PARANASAL SINUSES
Ap.Dr.ALI MOHSIN HASANDGS FICS CABS MRCS FRCS
OBJECTIVES:
Anatomical locationConnections
Development
Neurovascular supply
Applied anatomy
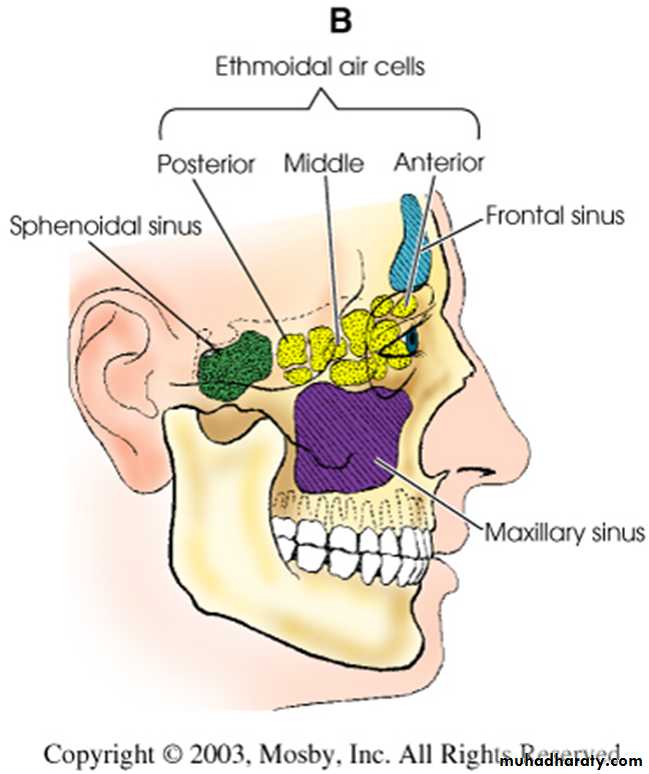
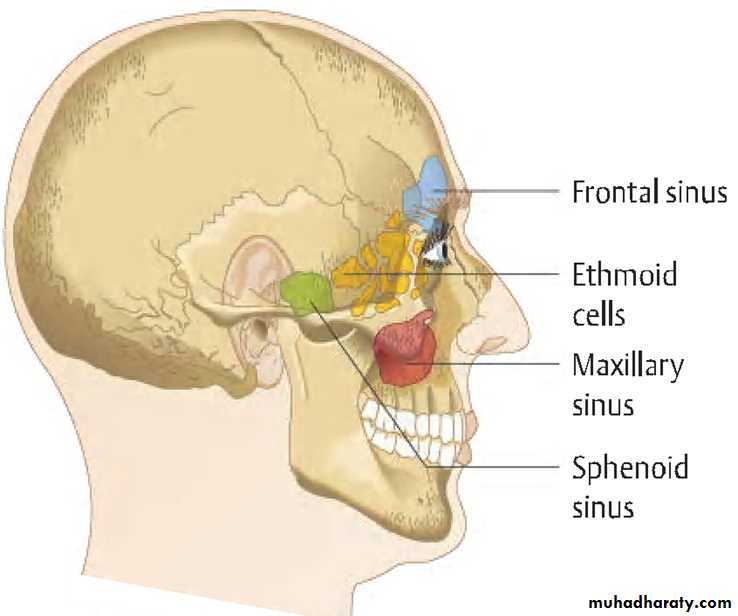
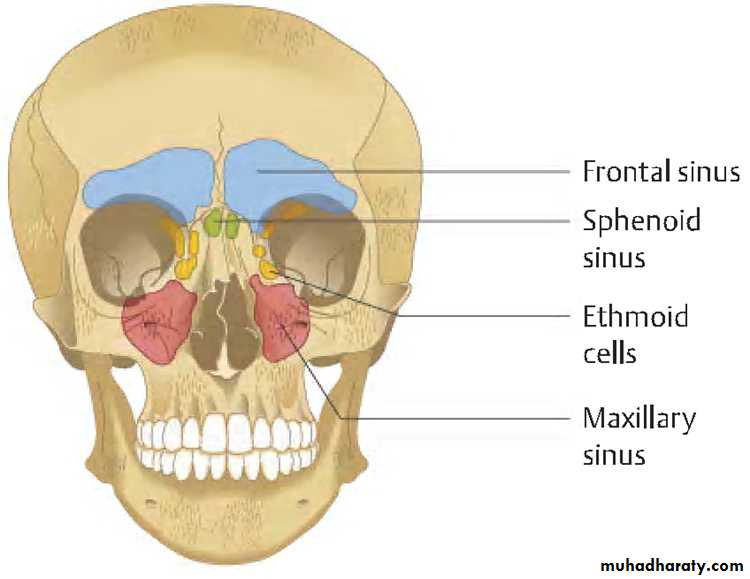
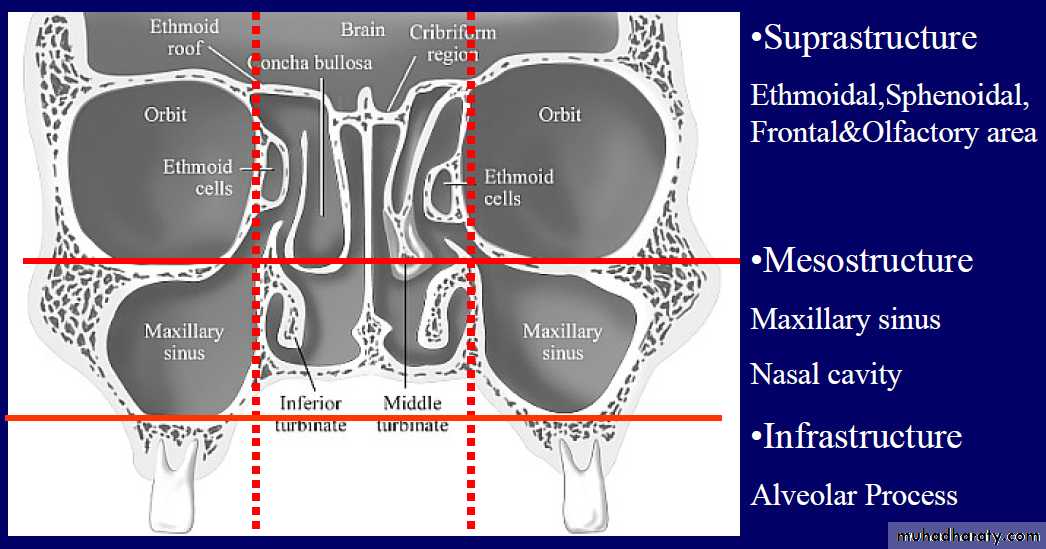
PNS:
Air containing cavities4 pairs :-
FrontalMaxillary
Ethmoidal
Sphenoidal
FUNCTION:
To make the skull lighter and add resonance to the voice.The sinuses are rudimentary or even absent at birth.
Enlarge rapidly during the age 6yr and then afterwards.
