Root Canal Obturation Techniques
معالجة \ اسنان خامسد. معتز (م2)
15\12\2016
Aims and objectives of obturation
To establish barrier to passage of microorganisms from the oral cavity to the periradicular tissue.To entomb and isolate any microorganisms that may survive the cleaning and shaping process.
To prevent leakage into the canal system of potential nutrients that would support the microbial growth.
To reduce the risk of bacterial movement or fluid percolation into the canal system space from the gingival sulcus or periodontal tissue.
Trial filling
Satisfactory trail filling:Master points should be insert up to the working length .
Tug-back action should be felt.
At the working length:
No tug-back action.
Go for larger point.
Tug back action:
Before the working length.
Enlarge the canal using master file.
Which canal is ready for obturation
• Absence of pain.• Absence of swelling.
• Absence of persistence exudates in the canal.
• Thoroughly debrided root canal system.
• Adequate time to complete the procedure.
Completion of procedure on the same day
• Immediately after the preparation, canal system is cleaner than any other time and clinician is more familiar with canal system.• temporary restoration leakage and potential recontamination minimum.
• Less opportunity to fracture because definitive restoration can be placed earlier.
• Financial and time saving.
• Patient who need antibiotic cover are particularly beneficial.
The ideal root canal material
• Induce or support regeneration of support tissues.• Be antimicrobial & radiopaque.
• Nontoxic & nonirritant to the periradicular tissue.
• Be adhesive and easily adapted to canal walls.
• Have good handling & flow characteristics.
• Non stain dentine.
• Be impermeable to tissue fluids.
• Be dimensionally stable.
• Be cheap & have long shelf life.
• Reinforce and strengthen the root structure.
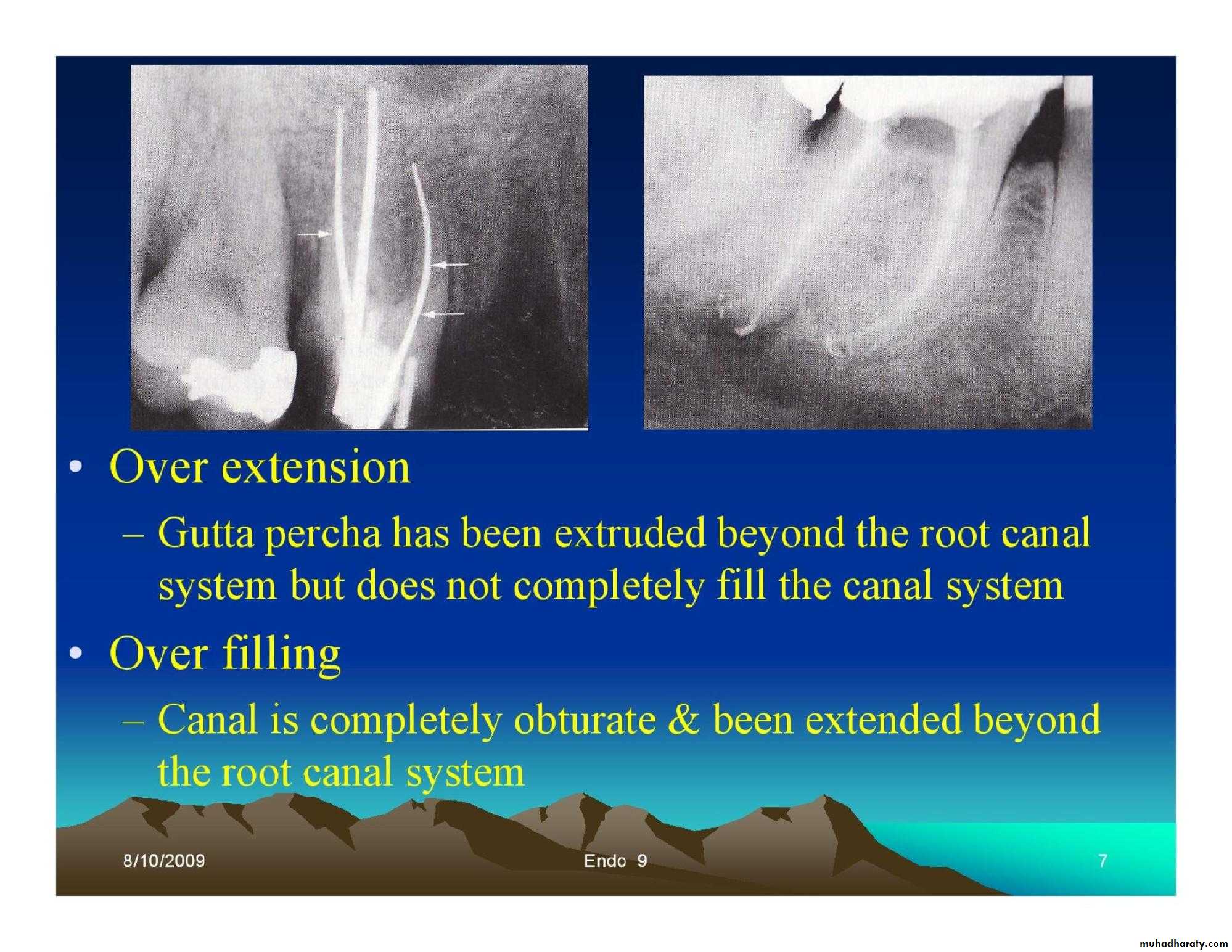
Over extention:
Gutta percha has not been extruded beyond the root canal system, but does not completely fill the canal system.
