
Renal Tumours
Prof. Issam Al-Azzawi
Head of Urology Department
Al-Mustansiriya University

neoplasms
Benign
Adenoma
Angioma
Angiomyolipoma
neoplasms
Malignant
Wilms tumour
Grawitz tumour
Transitional cell Ca. of renal pelvis / Ureter
Squamous cell Ca. of renal pelvis

Nephroblstoma ( Wilms Tumor )
Mixed tumour ( epithelial & connective )
Arise from embryonic nephrogenic tissue
Usually presents in the 1
st
4 years of life
In one or other pole of one kidney / sometimes
it is bilateral
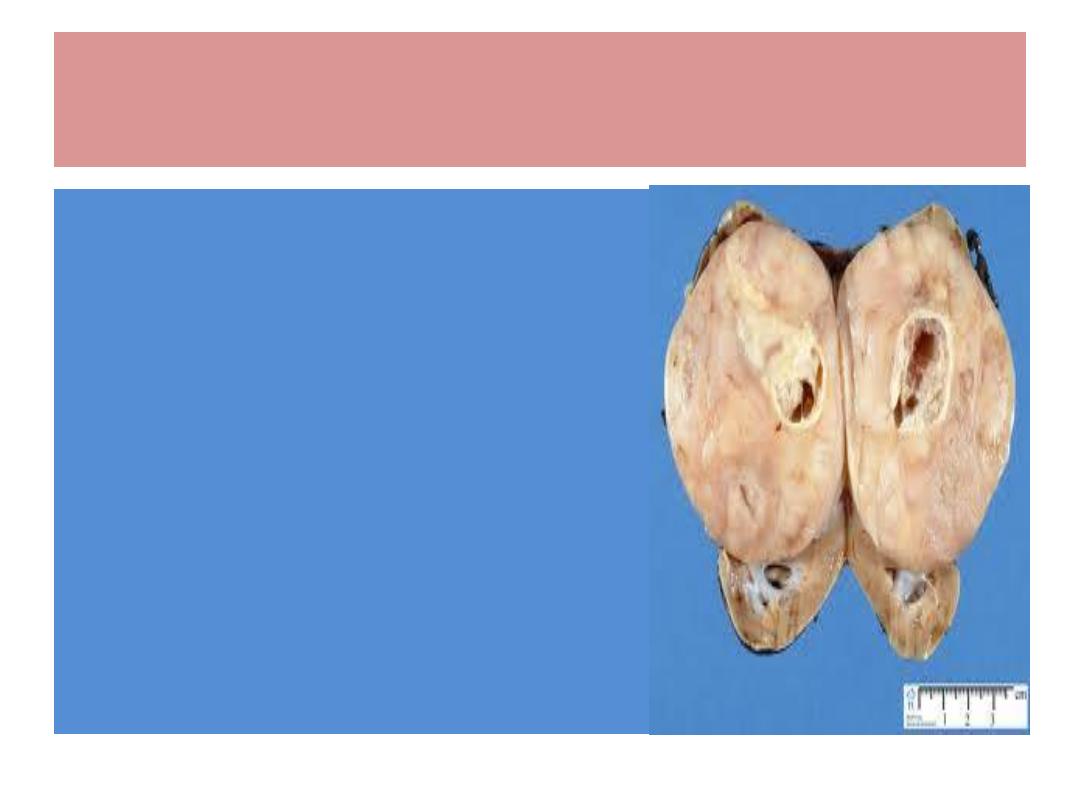
Wilms Tumour / pathology
Cut surface is greyish / pinkish
white
Microscopically : epith. &
connective tissue cells ( bone ,
cartilage, muscle … )
Metastasis : Lungs , liver, bone ,
brain,
Lymphatic spread : uncommon