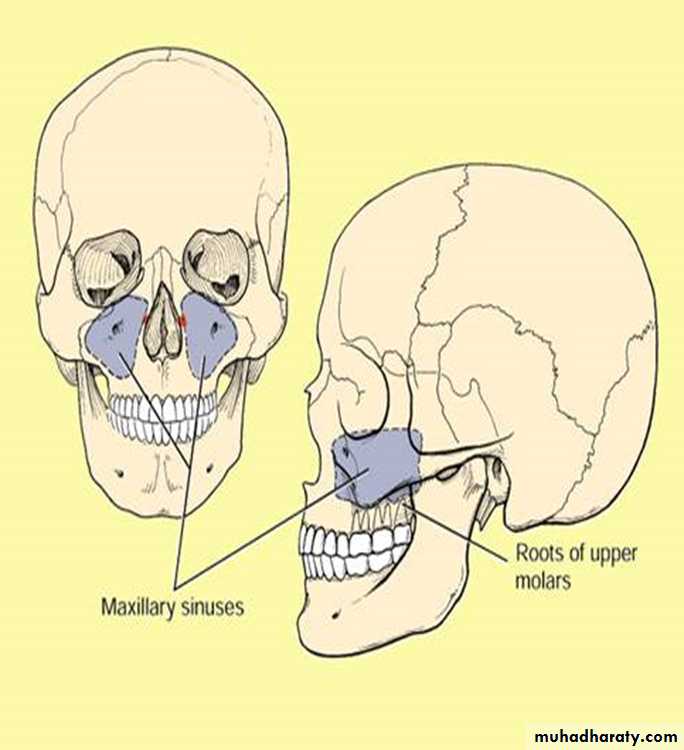
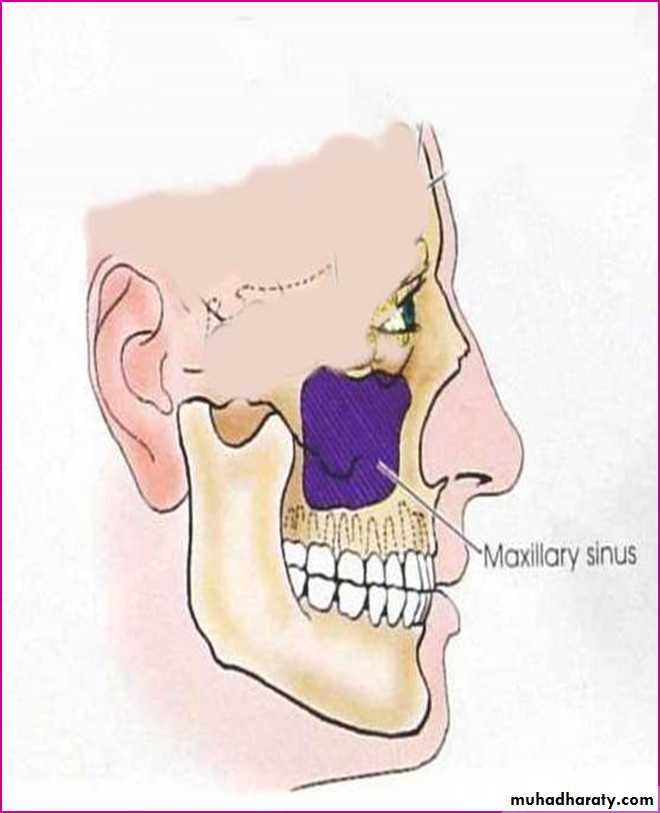
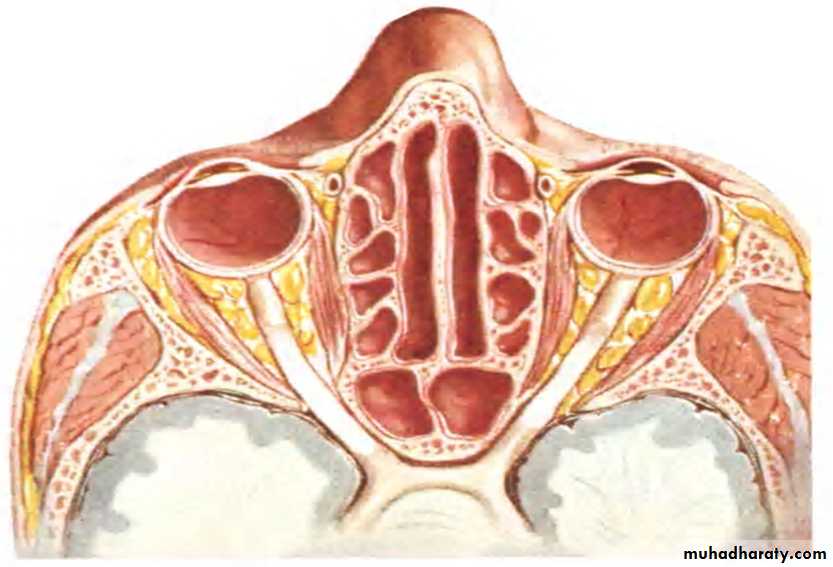
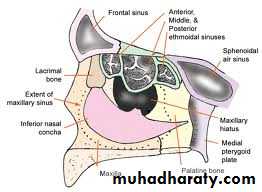
MAXILLARY SINUS:
Largest of allPyramidal in shape
Base pointing to lateral wall of nose.
Apex laterally in the zygomatic process of maxilla.
BOUNDARIES:
Anterior:- facial surface of maxillaPosterior:-infratemporal and pterygopalatine fossa
Medial:- middle and inferior meatus
Floor:- alveolar and palatine processes of maxilla
Roof:-floor of orbit
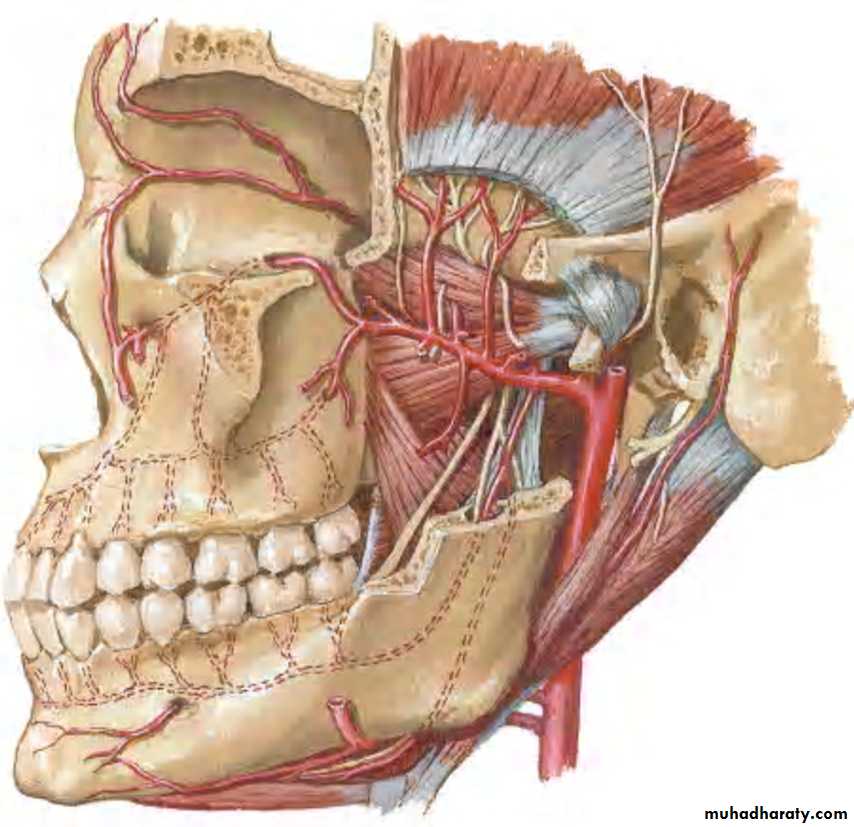
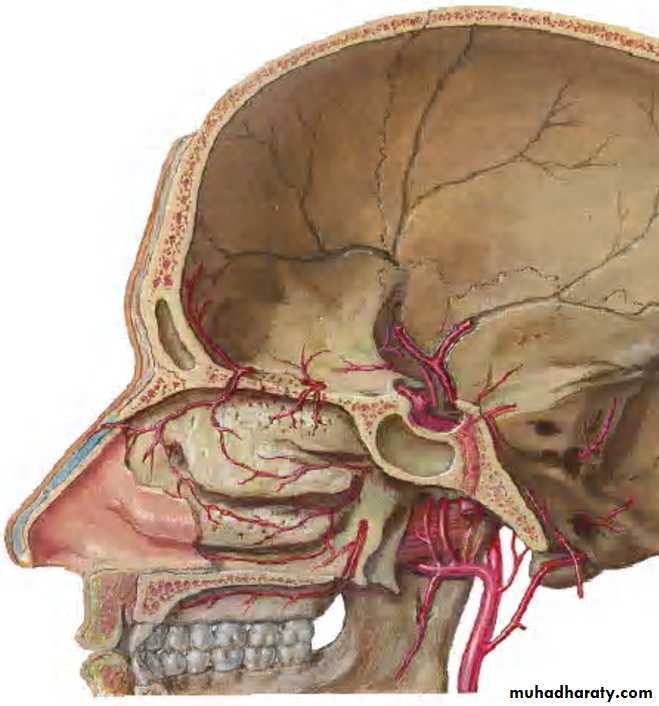
BLOOD SUPPLY:
ARTERIAL:By facial artery branch of ECA.
