PCV (%)
RBC count
(million/mm
3
)
× 10
fL=10
-15
L
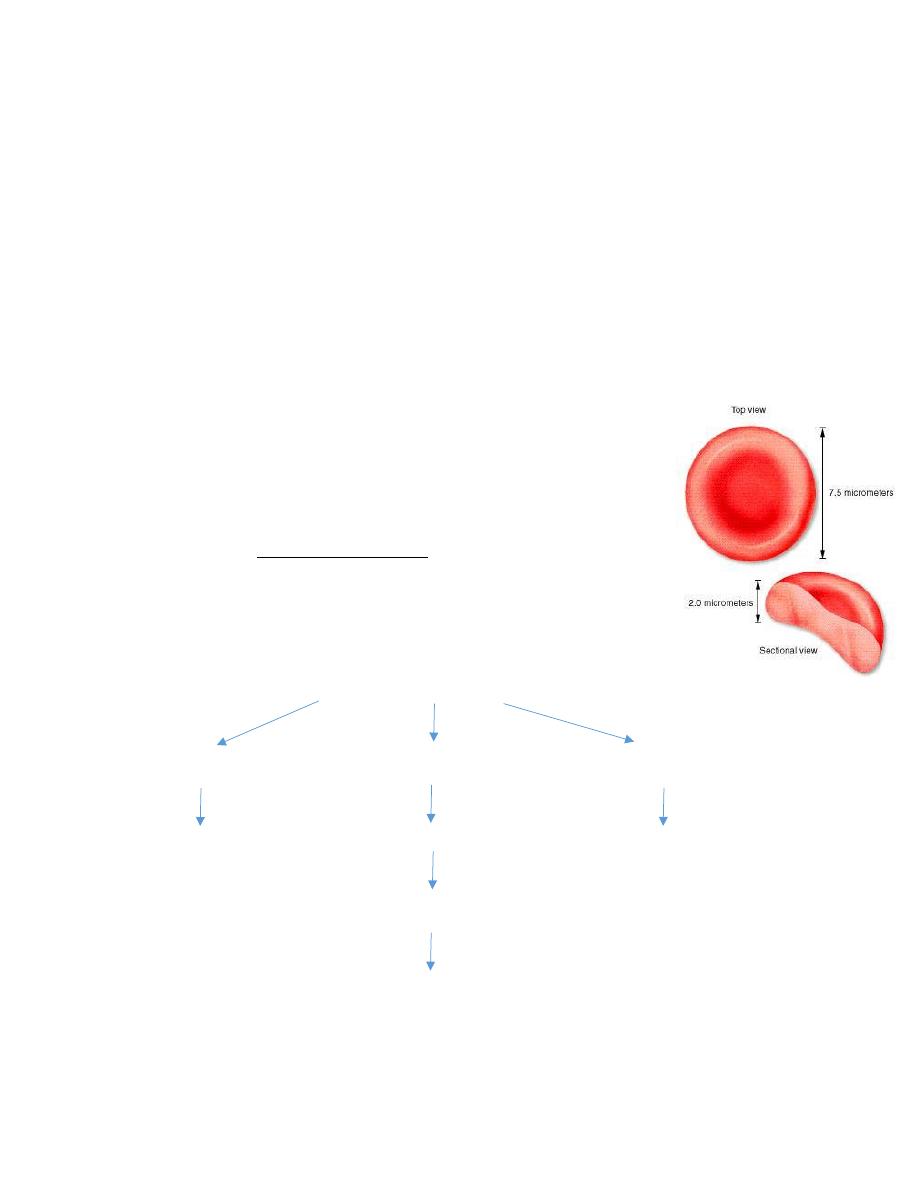
Normocytic
Within the range
More
Less
Macrocytic
Microcytic
Anemic patient
Iron deficiency anemia
Kidney failure
Thalassemia
Lead poisoning
Anemia of chronic disease
Folic acid deficiency
Vitamine B12 deficiency
Cirrhosis
Excessive alcohol intake
Liver disease
Hypothyroidism
Hemolytic anemia
Bone marrow failure
Myelodysplastic
syndrome
With anemia
Acute hemorrhage
Sickle cell anemia
G6PD deficiency
RBC indices
- Red blood cell (RBC) indices are part of the complete blood count (CBC) test.
