Amelogenesis
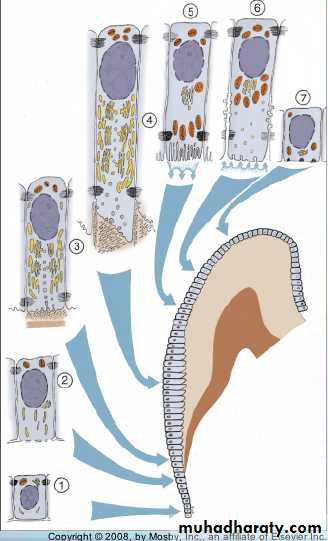
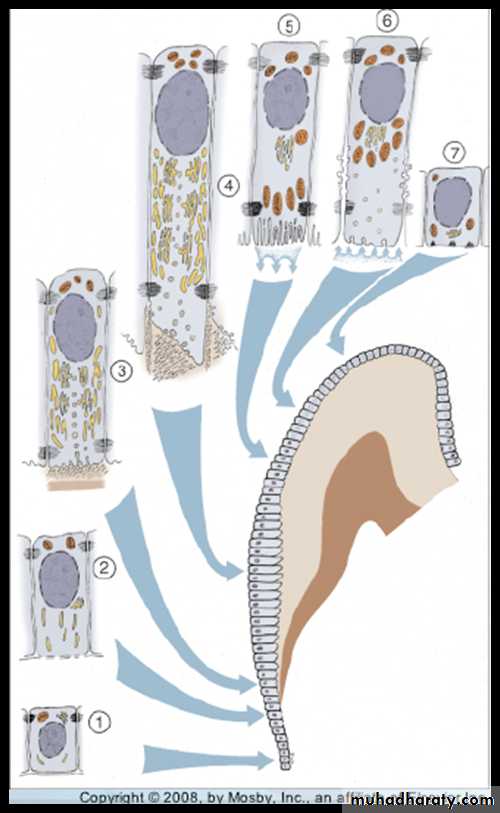
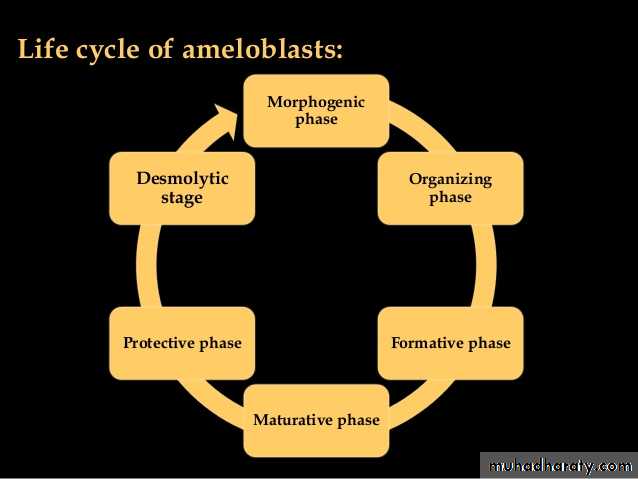
Amelogenesis has six phases but generally is subdividing into three main functional stages referred to as the presecretory, secretory and maturation stages.The six phases of ameloblasts are:
Morphogenetic.
Organizing(differentiation).
Secretory (formative).
Maturative.
Protective.
Desmolytic.
Morphodifferentiation
differentiation3. Secretory (initial)
4. Secretory (Tomes’ process)
Maturation (ruffle-ended)
Maturation (smooth-ended)
Protective
amelogenesis
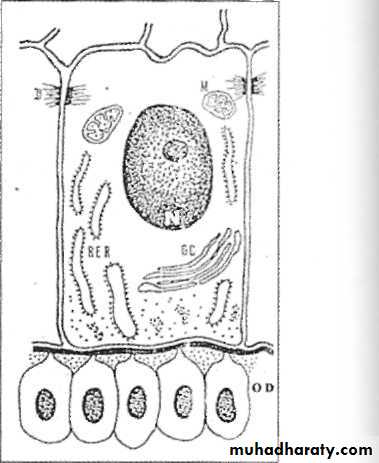
To understand the amelogenesis (formation of enamel) we must understand the life cycle of ameloblast (cells that forming the enamel).Life cycle of amelobalst
Morphogenic Stage
Differentiation Stage
Secretory Stage
Maturation Stage
Protective Stage
Desmolytic Stage
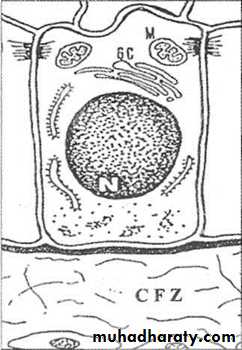
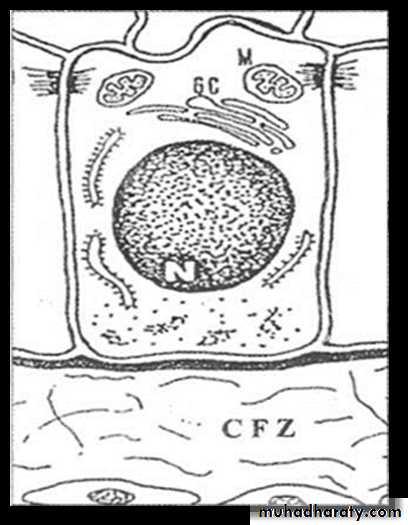
Morphogenetic Stage
Inner Enamel EpitheliumLow columnar to cuboidal cells
Centrally placed nucleus
Golgi bodies placed proximally.
