
Lec 1 : Computer Basics
Learning objectives
• Understand the purpose and elements of
information systems
• Recognize the different types of
computers
• Distinguish the main software types
• Identify the components of a computer
system

Understanding Information
Systems
An
information system
is a complete interconnected environment in which
raw data—quantifiable facts and figures—is turned into useful information. An
information system includes the following parts:
people, hardware, software,
procedures, and data
.
People: If you think about it, the only reason computers exist is to help
people accomplish their goals. Therefore when planning an information
system, it’s critical to understand what the people hope to get out of it. Do
they need certain information? Do they need for the computer to activate a
device that performs a task? Are they looking to be entertained or
educated? The first step in planning an information system is to analyze the
requirements of the people.

information syst
Hardware: When most people think of computers, they immediately think of
hardware, the physical parts of the computer system. The hardware includes circuit
boards with silicon chips and transistors mounted on them, input devices like
keyboard and mouse, and output devices like printers and monitors.
Software
: Computer hardware just sits there idle unless it has software, which is a
program that tells the hardware what to do. There are many different levels of
software, including the operating system (like Windows or Mac OS) and
applications (like a word processing or accounting program).
Procedures: The software doesn’t run itself (usually). People must interact with
the computer to tell it what software to run. For example, before you can write
checks with your accounting software, you must start up the software, open the file
that stores The data for the business, and issue the command that opens the
checking account register. You can learn procedures from the online Help system in
the application, from a printed user manual, from a training class, or by trial and
error.

information syst
Data: Computer programs operate upon the data they receive. For example,
in your accounting software, you enter data about the checks you are
writing—the date, the amount, the recipient—and the program stores that data
so you can recall it later.

Identifying Computer Types
• As you learned in the preceding section,
hardware is the physical part of the computer
system. Hardware consists of components
inside a computer as well as the external
devices that interact with it, such as printers,
cables, and monitors.
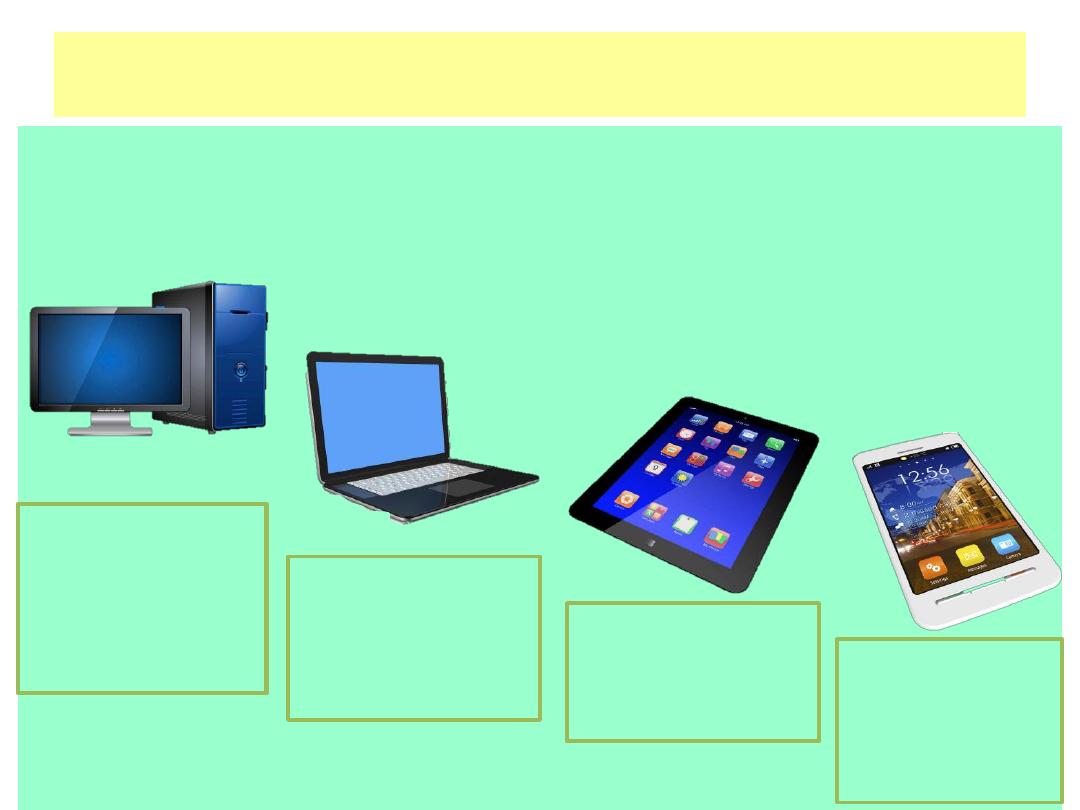
Computer Types
Personal Computers :This type of computer is called
personal because it is
designed for only one person to use at a time. Personal computers fall into
several categories that are differentiated from one another by their sizes. The
most common sizes are:
Desktop PC
A
computer designed to
be set up at a desk and
not often moved, with
input and output devices
separate from the
system unit.
notebook PC
A portable
PC here the screen and
keyboard fold up against
one another for storage
and transport; also
known as a laptop.
tablet PC
A lightweight
slate-style computer
with a touch screen,
designed for easy
portability.
smartphone
A cellular
phone that includes
computer
applications and
Internet
access capability.

