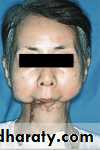
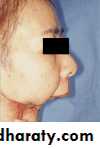
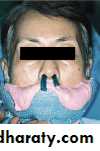
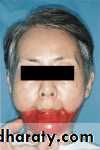
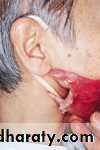
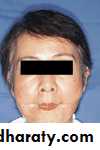
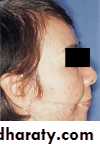
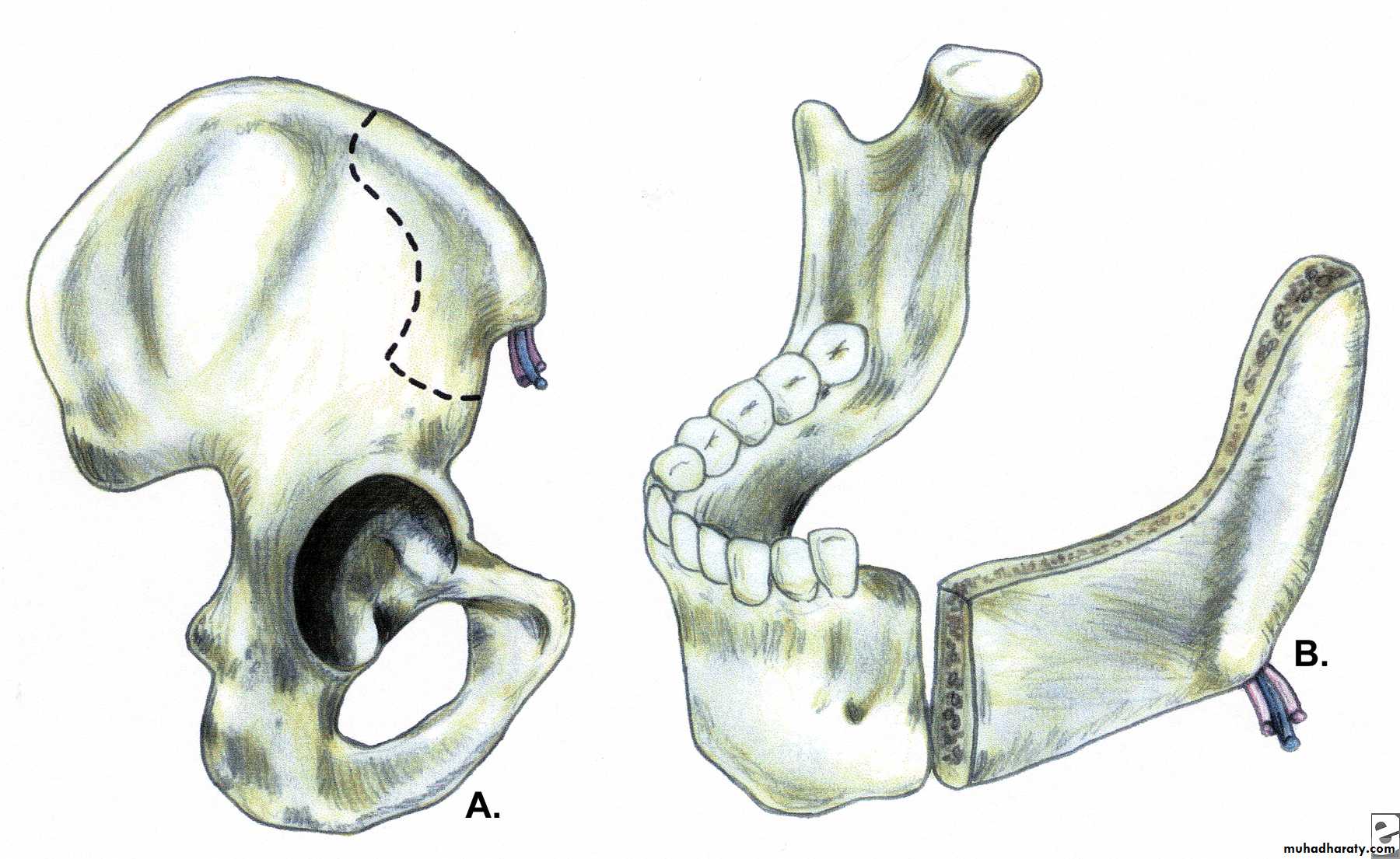
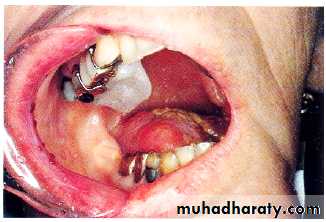
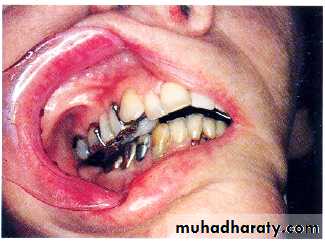
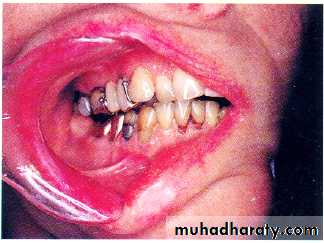
Acquired mandibular defects
خامس \ صناعة اسناند. منية م(10)
2\ 4\ 2017
Etiology
Trauma.Resection of primary tumor.