They are used to help diagnose the cause of anemia, a condition in which there
are too few red blood cells and/or low Hb concentration.
- The indices include:
Mean Cell Volume (MCV)
Mean Cell Hemoglobin (MCH)
Mean Cell Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC)
Mean Cell Volume (MCV)
- Index for: the average RBC size
- Calculation:
MCV (fL) =
- Normal range for MCV is 80–100 fL/cell
Hb (g/dl)
RBC count
(million/mm
3
)
× 10 =
pg /RBC
pg=10
-12
g
Hb (g/dl)
PCV (%)
× 100 =
g/dl
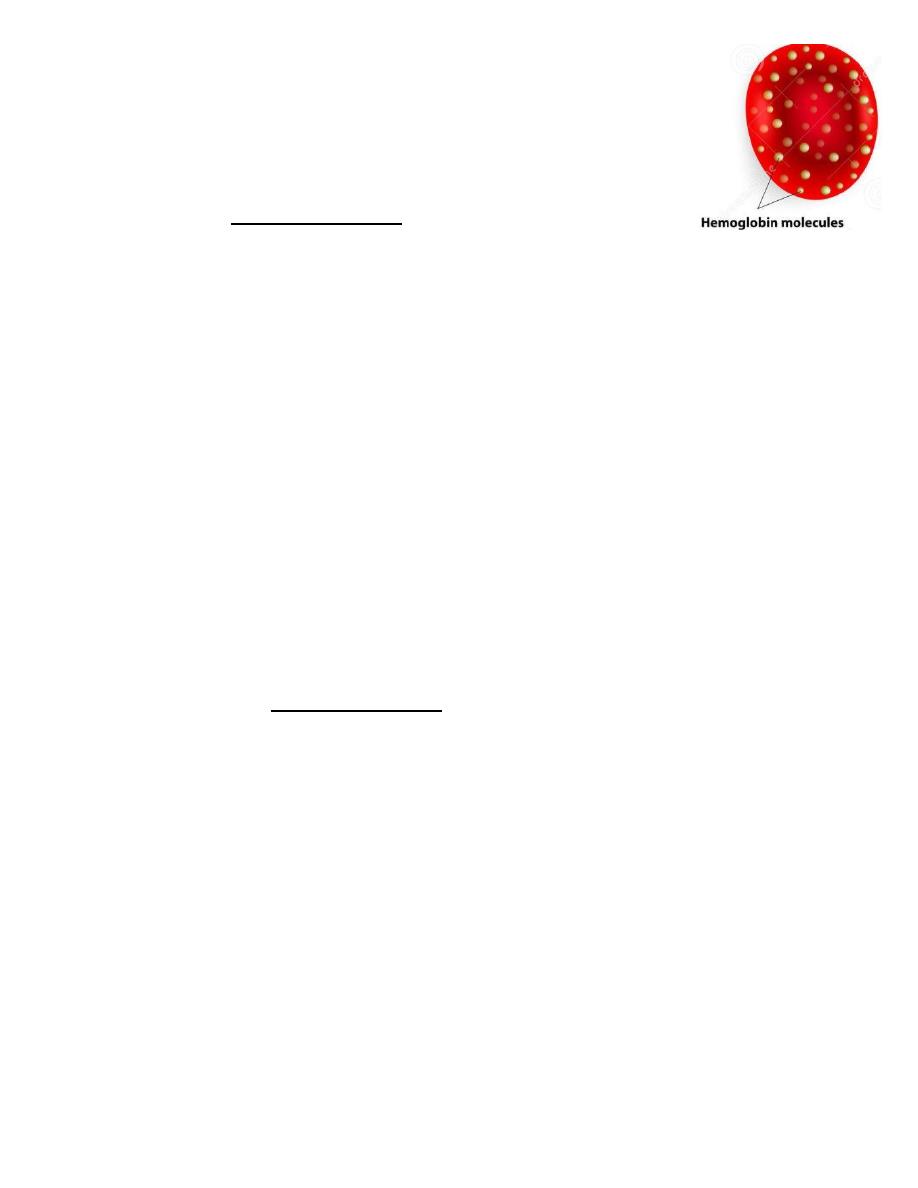
Mean Cell Hemoglobin (MCH)
- Index for: Hb amount per RBC
- Calculation:
MCH (pg) =
- Normal range for adults: 27-33 picograms (pg)/RBC in adults
Within the range Normochromic
