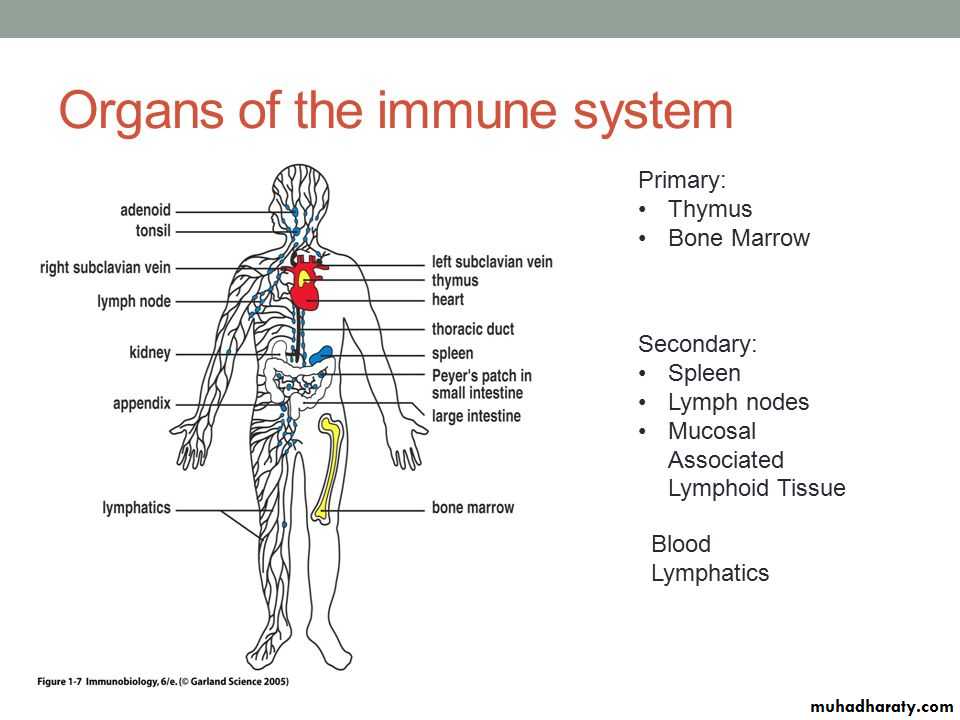
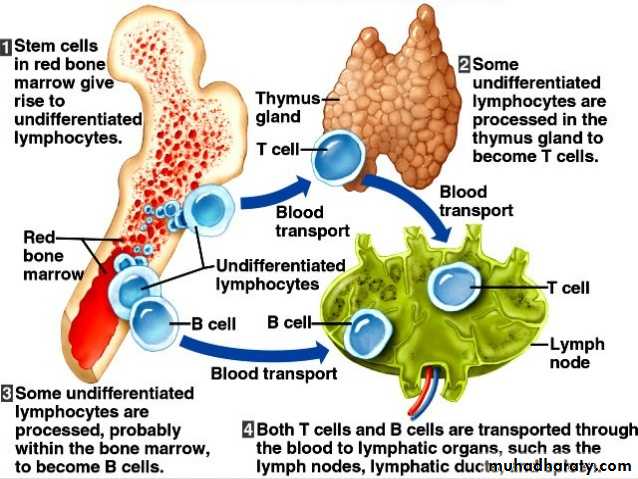
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
Primary (central organs)Secondary (peripheral organs)
PRIMARY LYMPHOID ORGANS(BONE MARROW & THYMUS)
SECONDARY LYMPHOID TISSUE(SPLEEN, LYMPH NODE & MALT)
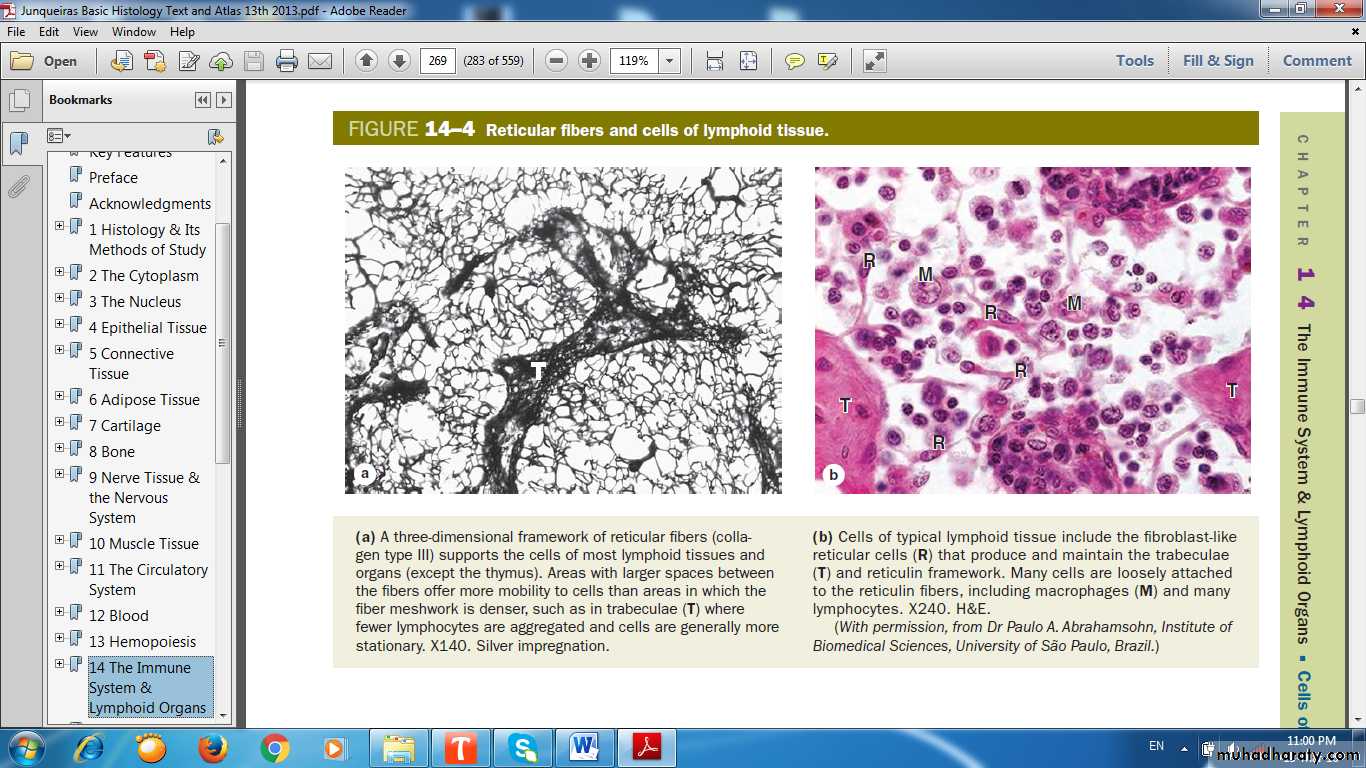
LYMPHOID TISSUE(RETICULAR FIBRES & CELLS)
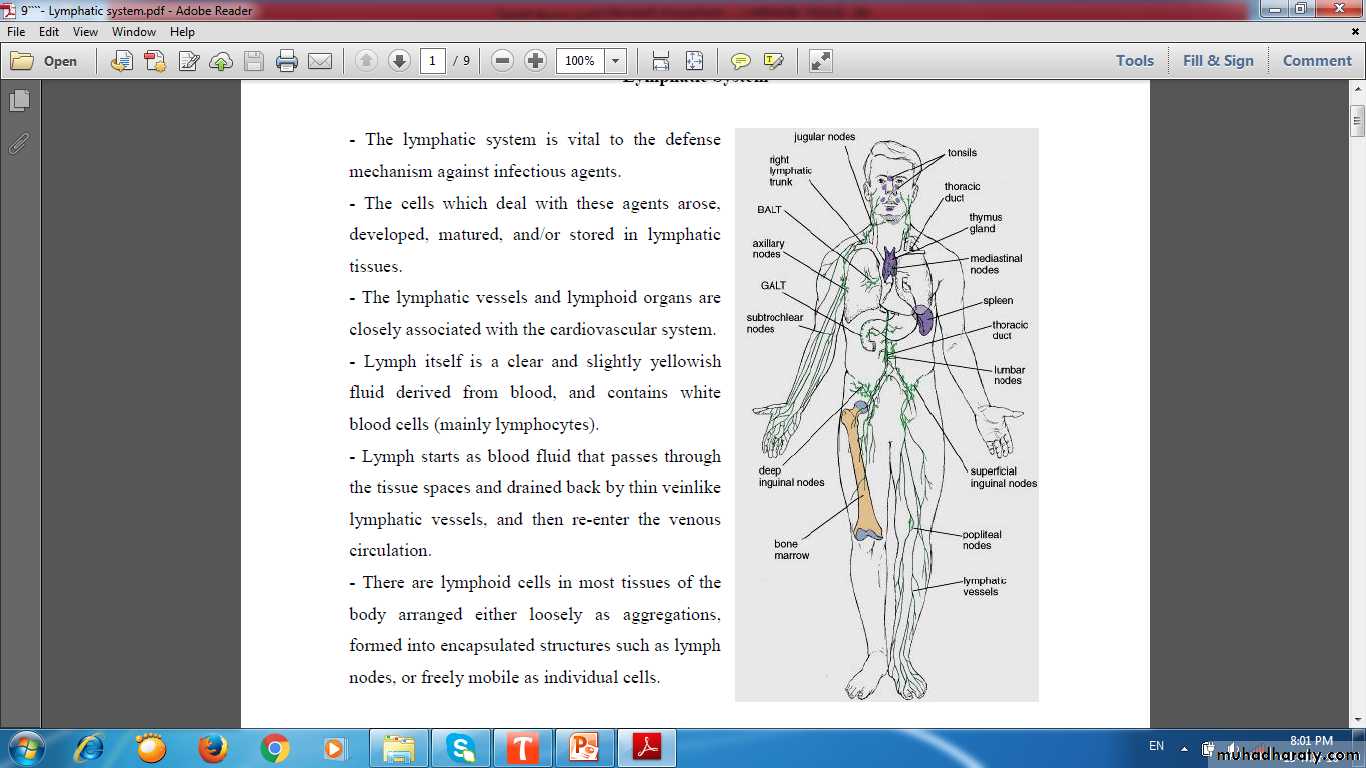
