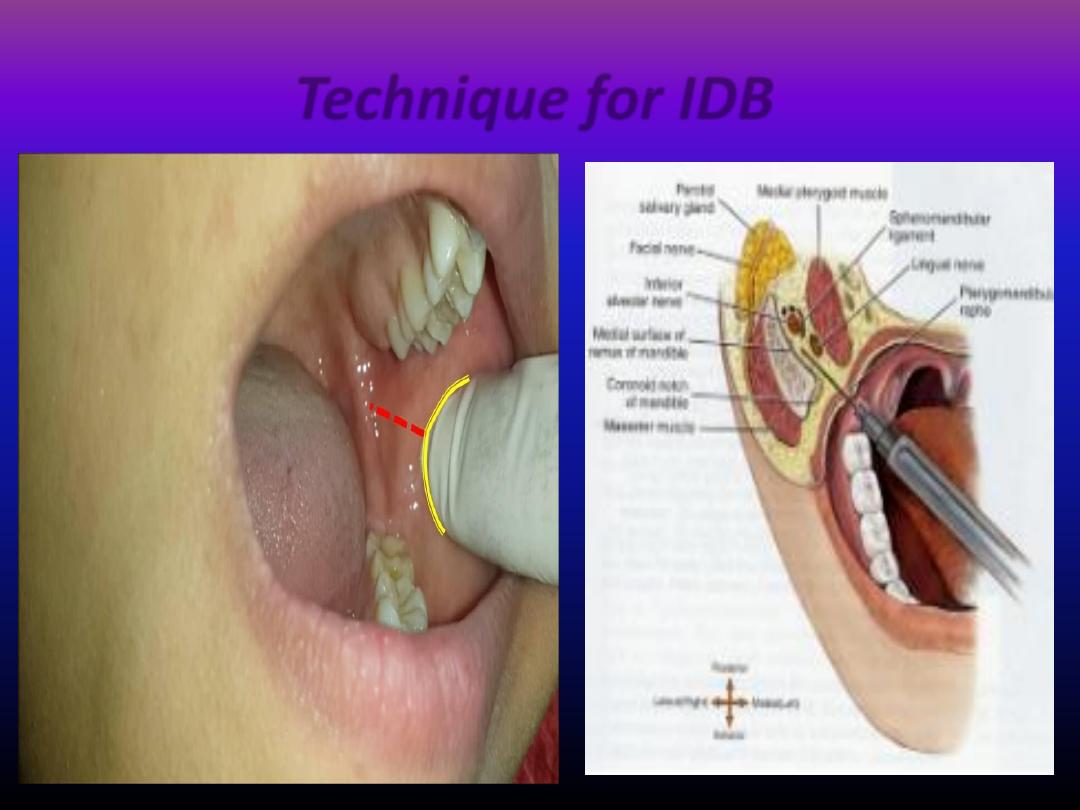
Technique for IDB
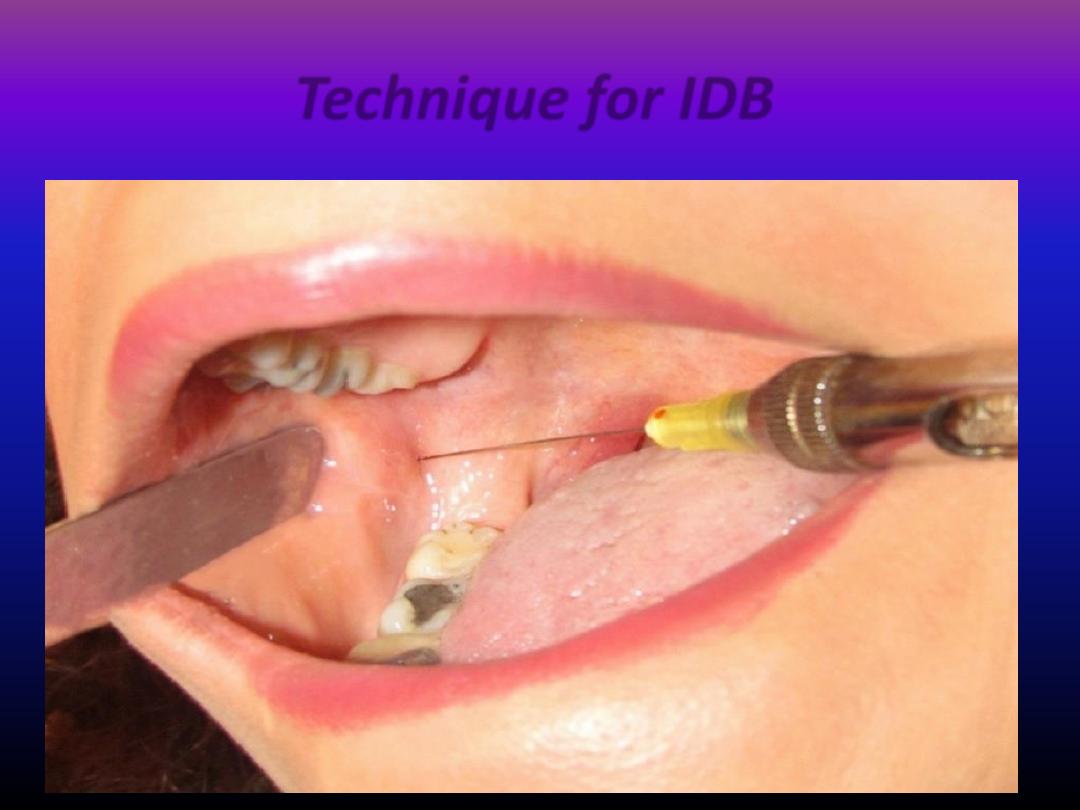
Technique for IDB



Notes
• The dimentions and shape of the mandible may vary in
patients of differing race , size , age so the width of the
ascending ramus and the position of the mandibular
foramen may vary between individuals.
• Its better to palpate the anterior and posterior border of the
ascending ramus by the thumb and index fingers and the
needle directed midway between the two fingers