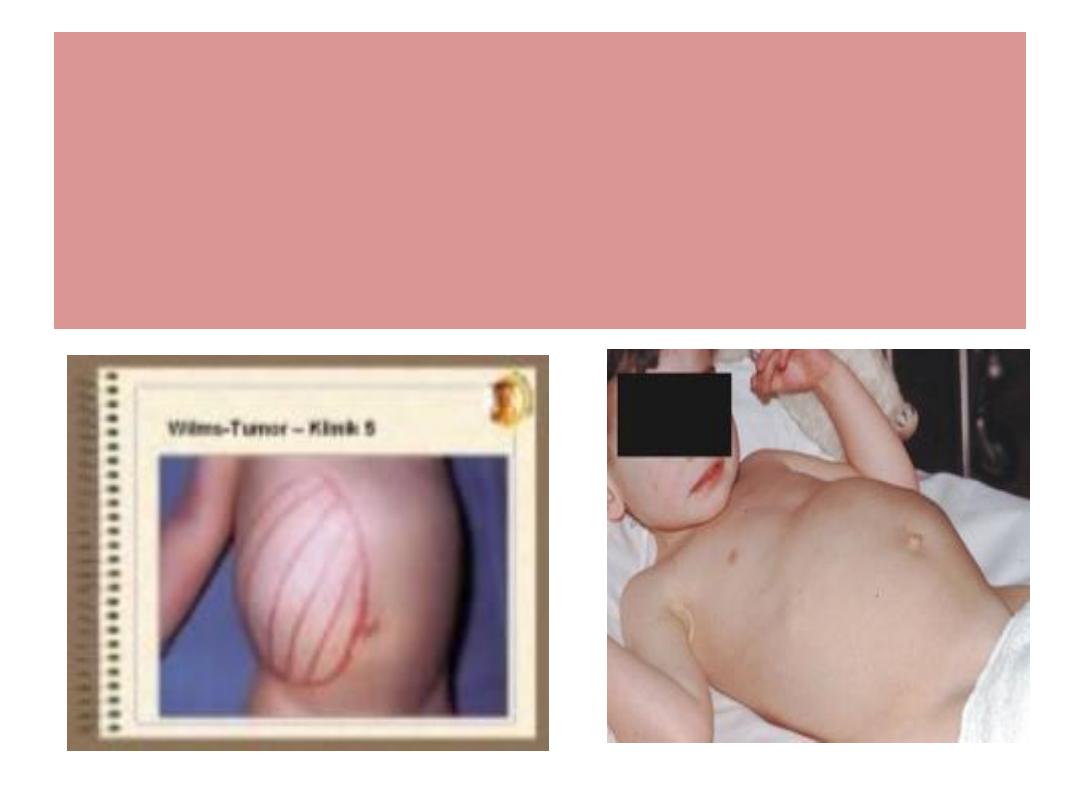
Wilms Tum. / clinical features
Abd. Mass / pyrexia / Hematuria

RX
SURGERY : RADICAL NEPHRECTOMY, PARTIAL
NEPHRECTOMY
RADIOTHERAPY
CHEMOTHERAPY
Diagnosis : U/S , IVU , CT Scan : a solid
space occupying lesion in the kidney
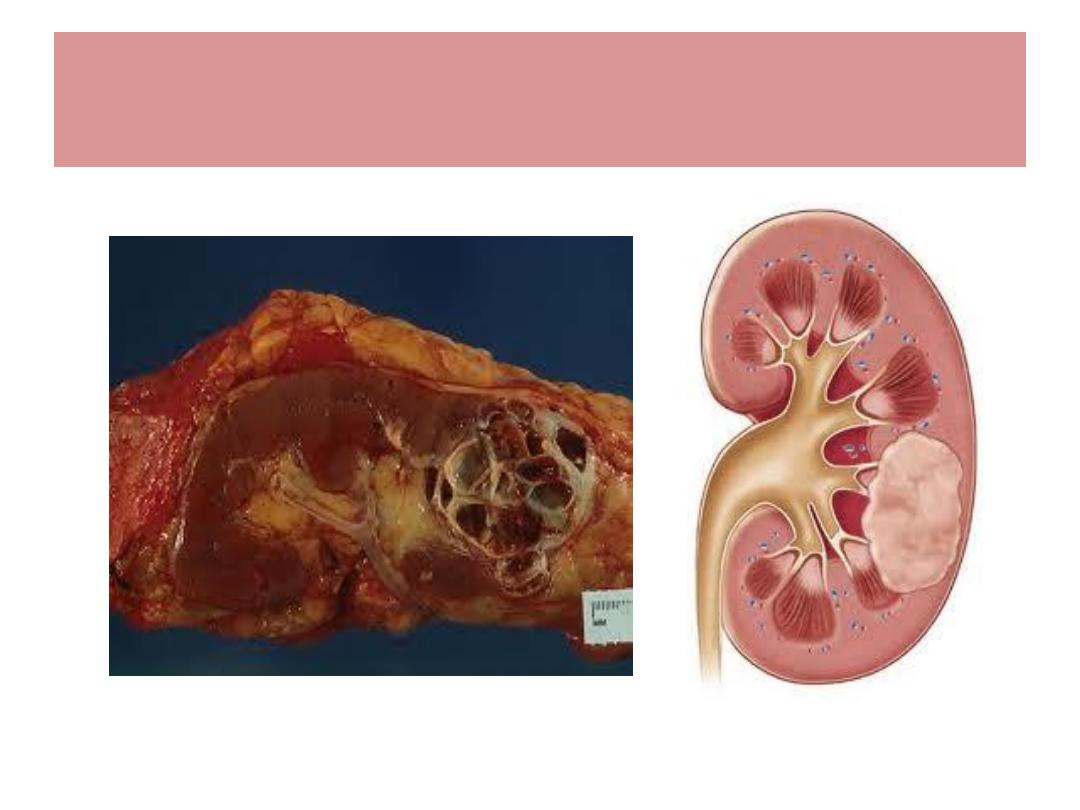
Renal cell Ca. ( Hypernephroma )
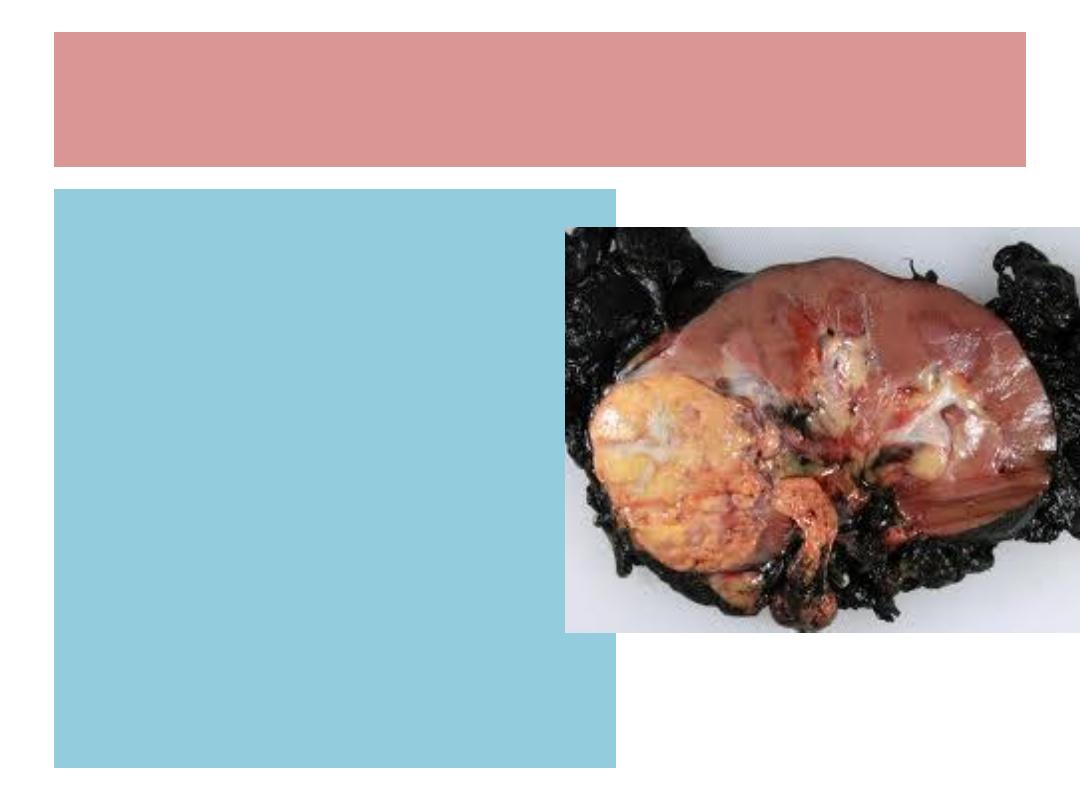