Computer Types
Multi-User Computers: Multi-user computers are designed to serve
groups of people, from a small office to a huge international
enterprise. Here are some common types of multi-user computers:
Server: A computer that to performing network tasks such as managing
files, printers, or email for multiple users.
Mainframe: A large and powerful computer capable of serving many
users and processing large amounts of data at once.
supercomputer The largest and most powerful type of computer,
surpassing the capability of a mainframe, typically used in research and
academics.
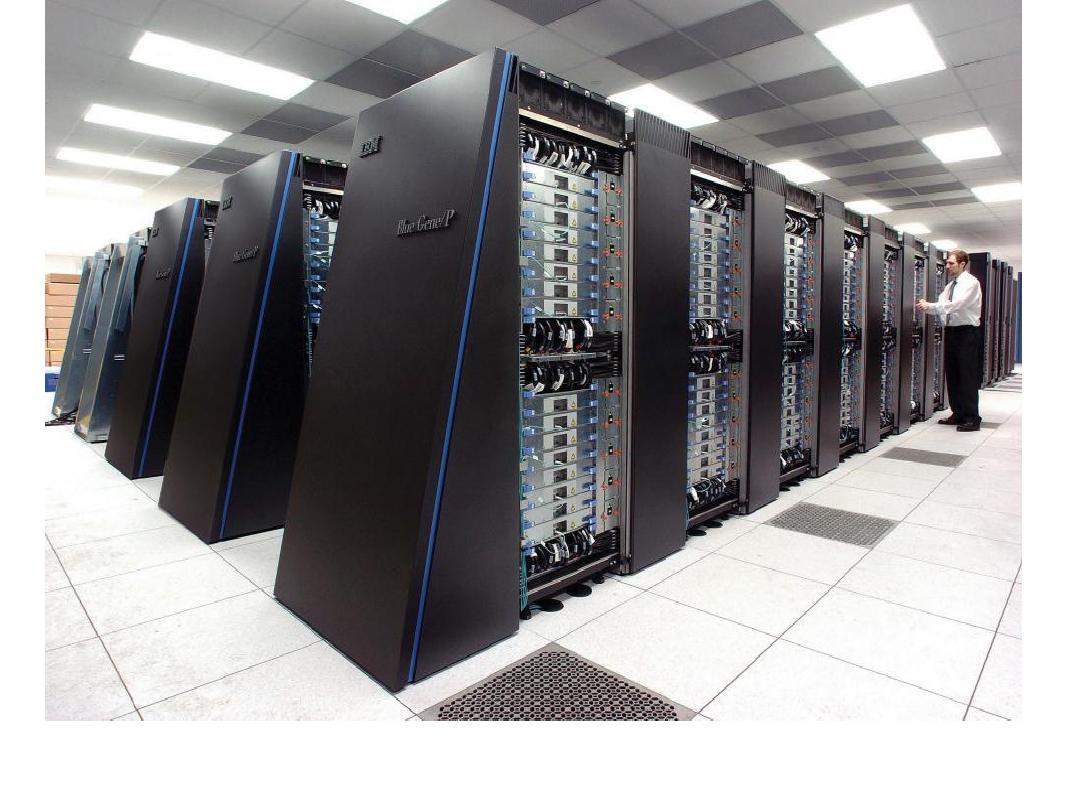

This IBM Blue Gene/P supercomputer is located at the Argonne National
laboratory in Lemont, Illinois, USA.

Understanding Software Types
Software tells the hardware what to do, but different kinds of software accomplish that
at different levels. The following sections provide an overview of the types of software
a computer might include.
BIOS : The most basic software is the Basic Input Output System (BIOS). This
software is stored on a read-only chip on the motherboard so that it
doesn’t
accidentally get changed or corrupted. This important software helps the
computer start up and performs some basic testing on the hardware.
Operating Systems : The operating system (OS) manages all the
computer’s
activities after startup. The operating system serves several purposes:
1. It provides the user interface that humans use to communicate commands and receive
feedback.
2. It runs applications, and enables humans to interact with them.
3. It controls and manages the file storage system.
4. It communicates with the hardware, instructing it to take action to accomplish tasks.
For example, the OS tells the printer to print a document, and tells the monitor what
image to display.