• Bilateral IDB should be avoided as possible ( patient feel
discomfort , difficulty in swallow and to avoid self injury to
the anasthetized tissues)
• Lingual nerve can be asnasthetized by infiltration technique
by injection of about 0.5 ml of the solution in the lingual
sulcus adjacent to the target tooth
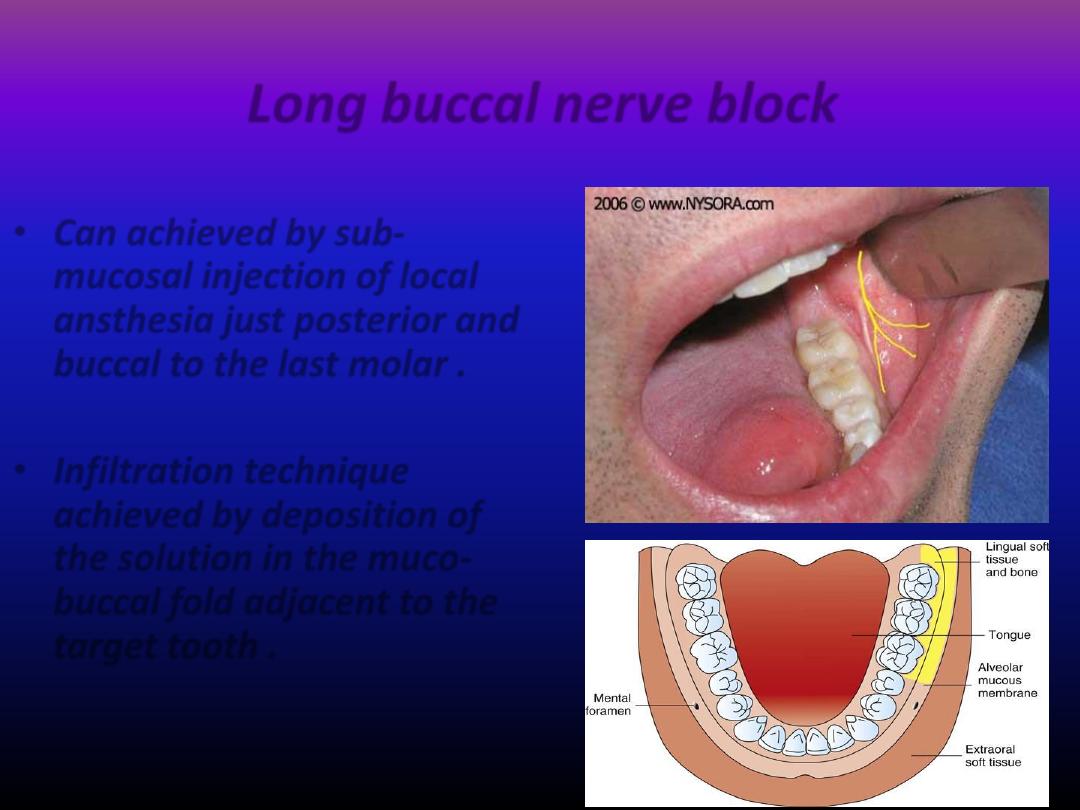
Long buccal nerve block
• Can achieved by sub-
mucosal injection of local
ansthesia just posterior and
buccal to the last molar .