Over filling:
Canal is completely obturate & been extended beyond the root canal system.
Gutta-percha points
• Gutta percha 19-22%• Zinc Oxide 59-75%
• Metal sulphates 1.5-17%
• Waxes 1-2%
• Resins 1-2%
Root canal sealers
• Biocompatible.• Adhere to canal walls.
• Impermeable to tissue fluids.
• Dimensionally stable.
• Antiseptic.
• Not discolor to the tooth.
• Easily manipulated.
• Radiopaque.
• Should fill the discrepancies.
• Should lubricate GP.
Root canal sealers
• ZnO/E based cements-Roths.
• Ca(OH)2 dased cements-apexit.
• Resin based cements-AH26.
• Silicone based cements-lee Fndofill.
• GIC based cements-Ketac Endo.
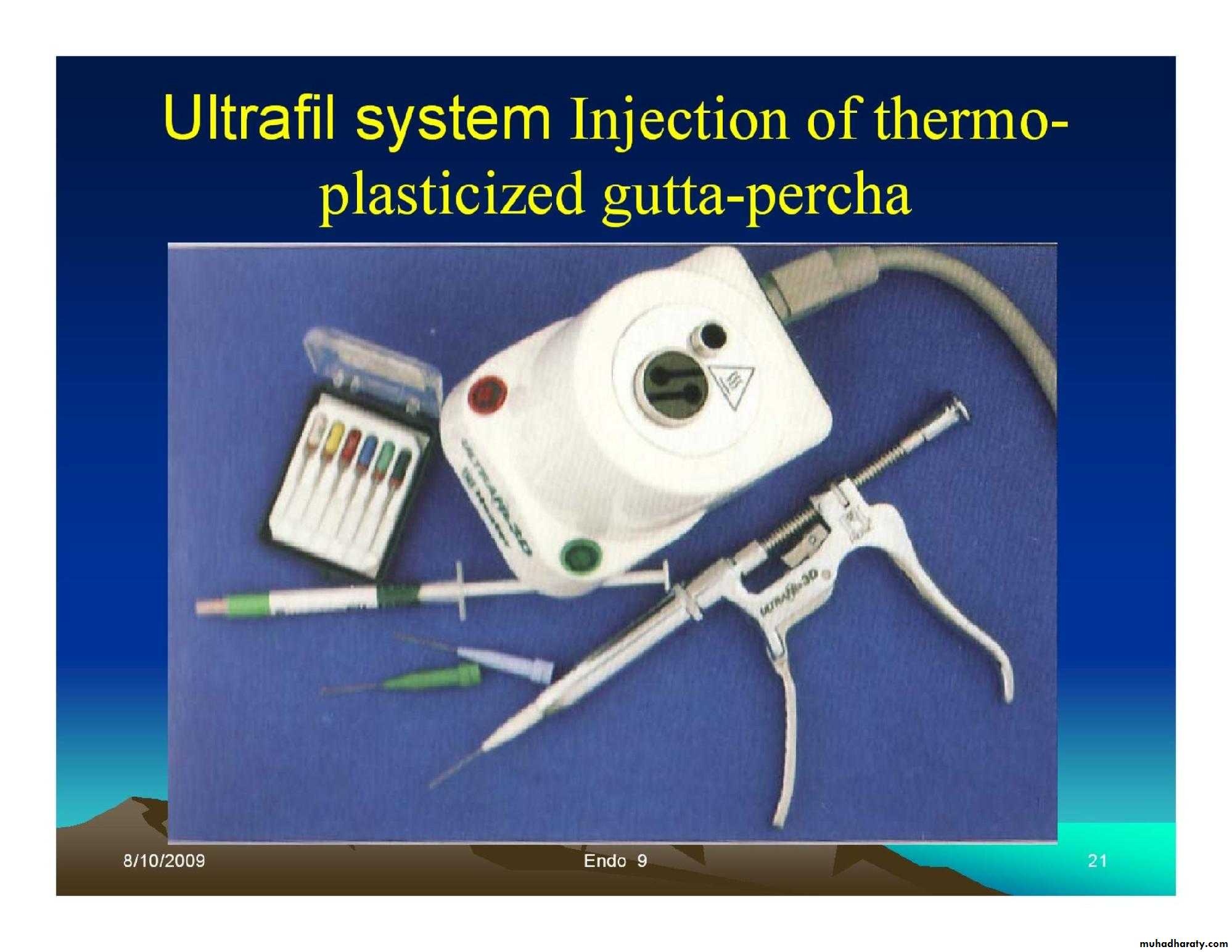
