Order: Pseudomonadales
F: PseudomonadaceaeG: Pseudomonas
PseudomonaceaeIt’s a family widely distributed in nature contains several genera like Pseudomonace and the important medical species is P.aeruginosa which present in soil, water and sometime colonizes human and is considered as a major human pathogen.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
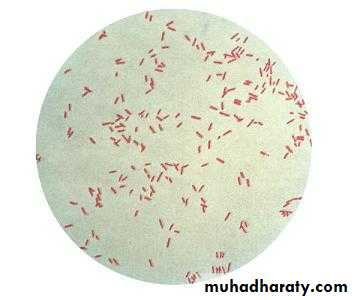
It is motile bacterium rod shape, Gram-negative, measuring about 0.6 × 2 µm and occurs as single bacteria, in pairs and occasionally in short chain.Growth and culturing characteristics:
1- P. aeruginosa is an obligate aerobe that grows easily on many types of culturing media
2- producing specific odor like sweet or grap-like odor.
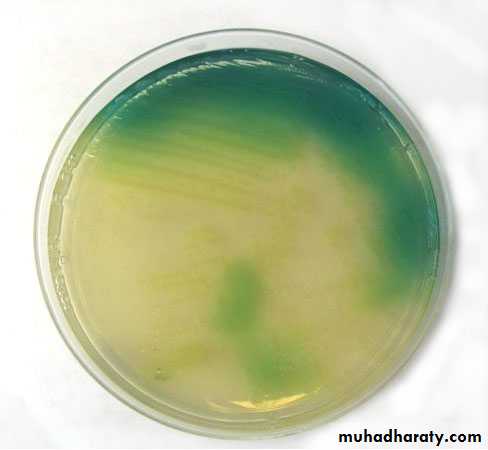
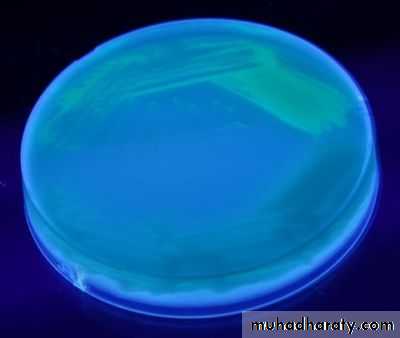
3- its form smooth, round colonies with fluorescent greenish color or non fluorescent bluish color (pyocyanine) which diffuse into the agar (characteristic feature). Other species produce dark red color pigment (pyorubin or black pigment which is pyomelanin.
4- some strains produce hemolysis on blood agar.
5- cultures from patients with cystic fibrosis produce P.aeruginosa with mucoid colonies as a results of over production of alginate (an exopolysaccharide)
6- its grows well at 37-40 C°, oxidase test positive, it does not ferment CHO, but many strains oxidize glucose
Gram-negative P.aeruginosa
Greenish pigment of P.aeruginosa
Flourescent isolates of P.aeruginosa