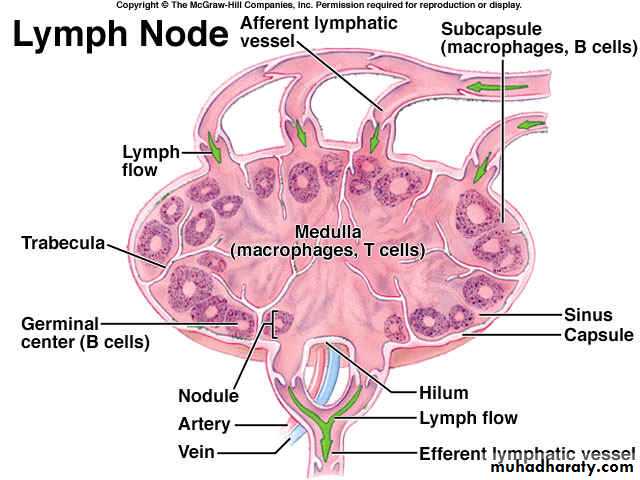
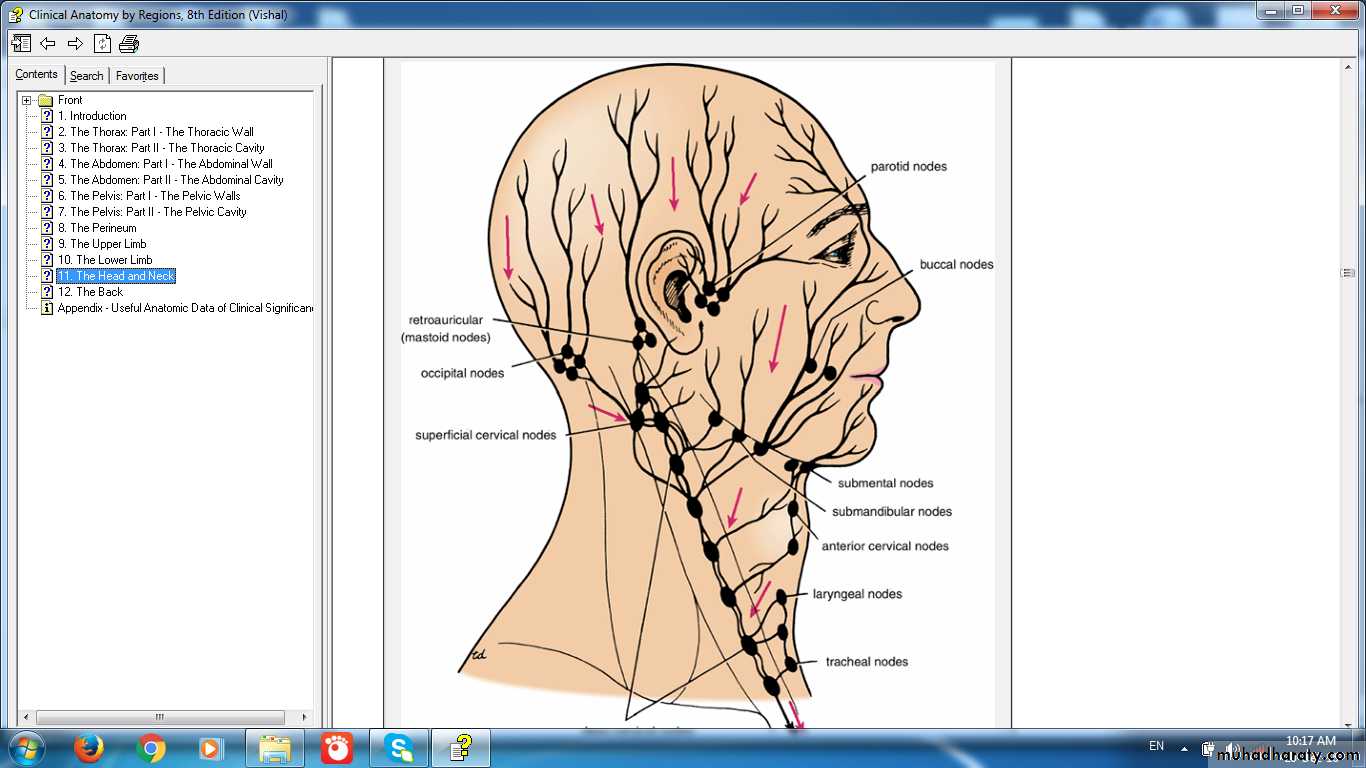
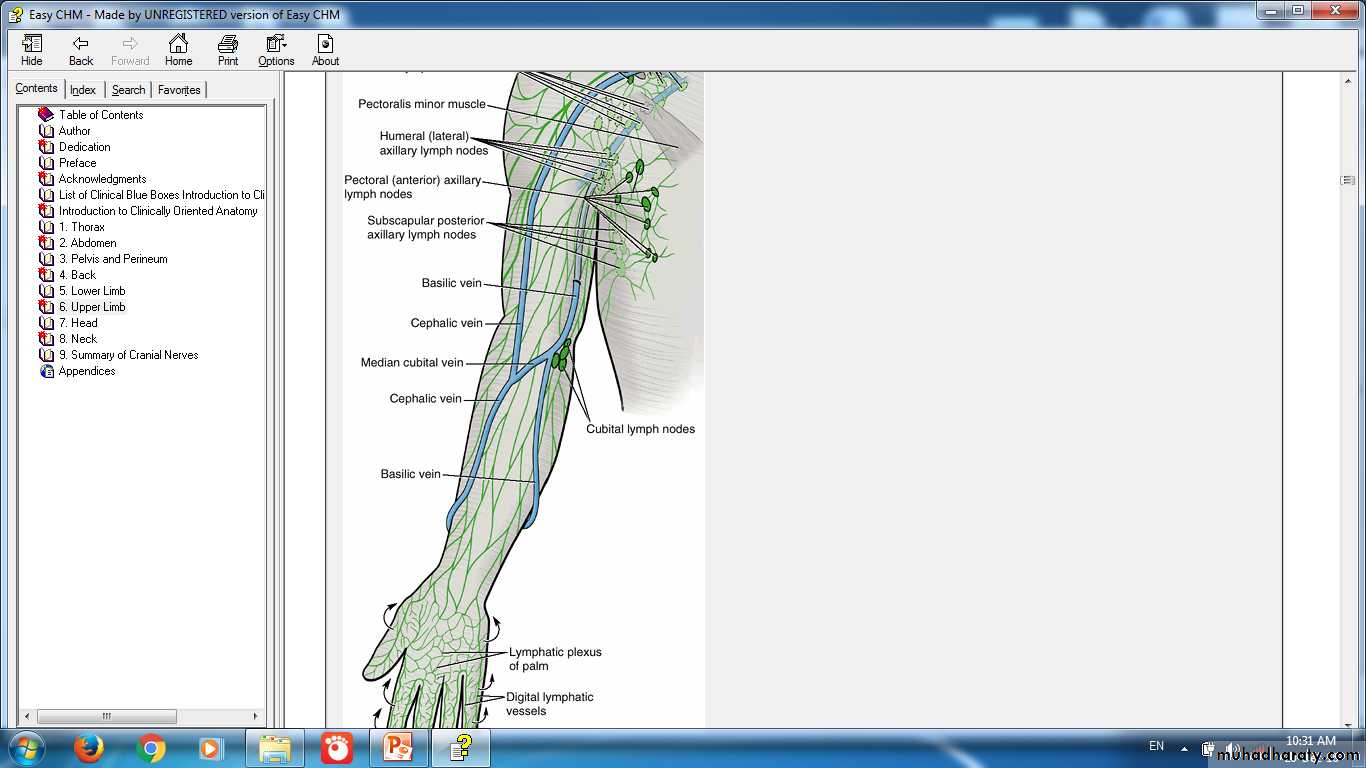
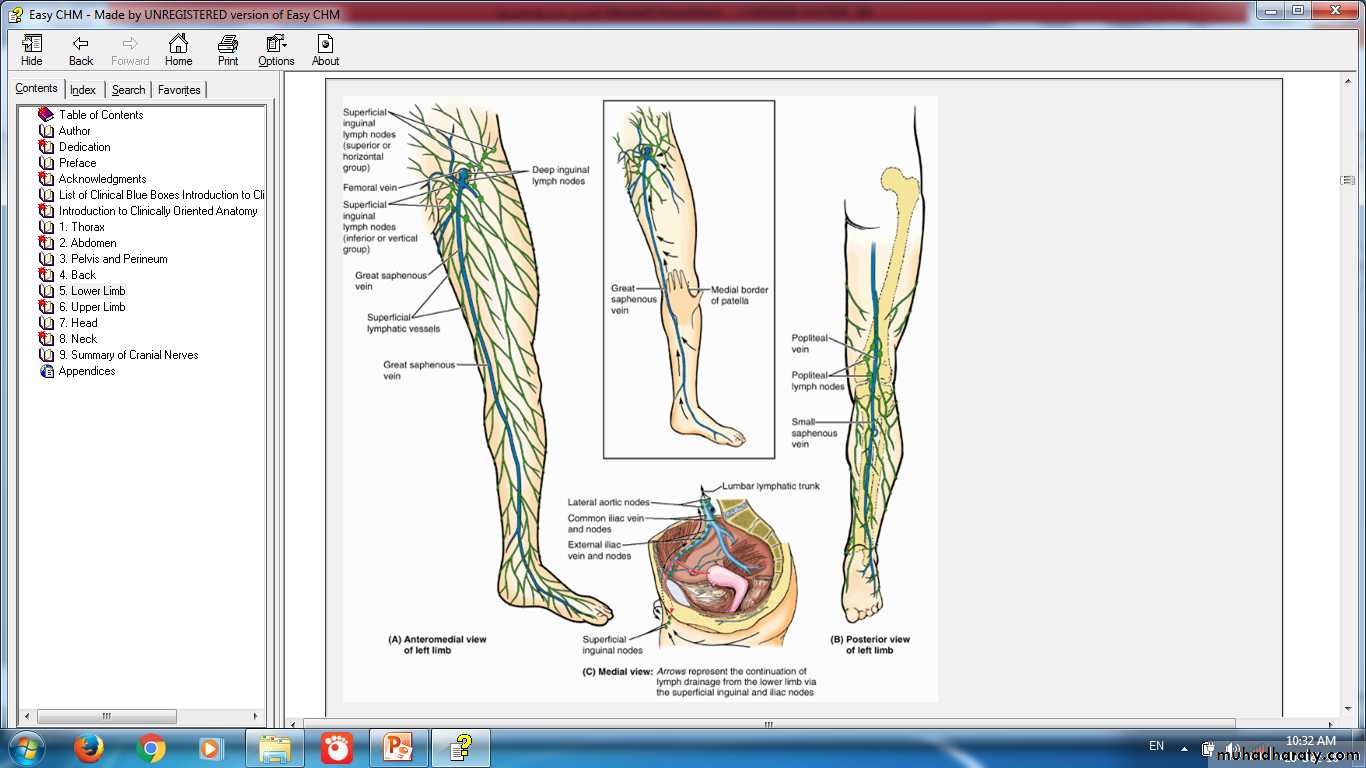
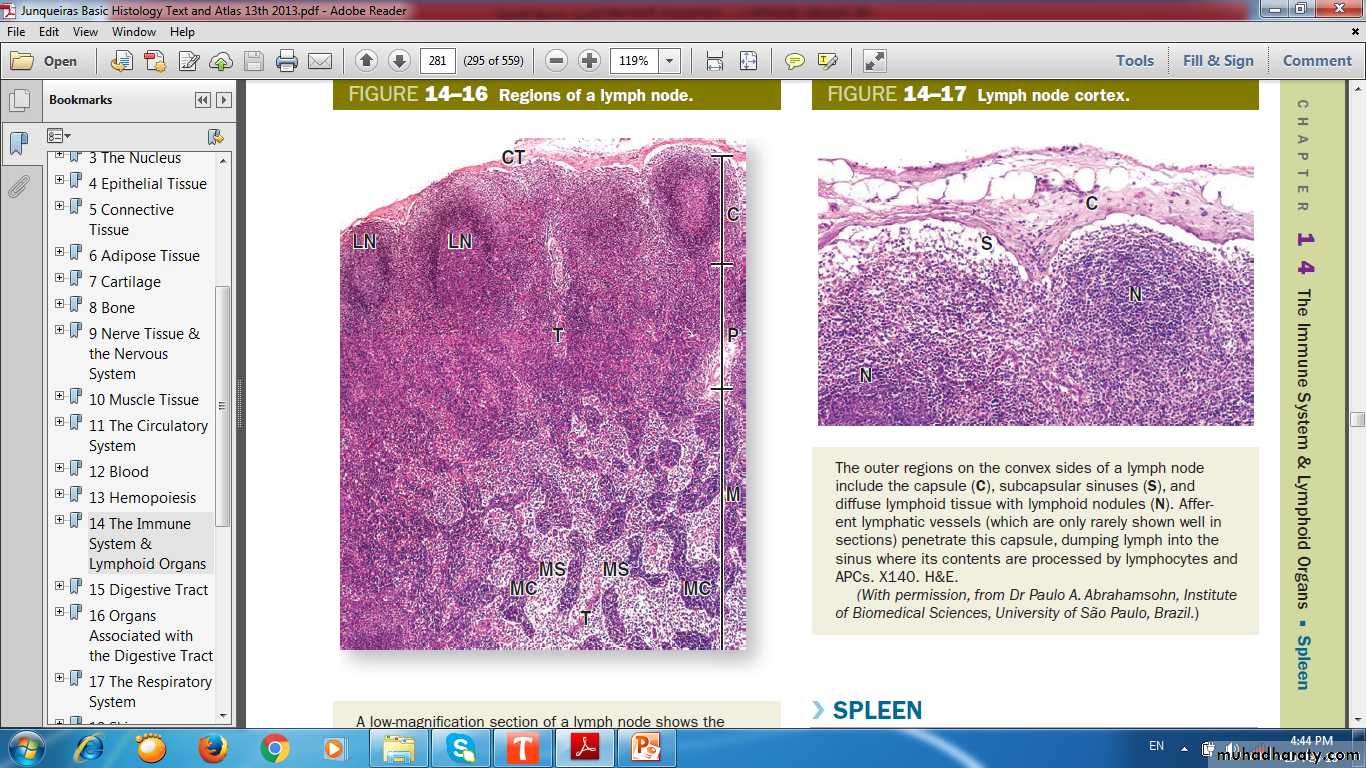
Lymph Node GroupsRegions of lymph node
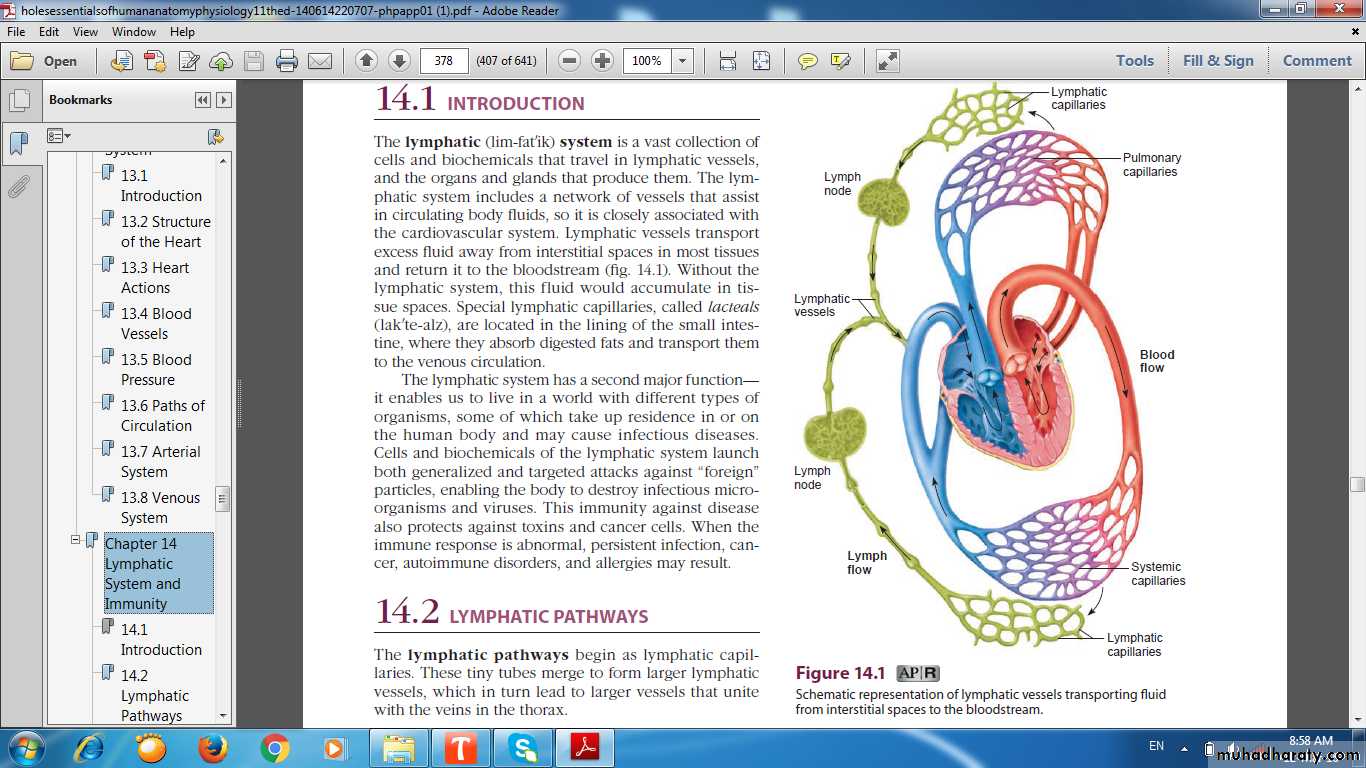
LYMPH FLOW
FILTER OF LYMPH
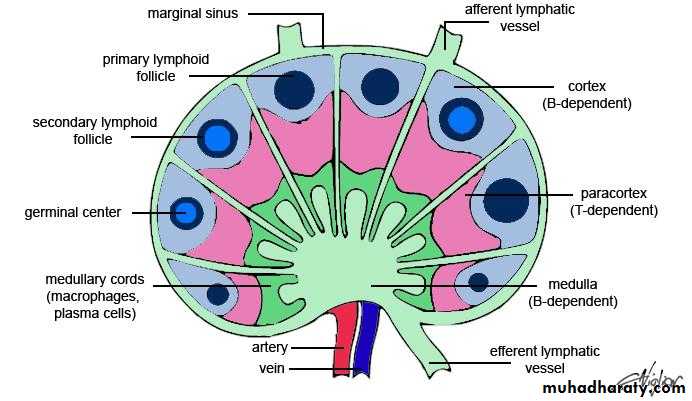
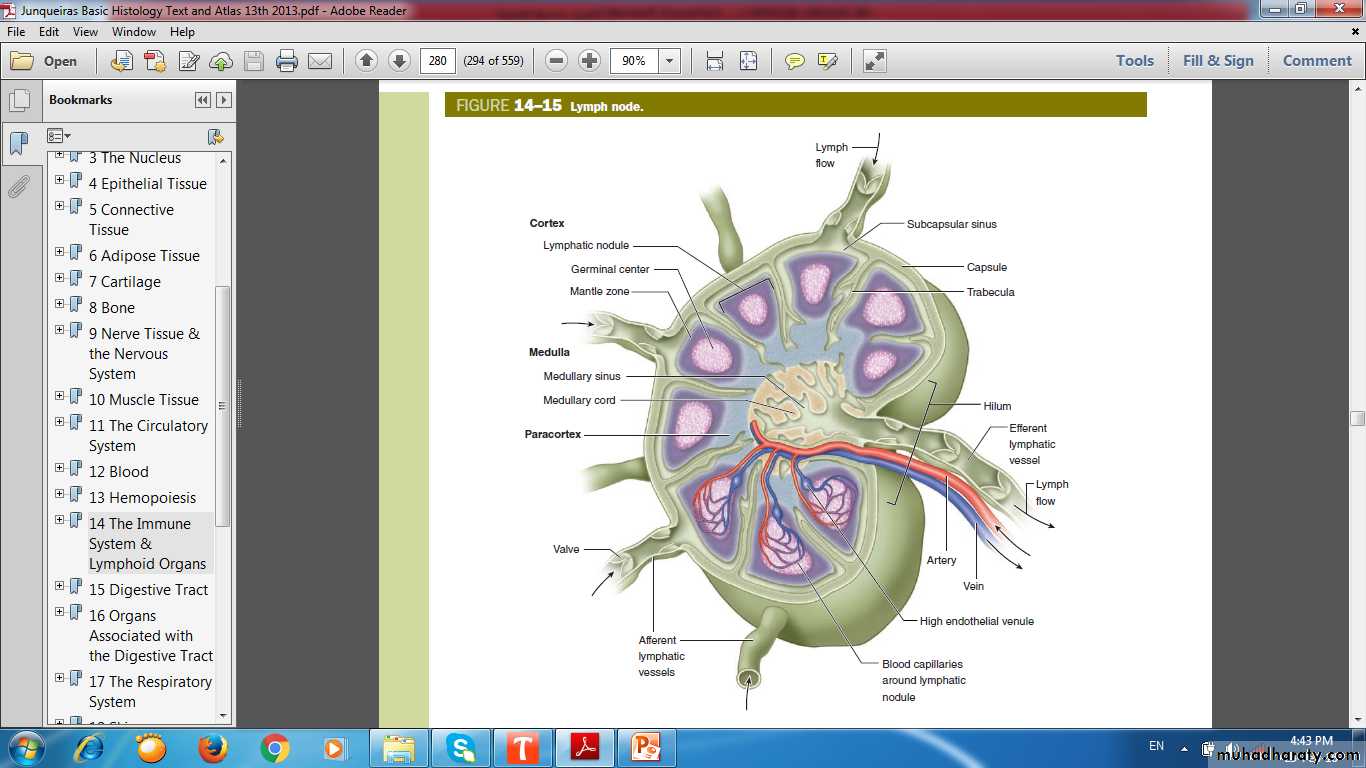
