1
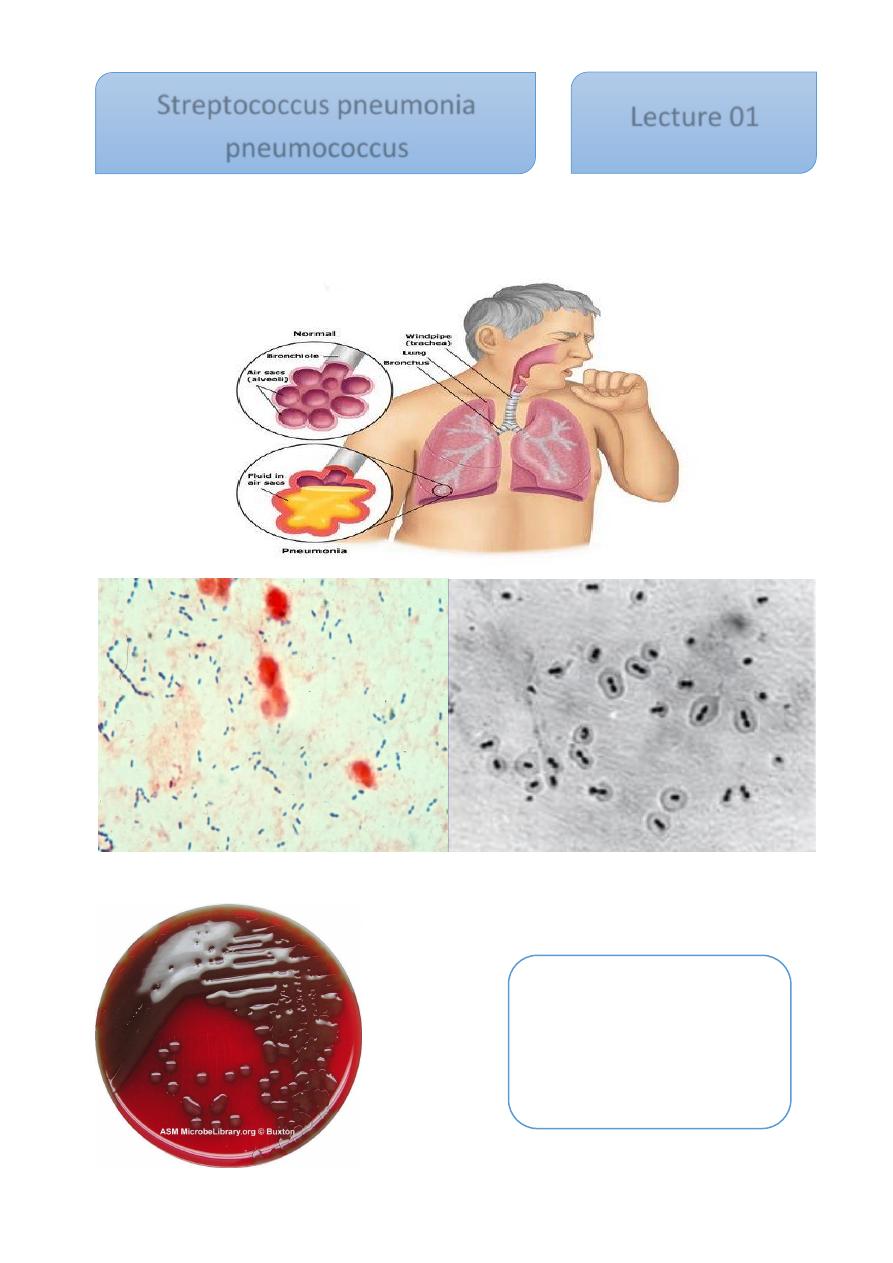
This bacterium G +ve, diplococci gived alpha hemolytic on blood agar, which caused lobar
pneumonia but it, May also cause otitis media, sinusitis, meningitis and endocarditis
Streptococcus pneumonia
Streptococcus pneumonia,
mucoid colonies
Streptococcus pneumonia
pneumococcus
Lecture 01

2
Way of infection
By the droplet
Clinical picture of lobar pneumonia:
1- Sudden onset of fever.
2- Sharp pleural pain.
3- Sputum is exudative and rusty.
4- In untreated cases consolidation of the lung will occur.
Virulence factor
• The virulence of the organism is a function of its capsule which prevent or
delays ingestion of pneumococcus by phagocytes,
Pathology
Capsule protects the pathogens from phagocytosis and is the most important
determinant of pneumococcal virulence.
Unencapsulated variants are not capable of causing disease. Other potential
virulence factors include: pneumolysin and IgA protease.
Predisposing factor of pneumococcus
1- Viral and other respiratory infection that damage surface cells.
2- Alcohol drinking.