More than the range Still Normochromic but there may be Macrocytic
anemia
Less than the range Hypochromic (Low Hb) e.g. Iron deficiency
anemia and thalassemia
Mean Cell Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC)
- Index for: The amount of hemoglobin relative to the size of the cell
(hemoglobin concentration) per red blood cell
- Calculation:
MCHC (g/dl) =
- Normal range for adults: 33-36 g/dL
Within the range Normochromic
More than the range Normochromic, but may be due to low PCV as in
sickle cell anemia
Less than the range Hypochromic (Low Hb)
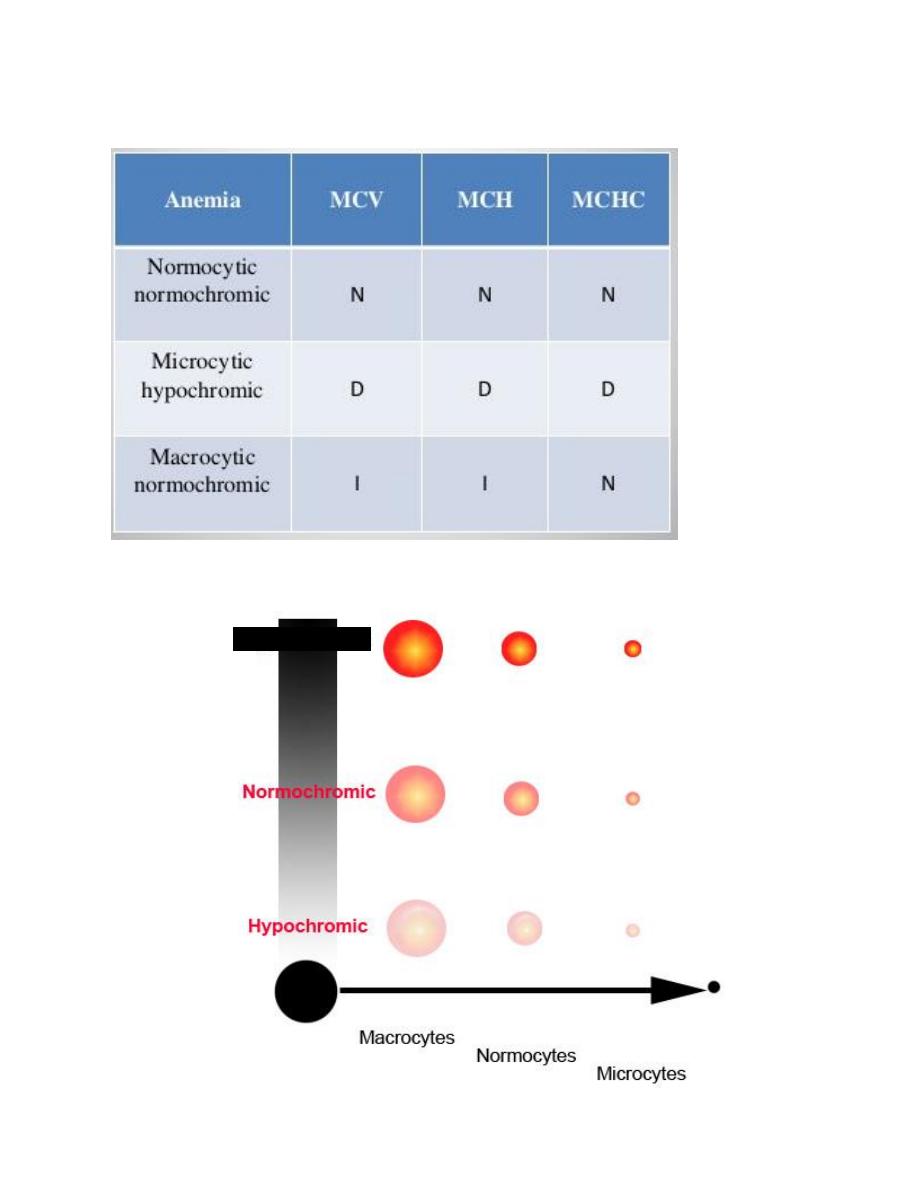
N: Normal
D: Deficiency
I: Increasing
Summary of RBC indies in common anemias:
Normochromic
