Fifth stage
MedicineLec-2p1
د.فاخر
30/10/2016
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
Definition
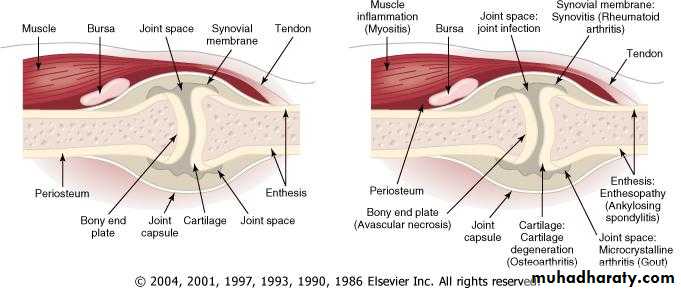
Chronic systemic inflammatory disorder affected synovium bone, cartilage, ligaments with extra-articular manifestationsRA is a chronic disease that leads to joint damage within the first 2 years, causes marked functional limitation and a 30% loss of work within the first 5 years, and shortens life by 5 to 7 years.
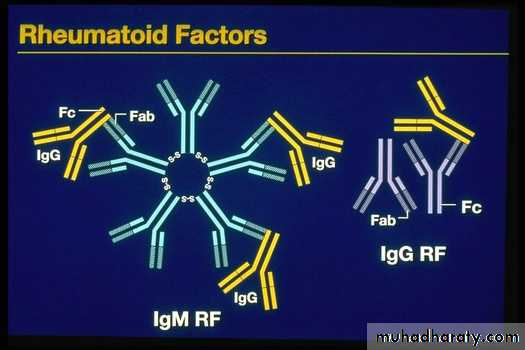
Rheumatoid factor (RF)
an immunoglobulin M (IgM) auto-antibody against the Fc portion of an IgG molecule first described by Waaler in 1940, is the main serologic marker, found in 75% to 80% of patientsEpidemiology
RA occurs throughout the world and in all ethnic groups. The prevalence is lowest in black Africans and Chinese, and highest in the Pima Indians of Arizona. In Caucasians it is around 1.0-1.5% with a female:male ratio of 3:1. Before the age of 45, the female:male ratio is 6:1. Prevalence increases with age, with 5% of women and 2% of men over 55 years being affected.Etiology
Genetic factors:in RA are important in defining disease susceptibility and severity
Family studies have demonstrated an increased risk for disease in siblings of persons affected with RA. Concordance in monozygotic has been found to be 12% to 15% and 4% in dizygotic twins strong evidence for a major influence of genetic factors in disease causation
Enviromental:
viruses (e.g., parvovirus B19, Epstein-Barr virus)
Mycoplasma, and other bacteria (e.g., streptococci).
Possible auto-antigens include type 2 collagen proteoglycan
Chondrocyte antigens, heat shock proteins.
Urbanization :has a major impact on incidence & severity of R.A.
cigarete smoking
Histopathology
In the early months of RA, edema, angiogenesis, hyperplasia of synovial lining, and inflammatory infiltrate are already present. Once the disease enters a more chronic phase, massive hyperplasia, mainly of type A synovial cells, and subintimal mononuclear cell infiltrationThe synovium of RA assumes the appearance of a reactive lymph node because of the extensive infiltration by plasma cells, macrophages, and lymphocytes in the form of large lymphoid follicles.