Renal cell Ca. ; Pathology
Arises from renal tubules
Often occupy the poles
•
Cut surface : yellow or dull
white with areas of Hge. /
necrosis
•
Microscopically : clear cell /
granular cell
•
Spread : Lungs ( cannonball)
Bone, lymph nodes, veins

Renal cell Ca. / clinical features
More common in males
Hematuria / clot colic
Loin mass / dragging discomfort
Left varicocele in men
Symptoms due to metastasis ; bone pain,
cough, haemoptysis
Pyrexia / Anemia / polycythemia/
hypercalcemia
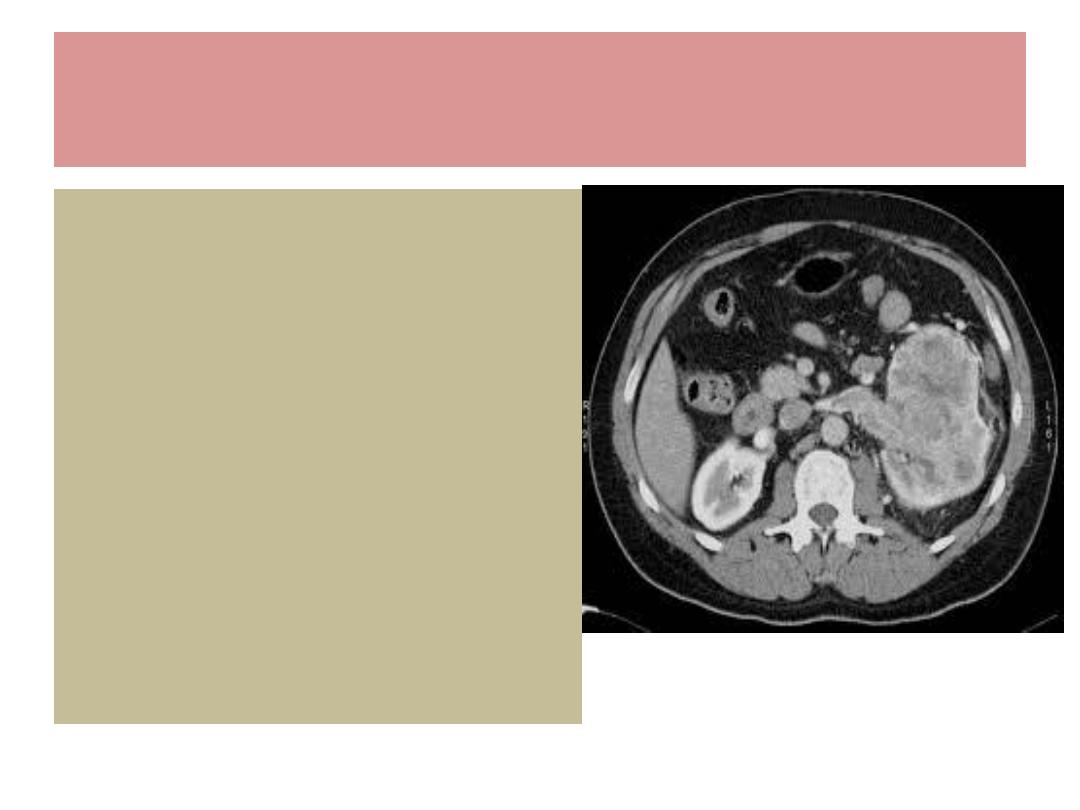
Renal cell Ca. / Diagnosis
U/S
IVU
CT With enhancement
Renal angiography
CXR
Isotope bone scan
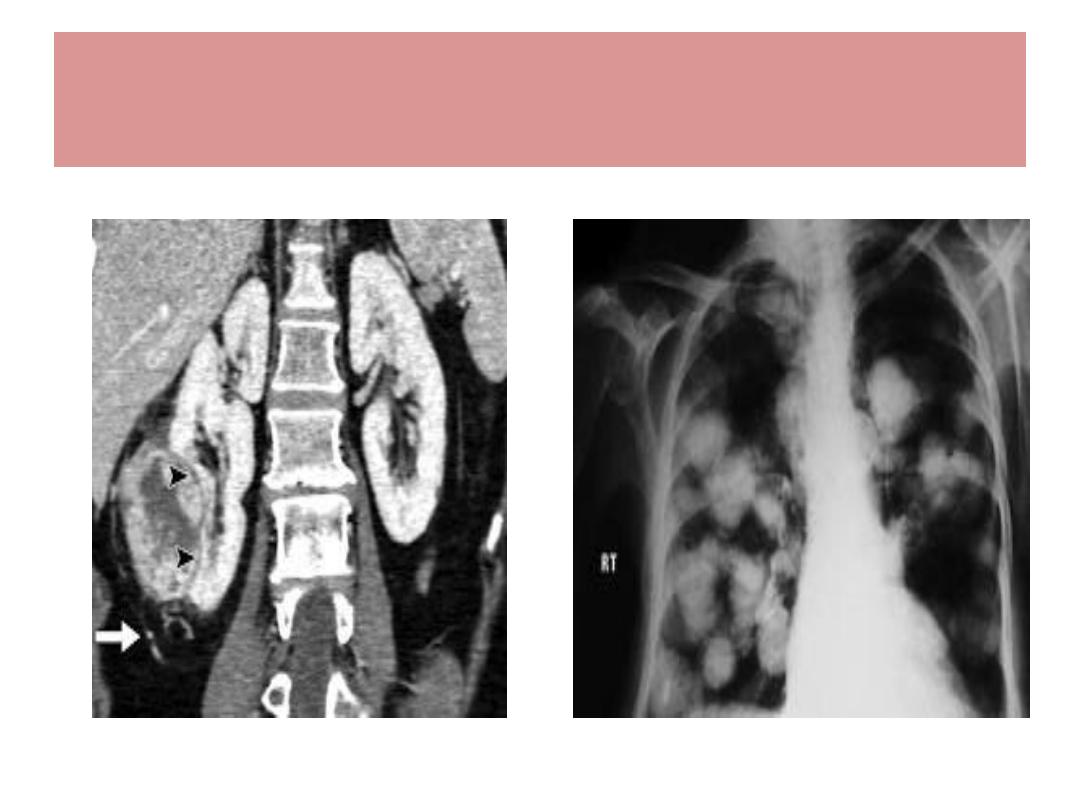
RCC
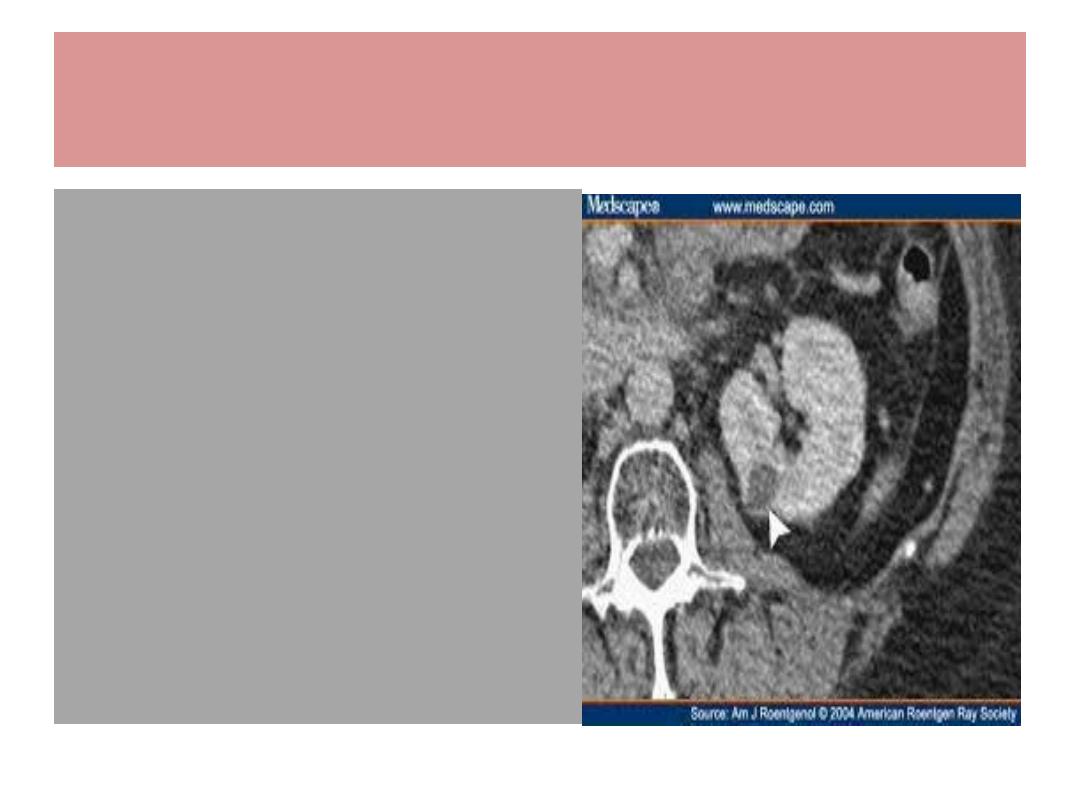
RCC / Treatment
Radical nephrectomy
Partial nephrectomy