By infra orbital & greater palatine arteries branch of max. art which is branch of ECA.
VENOUS:
To anterior facial vein& pterygoid plexus.
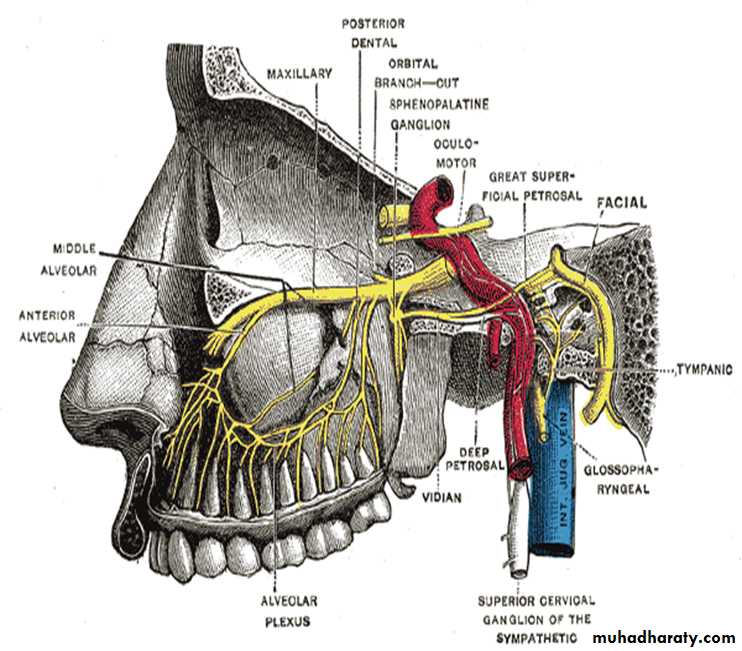
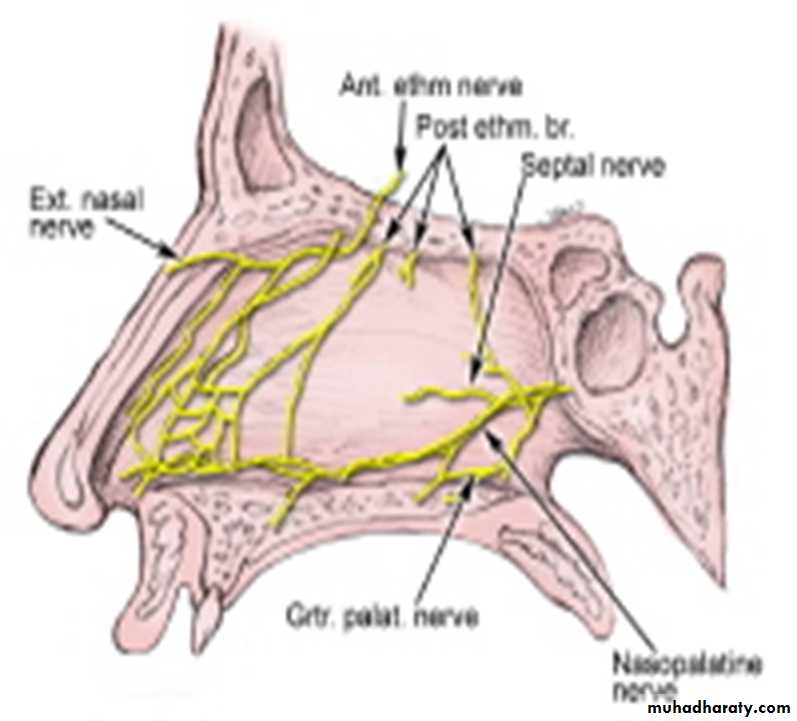
NERVE SUPPLY:
Infraorbital nerveAnterior superior alveolar nerve
Middle superior alveolar nerve
Posterior superior alveolar nerve
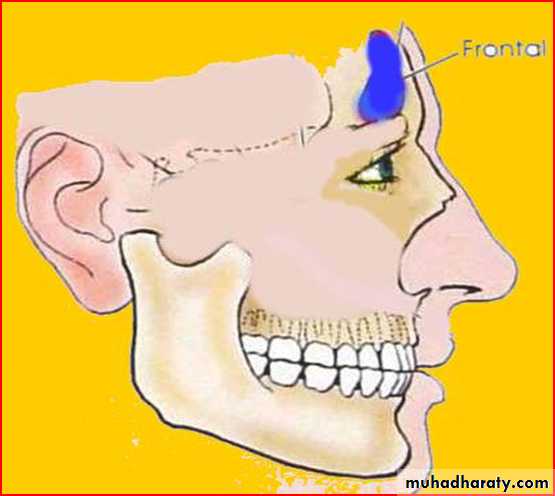
FRONTAL SINUS:
Resides in frontal bone2nd largest
Asymmetrical
Right n left are usually unequal
RELATIONS:
Anterior:- skin over the foreheadInferior:-orbit & its contents
Posterior:- meningeal and frontal lobe of brain
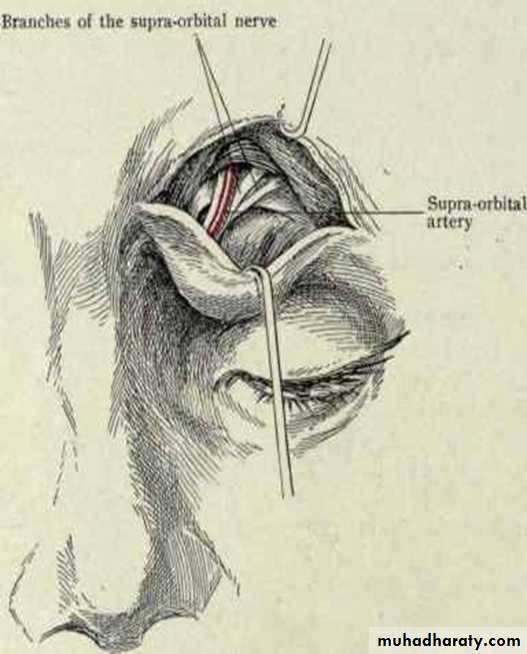
NEUROVASCULAR SUPPLY:
Blood supply - Supra orbital arteryVenous return - Anastomotic veins in supra orbital notch, connecting supra orbital and supra ophthalmic veins.
Lymphatic drainage - Submandibular nodes.