One characteristic feature of RA is the invasion of and damage to cartilage, bone, and tendons by an infiltrating inflammatory synovial tissue mass called the pannus
Clinical Characteristics of Rheumatoid Arthritis
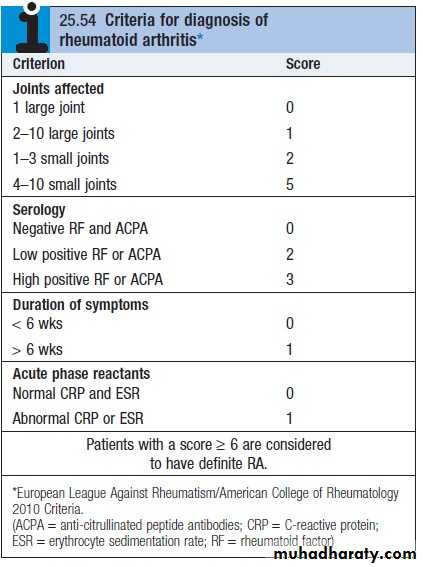
Diagnosis of RA is made with four or more of the following
Morning stiffness (> 1 hour)
Arthritis of three or more joint areas
Arthritis of hand joints
Symmetrical arthritis
Rheumatoid nodules
Rheumatoid factor seropositive (rheumatoid factor positive )
Radiological changes
Duration of 6 weeks or more
Joints Affected :
Typically involves elbows, wrists, MCP, and PIP joints1st & 2nd cervical vertebrae frequently involved
Unaffected joints :
Thoracolumbar spine, DIPs & SI joints
Rheumatoid Arthritis: PIP Swelling
Swelling is confined to the area of the joint capsuleSynovial thickening feels like a firm sponge
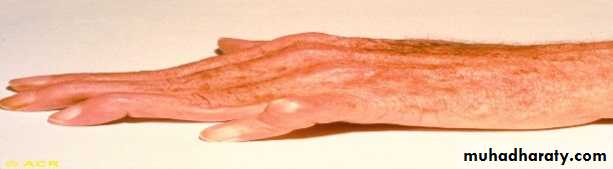
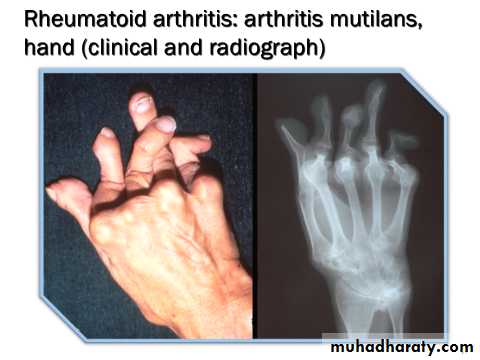
Rheumatoid HAND
An across-the-room diagnosis
Prominent ulnar deviation in the right hand
MCP and PIP swelling in both hands
MCP sublaxation
Synovitis of left wrist
