Second Week of Development:Bilaminar Germ Disc
Dr. Haythem Ali AlsayighMB.CH.B.-F.I.M.B.S.
Surgical clinical anatomy
Although the rate of development usually variable, the following major events could be approximately described:
Question 1
1. The second week of development is known as the week of twos.Formation of what structures supports this statement?
Question 2
2. During implantation, the trophoblast is invading maternal tissues, and because it contains approximately 50% paternal genes, it is a foreign body. Why is the conceptus not rejected by an immunologic response from the mother's system?Question 3
3. A woman who believes she is pregnant complains of edema and vaginal bleeding.Examination reveals high plasma human chorionic gonadotropin concentrations and placental tissue, but no evidence of an embryo.
How would you explain this condition?
Question 4
4. A young woman who has missed two menstrual periods complains of intense abdominal pain.
What might an initial diagnosis be, and how would you confirm it?
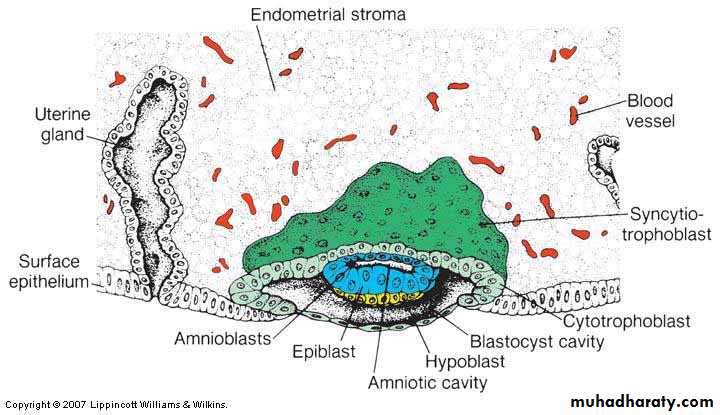
• DAY 8
• The blastocyste is partially embedded in the uterine mucosa. In the area over the embryoblast• DAY 8
• The trophoblast at the embryoblast form two layers;• Inner mononucleated cytotrphoblastic cells that divide by mitosis forming layer b.
• Outer multinucleated syncytiotrophblastic zone of fused cell losing their membrane, also called the syncytium.
DAY 8
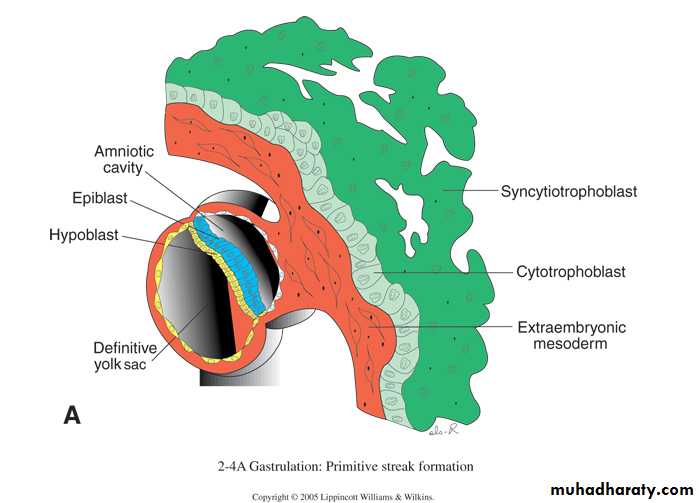
The inner cell mass cells (the embryoblast) forms the two layers of the bilaminar germ disc;a. small cubiodal hypoblastic cells near the blastocele.
b. high columnar epiblastic cells.The amniotic cavity develops between these cells.
DAY 8
Amniotic cavity is lined by the epiblast proper cells,The endometrial mucosa is edematous,
highly vascular, and secrete glycogen and mucus from its large glands. Epiblast cells adjacent to the cytotrophoblast are called amnioblasts; together with the rest of the epiblast, they line the amniotic cavityThe endometrial stroma adjacent to the implantation site is edematous and highly vascular. The large, tortuous glands secrete abundant glycogen and mucus.
Summary
human blastocyst, partially embedded in the endometrial stroma.The trophoblast consists of an inner layer with mononuclear cells, the cytotrophoblast,
and an outer layer without distinct cell boundaries, the syncytiotrophoblast.