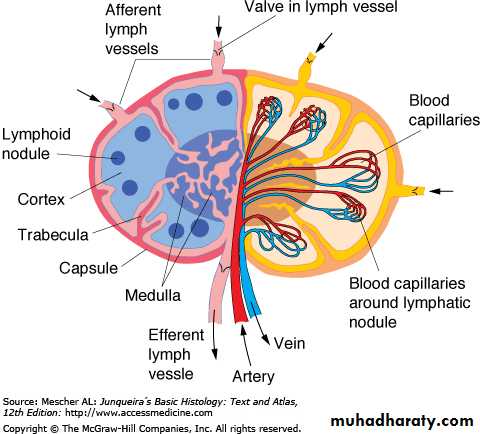
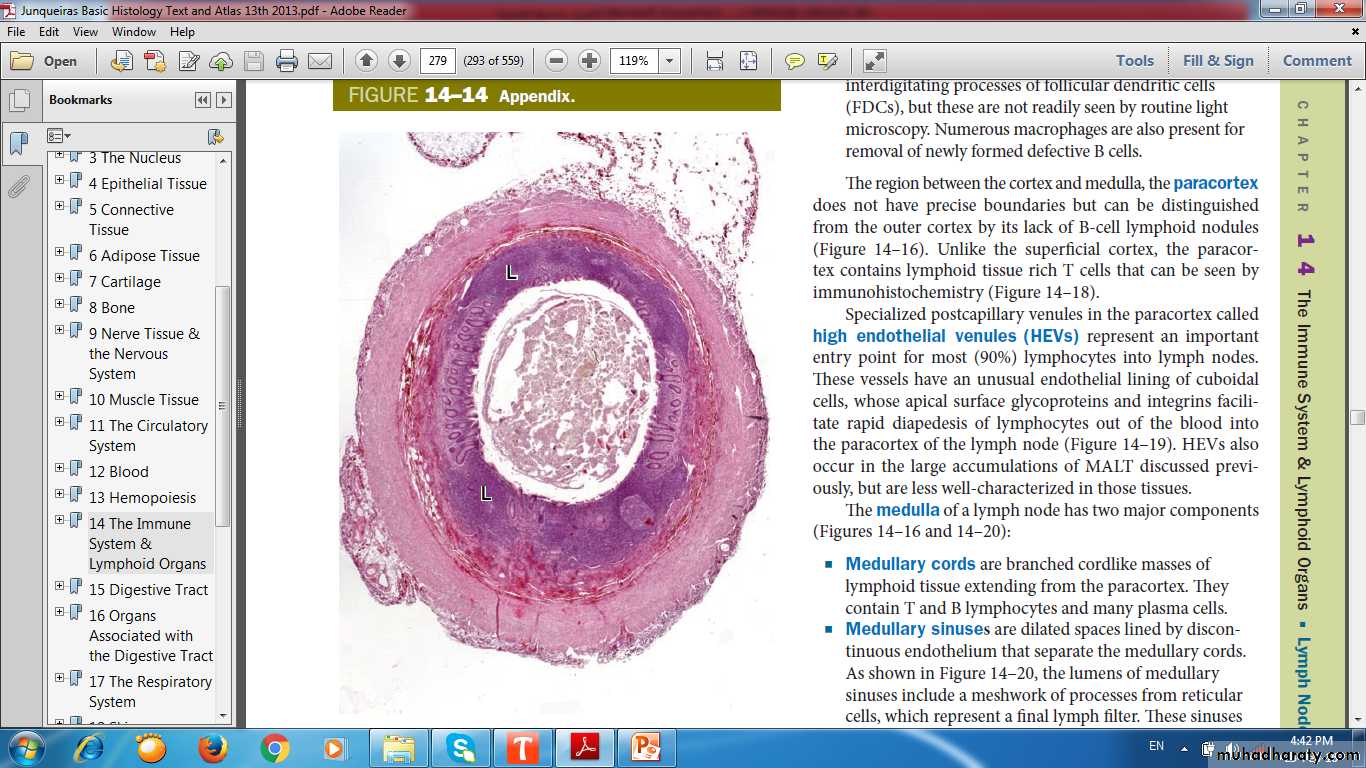
Regions of lymph node
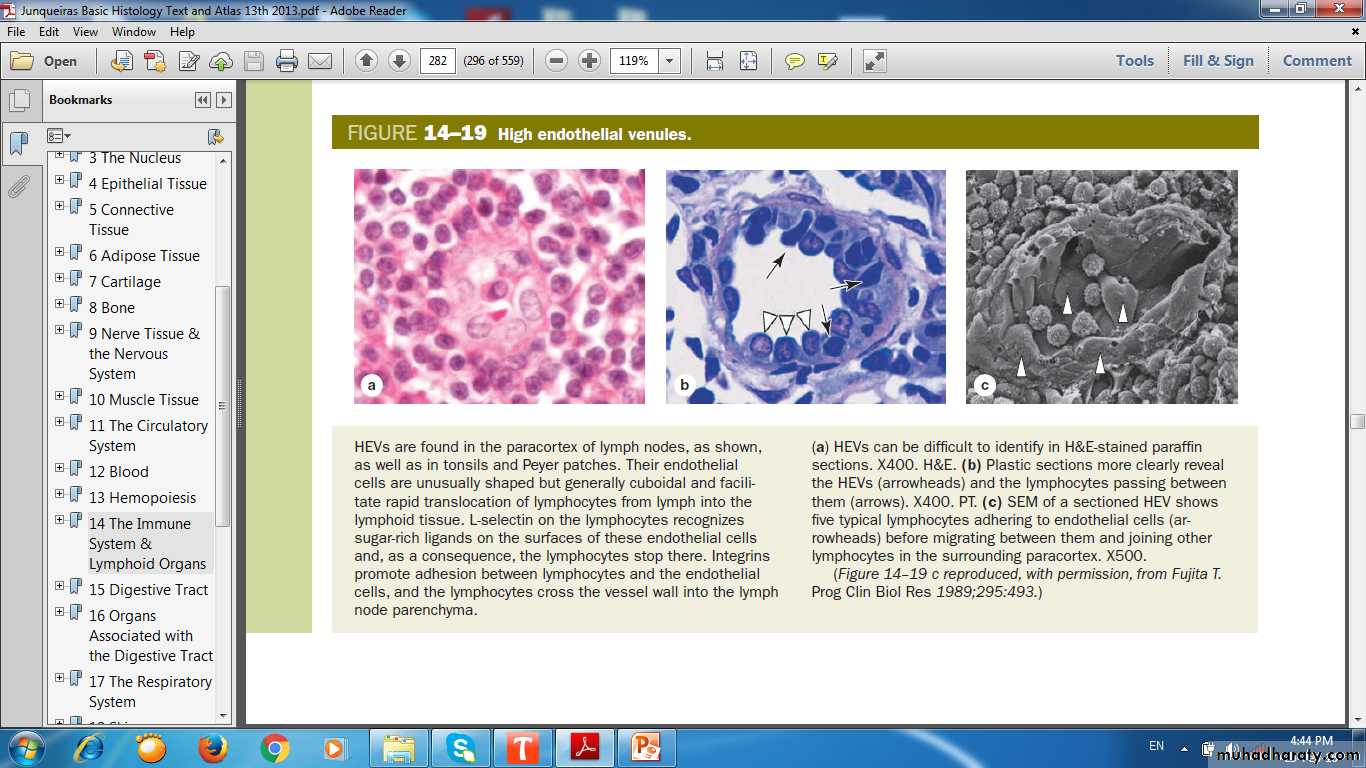
High Endothelial Venules (HEV)
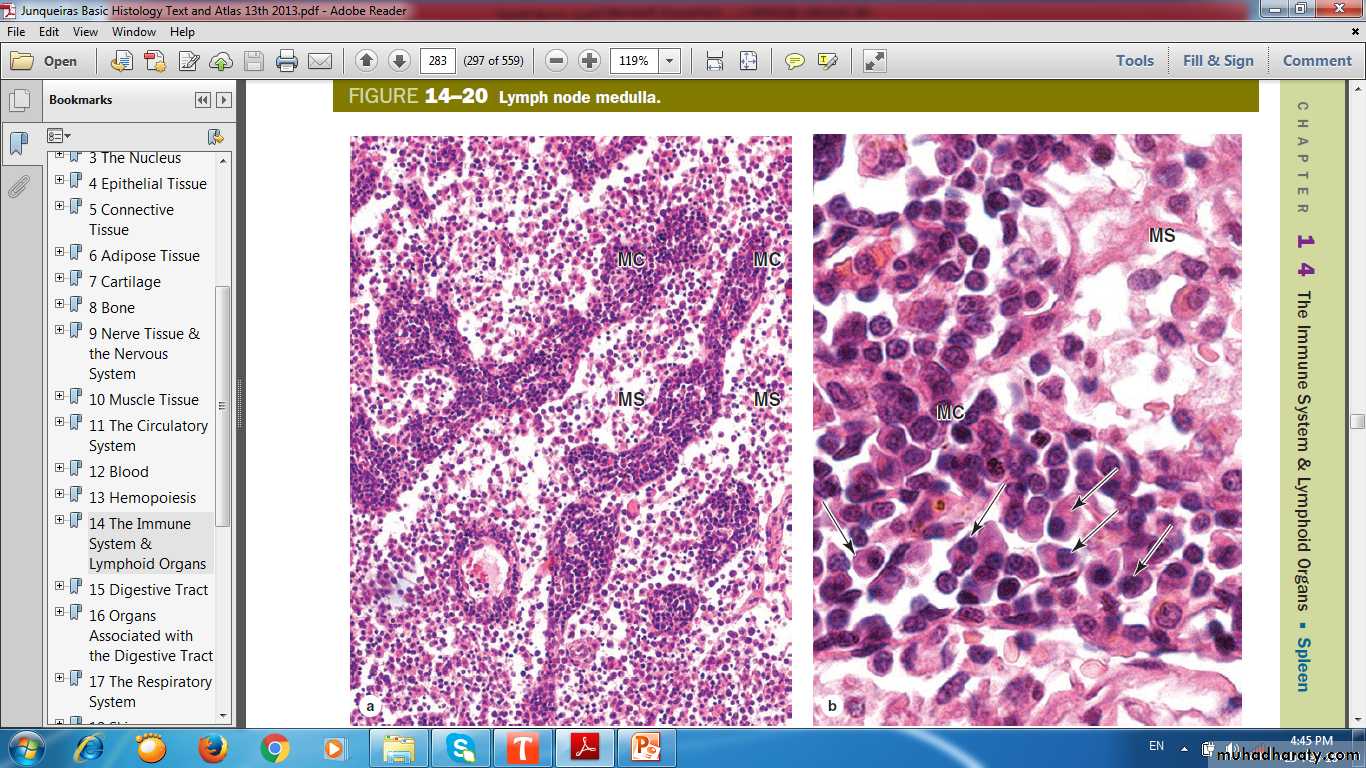
Lymph node medullaMedullary cordsMedullary sinuses
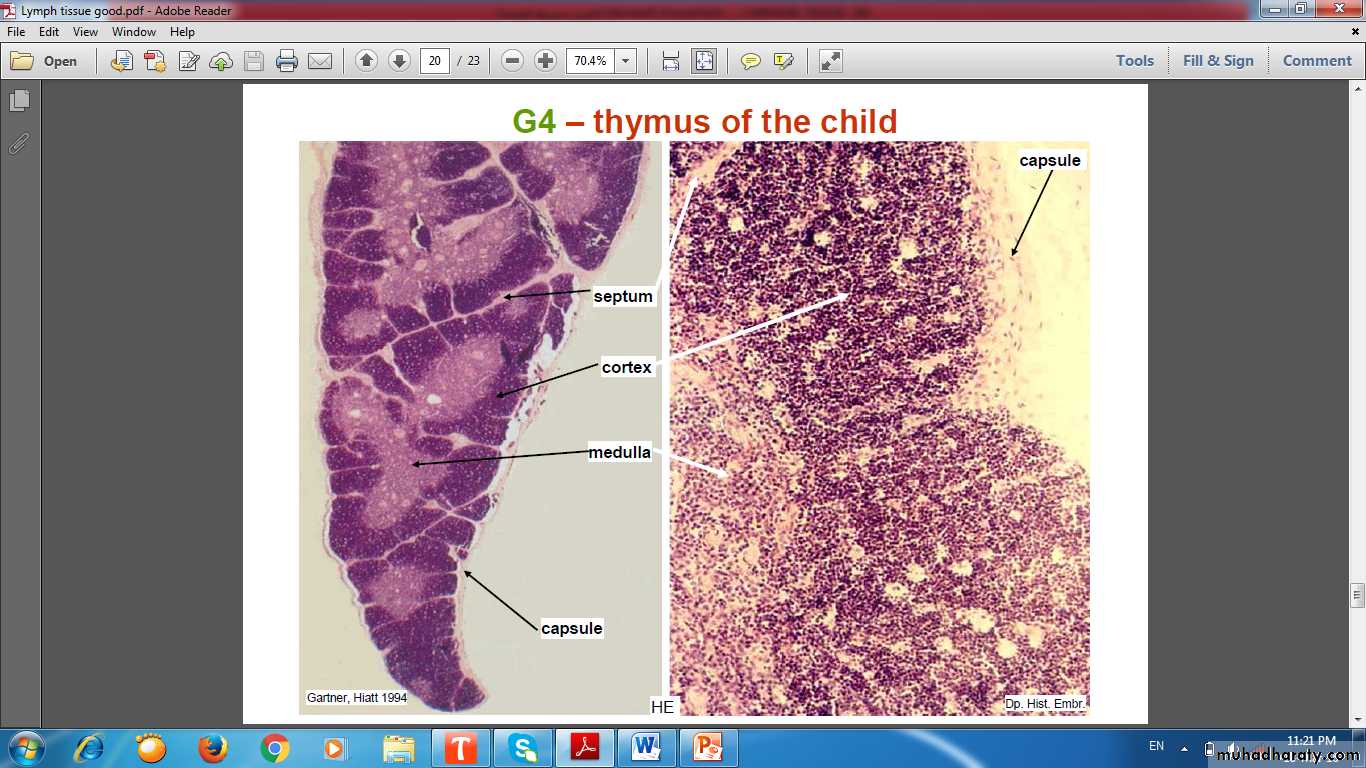
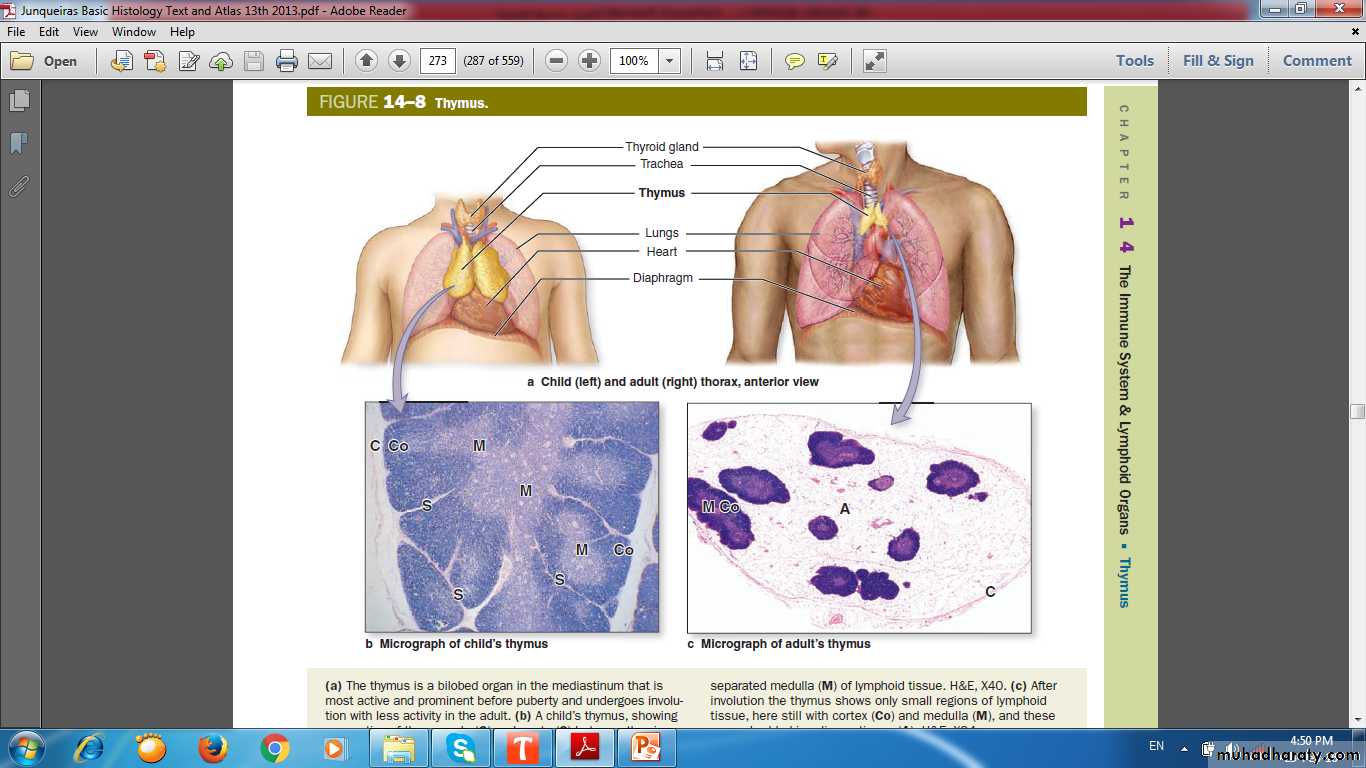
Thymus (thyme leaf)