3- Pulmonary congestion
4- Malnutrition
5- Heavy smoking
Antigenic structure
1- Peptidoglycan
2- Teichoic acid
3- Polysaccharide capsule, so the pneumococcus can be serologically classified
into more than 90 types
4- M-protein

3
Optochin Sensitivity
Pneumococci are sensitive to optochin (ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride).
Method:
Placing a disc (5g) on a primary sputum culture and culturing the plate aerobically
(not in CO2) can help to provide a rapid.
Result:
The zone of inhibition should be at least 10mm. Most viridans streptococci and
other alphaemolytic streptococci are resistant to optochin. If the zone oh inhibition is less
than 10mm (6mm disc) the colonies should be tested for bile solubility.
Bile Solubility Test
Method
: a tube technique, the results of which are easy to read. Some workers, however
prefer to test suspect alpha-haemolytic colonies directly on a culture plate by touching a
colony with loopful of 2% sodium deoxycholate.
Diagnosis
• Blood is drawn for culture and sputum is collected for demonstration of
pneumococci by smear and culture.
• The sputum is examined by:
1- direct smear stained by gram stain, show G+ve diplococci lancet –
shaped, there is unstained halo around the organism which represent
its capsule
2- Culture on blood agar: the colonies r alpha haemolytic and similar
to Strep. Viridinas
3- Biochemical reaction its bile solubility, sensitive to optochin, and
ferement inulin to produce acid only.
4- Intraperitoneal injection of the sputum into white mouse, will lead
to severe fatal septicaemia in the inoculated animal, and
pneumococcus can be isolated and demonstrated in blood smear.
5- Serological typing: fresh emulsified sputum mixed with antiserum
gives capsule swelling this reaction called quellung reaction.
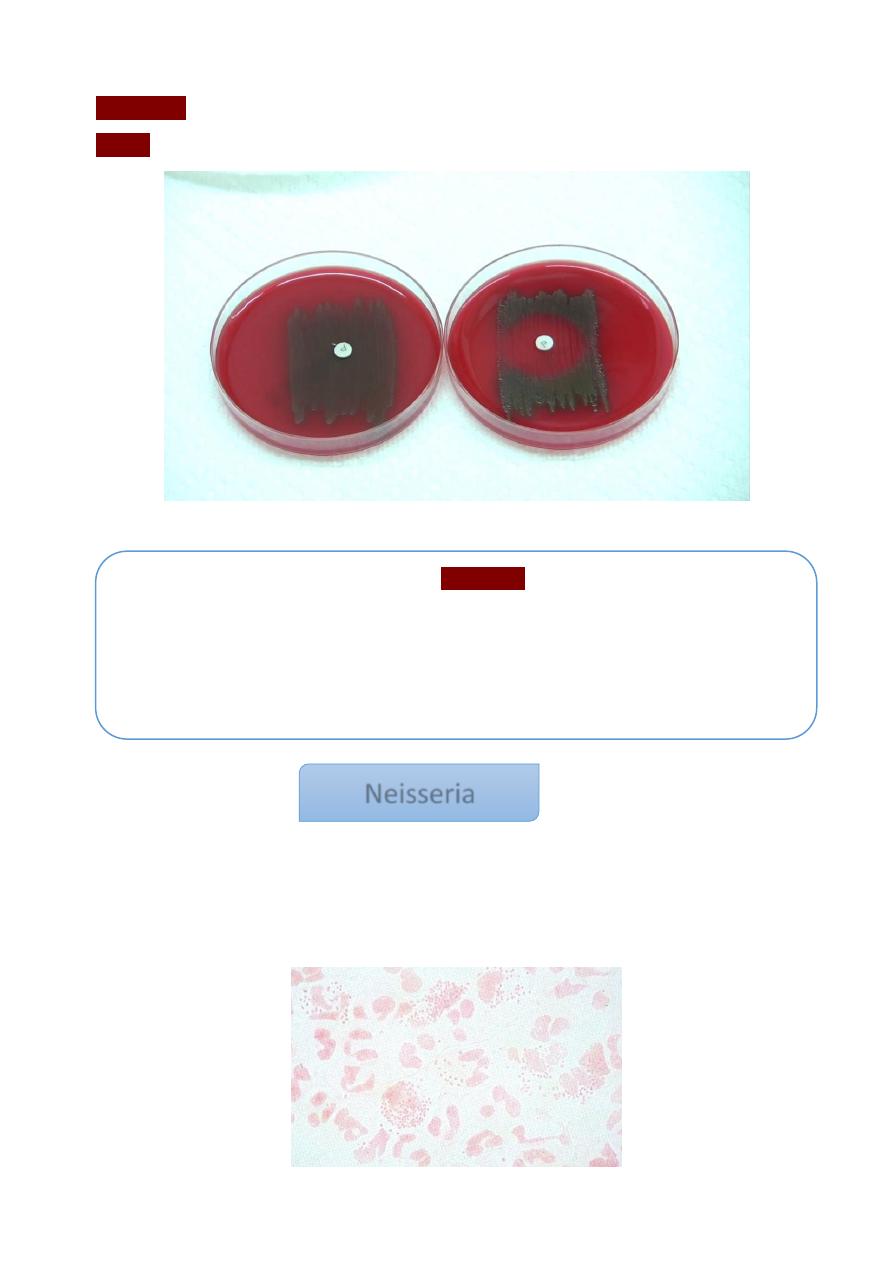
4
Incubation:
at 35-37 C for 30 minutes.