The embryoblast is formed by the epiblast and hypoblast layers.
The amniotic cavity appears as a small cleft.
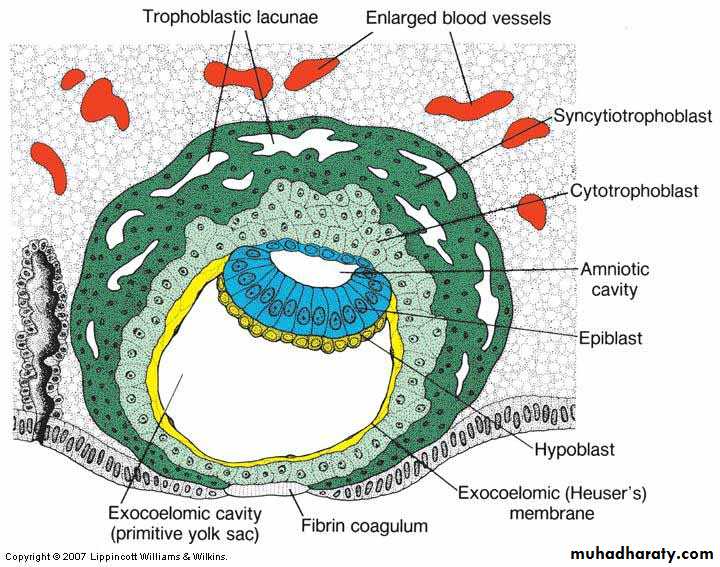
DAY 9
The blastocyst embedded more, the small defect closed by fibrin coagulum.SummaryA 9-day human blastocyst.
The syncytiotrophoblast shows a large number of lacunae.Flat cells form the exocoelomic membrane.
The bilaminar disc consists of a layer of columnar epiblast cells and a layer of cuboidal hypoblast cells.
The original surface defect is closed by a fibrin coagulum.
DAY 9
Vacules in syncytium, fusion form lacunae thus (lacunar stage) of development.DAY 9
Flat cells originate from the hypoblast forming theexocoelomic Heuser's membrane forming the exocoelomic cavity or called the primitive yolk sac.
1
DAY 11 & 12
1-The blastocyst is completely embeddeddefect is almost covered by the mucosal cells.
DAY 11 & 12
2-The blastocyst now produces a slight protrusion into the lumen of the uterusThe trophoblast is characterized by lacunar spaces in the syncytium that form an intercommunicating network.
This network is particularly evident at the embryonic pole; at the abembryonic pole, the trophoblast still consists mainly of cytotrophoblastic cells
S0
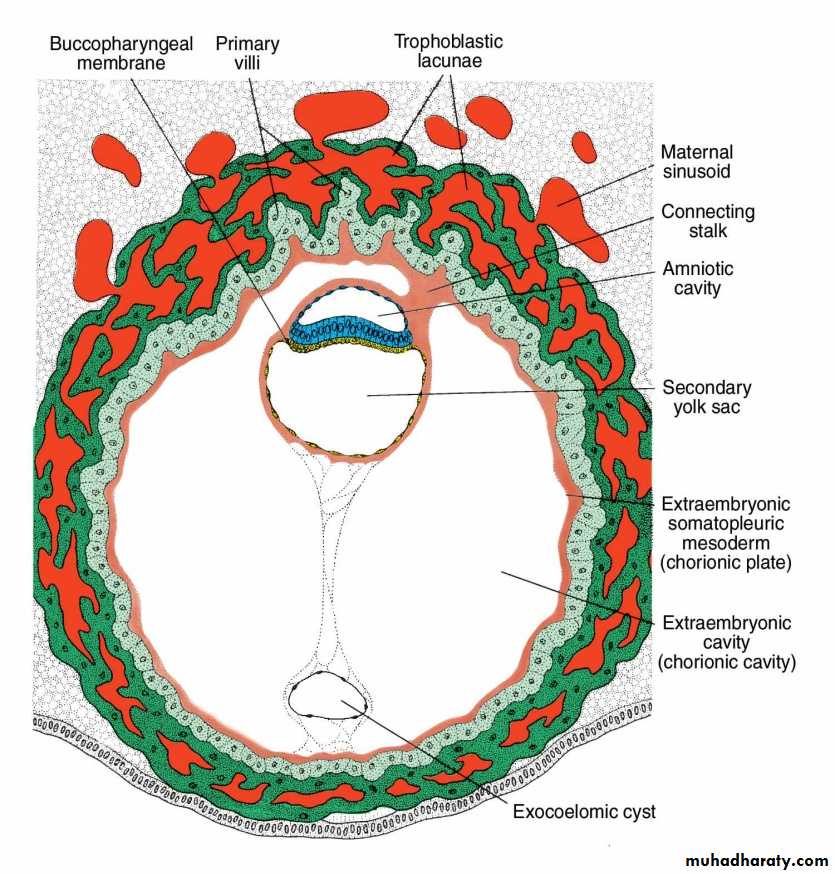
Human blastocyst of approximately 12 days.