Nerve supply - Supra orbital nerve(ophthalmic nerve)
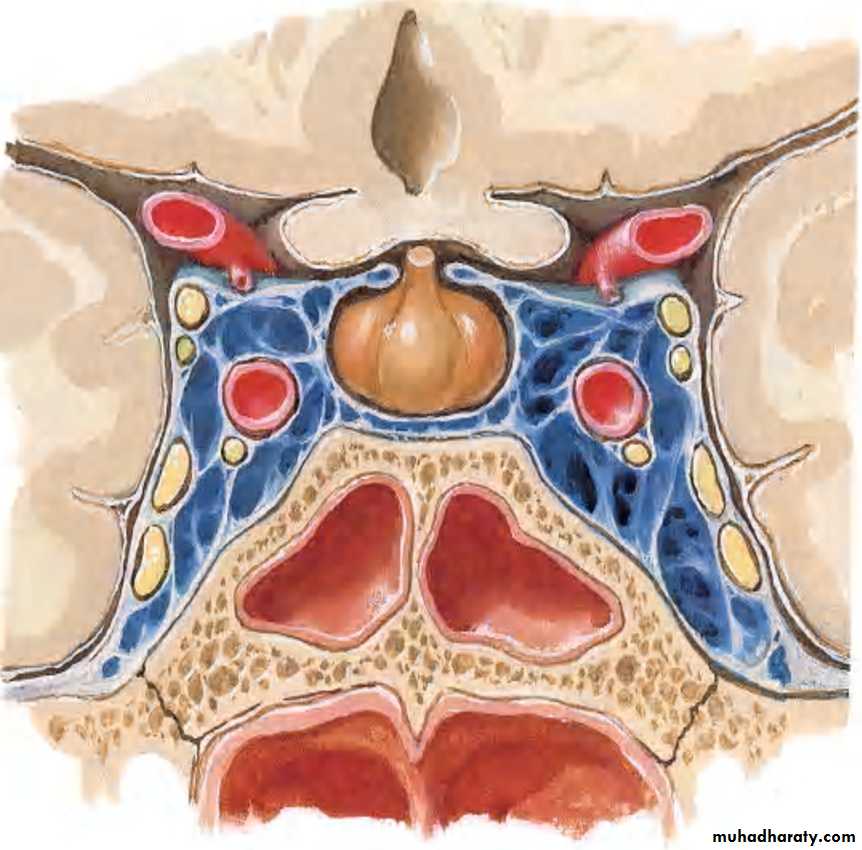
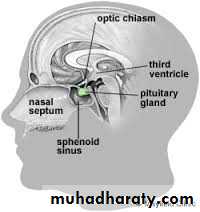
SPHENOIDAL SINUS:
Resides in body of sphenoidMay be single or paired
Asymmetrical
Unequal in size
RELATIONS:
1.Cavernous sinus lies laterally containing the:
• IIIrd,• IVth,
• Vth (ophthalmic
and maxillary-
divisions) and
• VIth cranial nerves,
2.Internal carotid artery
SUPERIORLYOptic chiasma
Hypophysis cerebri
NEUROVASCULAR SUPPLY:
Blood supply:Posterior ethmoidal artery
Venous drainage:
Pterygoid plexuses
Nerve supply:
Posterior ethmoidal nerve
Lymphatic drainage: Retropharyngeal nodes
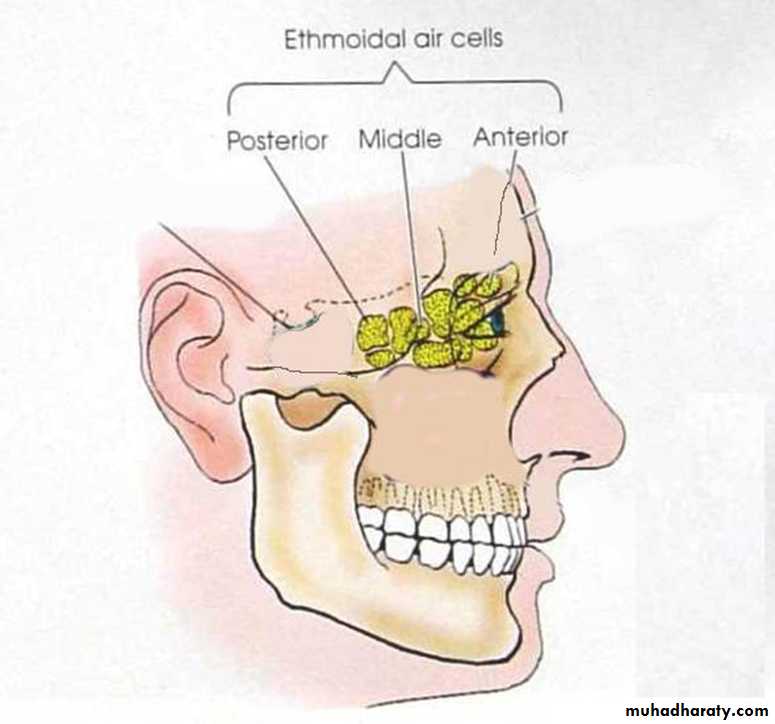
ETHMOIDAL SINUS:
Resides in ethmoid bone3 groups:-
Anterior
Middle
Posterior
Number varies from 3-18
Present from birth
RELATION:
Above:orbital plate of frontal boneBehind:orbital process of palatine bone
Anteriorly:
lacrimal bone
NEUROVASCULAR SUPPLY:
Arterial supplyAnterior ethmoidal artery(ophthalmic artery)
Post. Ethmoidal artery
Sphenoidal artery(maxillary artery)
Venous drainage
Ant. Ethmoidal vein
Post. Ethmoidal vein
Nerves :