Mitochondria and other cytoplasmic bodies are scattered.
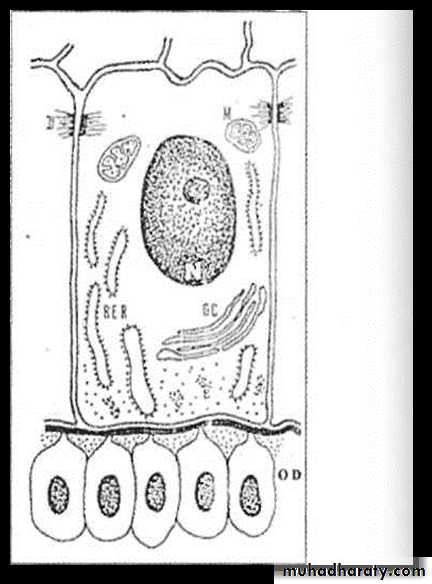
Differentiation Stage
IEE AmeloblastsAmeloblasts (Histological changes)
Cell Elongates
Nucleus shifts proximally.
Golgi complex increases in volume & migrate to central core of cell.
Increase in ER
Mitochondria shift proximally.
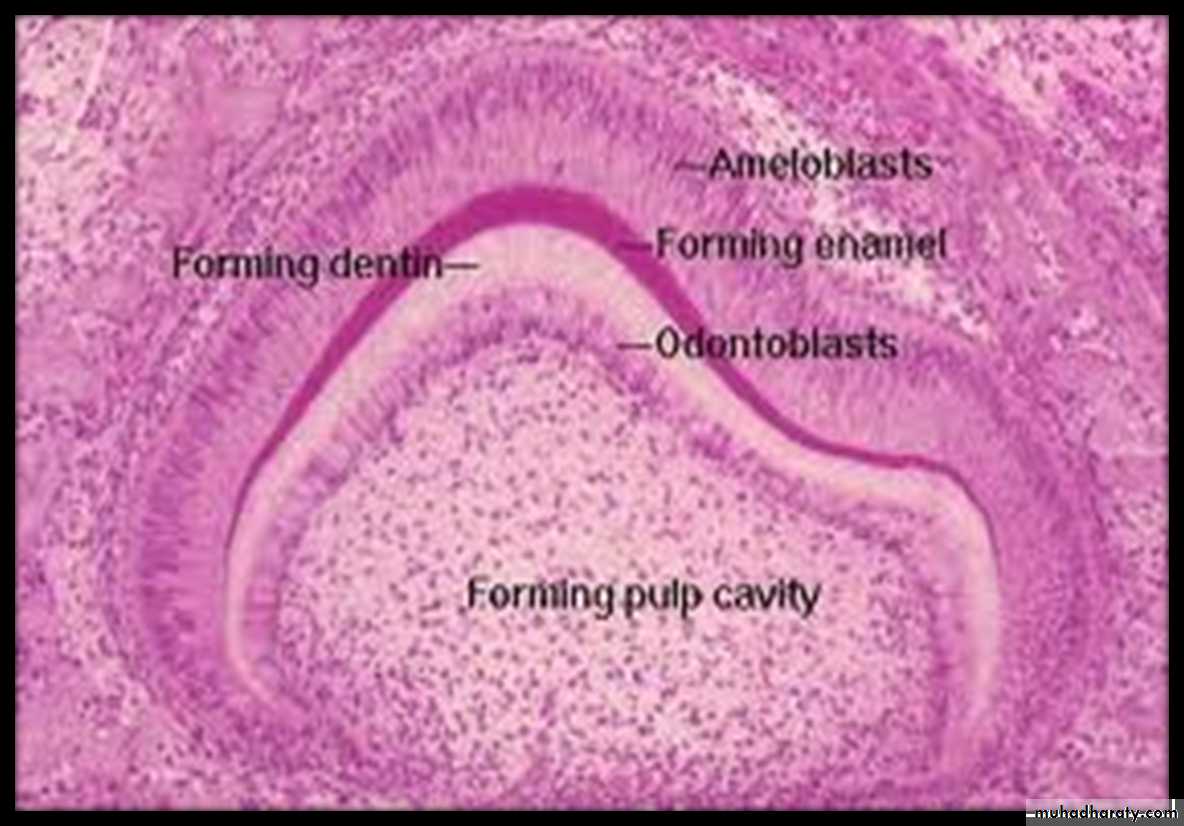
Secretory Stage
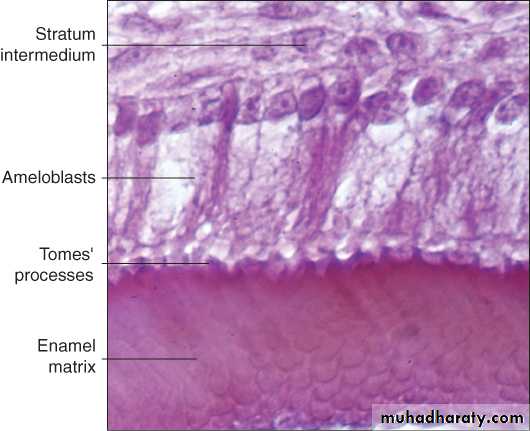
Synthesis of enamel proteinsWhen first increment of enamel is formed, the ameloblasts begin to move away from the dentin surface (outward), and, as they do, each cell forms a conical projection called Tomes processes.