Radiotherpy : poor
Chemotherapy : ?
Immunotherapy :
interleukin 2
Arterial embolization
Cryotherapy
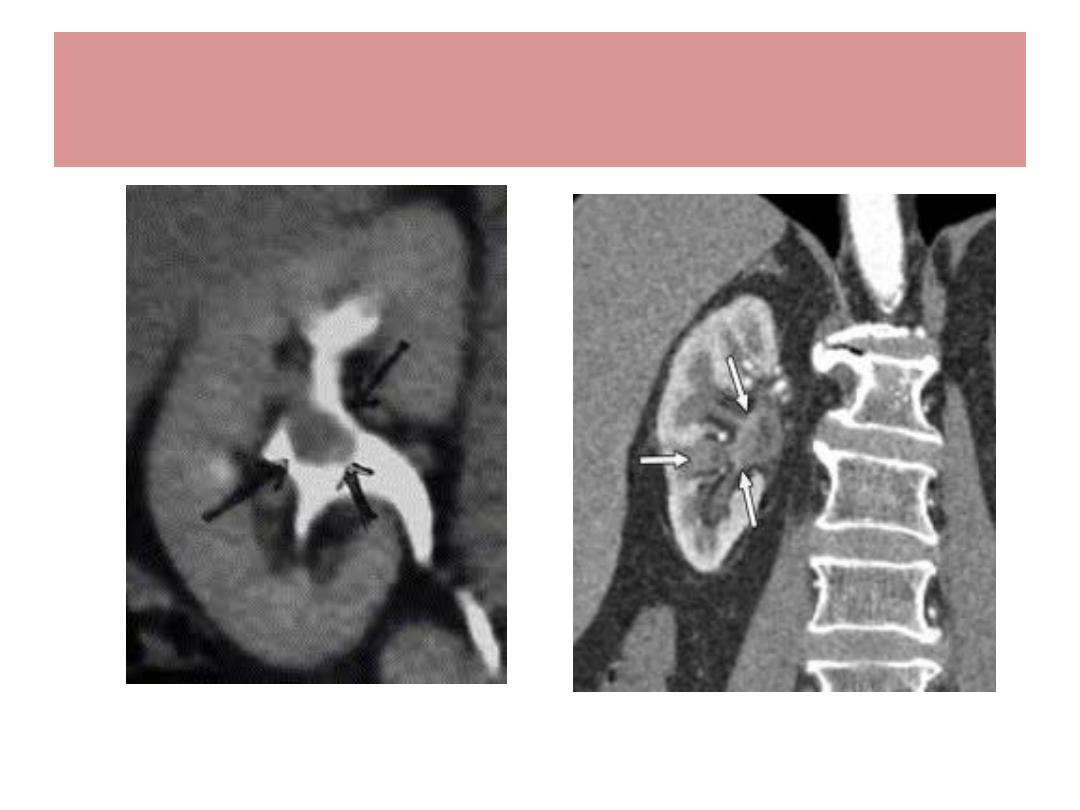
Transitional cell Ca. of renal pelvis

TCC of Renal pelvis & ureter
Much less common than TCC of Bladder
Strong tendecy of tumor to be multifocal / ureter
Balkan nephropathy is a risk factor
Hematuria is the most common symptom