• Infiltration technique
achieved by deposition of
the solution in the muco-
buccal fold adjacent to the
target tooth .
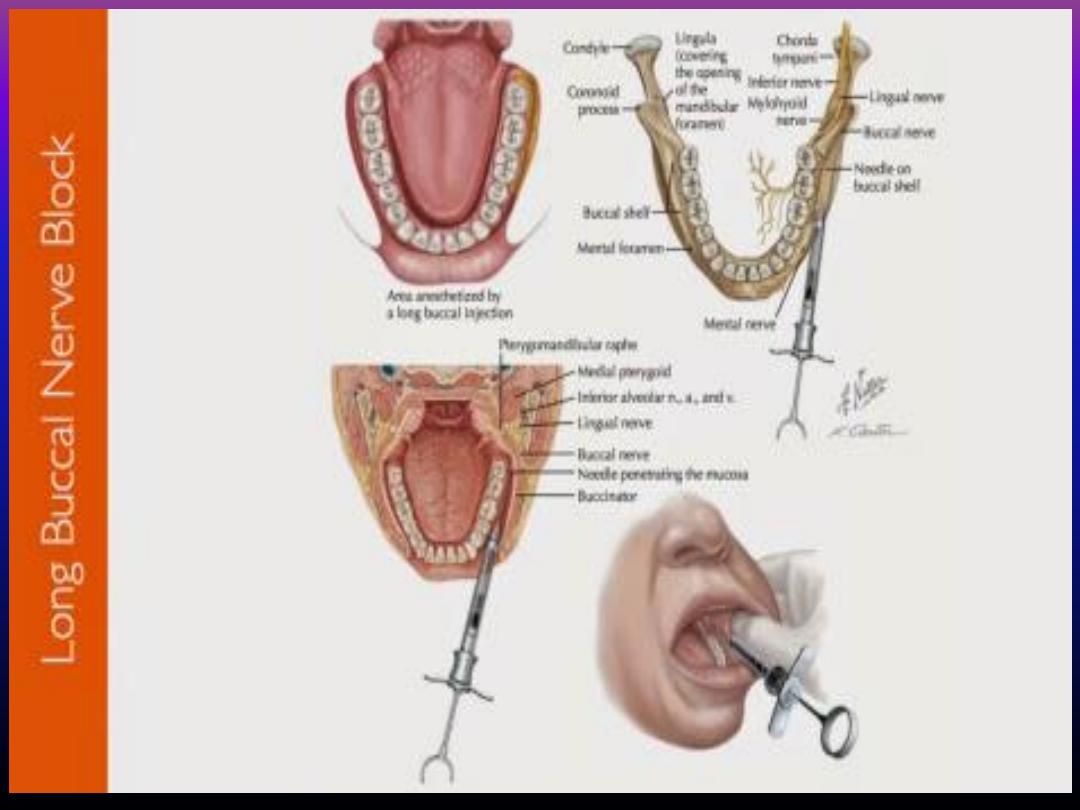

Notes
• When the long buccal nerve anasthetized the
patient rarely experiences any symptoms due
to the small size of the anasthetized area .