The trophoblastic lacunae at the embryonic pole are in open connection with maternal sinusoids in the endometrial stroma.
Extraembryonic mesoderm proliferates and fills the space between the exocoelomic membrane and the inner aspect of the trophoblast.
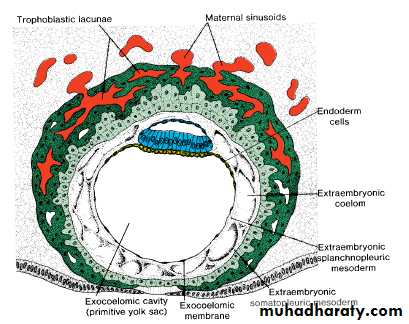
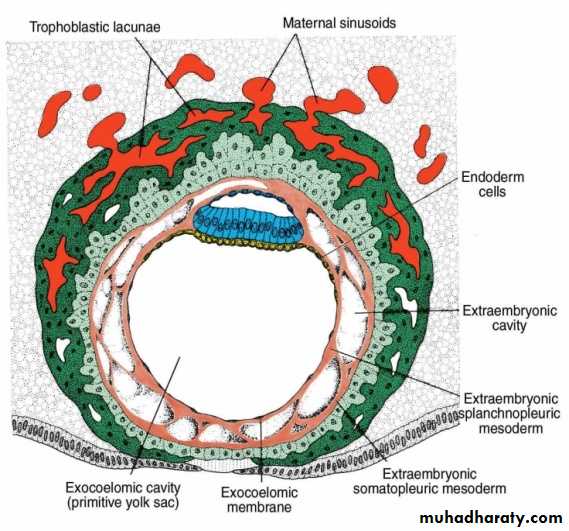
DAY 11 & 12
3-The intercommunicating network of lacunae at the embryonic pole penetrate the maternal sinusoidal capillaries and the maternal blood begin to flow in the trophblast lacunae establishing the uteroplacental circulation.In the meantime, a new population of cells appears between the inner surface of the cytotrophoblast and the outer surface of the exocoelomic
DAY 11 & 12
4-New cells originatefrom the
yolk sac cells forming the extraembryonic mesodermal connective
DAY 11 & 12
5-Except connecting stalk region, cavitations of this mesoderm will form the chorionic cavity or called the extraembryonic coelom
DAY 11 & 12
• The chorionic cavity divides the extraembryonic mesoderm into two parts;DAY 11 & 12
• Somatopleuric mesoderm (or called the chorionic plate) lining the cytotrophblast and the amnion.• Splanchnopleuric mesoderm covering the primitive yolk sac.
DAY 11 & 12
• Decidual reaction occur in the endometrial cells of the uterine mucosa, the mucosal cells become polyhedral, loaded with glycogen and lipid.DAY 13
The mucosal defect heals.Sometimes bleeding occurs from the increased lacunar blood flow, this bleeding may be confused with the normal menstrual bleeding as it occurs near the 28th day of the cycle. This bleeding called false menstruation.
DAY 13
1-Primary villi formationDAY 13
The hypoblast will form a new cellular layer lining the inside of the exocoelomic membrane. The new cavity formed by these new cells called the secondary or definitive yolk sac.DAY 13
The exocoelomic membrane lining the exocoelomic cavity is largely pinched off forming the exocoelomic cysts that are often seen floating in the chorionic cavity.DAY 14
The epiblast forms the floor of the amniotic cavity, and the hypoblast forms the roof of the definitive yolk sac.The buccopharyngeal membrane appears as a thickening in the cephalic region of the hypoblast that is firmly attached to the epiblast.