Ix : urine cytology, IVU , CT Scan , cystoscopy
About half of TCC of upper UT ( pelvis, ureter ) will
have tumours in Bladder
Treatment : Nephro-ureterectomy
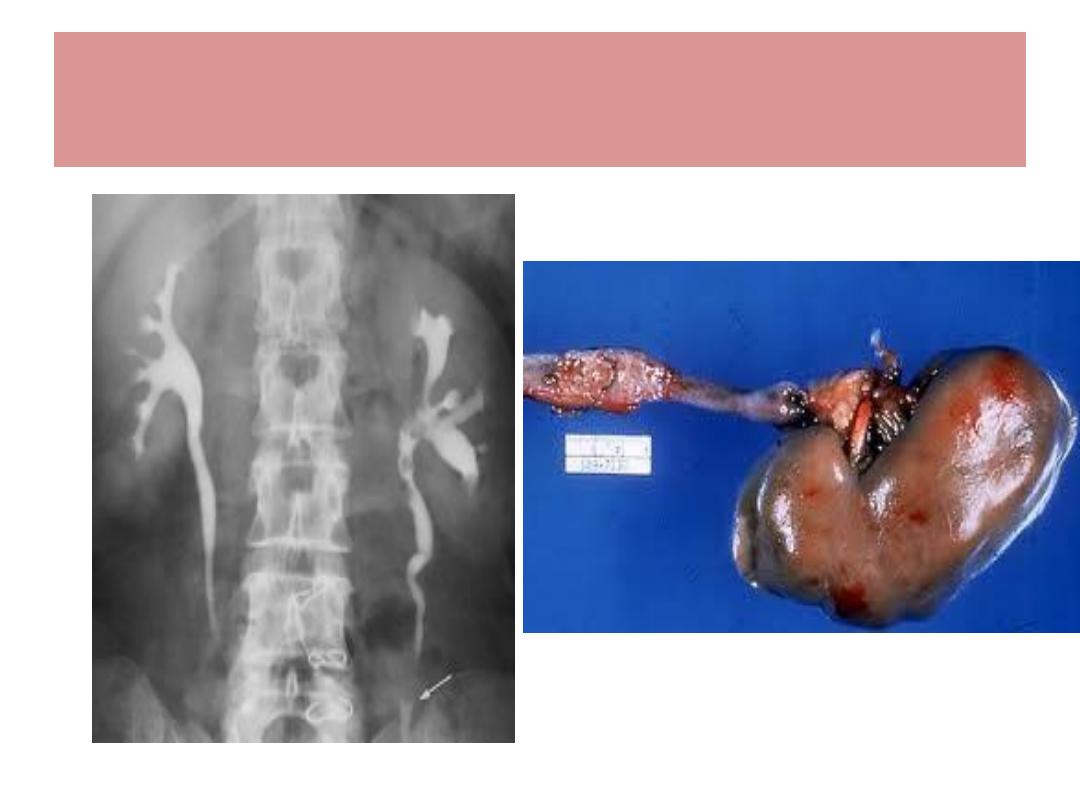
TCC of Ureter

Squamous cell Ca. of renal pelvis
Rare tumour
Often ass. With chr. Inflamm./leucoplakia
resulting from stones
Radio-sensitive
Early metastasis / poor prognosis

Thank you