• The depth of penetration of the needle not
more than 2-4 mm .
Anasthesia of the lower anterior teeth
lower anterior teeth usually have innervation from
both sides of dental nerve by anastomosing its
terminal branches at these region.
Unilateral IDB usually not enough
Infiltration technique is effective because the labial
bone plate at this region are thinner and more
porous than other parts of mandible .
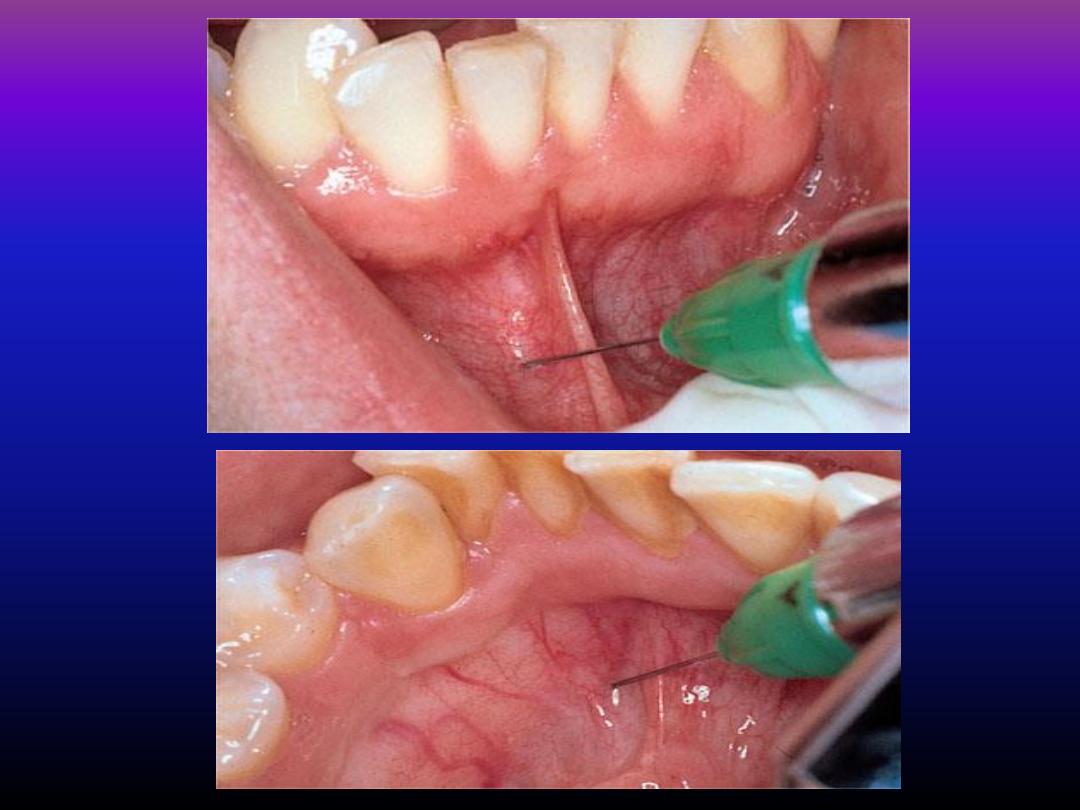
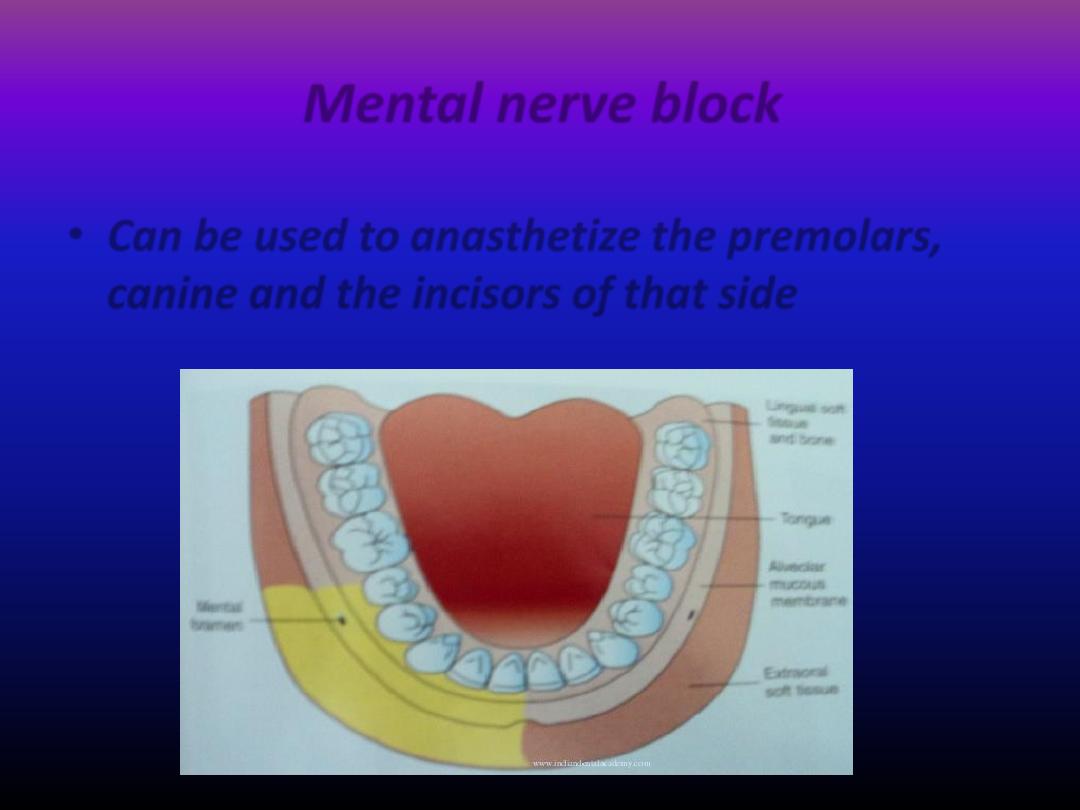
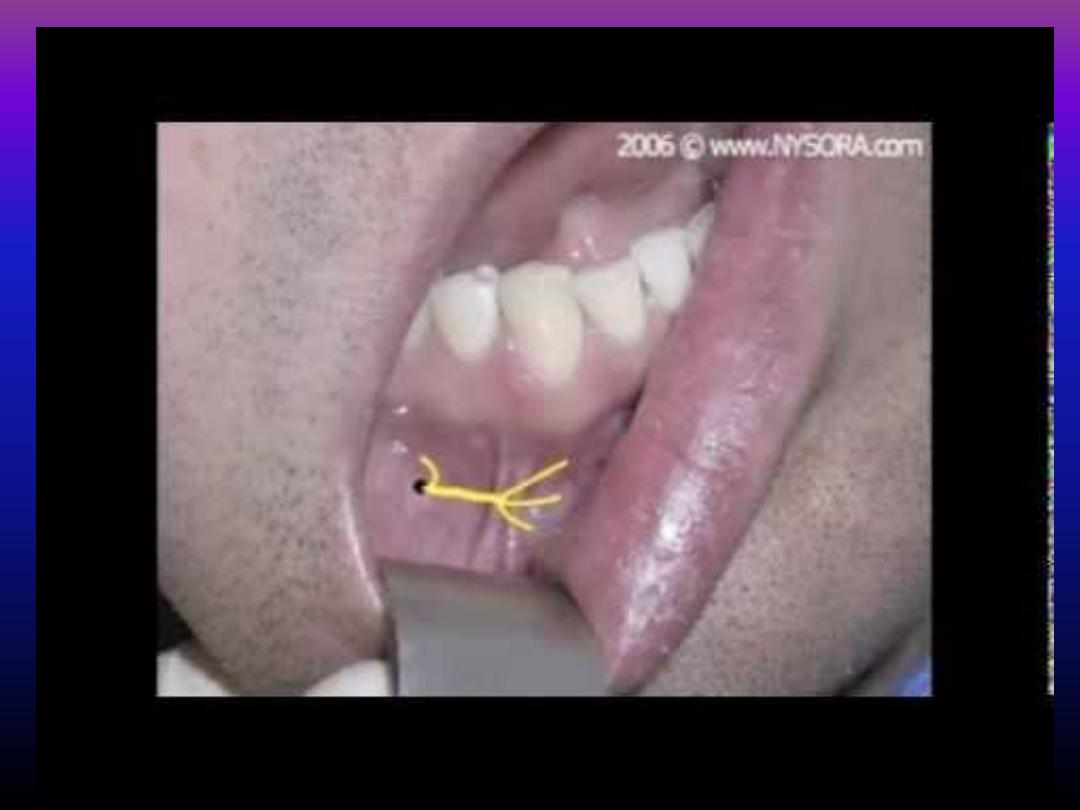
Mental nerve block
• Can be used to anasthetize the premolars,
canine and the incisors of that side