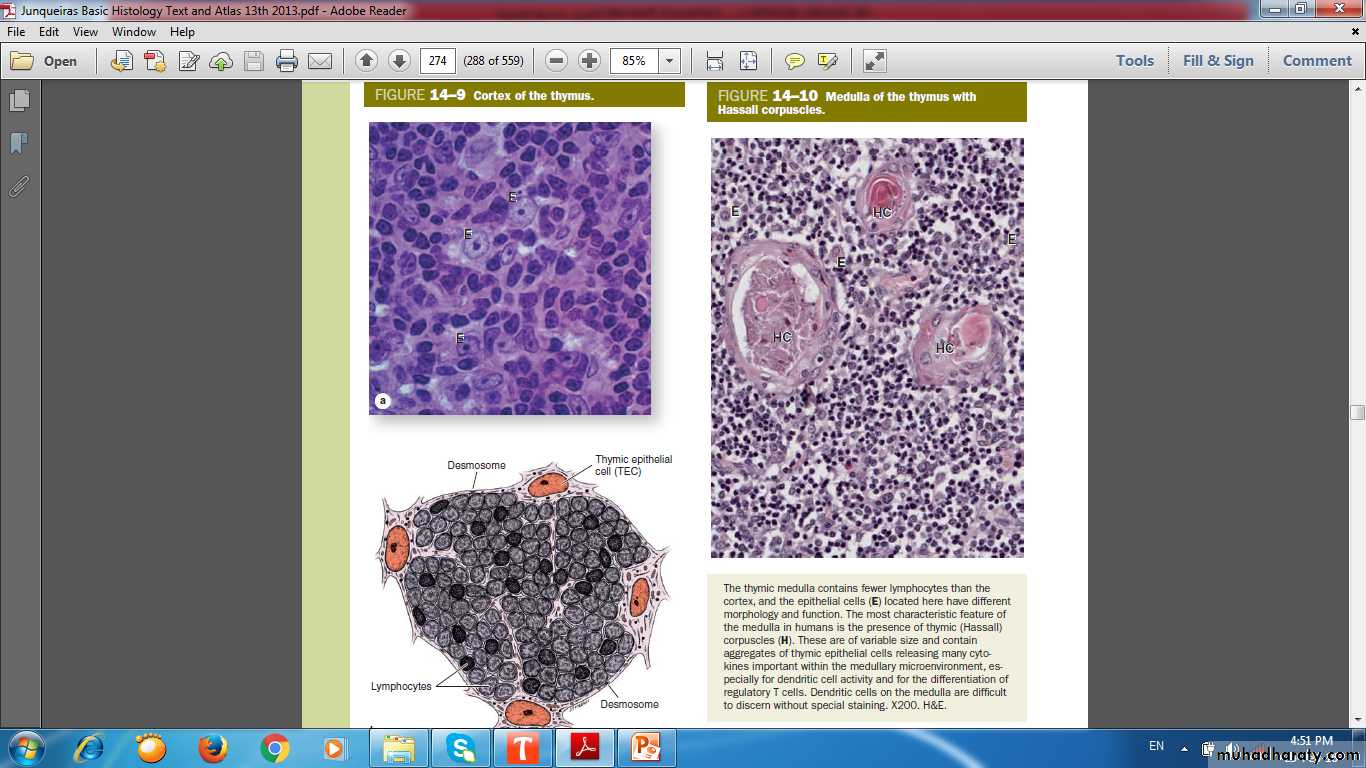
CORTEX & MEDULLAThymic cortex contains
Extensive population of T lymphoblasts ( Thymocytes)Macrophages
Thymic epithelial cells (TECs) that have certain features of both epithelial and reticular cells.
THYMUS – EPITHELIAL RETICULAR CELLS
Joined by desmosomesForm stroma (cytoreticulum)
Produce factors for T cell differentiation (thymopoietin, thymosin)
Blood-thymus barrier – prevents most circulating antigens to enter into cortex
TEC
Thymic Medulla
More lightly stainedcontains fewer & larger, more mature lymphocytes
Medullary TECs form the following:
A second layer of the boundary between cortex and medulla.A cytoreticulum
Large aggregates of TECs, sometimes concentrically arranged, called Hassall corpuscles or (thymic corpuscles) are unique to the medulla.