Rheumatoid arthritis: swan-neck and boutonnière deformity, hand-----------------------------------------------
Nonreducible flexion at the PIP joint with concomitant hyperextension of the DIP joint of the finger (boutonniere deformity, occurs as a consequence of synovitis with stretching of, or rupture of, the PIP joint through the central extensor tendon with concomitant volar displacement of the lateral bands.
Hyperextension at the PIP joint with flexion of the DIP joint (swan-neck deformity, may be initiated by disruption of the extensor tendon at the DIP joint with secondary shortening of the central extensor tendon and hyperextension of the PIP joint,
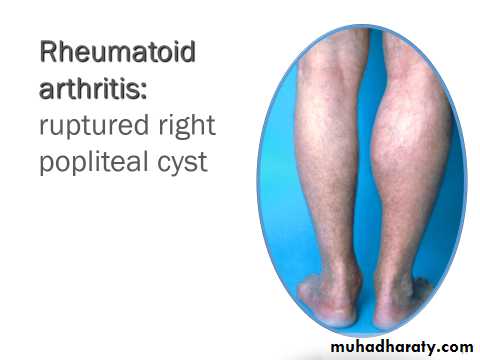
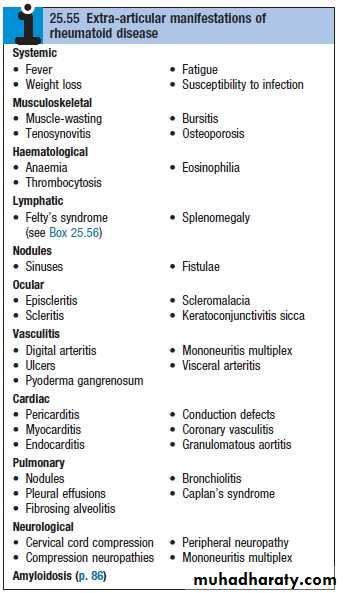
EXTRA-ARTICULAR MANIFESTATIONS OF RHEUMATOID DISEASE
HaematologicalAnaemia
Thrombocytosis
Eosinophilia
Lymphatic
Splenomegaly
Felty's syndrome
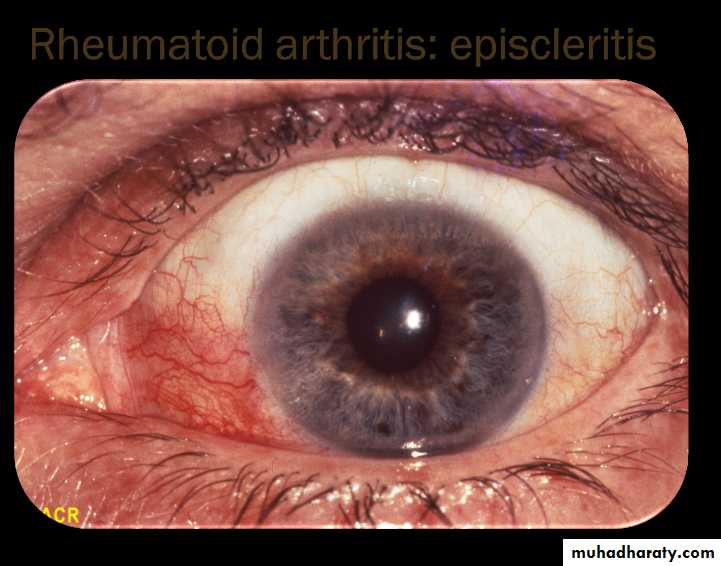
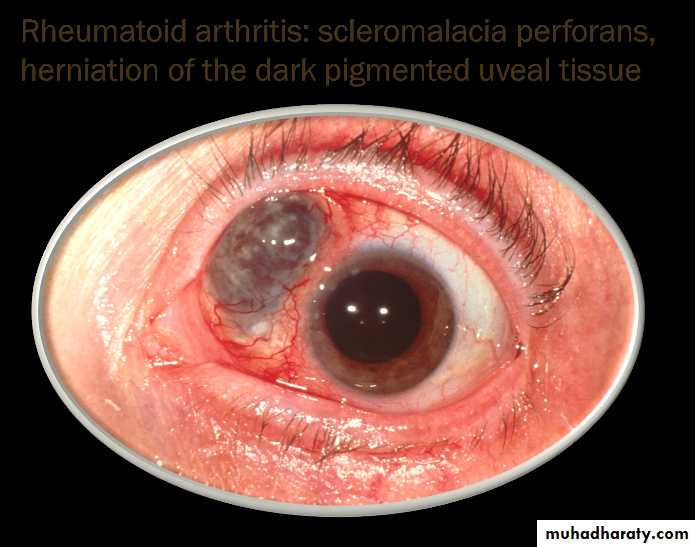
Ocular
Eapiscleritis
Scleritis
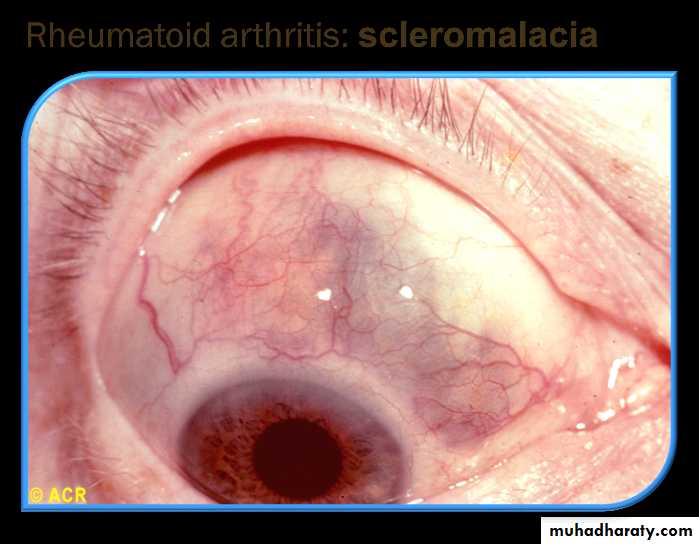
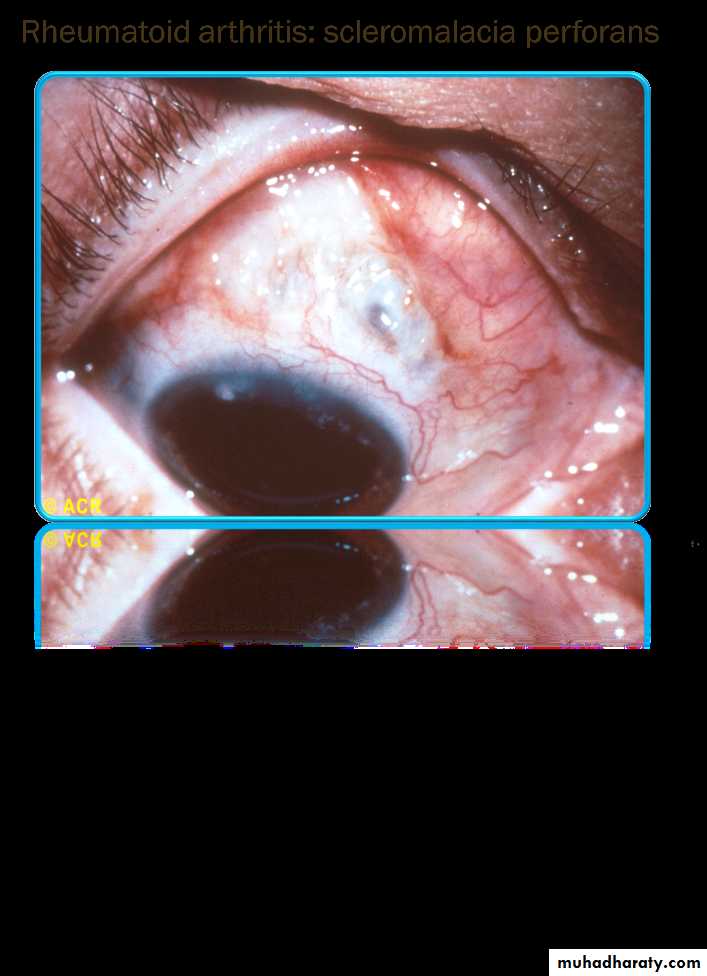
Scleromalaciaa
Keratoconjunctivitis sicca