15 Days
2nd Week = Week of Two’sTrophoblast:Cytotrophoblast & Syncytiotrophoblast
Extraembryonic Mesoderm: Visceral (splanchnic) & Parietal (somatic) LayersEmbryonic Disc: Epiblast & Hypoblast
Cavities : Amniotic cavity & Yolk sac
(Parietal layer)
(Visceral layer)
CLINICAL CORRELATES
Syncytium…… hCG ….the end of 2nd week… detected by RIA (basis for PT)(The syncytiotrophoblast is responsible for hormone production (see Chapter6), including human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). By the end of the second week, quantities of this hormone are sufficient to be detected by radioimmunoassays,(RIA) which serve as the basis for pregnancy testing.
CLINICAL CORRELATES
in blood : 6-12 days after ovulation.
Urine PT done 1 week after missed period.
Because 50% of the implanting embryo’s genome is derived from the father, it is a foreign body that potentially should be rejected by the maternal system.
Recent evidence suggests that a combination of factors protects the conceptus, including production of immunosuppressive cytokines and proteins
and the expression of an unusual major histocompatibility complex class IB molecule (HLA-G) that blocks recognition of the conceptus as foreign tissue.
If the mother has autoimmune disease, for example systemic lupus erythematosus, antibodies generated by the disease may attack the conceptus and reject it.
What makes the conceptus not to be rejected by the mother immune system?
placental trophoblast, does not express the polymorphic class I and class II MHC genes and instead expresses HLA-G, a non polymorphic gene. Therefore, antibodies against the fetal proteins not developedThe production of immunosuppressive cytokines and proteins.
There is a Fas ligand on the surface of the placenta, and this bonds to T cells, causing them to undergo Apoptosis
ABNORMAL IMPLANTATION
Primary ov preg
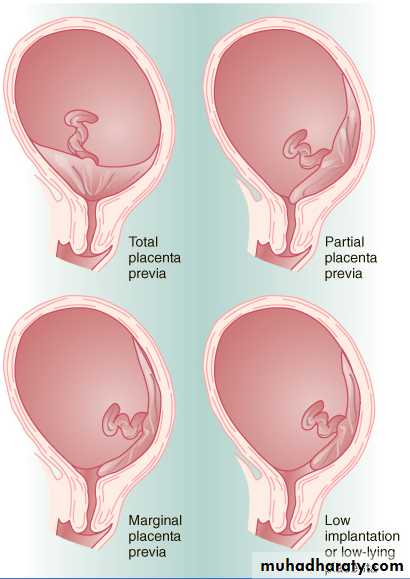
mostlyPlacenta previa
Normally …. Ant. Or post. Wall of the uterus
Implants close to the int os …. Placenta previa (antepartum hemorrhage in form of painless vaginal bleeding in the third trimester,10% diagnosed incidentally by ultrasonography or at term.)