Anterior and posterior ethmoidal nerves.Orbital branches of pterygopalatine ganglionLymphatic drainage : Submandibular nodesRetropharyngeal nodes
DEVELOPMENT:
Outpouching from mucus membrane of noseat birth:-Maxillary and ethmoidal present
At 6-7 yrs:- frontals and sphenoids
At 17-18 :- all fully developed
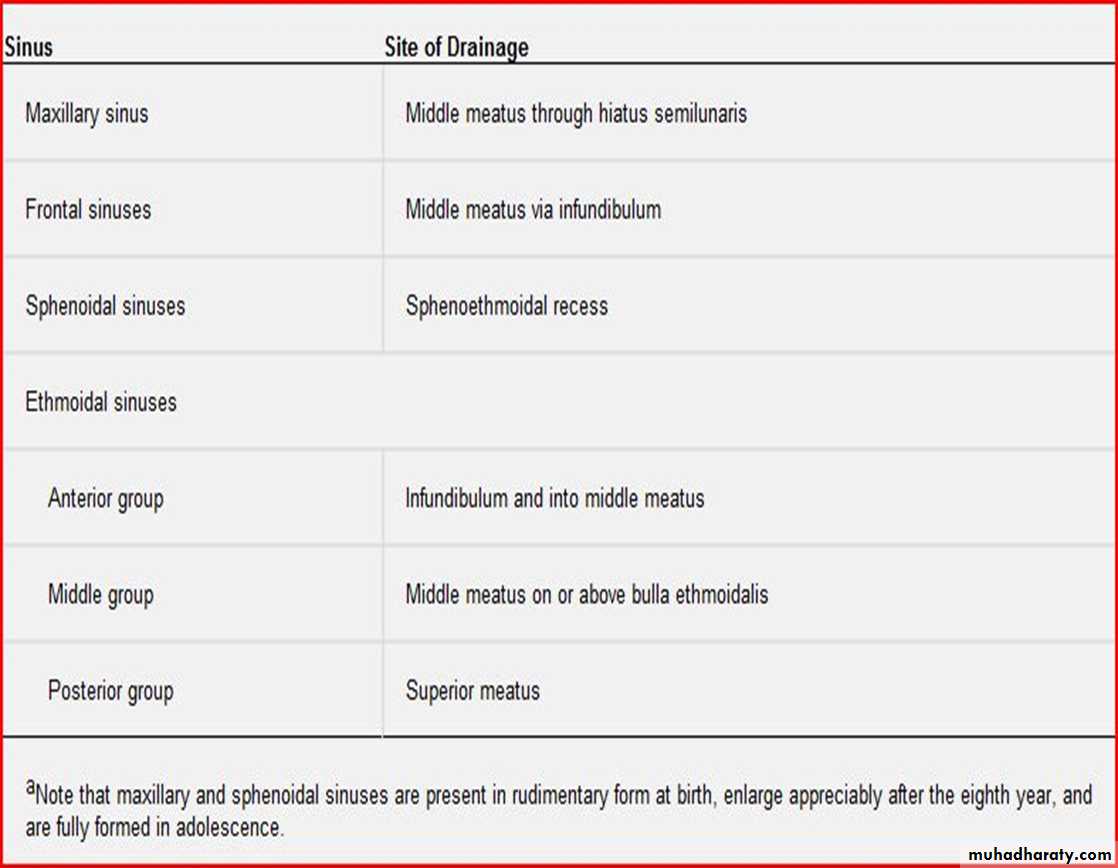
DRAINAGE:
APPLIED ANATOMY:
SINUSITIS:Infection of sinus
S/S:
Headache
Thick purulent discharge from nose
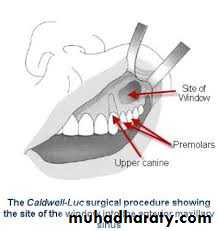
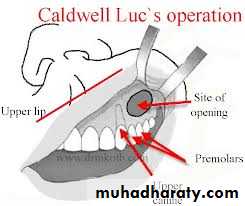
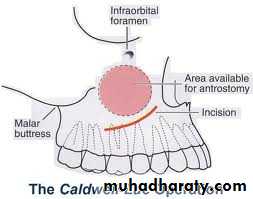
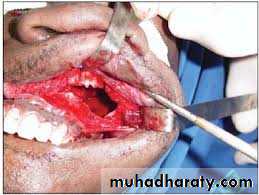
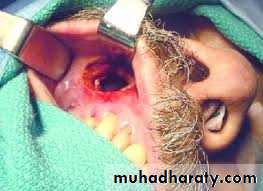
DRAINING MAXILLARY SINUS:
SITE OF INCISION:
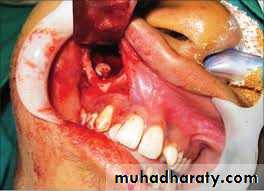
CLINICAL PICTURE:
APPLIED:
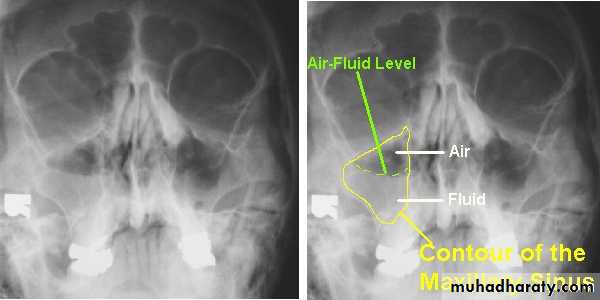
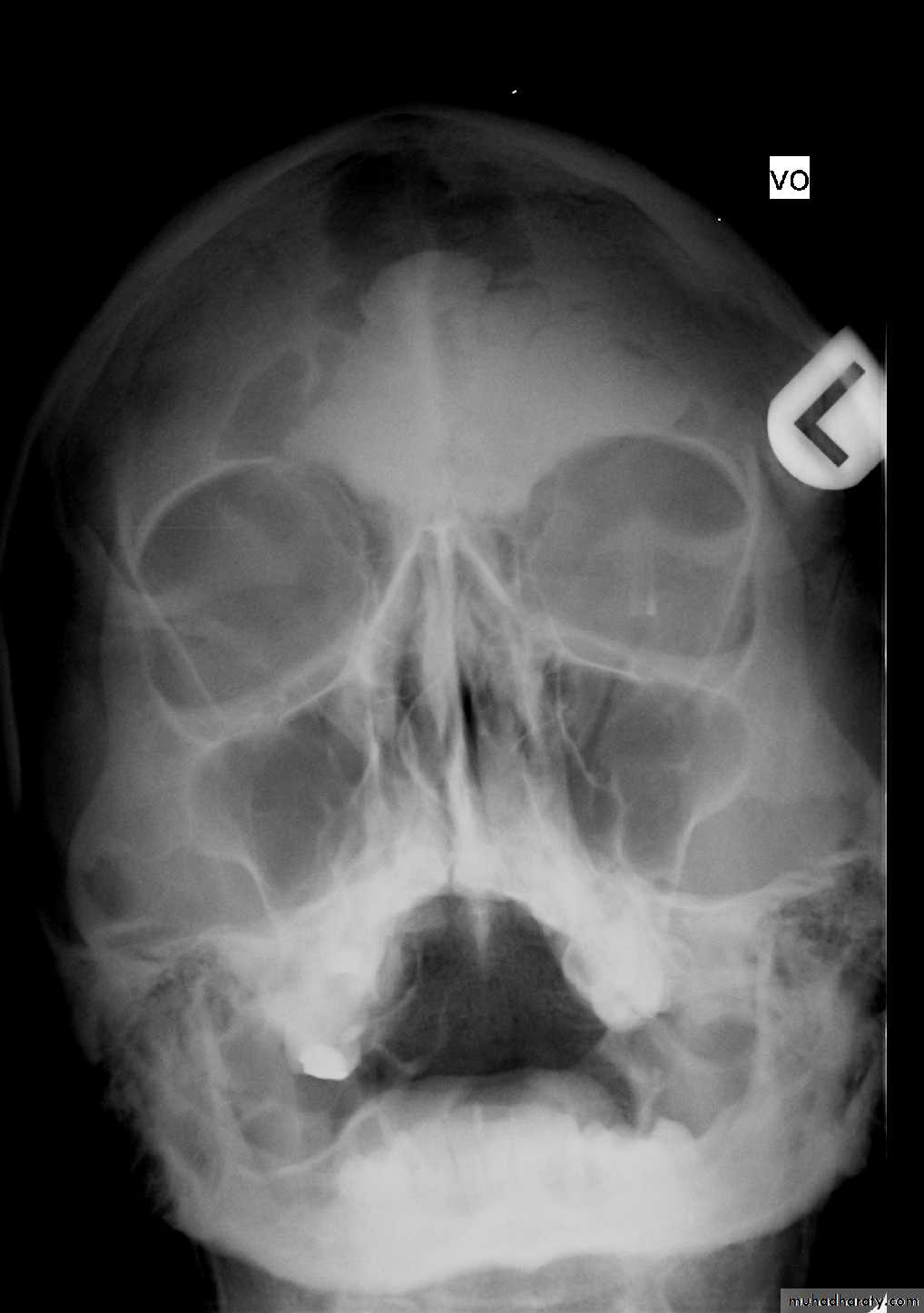
Frontal sinusitis and ethamoidal sinusitis can cause edema of the lids secondary to infection of the sinusesRADIOGRAPHIC FINDINGS:
BENIGN NEOPLASMS
OsteomasFibrous Dysplasia
Ossifying Fibroma
Ameloblastoma
Inverted Papilloma
OSTEOMA
15 to 40 yearsFrontal > Ethmoid > Maxillary
Slow-growing bone tumour &
often remains asymptomatic.