Result:
examineing for lysis (disappearance of the colony, indication S. pneumoniae).
Right (optochin positive), left (optochin negative)
The genus Neisseria includes large number of Gram-negative cocci. Many of these are
commensals in the respiratory tract, which is called N. pharynges. In this genus, there are
two pathogenic members called: N. gonorrhoeae (gonococcus) & N. meningitides
(meningococcus).
Treatment
• Pneumococcus is sensitive to many antimicrobial drugs, early treatment
usually results in rapid recovery.
• Penicillin G is the drug of choice, other beta lactam drugs like cephalosporin
generations
• Also pnumococcus susceptible to vancomycin.
Neisseria

5
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
This species can cause 2 types of infections include :-
A. Venereal infection : gonorrhoea which is transmitted by sexual contact .
B. Non-venereal infection : Ophthalmia neonatorum is transmitted by
contamination of infant's eye during labour through the birth canal of a
gonorrhoeal mother and vulvo-vaginitis in small girls through contaminated
toilet seats & contaminated towels .
Neisseria gram stain
Antigenic structures of Neisseria:
1- Outer membrane protein (omp): which antigenic and antiphagostic factor
2- Lipopolysaccharide which act as endotoxine
3- Pili which help neisseria to attach with epithelial host cells
Gram stain of
N.gonno

6
Clinical manifestations
In the male, there is cause urithritis with yellow creamy pus & painful urination,
the process may extend to prostate & epididymis.
In female the infection may extend to the cervix to cause mucopurulent discharge,
it may be then progress to the fallopian tube causing pelvic inflammation, fibrosis
& obliteration of tubes with consequent sterility, chronic gonorrhoea is often
asymptomatic.
Diagnosis of gonorrhea:-
Acute gonorrhea can be detect by:
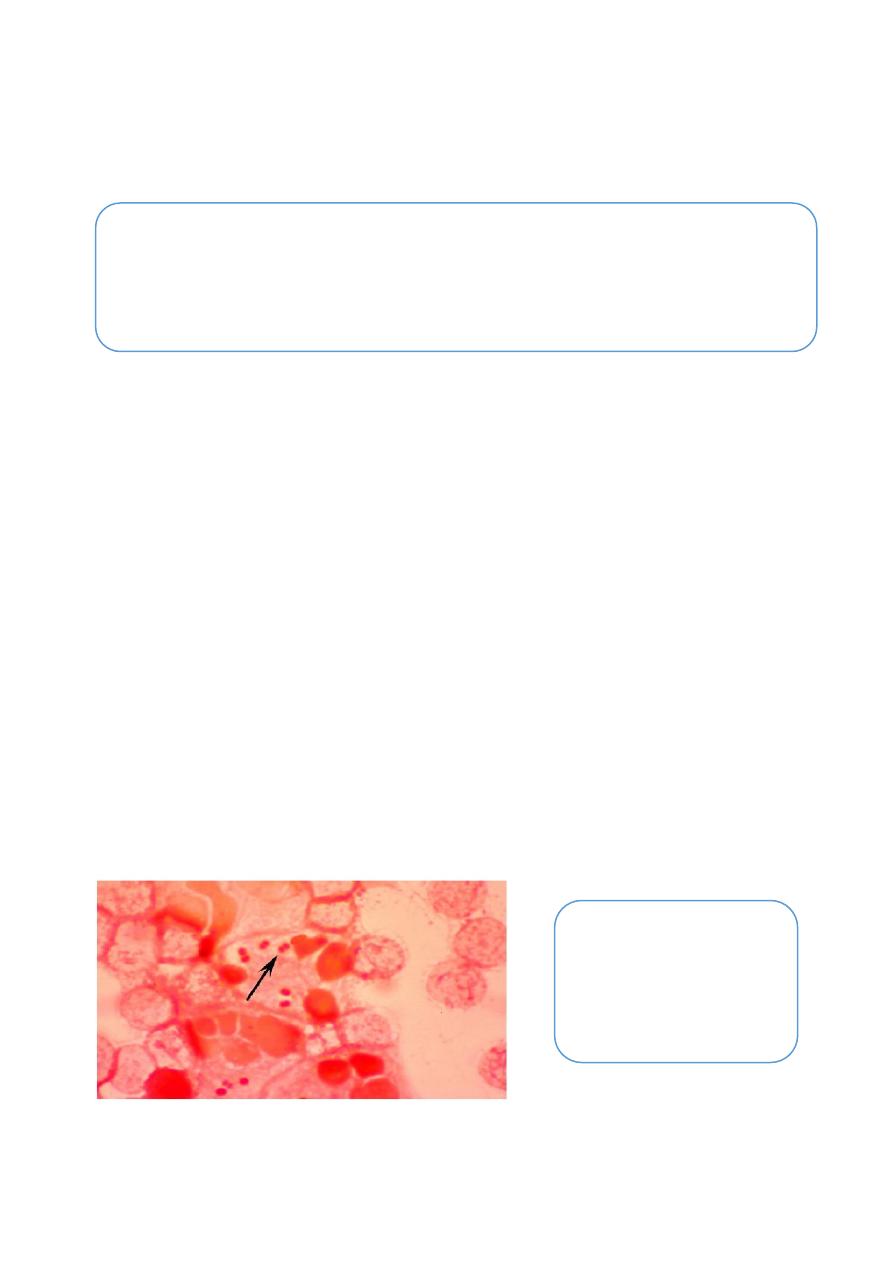
a. Microscopically examination: direct smear from the discharge stained with Gram's
stain to show the kidney shape G
-ve
diplococci present intracellular & extracellularly,
non-spore forming.
b. Culture: this perform on blood agar or chocolate agar or Thayer-Martin medium
incubated in 5% CO
2.
The colonies are non-hemolytic, non-pigmented or gray in
color, smooth, circular, small & convex.
While in case of chronic gonorrhea, in male, the morning drop of discharge or
prostatic secretion after massage can be examined as before. In female,
cervical swab may give positive results.
Virulence Factor
Pili: most important virulence factors helping the gonococci to stick on the
epithelial cells.