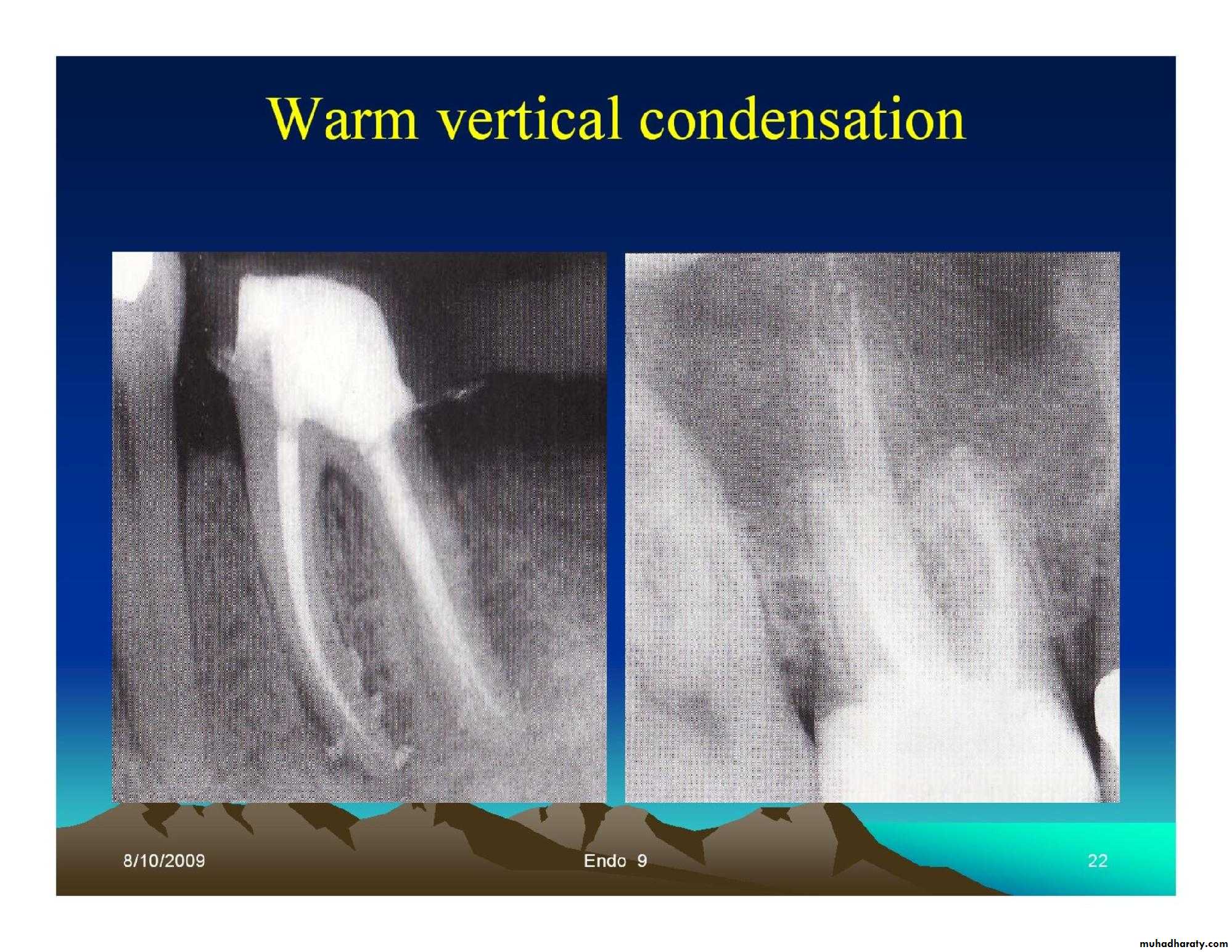
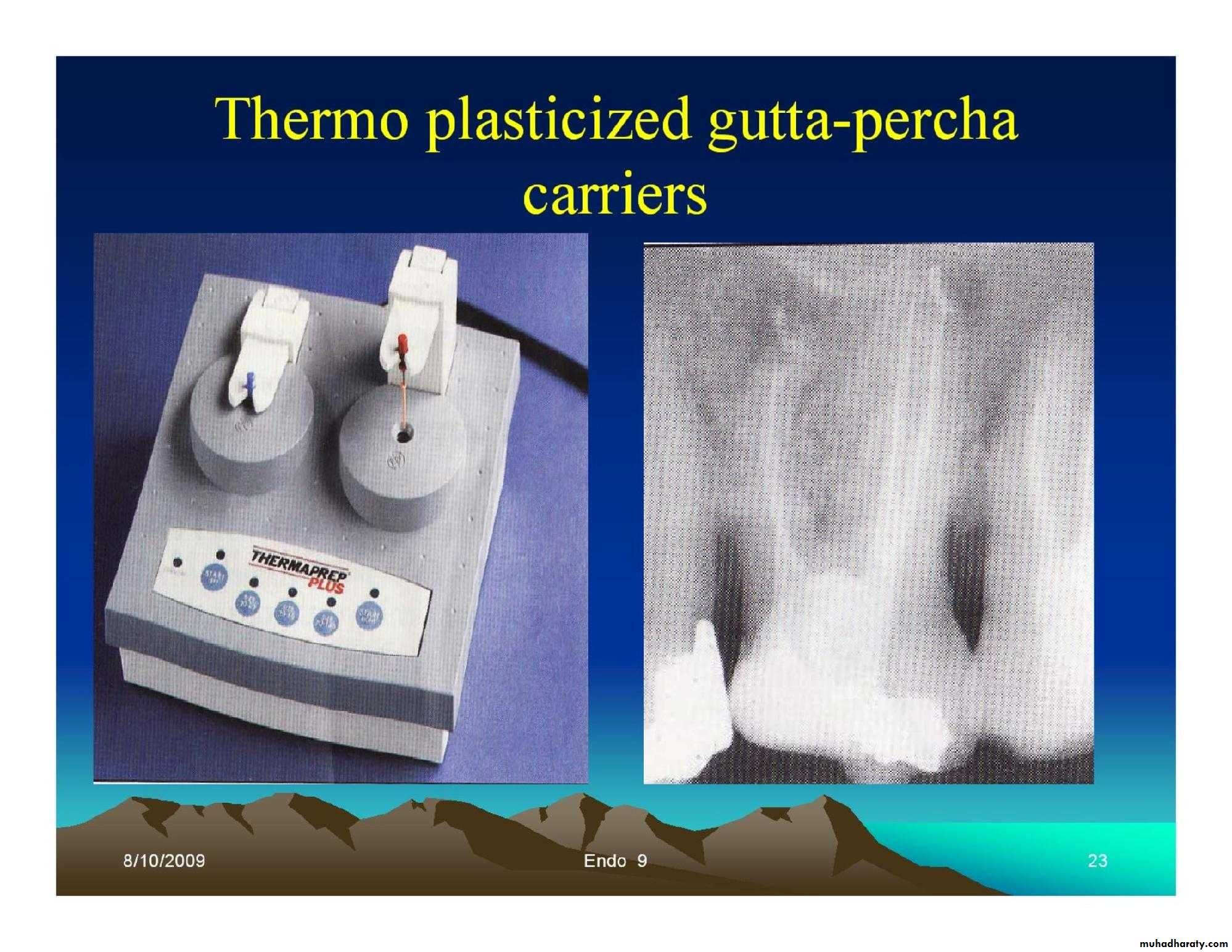
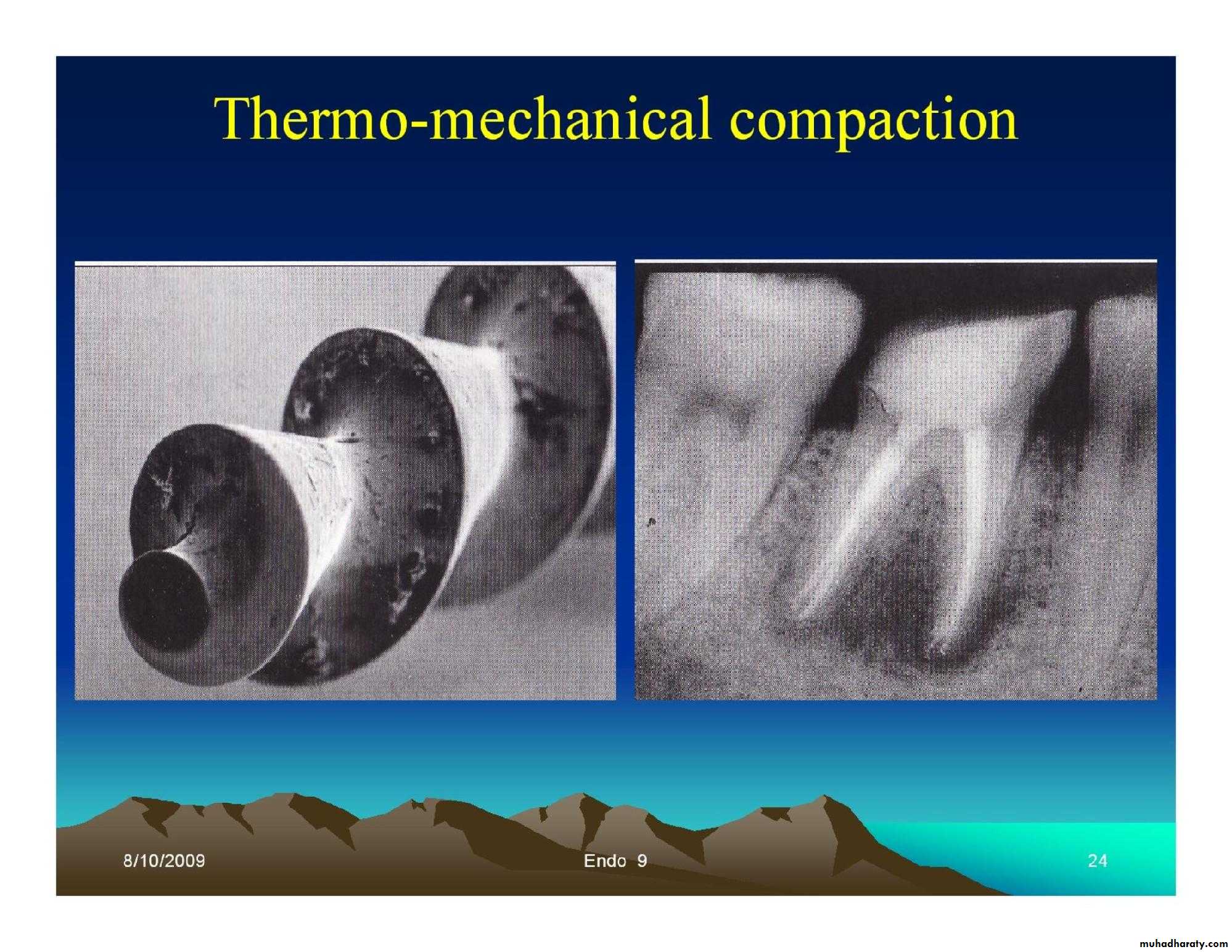
Obturation techniques