It can cause
obstruction of ostium
mucocele formation
pressure symptons
Rx :Local excision
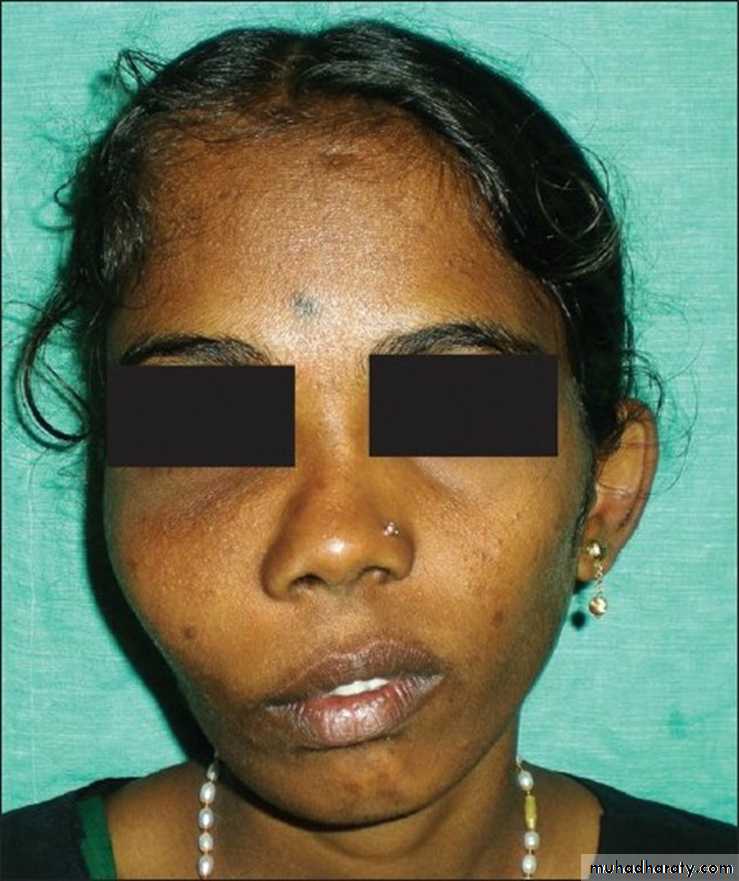
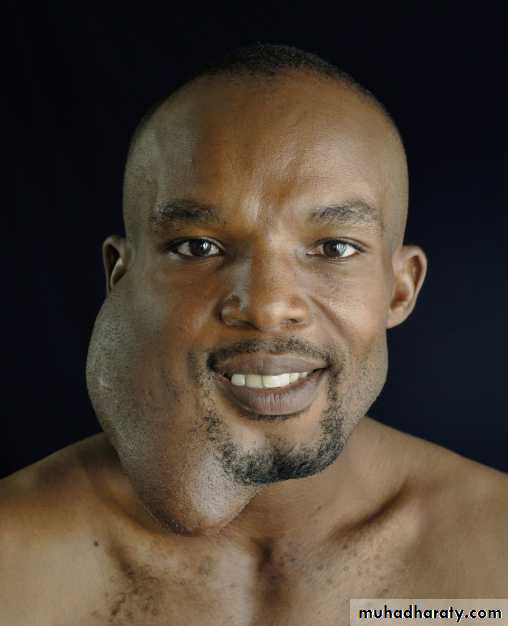
FIBROUS DYSPLASIA
Bone replaced by Fibrous tissueMaxilla > Ethmoids & Frontal
C/F:
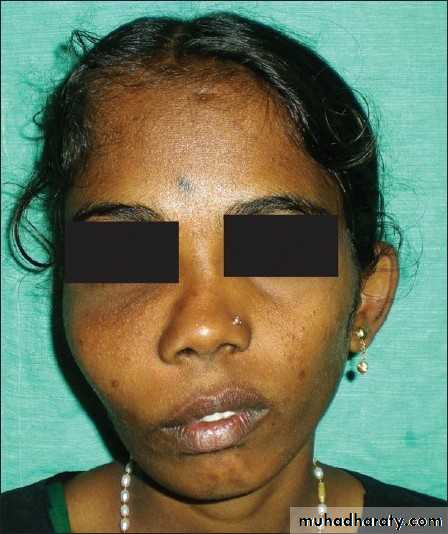
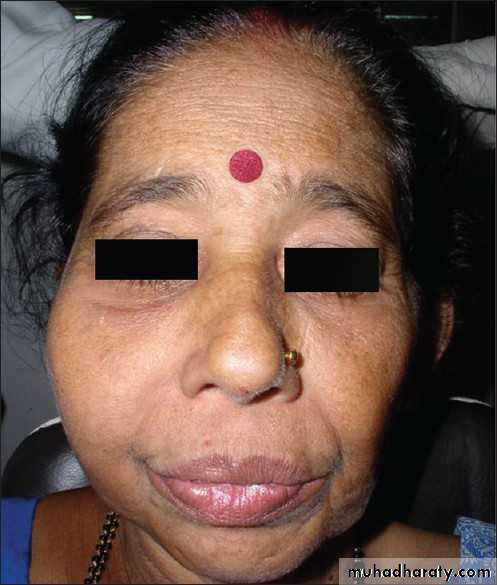
Disfigurement of Face
Nasal Obstruction
Displacement of eyes
Radiology:
Diffuse margins with Ground glass appearance
Rx - Cosmetic restructuring surgery
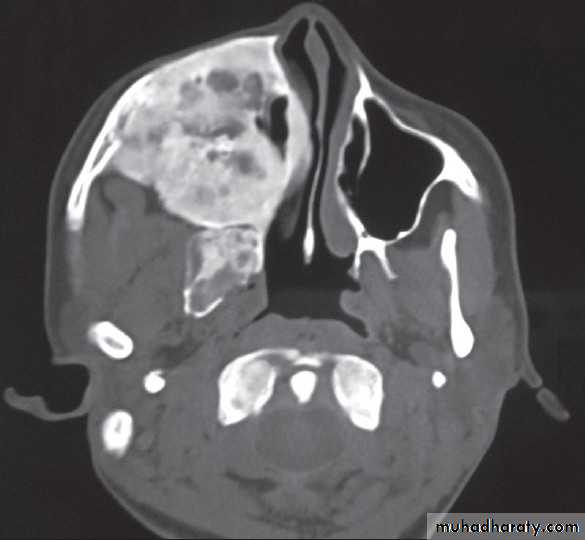
FIBROUS DYSPLASIA
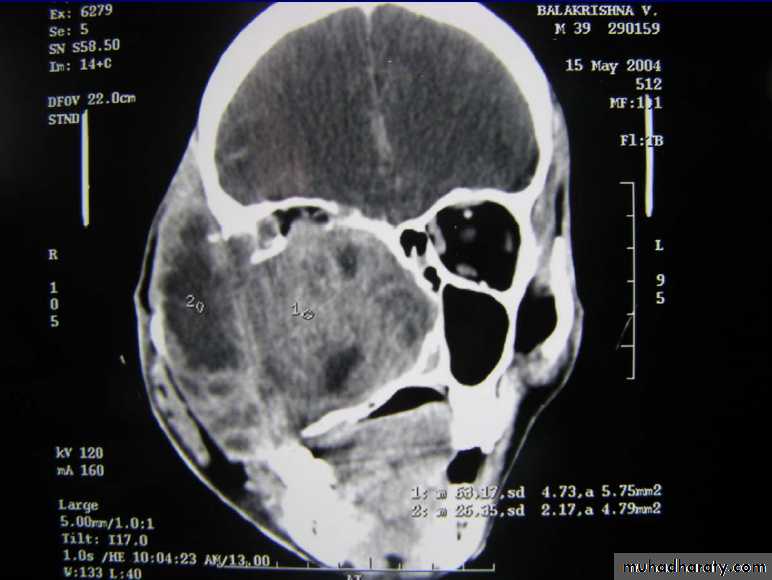
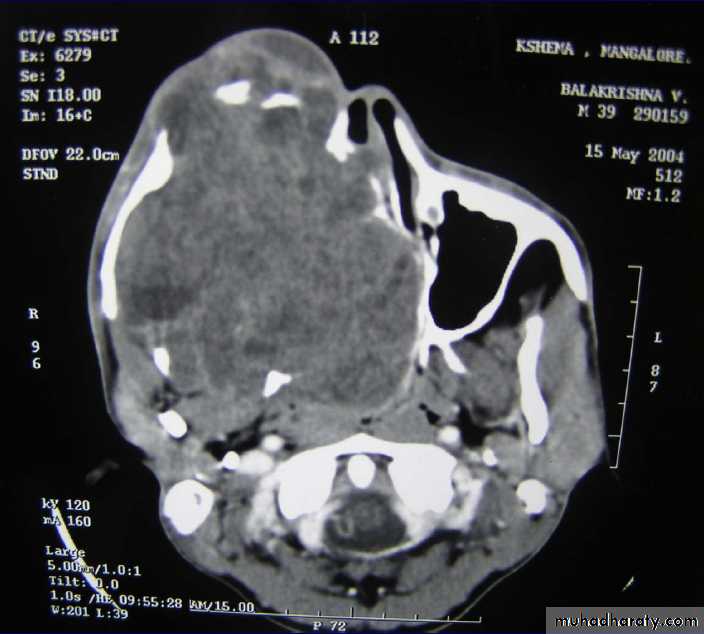
Axial CT shows radiopaque mass oblitearating maxillary sinus and nasalcavity on the right sideAmeloblastoma(ADAMANTINOMA)
Arises from odontogenic tissueLocally aggressive
Invades maxillary sinus
Rx :surgical excision
MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS
Ca nose & PNS constitute 0.44% of all malignancies in indiaFrequency = Max.s > Ethm.s > Frontal.s > Sphenoid.s
AETIOLOGY
Nickel & Chromium refineries(Sq. Cell Ca & Anaplastic).