Classification of medically important Pseudomonads
rRNA\DNA group Genus and speciesFluorescent group P.aeruginosa
P. flurescens
P. putida
Non fluorescent gr. P. stutzeri
P. mendocine
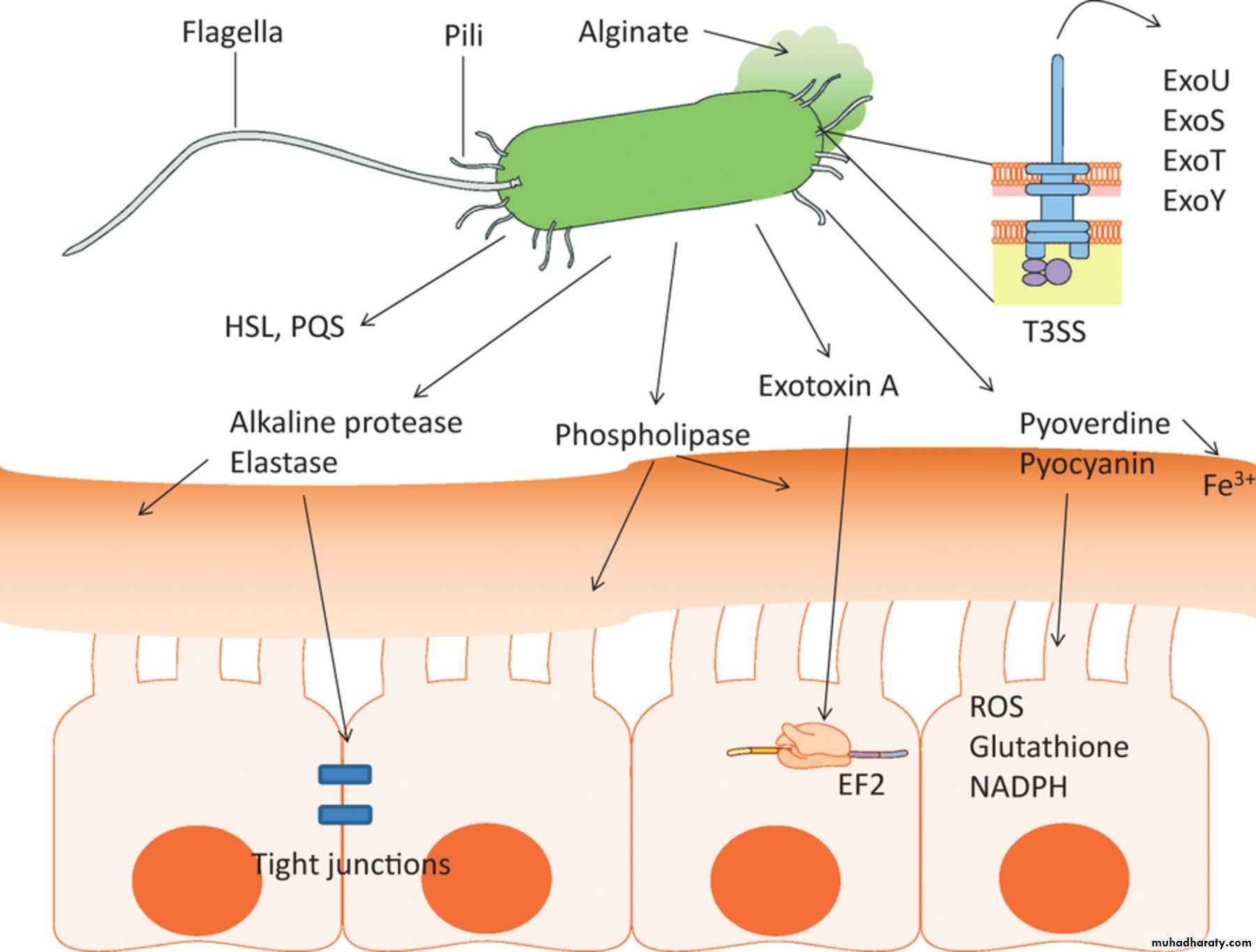
Antigenic structures and toxins
1- pili promote attachment to host epithelial cells2- exopolysaccharide (alginate)responsible for mucoid colonies and antiphagocytic factor.
3- lipopolysaccharide (endotoxines)
4- extracellular enzymes like elastase, protease, and two hemolysins (heat- labile phospholipase C and a heat- stable glycolipid
5- exotoxin A: which causes tissues necrosis and is lethal for animals when injected in purified form.
Pathogenesis
1-P.aeruginosa is pathogenic only when introduced areas devoid of normal defenses.2-the bacterium attaches to and colonizes the m.m. or skin, invade locally, and produces systemic diseases like shock, septicemia and multiple organ dysfunction.
3- these processes are promoted by pili, enzymes and toxins.
4- these bacteria are considered as multi-drugs resistant.
Clinical signs
1- P.aeruginosa produces infection of wounds and giving rise to blue-green pus.2- meningitis when introduced by lumbar puncture. Also causes UTI when introduced by urinary catheters, respiratory infection, mild otitis, infection the eye.
3- bacteria may invade the bloodstream and causes fatal sepsis, this condition occurs in patients with abnormal immune state (lymphoma, leukemia and patient with severe burn.