ABRUPTIO PLACENTAE, (premature separation of the normally implanted placenta, may result in fetal death) Clinically: painful vaginal bleeding in association with uterine tenderness, hyperactivity, and increased tone
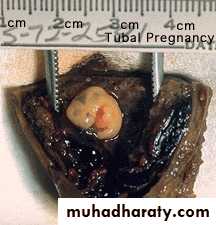
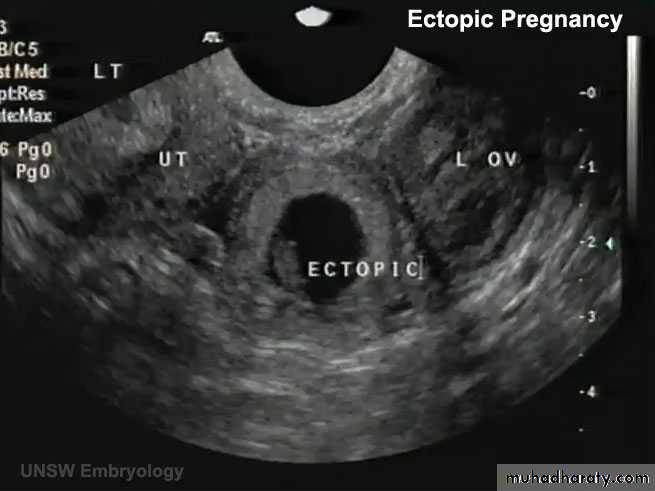
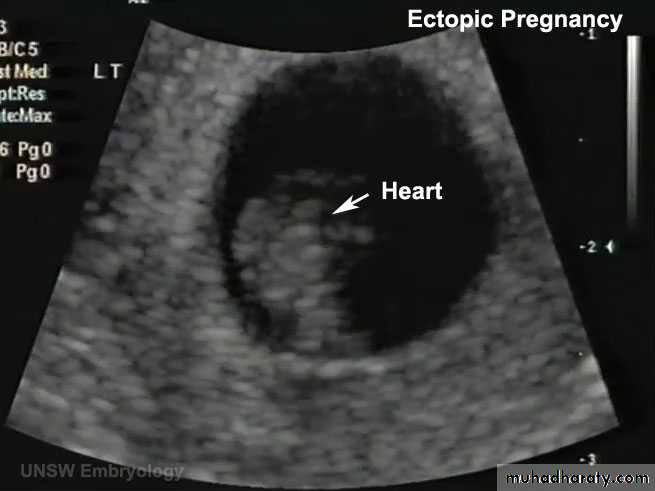
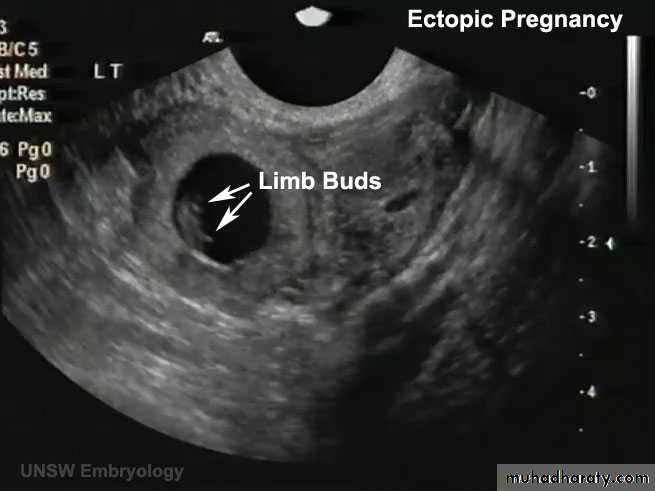
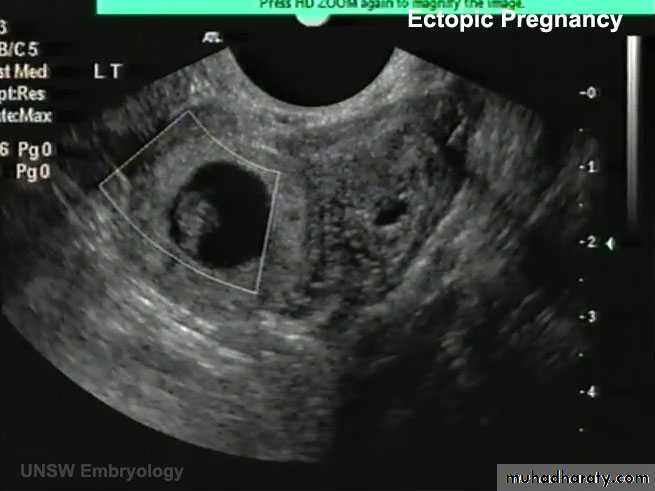
ECTOPIC PREG (EXTRAUTERINE PREG):
- 95% …. Uterine tube… and mostly in the ampula
ABNORMAL IMPLANTATION
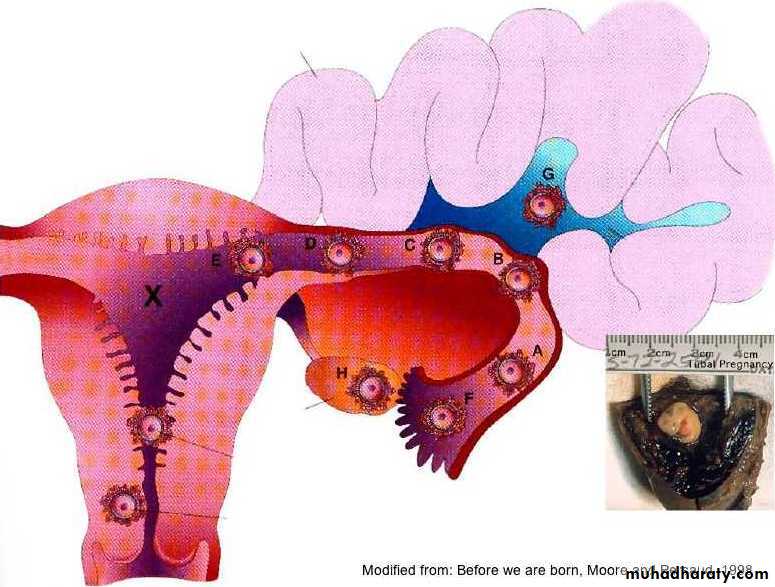
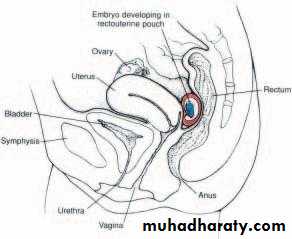
Abnormal implantation sites of the blastocyst.
1, implantation in the abdominal cavity. The ovum most frequently implants in the rectouterine cavity (Douglas’ pouch) but may implant at any place covered by peritoneum.2, implantation in the ampullary region of the tube.
3, tubal implantation.
4, interstitial implantation, that is, in the narrow portion of the uterine tube.
5, implantation in the region of the internal os, frequently resulting in placenta previa.
6, ovarian implantation.
Placenta previa
ABNORMAL IMPLANTATION
ABNORMAL IMPLANTATION
ABNORMAL IMPLANTATION
ABNORMAL IMPLANTATION
ABNORMAL IMPLANTATION
ABNORMAL IMPLANTATION
In the abd cavity the blastocyst most frequently attach to the perit lining of douglas pouch. And st to the perit covering the intestine or to the omentum.
ABNORMAL IMPLANTATION
In most ectopic preg the embryo dies in the second month of gestation… causing sever hrg and abd painMost abnormal blastocyst would not have any signs of preg bec of inferior trophoblast… no hCG … corp luteum not persist