Mahogany wood industries (Adeno Ca).
Leather Tanning industries.
Bantus tribes of South Africa –max s Ca due to use of stuff containing Ni & Cr.
Malignant NEOPLASM-lesions
Squamous cell carcinoma-------80%
Adenocarcinoma
Adenoid cystic carcinoma 20%
Melanoma
Sarcomas
etc
CA MAXILLARY SINUS
Arises from the lining of max sinus.• Middle aged males(40 -60yrs)
Remain silent for a long time or showing only symptons of sinusitis
Late :destroy bony walls & invades in to surrounding structures.
CA MAXILLARY SINUS
Clinical FeaturesNasal Stuffiness
Blood stained Nasal discharge
Parasthesia or pain over cheek
Epiphora
These are early C/F.
Often misdiagnosed and treated as sinusitis.
CA MAXILLARY SINUS
Clinical Features based on extentionMEDIAL SPREAD=Nasal obstruction + discharge + epistaxis
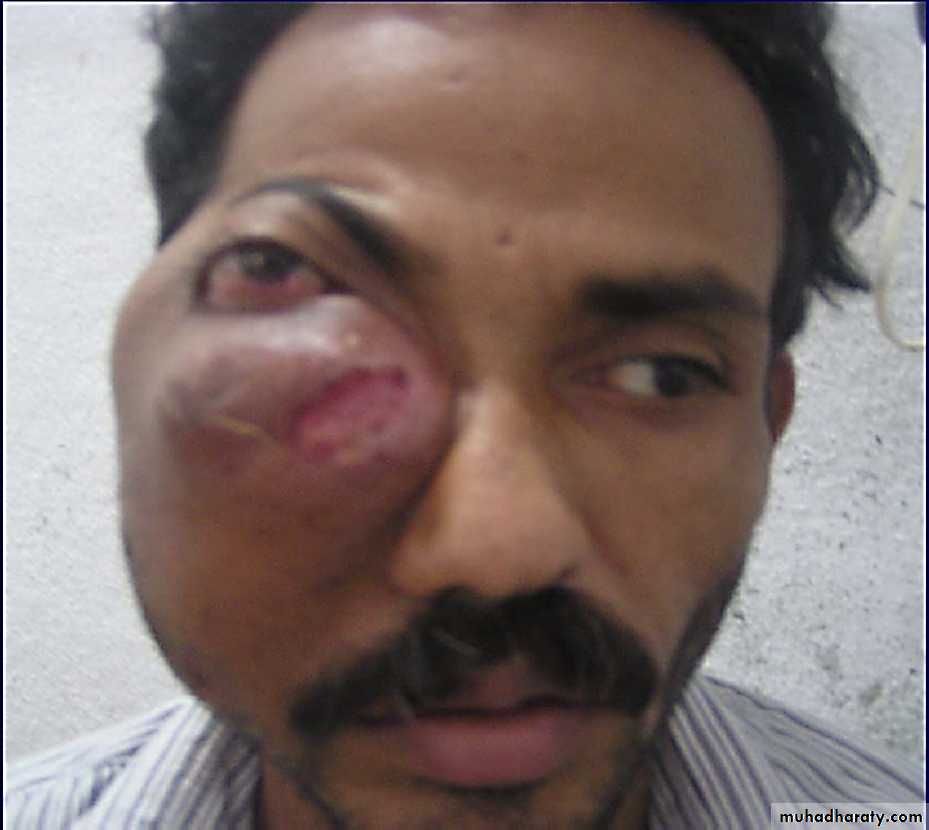
Superior spread=Proptosis + diplopia + ocular pain + epiphora
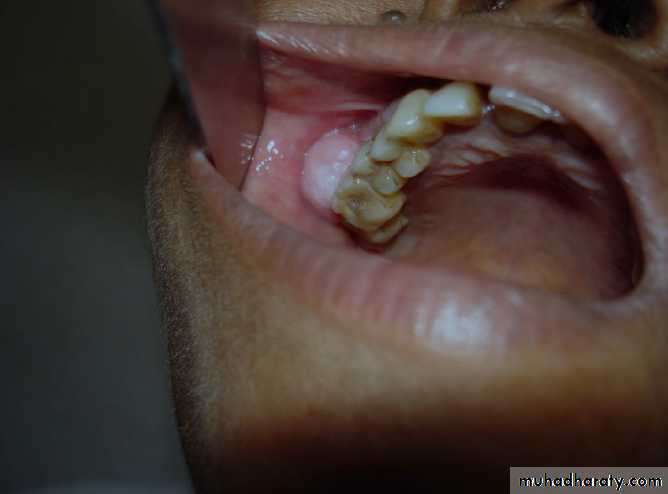
INFERIOR SPREAD=Expansion of alveolus + denatal pain + loosening teeth + poor fitting dentures + ulceration of gingiva + swelling hard palate.
ANTERIOR SPREAD=Swelling of cheek + invasion of facial skin
POSTERIOR spread=Trismus
INTRACRANIAL spread=Via ethmoid , cribriform plate or foramen lacerum
LYMPHATIC SPREAD=Submandibular , Upper jugular nodes and retropharyngeal nodes are enlarged in late stage.
SYSTEMIC SPREAD=in to lungs and occasionally to bones.