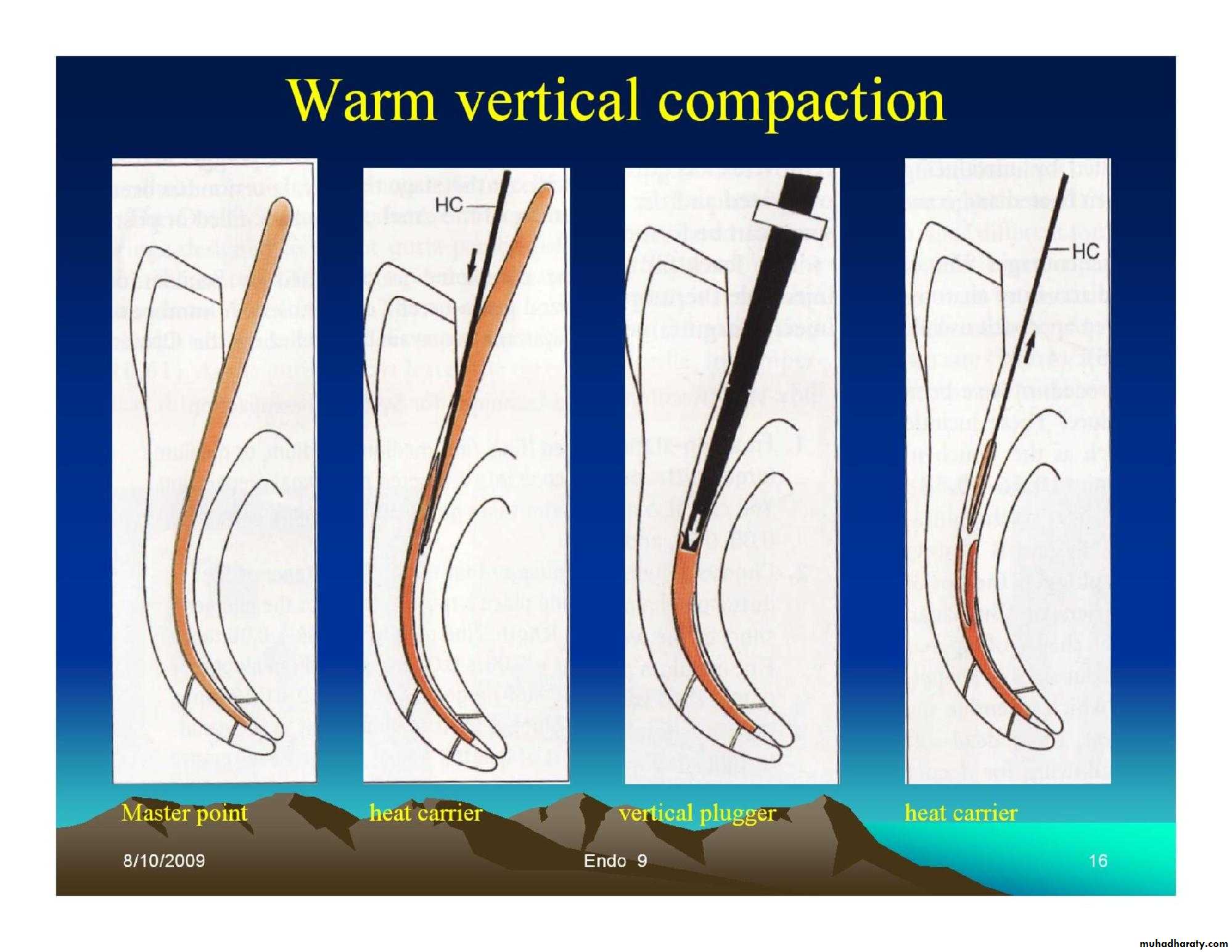
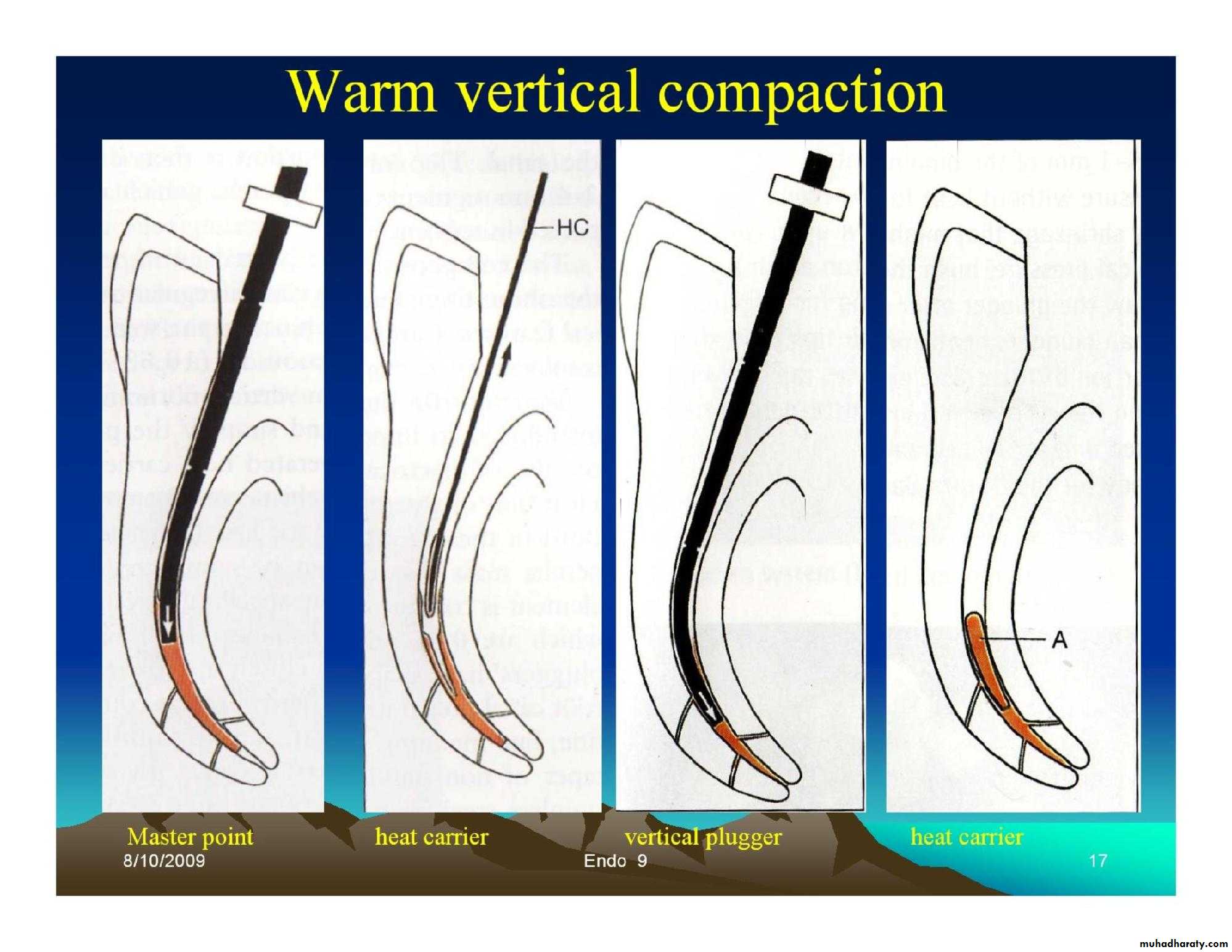
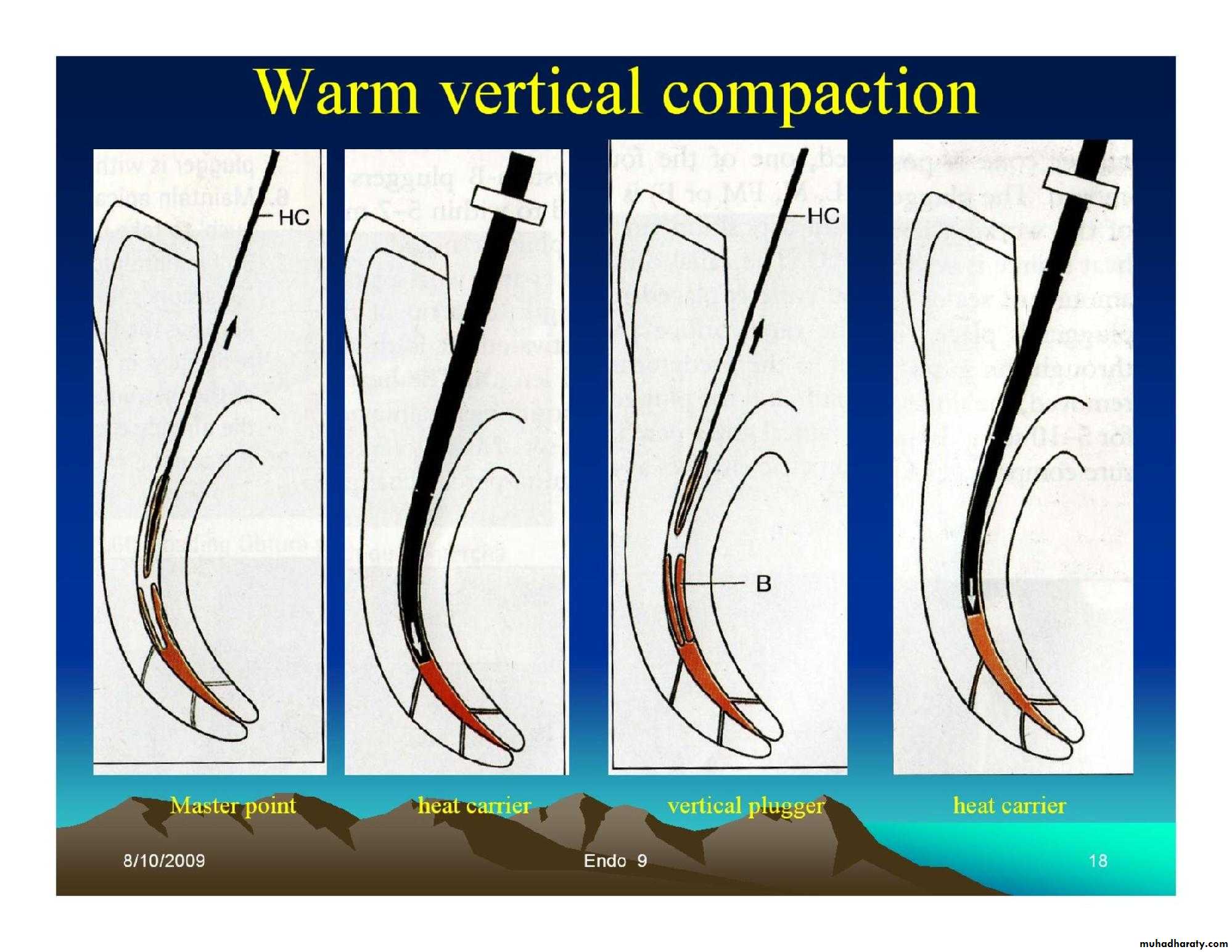
• Lateral condensation.• Warm vertical condensation.