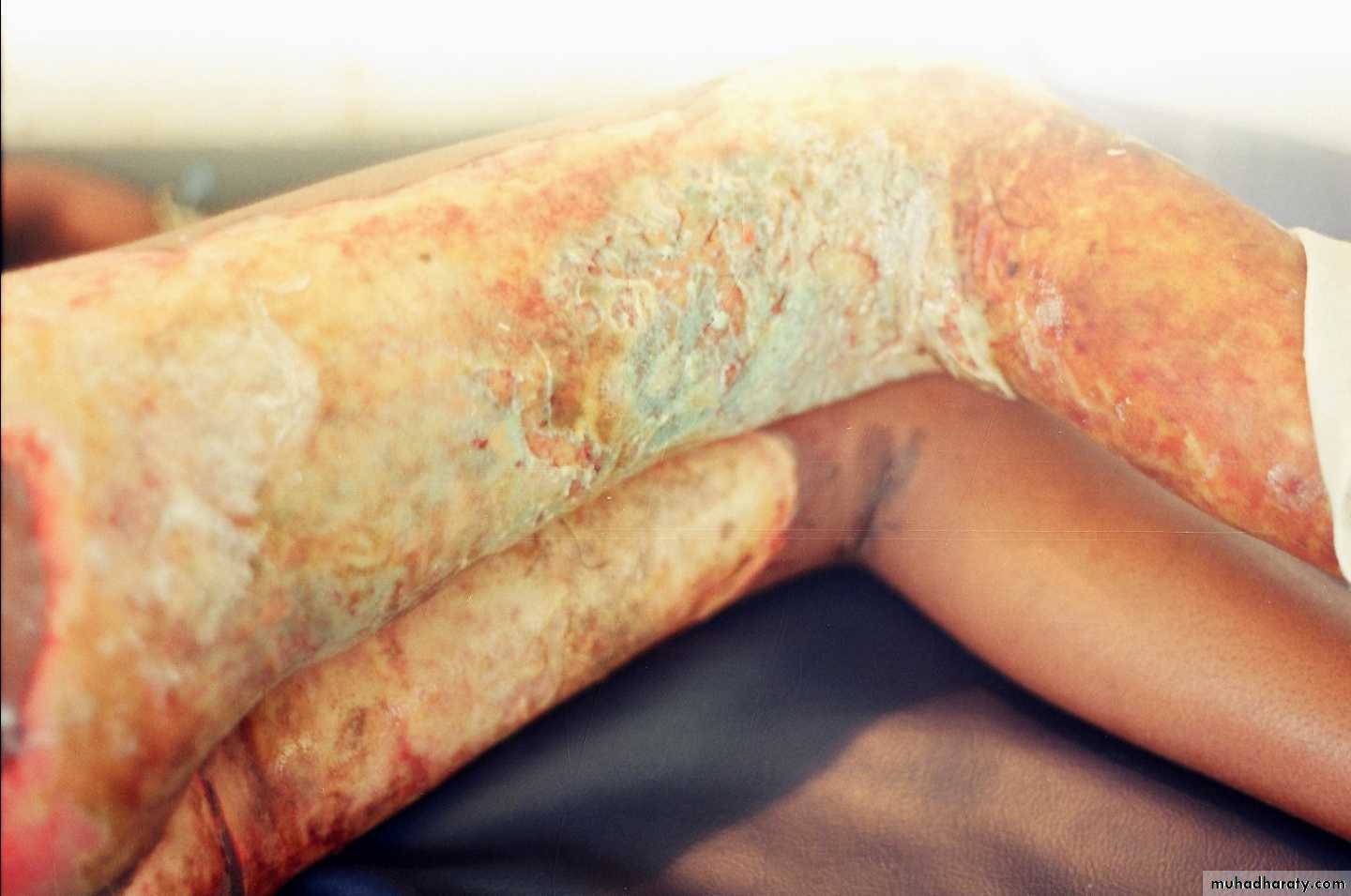
Burn case contaminated by P.aeruginosa
Green pus
Diagnosis1- specimens from skin, pus, blood, spinal fluid, sputum are cultured on blood agar, differential media like macConkey agar.
2- production of specific odor and pigment on culturing media.
3- gram stain
4- biochemical reactions like culturing on TSI (alkaline/alkaline), IMVC (-,-,-,+), Oxidase test +
5- identification by API NE System.
Treatment
1- Treatment of P. aeruginosa should be not occure by one antimicrobial agent due to the high rate of resistant pattern, therefor beta lactam drugs plus aminoglycoside usually useful in the treatment.