CA MAXILLARY SINUS
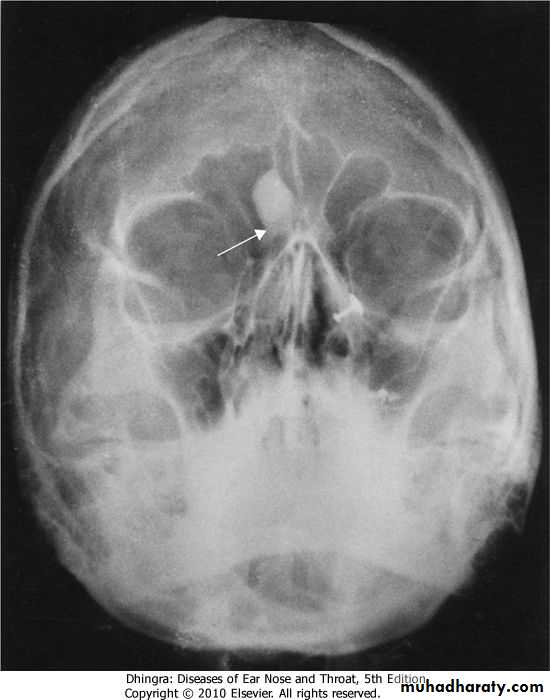
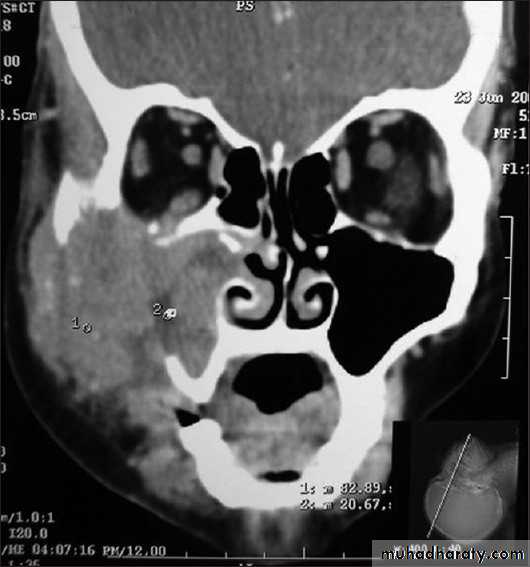
DIAGNOSIS:X-ray PNS.
CT Scan of PNS ( Coronal & Axial).
Biopsy - Nasal Mass / Endoscopic.
CA MAXILLARY SINUS
CA MAXILLARY SINUS-classification
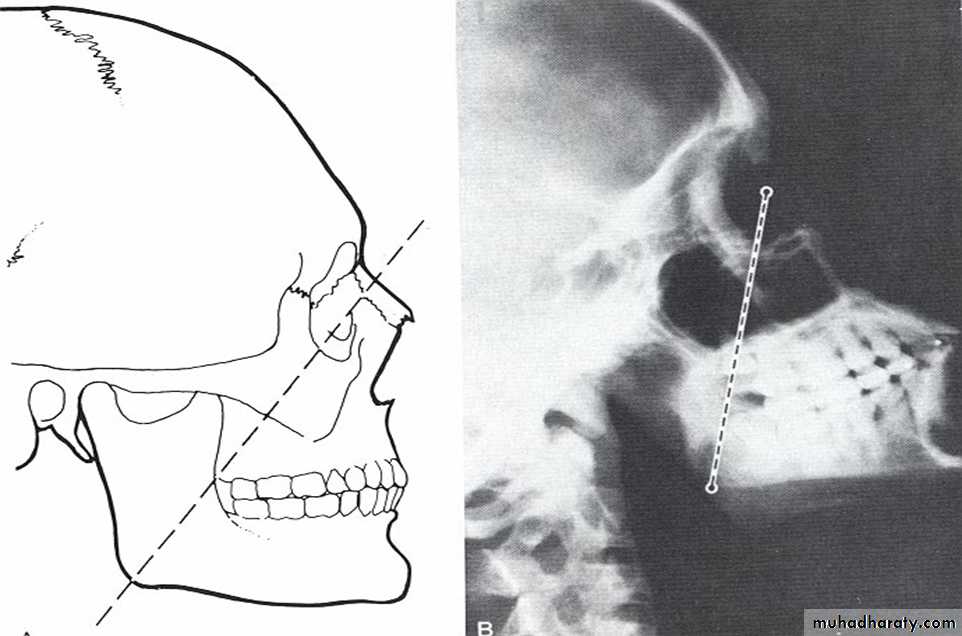
OHNGREN’s ClassificationImaginary plane drawn b/w medial canthus of eye & the angle of mandible
Lesion above this : suprastuctural—poor prognosis
Lesion below this : infrastructural
CA MAXILLARY SINUS-classification
AJCC(American Joint Committee on Cancer) ClassificationOnly for squamous cell Ca
Histopathological
• Well differentiated
• Moderately differentiated
• Poorly differentiated
CA MAXILLARY SINUS-classification
Lederman’s Classification
TNM staging of Ca maxillary sinus
TumourT1: Limited to antral mucosa without bony erosion.
T2: Erosion or destruction of the infrastructure, including the hard palate and/or middle meatus
T3: Tumor invades: skin of cheek, posterior wall of sinus, inferior or medial wall of orbit, anterior ethmoid sinus
T4: Tumor invades orbital contents and/or: cribriform plate, post ethmoids or sphenoid, nasopharynx, soft palate, pterygopalatine or infratemporal fossa or base of skull
CA MAXILLARY SINUS
TREATMENTFor SCC, combination of radiotherapy and surgery is the choice.
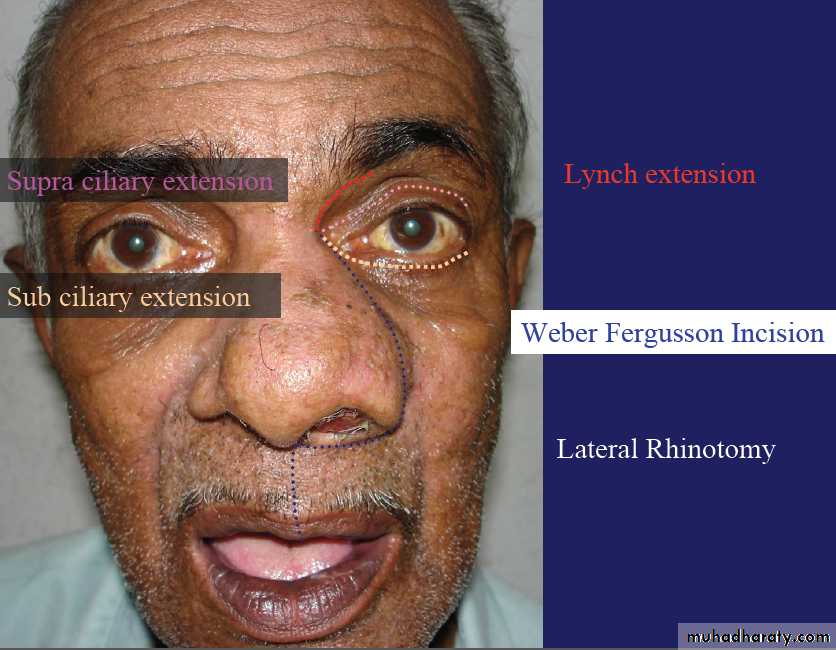
surgery
Total Maxillectomy
Partial Maxillectomy
PROGNOSIS
5yrs survival rate is 30%
ETHMOID SINUS MALIGNANCY
Primary lesion is not common in ethmoid sinusOccur as an extension from maxillary sinus growth
C/F :
Nasal obstruction
Blood stained nasal discharge
Retro orbital pain
Lateral displacement of eye & diplopia
Intracranial spread can cause meningitis
Rx :Pre operative radiation + Total ethmoidectomy
Prognosis : 5yrs survival rate is 30%
FRONTAL SINUS MALIGNANCY
Uncommon40-50 yrs age group ; males more
C/F :
Pain & Swelling in frontal region
Growth can go post to ant cranial fossa
Growth can extent through the ethmoids into orbit
Rx : Pre operative radiation + Frontal sinusectomy
THANKS A LOT FOR KIND ATTENDION !!!!!!!