Hassall Corpuscles
MALT (70% OF LYMPHOID TISSUE) BALT GALT
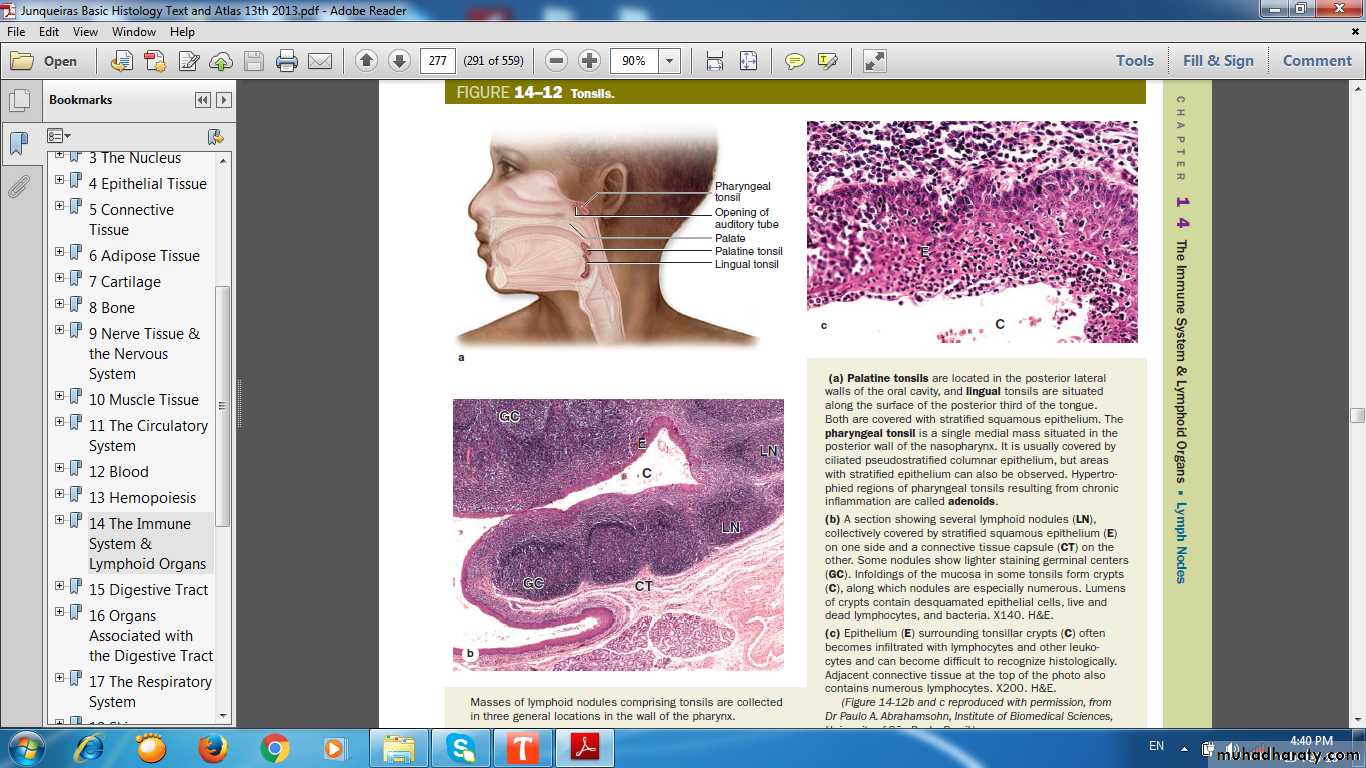
TONSILS• Palatine
• Lingual
• pharyngeal
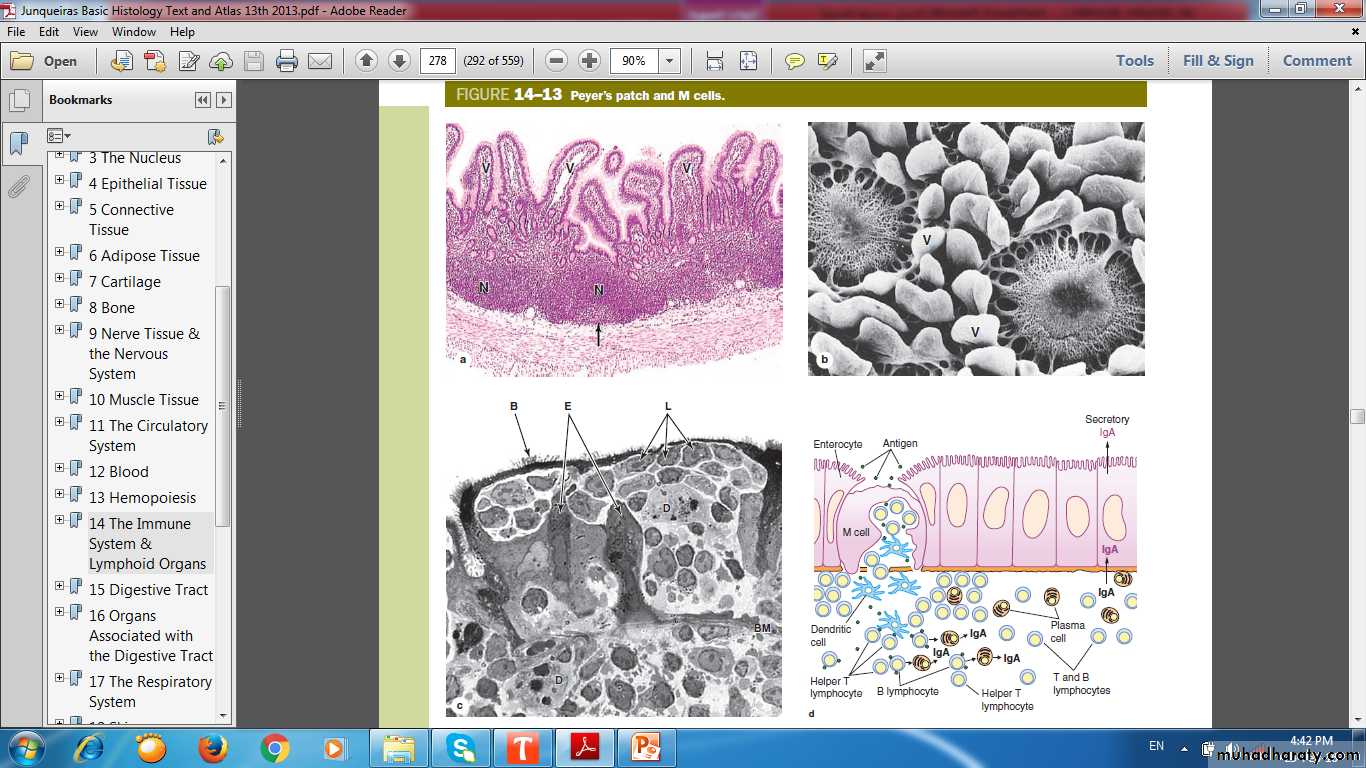
PEYER’S PATCHES
MALT of Appendix