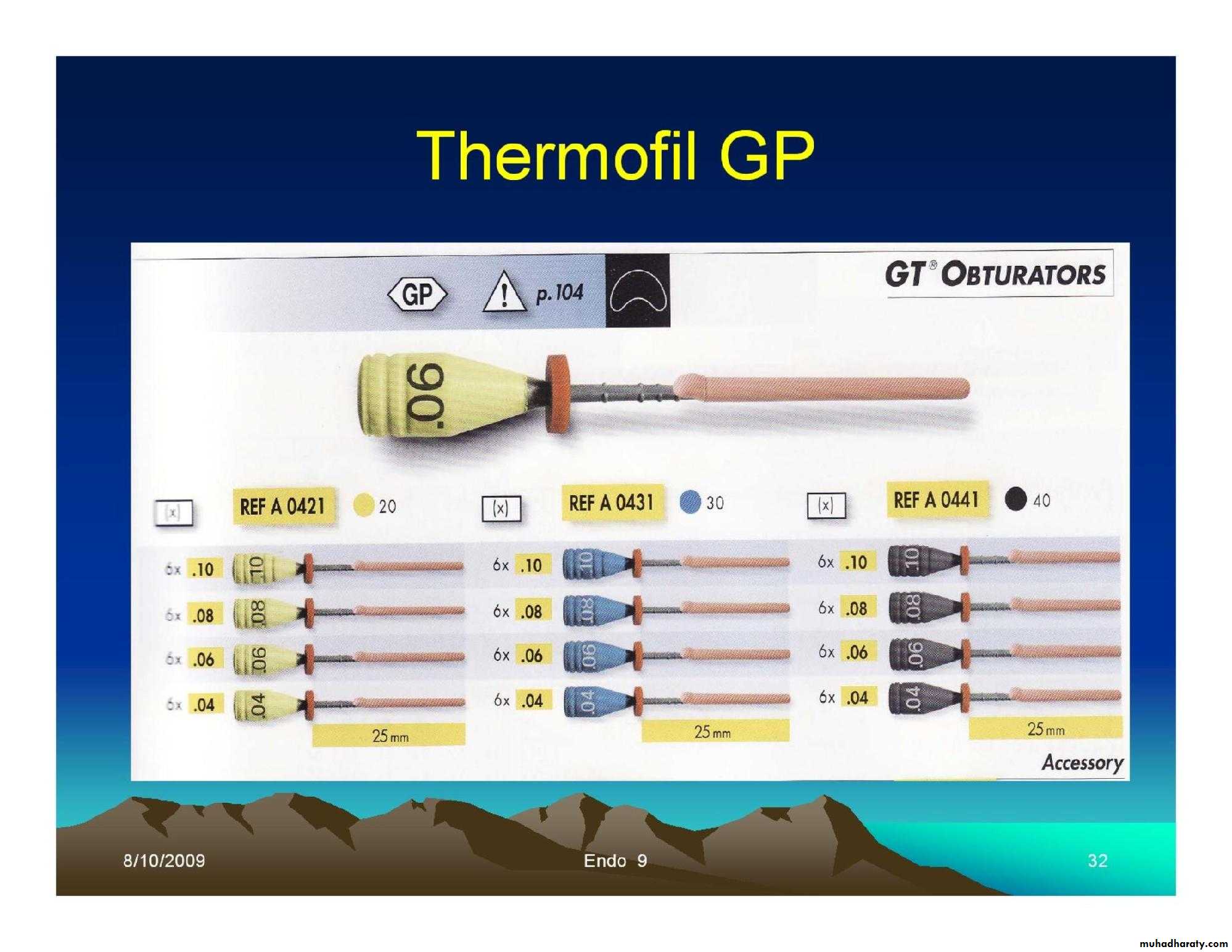
• Thermo-plasticized Gutta-percha carriers.
• Thermo-mechanical compaction.
• Injection of thermo-plasticized Gutta-percha.