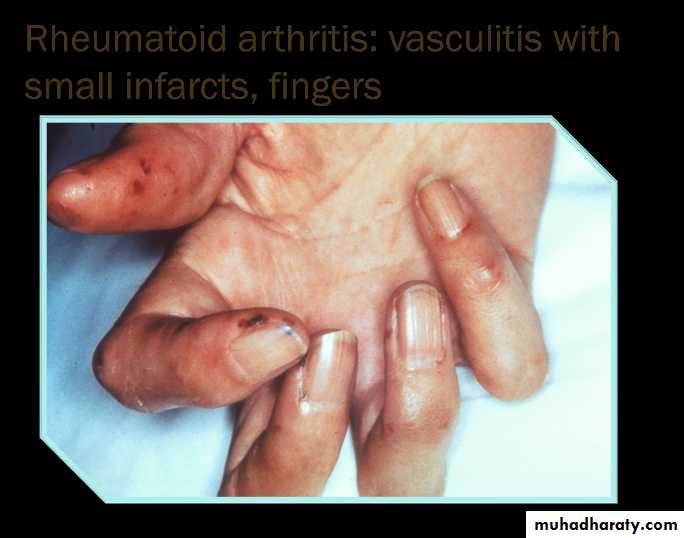
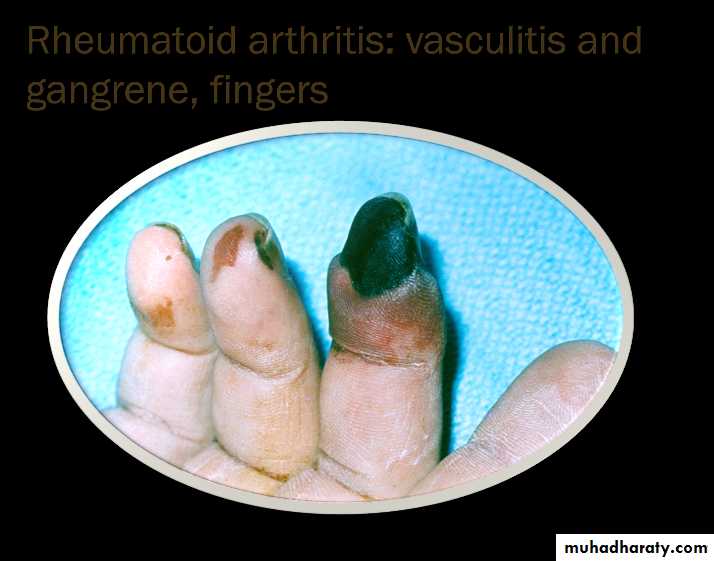
Vasculitis
Digital arteritis
Ulcers
Pyoderma gangrenosum
Mononeuritis multiplex
Visceral arteritis
Cardiac
Pericarditis
Myocarditis
Endocarditis
Conduction defects
Coronary vasculitis
Granulomatous aortitis
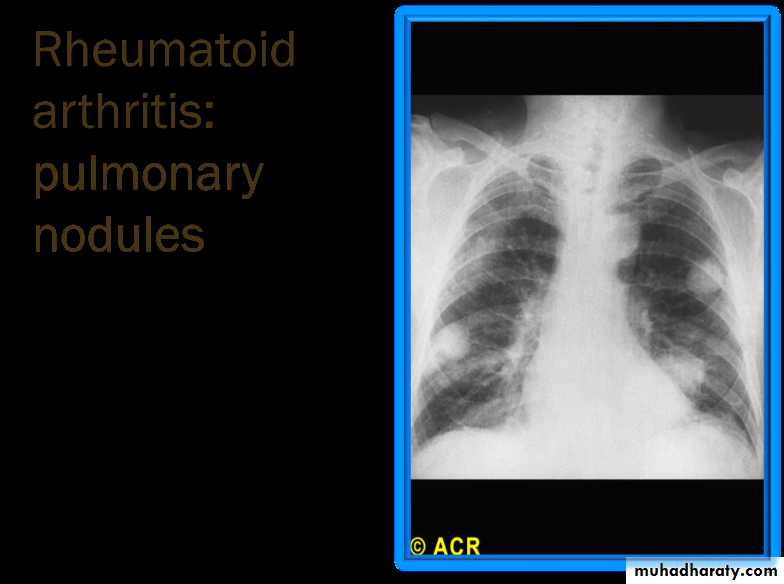
Pulmonary
Nodules
Pleural effusions
Fibrosing alveolitis
Bronchiolitis
Caplan's syndrome
Neurological
Cervical cord compression
Compression neuropathies
Peripheral neuropathy
Mononeuritis multiplex
Cutaneous features
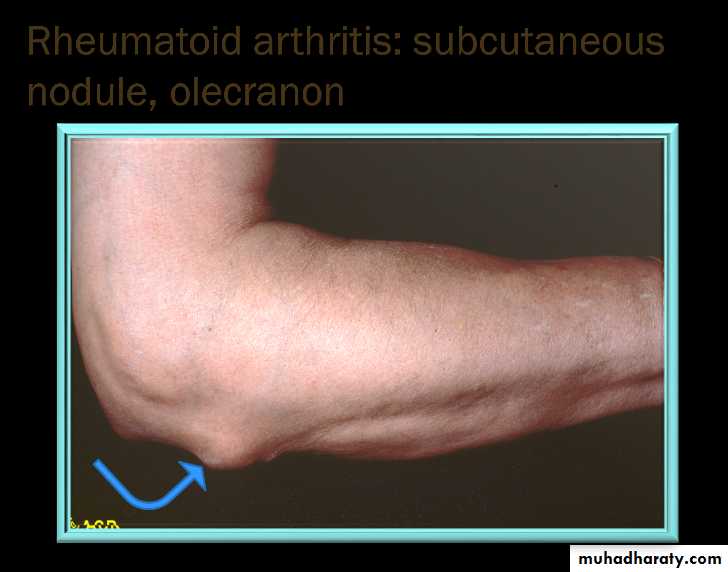
Subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules occur almost exclusively in seropositive patients, usually at sites of pressure or friction such as the extensor surfaces of the forearm, sacrum, Achilles tendon and toes
Laboratory Tests
Raised inflammatory markers . Reasonable correlation with clinical activityMild anemia & thrombocytosis
S. Rheumatoid factor (Agglutination method). Positive in near 70-80% cases (western countries). Not specific
Anti-CCP (citrulline – containing proteins) antibodies. Similar sensitivity to RF but more specific (up to 95%)
Examination of joint fluid
the most helpful laboratory procedure. The fluid is inflammatory, with more than 10,000 white blood cells and a predominance of polymorphonuclear leukocytes, typically 80% or more. Rheumatoid factor, an IgM antibody directed to IgG, is found in 80 to 90% of patients with RA... HYPERLINK "mk:@MSITStore:F:\\Cecil%20essentials%20of%20medicine%206th%20edition.CHM::/www.studentconsult.com/content/bookcontent.cfm@id=hc078004.htm"
XR-Findings
Peri articular osteopeniaMarginal erosions (at least months of persistent activity)
Joint space narrowing (cartilage loss)
Ankylosis (wrists)
Deformities
Joint damage progression in R.A. hand
Soft-tissue swelling, no erosionsThinning of the cortex on the radial side and minimal joint space narrowing
Marginal erosion at the radial side of the metacarpal head with joint space narrowing
Prognosis
The following factors at presentation are associated with a poor prognosis: higher baseline disabilityfemale gender
involvement of MTP joints
positive rheumatoid factor
disease duration of over 3 months.