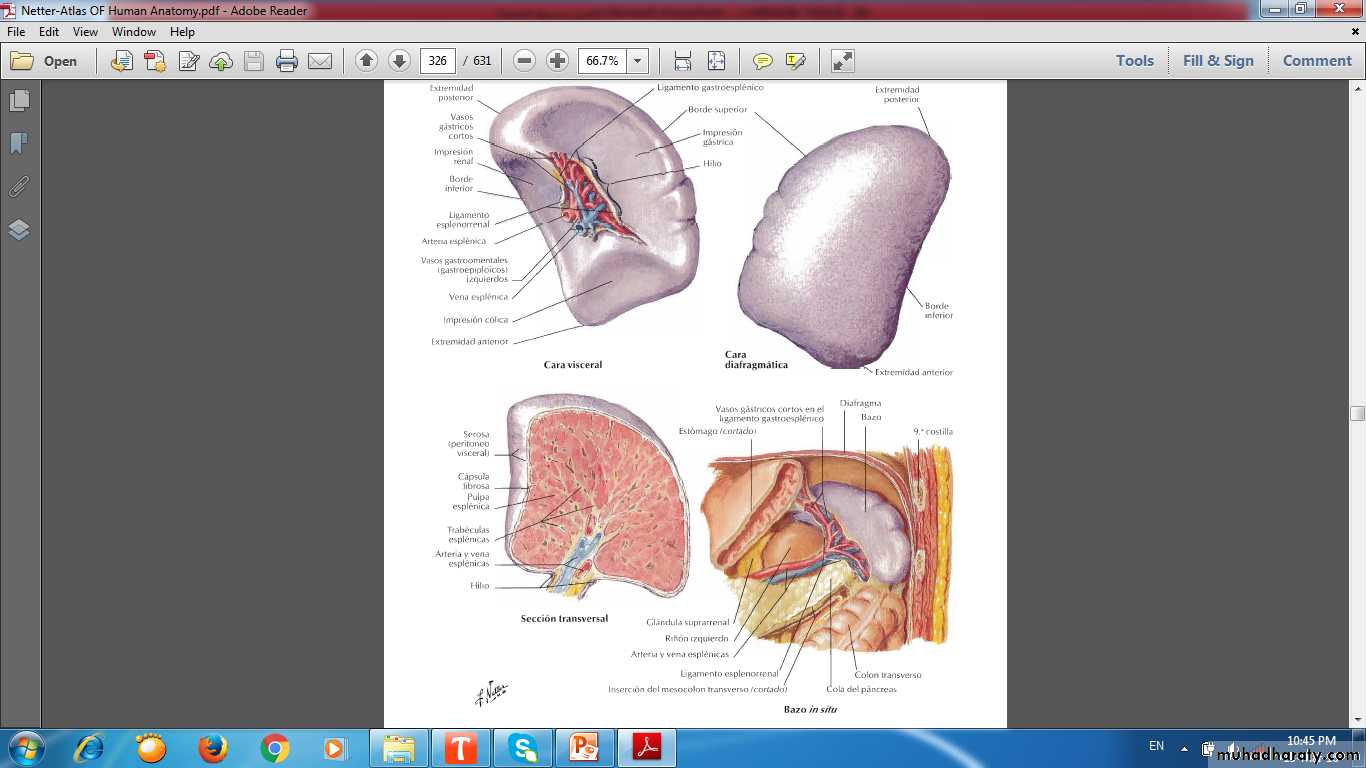
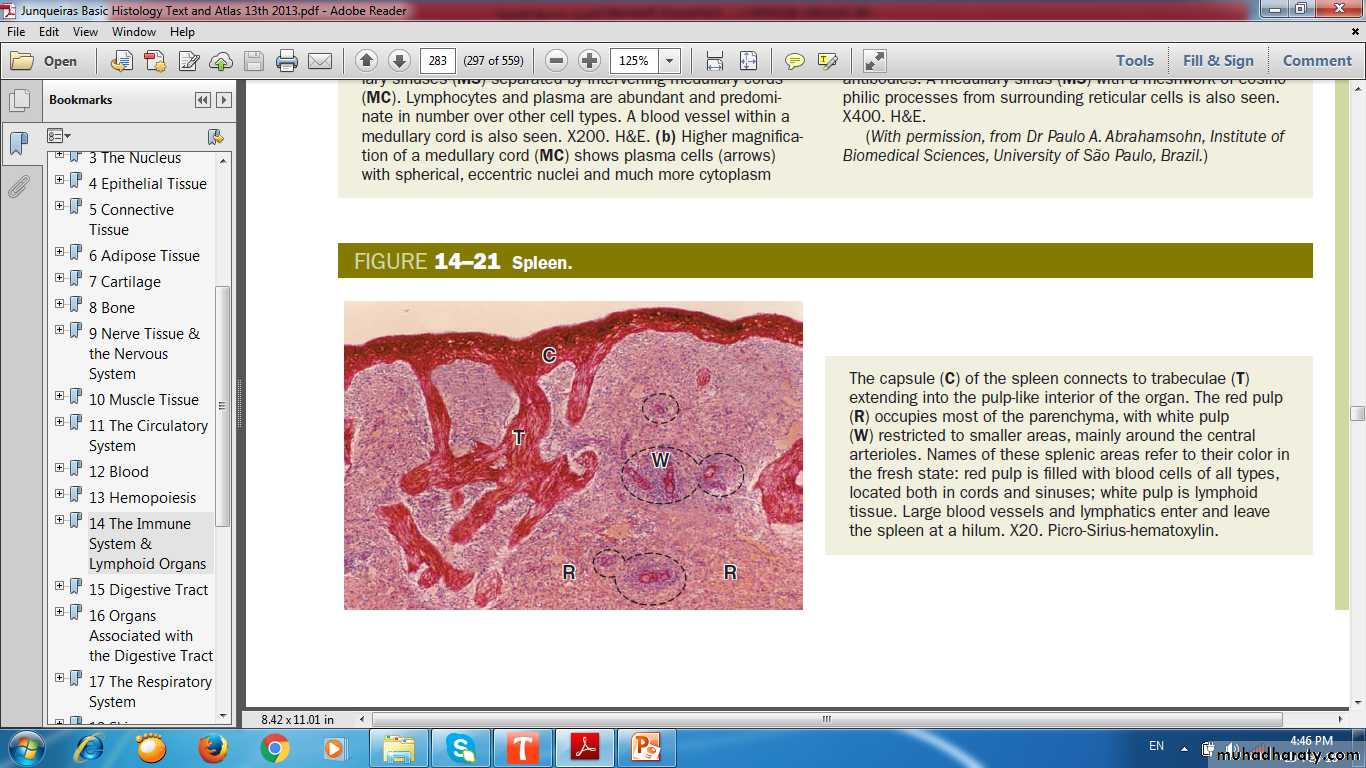
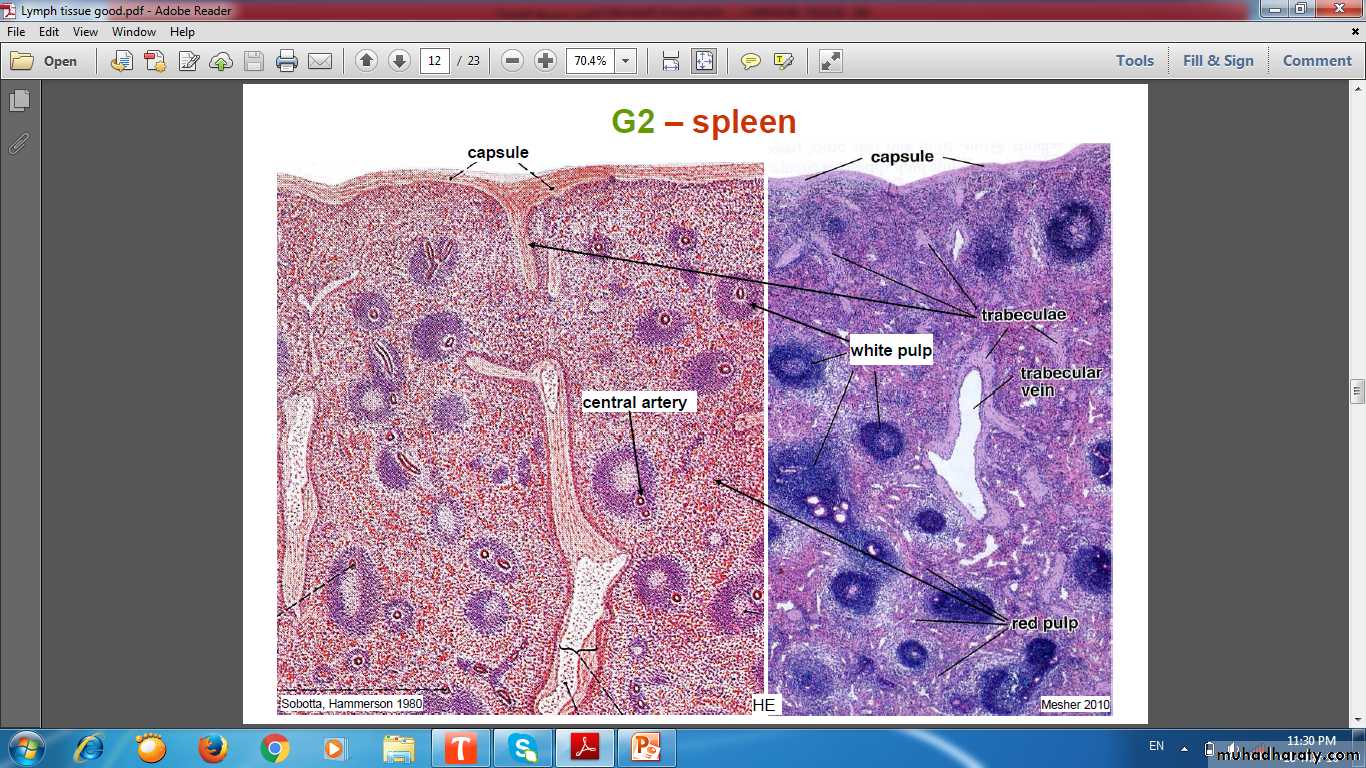
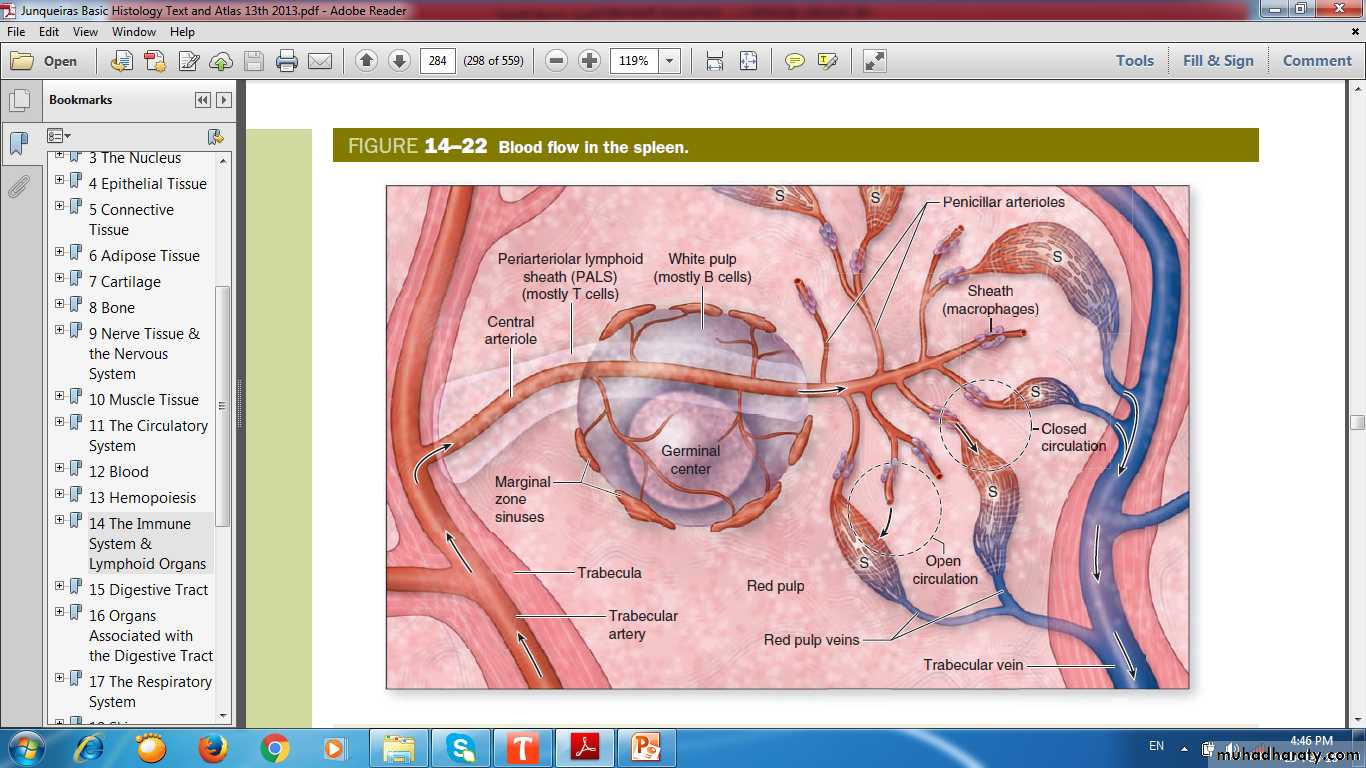
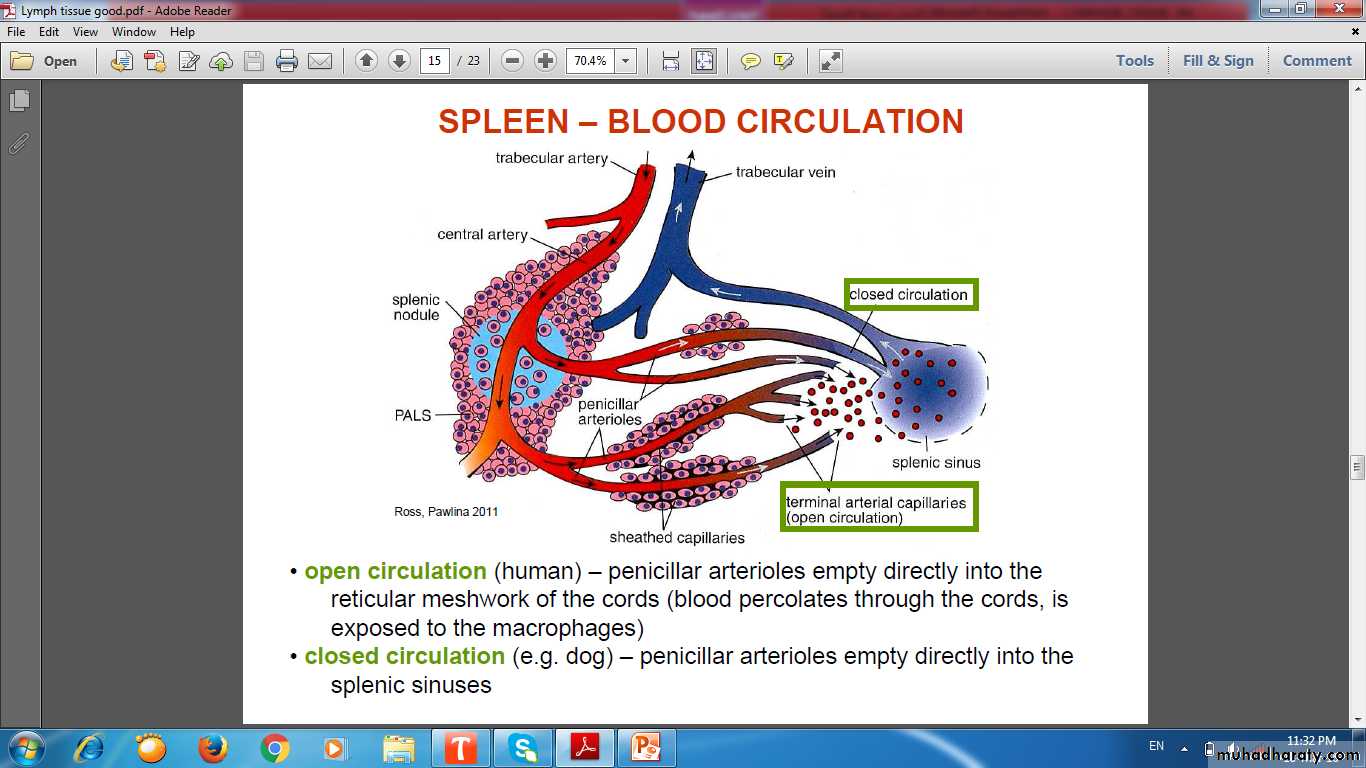
SPLEEN (FILTER OF BLOOD)Spleen