IgA protease that cleave IgA on mucosal surface.
Lipopolysaccharide damage tissue and prevent phagocytosis.
Salpinitis

7
c. Serology : in this tests can be use serum & genital fluid that contain IgG and IgA
antibodies against gonococcal pili , outer membrane proteins and
lipopolysaccharide
Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
Ceftriaxone
Penicillin
Chloramphenicol
Ampicillin
Trimethprimsulphonate
Neisseria meningitides
This bacterium mainly cause cerebrospinal meningitis but it also can cause pharyngitis ,
adrenal haemorrhages & rarely myocarditis , the infection transmitted from the patient or
carrier by droplets of nasopharyngeal secretions .
Virulence Factor
Polysaccharide capsule (13 serogroup the most pathogenic is A, B, C, Y, and
W-135).
Pili.
IgA protease.
Endotoxins.
Treatment :-
• Gonococci is treat by penicillin , but sensitivity test is indicated because
gonococcal resistance to pencillin has gradually increased, therefore used new
drugs like Ciprax single dose.
N.meningitidis
8
Clinical manifestation of cerebrospinal meningitis:
This infection causes sudden onset of fever, vomiting, stiff neck, hemorrhage, skin rash and
coma within a few hours.
Diagnosis :
1. C.S.F. examination :
Lumber puncture is done under complete aseptic conditions, the CSF appear turbid (it’s
clear colorless in normal case).
a. Direct smear: stained by Gram's stain, the bacteria appear as G
-ve
diplococci mainly
intracellularly usually coffee bean in shape, non-spore forming.
b. Culture : this bacteria no growth in ordinary media , but grow on blood & chocolate
agar in the presence of 5% CO
2
, the colonies on blood agar are non-hemolytic ,
moist , devoted , smooth , translucent , round & convex . Thayer-Martin medium
containing antibiotic can also be used.
2.
Blood culture
is perform in case of septicemia.
3.
Nasopharyngeal swab
for culture is perform.
4.
Biochemical reaction tests
: this include fermentation of glucose & maltose with
acid only. catalase & oxidase tests are positive
5. Serological test :
Antigenically , meningococci are divided into several groups are A,B,C,w- 135&y ,
group A found in a most countries , while group c and w-135 associated with the
epidemiology .
Specific anti-meningococcal antibody in serum to detect colony by agglutination test,
meningococcal antigen can be detect in C.S.F. of patient with active disease.
Mubark A. Wilkins
Treatment
• Penicillin G has become the drug of choice, also 80-90 % of strains are sensitive
to sulfonamide that is diffuse readily into C.S.F. Chloramphenicol or third
generation cephalosporin is used in-patient with allergy to penicillin.