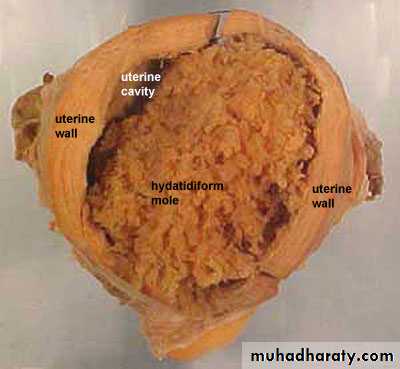
In some cases the trophpoblast developed and form placental memb with little or
no embryonic tissues … haydatidiform mole
High hCG…invasive mole or choriocarcinoma
ABNORMAL IMPLANTATION
ABNORMAL IMPLANTATION
Genetic analysis of hydatidiform moles indicates …male and female pronuclei may be genetically equivalent, they different functionally.cells of moles are diploid, their entire genome is paternal.
These suggest that paternal genes regulate most of the development of the trophoblast,
This tissue differentiates even in the absence of a female pronucleus.
ABNORMAL IMPLANTATION
Other examples of functional differences ….. certain genetic diseases depend on whether the defective or missing gene is inherited from the father or the mother.Example, inheritance of a deletion on chromosome 15 from a father produces Prader-Willi syndrome,
If from the mother results in Angelman syndrome
ABNORMAL IMPLANTATION
pws
Angelman syndrom
Angelman Syndrome is a rare neurological disorder disorder characterized by severe congenital mental retardation, unusual facial appearance, and muscular abnormalities
42%
Survive & normal
Aborted
Normal
Abnormal at birth
• A 23-year-old woman consulted her physician about severe right lower abdominal pain. She said that she had missed two menstrual periods. A diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy was made.
What techniques might be used to enable this diagnosis?
What is the most likely site of the extrauterine gestation (pregnancy)?
How do you think the physician would likely treat the condition?