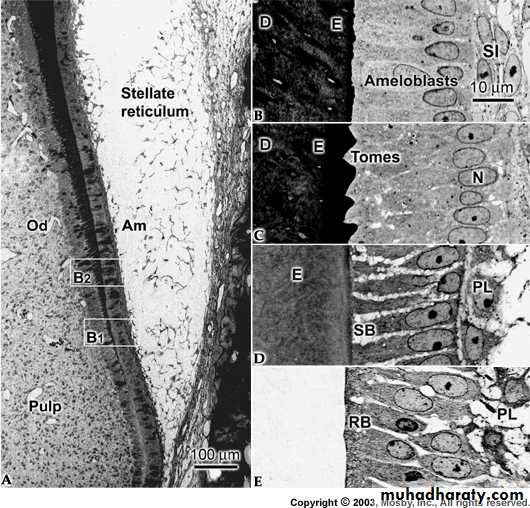
Maturative Stage
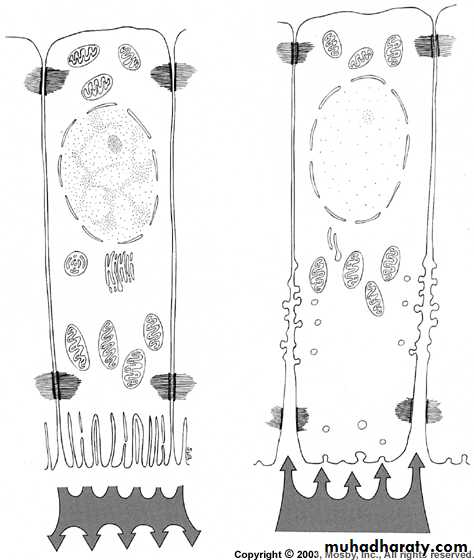
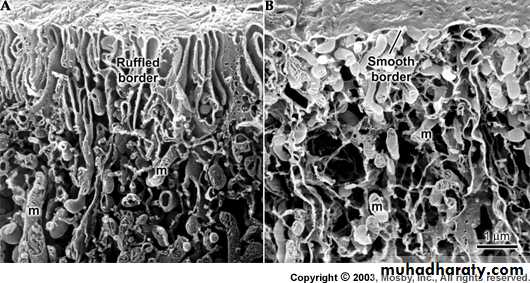
Water and organic material is selectively removed from enamel with addition of inorganic material.** Complex folding of the distal plasma membrane to form Striated border, which greatly increases the surfaces area of the extremity of Ameloblast and indicates rapid transport of material, also this end named ruffled border.
Amelogenesis - Maturation Stage
AmeloblastsRuffle-ended
Smooth-endedAmeloblasts
Protective
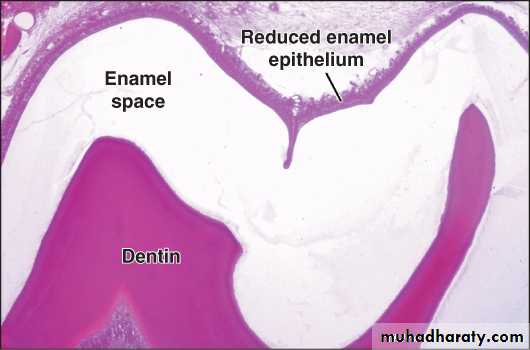
After complete formation and mineralization of enamel, the ameloblasts form 3-4 layers of stratified epithelium that cover the enamel and called reduced enamel epithelium.This reduced enamel epithelium protects the enamel by separating it from the connective tissue until the tooth erupts.