Microsoft Windows is the most popular operating
system interface. Other operating systems
include Mac OS and Linux for desktop and
notebook PCs, UNIX for mainframes and servers,
and Android for tablets and smartphones. Each
operating system has its own unique set of
features, benefits, and drawbacks, so it pays to
learn as much as you can about the operating
systems available and choose a computer that
will run the operating system that best fits your
needs
Understanding Software Types

utility software: software that performs some useful service to the
operating system, such as optimizing or correcting the file storage
system, backing up files, or ensuring security or privacy.
Application software is software that is designed to do something
productive or fun, something of interest to a human user. The OS
keeps the computer running, but the applications give people a
reason to use the computer.
Understanding Software Types
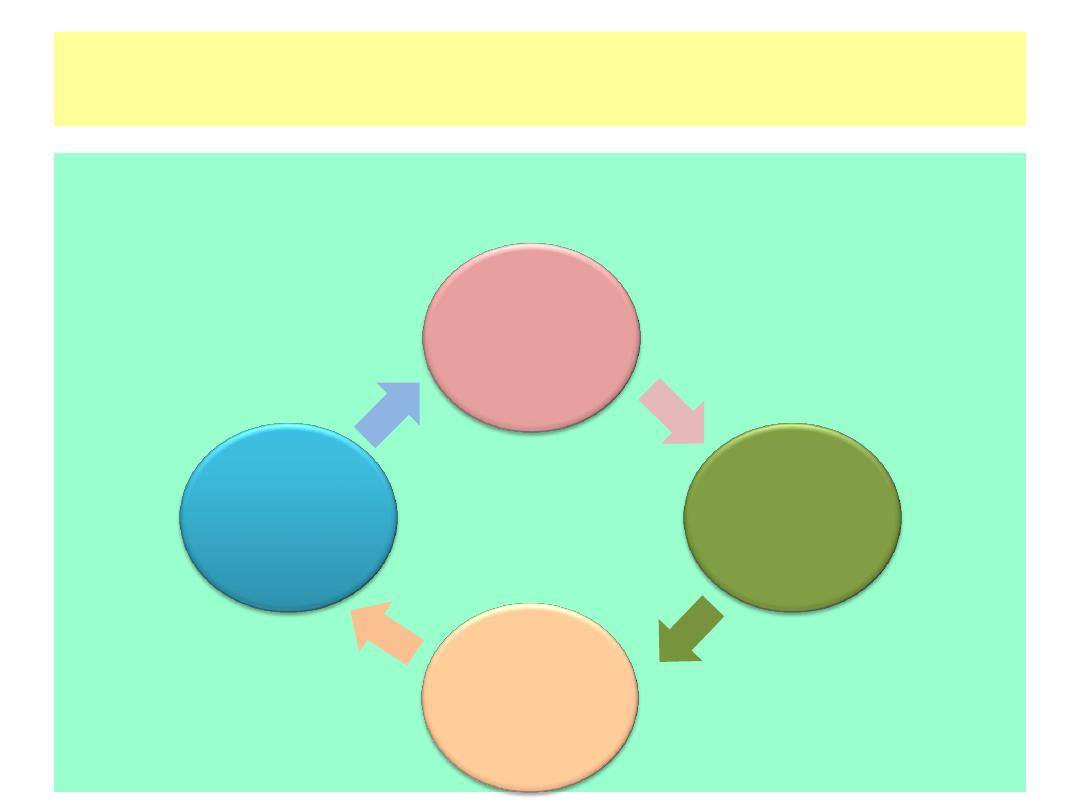
Computer System Components
Every computer system is made up of multiple electronic components. These
components fall into four broad categories that serve different purposes in the
information processing cycle.
Processing
Output
Storage
Input