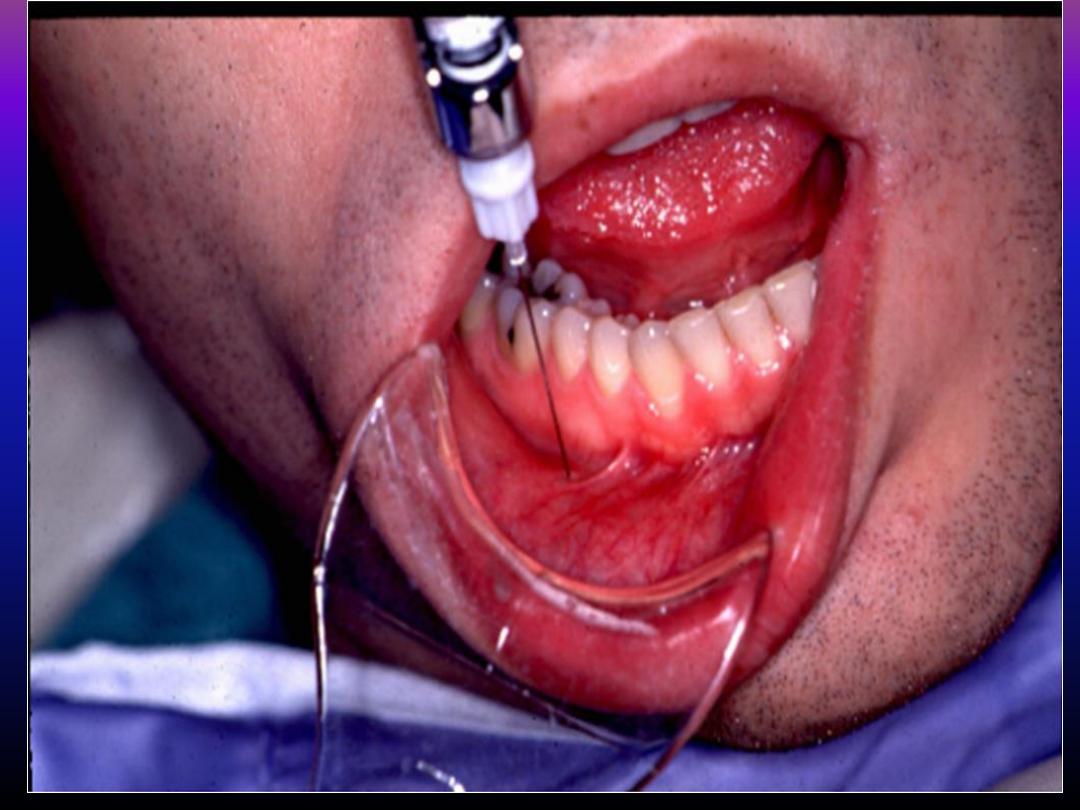

Anasthesia of the lower deciduous teeth
Infiltration technique highly effective

Thank you for listening , please watch
these videos :
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jHlFBg_u_70
And
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wL5m0fE9C6I