CAPSULE
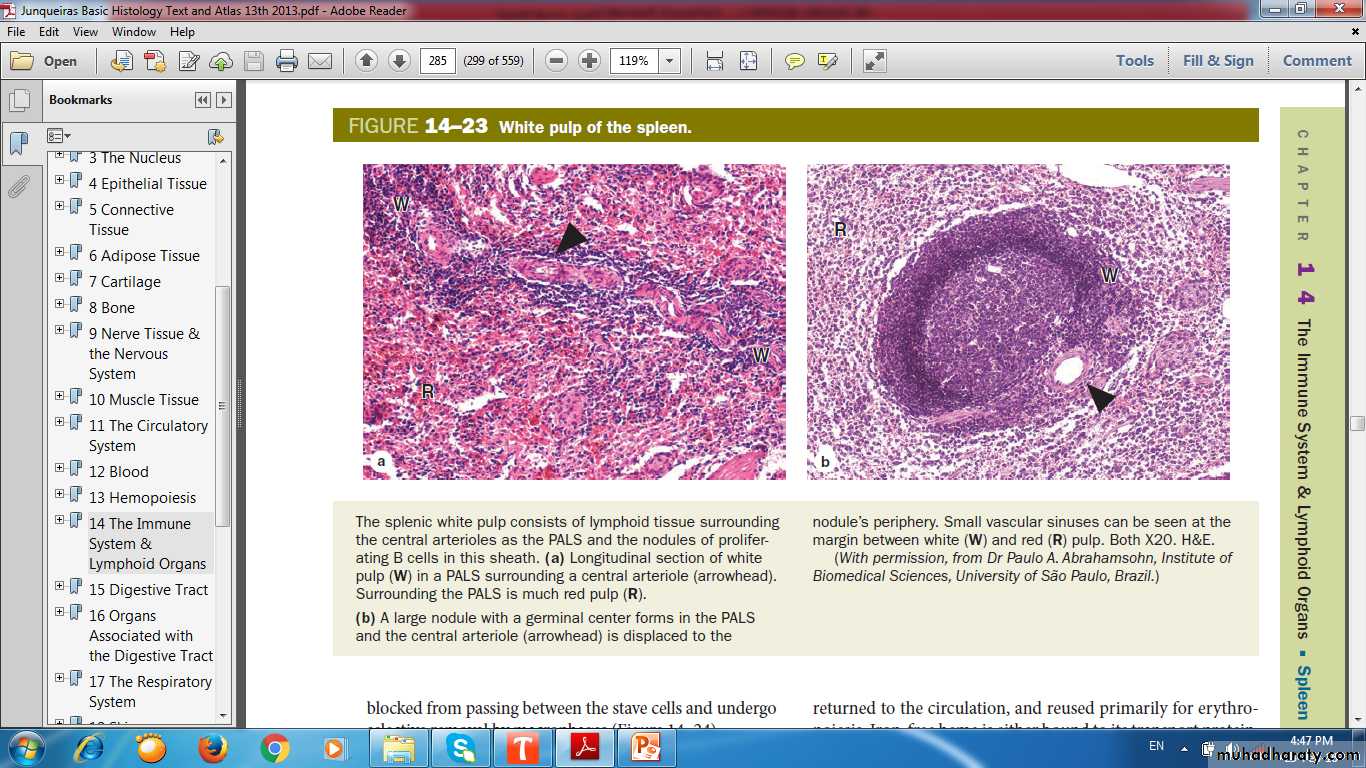
TRABECULAEWHITE PULP
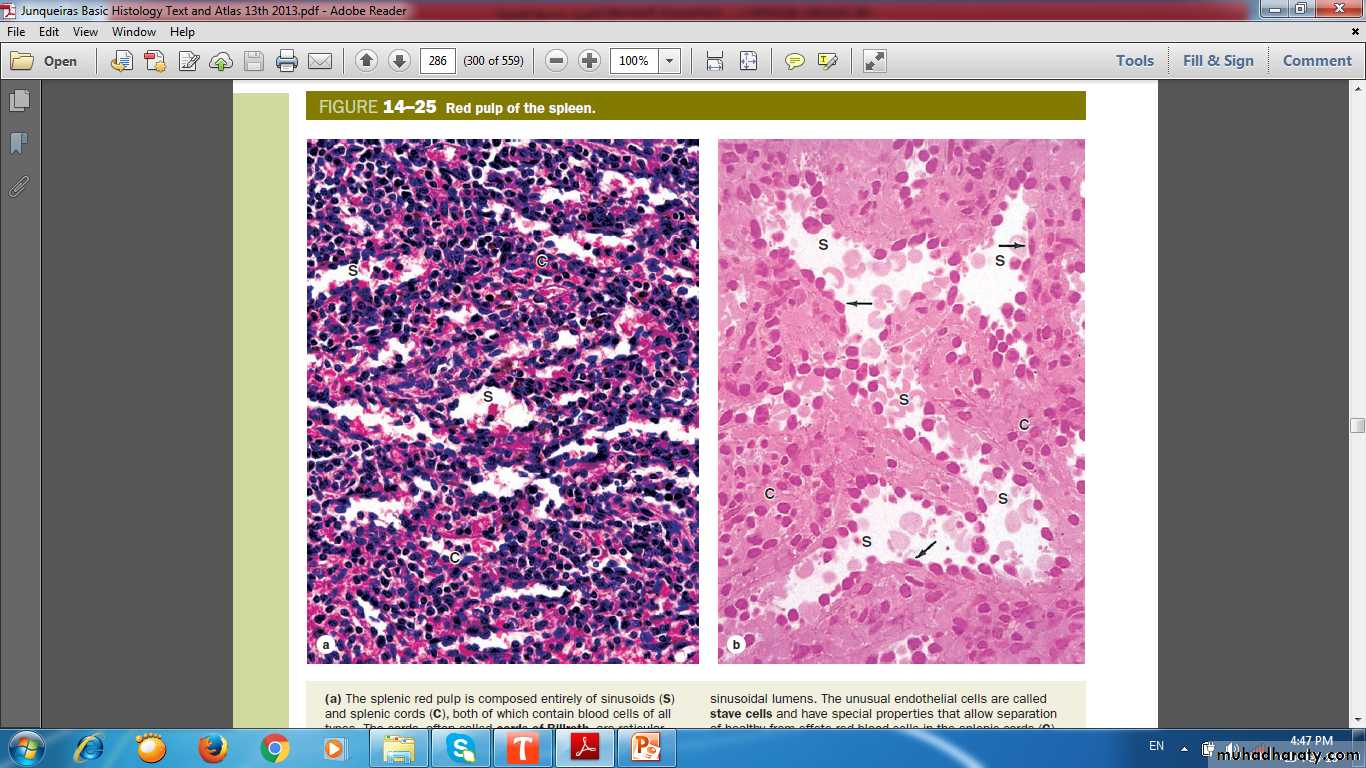
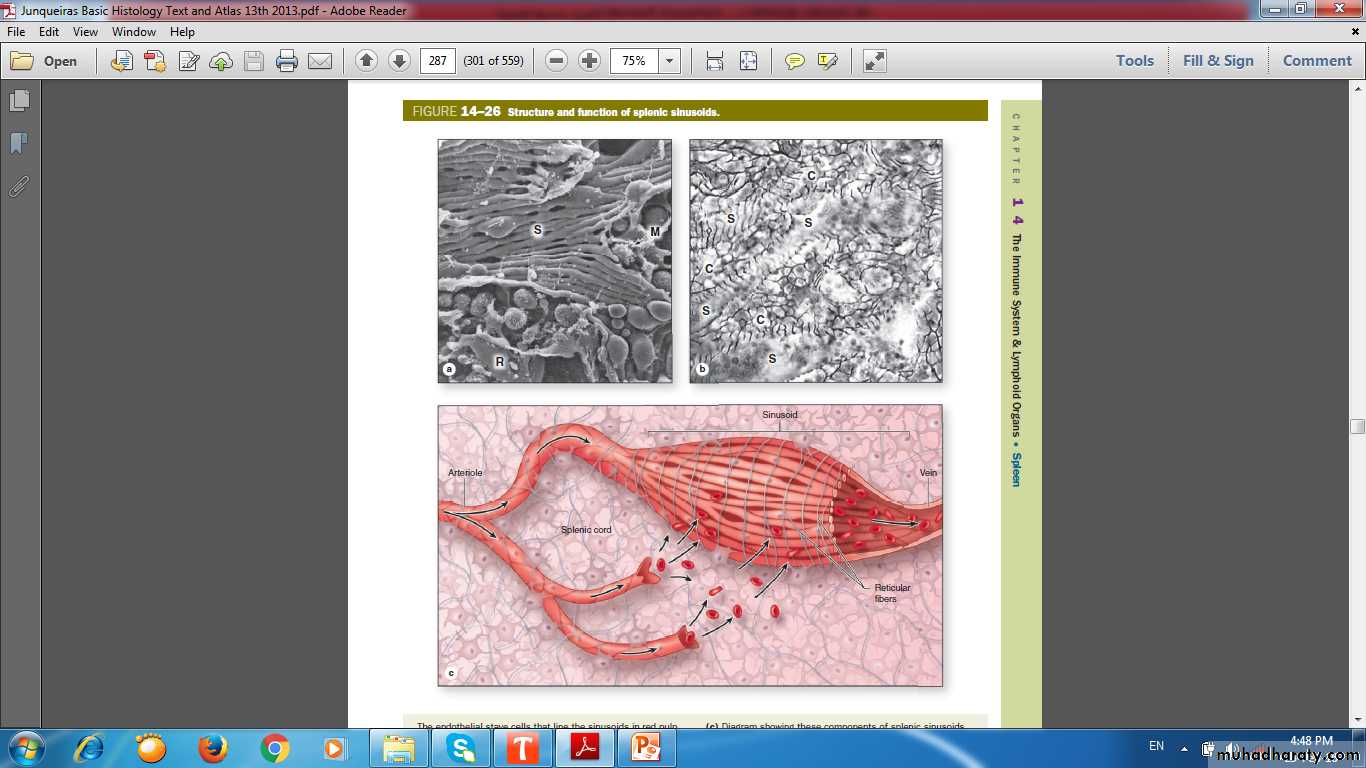
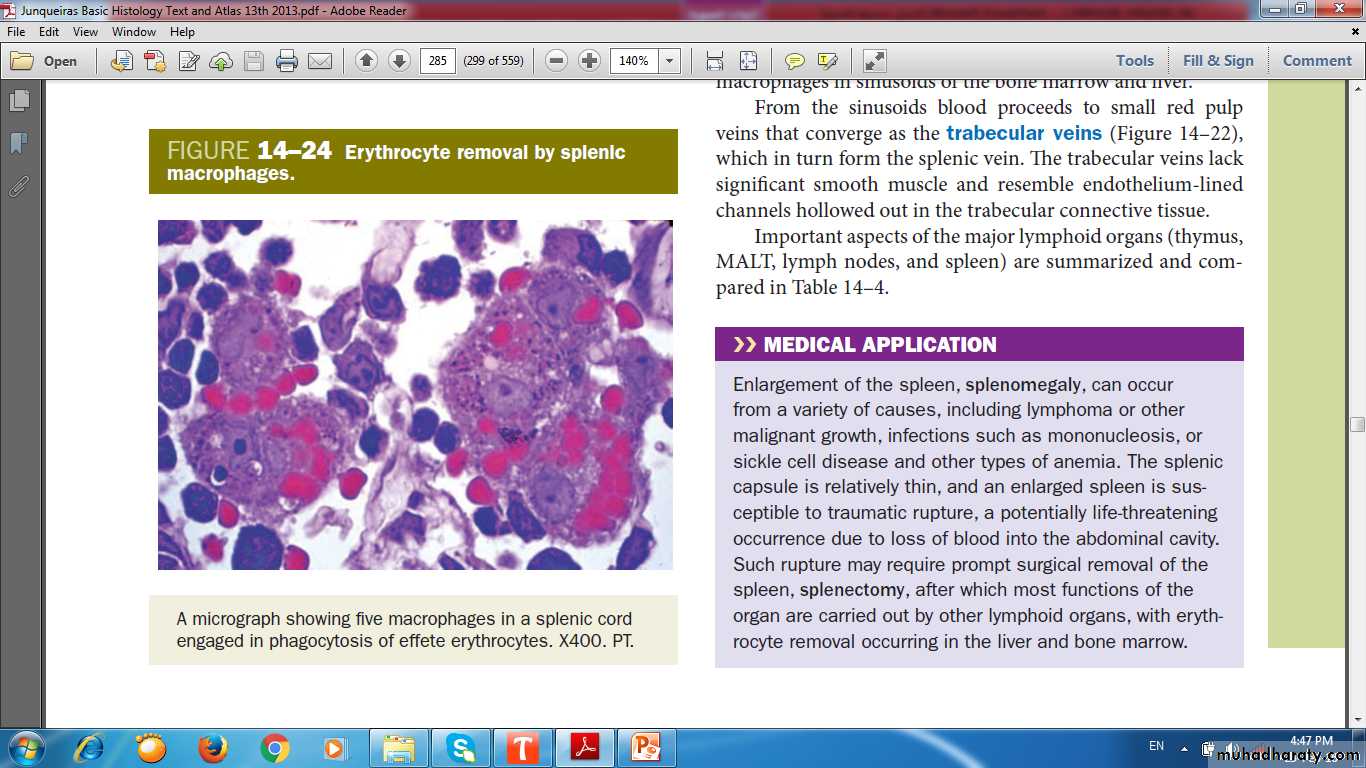
RED PULP
Spleen(Stroma)