Computer System Components
Input: Components that help humans put data into the computer.
Examples include a keyboard, mouse, and touch screen.
Processing: Components that move and process the data inside the
computer. The motherboard and its processor and memory chips fall
into this category.
Output: Components that provide the results of the processing to
humans. The monitor is the primary output device; other examples
include printers and speakers.
Storage: Components that store software and data until it is needed.
Storage components include hard drives, USB flash drives, and DVDs.
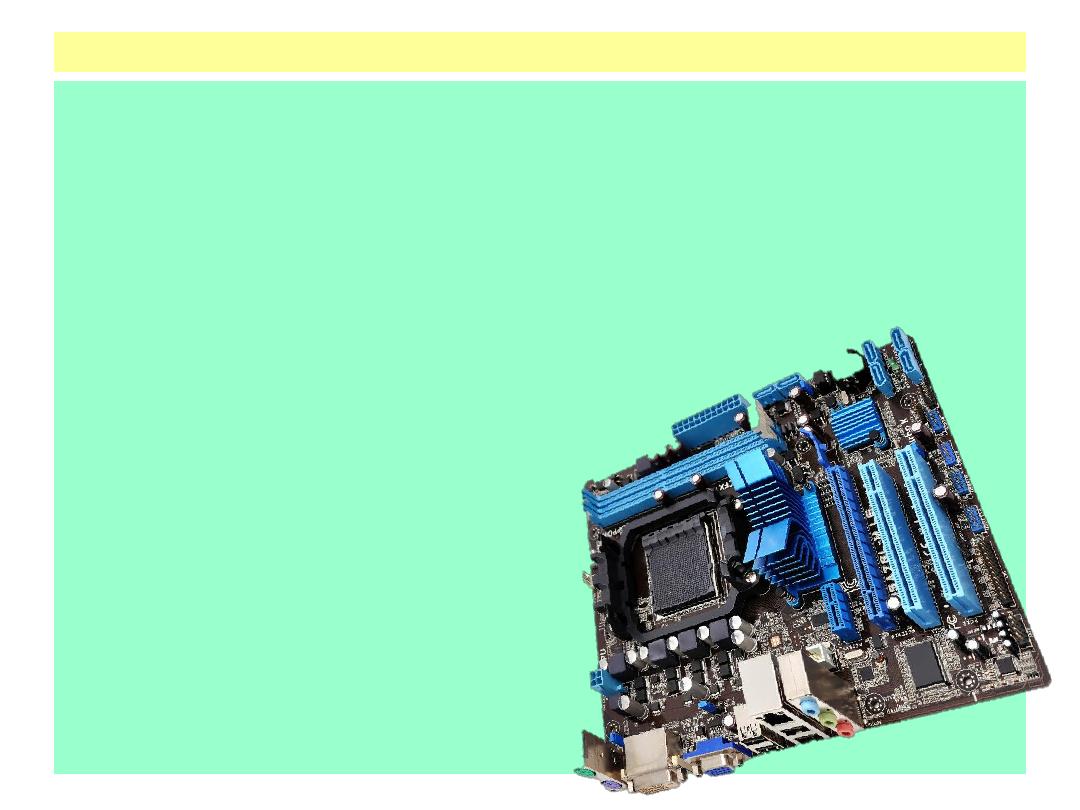
Computer System Components
Input Devices : An input device provides a way to get data into the computer. The
oldest and most common input device is a keyboard. A desktop PC has an external
keyboard, while a notebook PC has a built-in keyboard. Tablets and smartphones
have a software-based keyboard that pops up onscreen when needed. Computers
that use a graphical interface usually employ a pointing device. The pointing device
moves an on-screen pointer (usually an arrow) to align with objects onscreen, and
then the user presses a button on the pointing device to do something to the pointed-
at object. A mouse is the most common pointing device, but there are many other
types too, such as trackballs, touchpads, and touch-sensitive screens.
Processing Devices : The motherboard is the
large circuit board inside the computer that
everything else plugs into. The key
components located on the motherboard
are the processor (also called the Central
Processing Unit, or CPU) and the memory
(also called Random Access Memory, or
RAM). To support these components, the
motherboard has electrically conductive
pathways called buses that carry the data
from place to place, and a chipset, which
is a controller that directs the bus traffic.

Computer System Components
Output Devices : Information comes out of a computer through an output device such
as a monitor. When you move the mouse or type a character on a keyboard, you see
the results instantly on the monitor. The monitor helps you communicate with the
operating system; without the monitor, you
wouldn’t know if the OS had received and
understood your instructions or if the application had accepted the data you input.
Besides monitors, other output devices include printers (for producing hard-copy
output) and speakers (for providing audio feedback).
Storage Devices : Storage devices enable software and data to be preserved and
reused. Storage can be either removable or non-removable. (Non-removable storage
is actually removable too if you have the right tools and knowledge, but in this case
the distinction refers to being easily removable or not.) The most common type of
storage is an internal hard drive, which is a sealed metal box inside the system unit.
Hard drives are usually internal, making them non-removable. Some hard drives are
removable, though ; external hard drives easily connect to and disconnect from a
port on the outside of the system unit. Other removable storage devices include USB
flash drives and optical discs (CDs and DVDs).