Resection as a safety margin.Enhancement of prosthetic prognosis
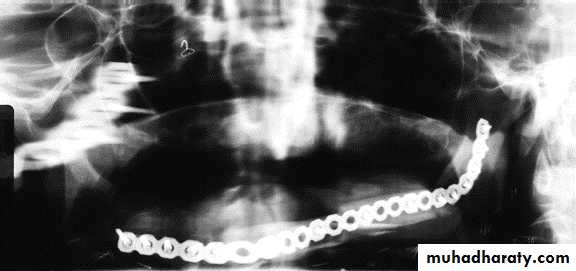
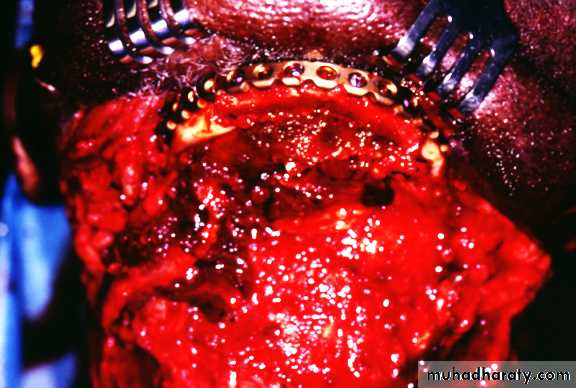
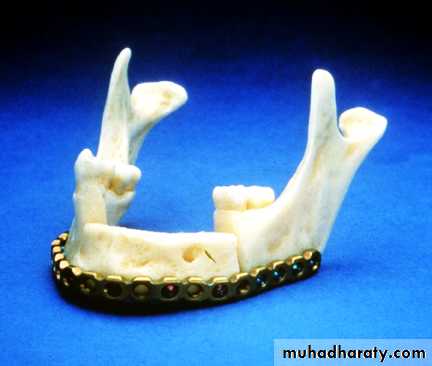
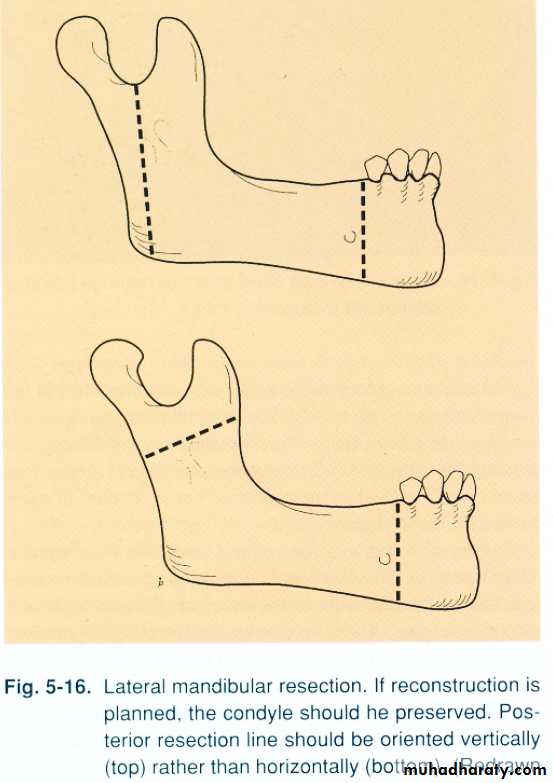
• Maintaining or re-establishing mand. Continuity, by fixation plates.• Sectioning in ramus area.
• Sectioning in dentulous portion.
• Method of closure .
• Resection of mylohyoid + geniohyoid in defect side To reduce mand. Deviation.
Disabilities associated with the tongue defect
• Cosmetic disfigurement.• Speech.
• Deglutition.(synergestic squeezing action).
• Trismus.
• Drooling of saliva.
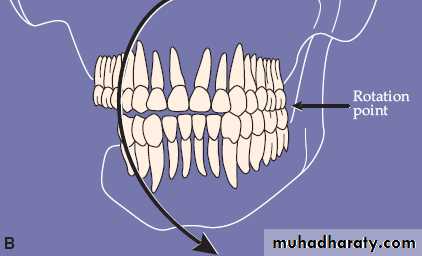
• Mandibular deviation.
• Frontal plane rotation.
Frontal plane rotation
• Internal jugular vein resection → local venous congestion + edema → compromise extension of lower complete denture.
• Resection marginal of denture mandibular branch of facial nerve → loss of motor innervations of lower lip.
• Disabilities associated with radiotherapy
• Sever scarring → trismus.• Dental caries.
• Impaired mucosal tolerance to prosthesis.
• Changed consistency and volume of saliva.
Disabilities associated with the floor of mouth defects
• Sever facial disfigurment:• Remaining posterior fragments pulled medially and superiorly →difficult construction of complete denture.
• Loss of anterior of mandible → patient looks like losing lower ⅓ of his face.
• Tongue retrusion → occlude airway.
• Primary closure of wound → ↓mobility of the tongue .→ loss of anterior vestibule.
• Mastication is impossible.
• Speech is affected.
• Sensory and motor innervations of lower lip is compromised → drooling of saliva.
Disabilities associated with tonsillar area defects:
• Mandibular resection is more posterior:• Loss of fewer teeth. Retention of more denture-bearing surface.
• Facial disfigurement is not noticeable.
• If the lesion external to the tonsillar pillar superiorly:
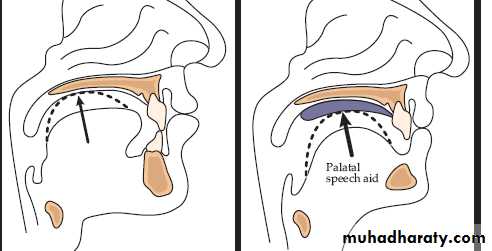
• Portion of soft palate is resected.
• velopharyngeal incompetence.
• Hypernasal speech.
• Fluid regurgitation.
Cont…
• Swallowing is impaired:• Poor mobility and control of tongue.
• Nasal regurgitation.
• Mandibular deviation.
• Speech problems.
• Control of saliva.
• Trismus.
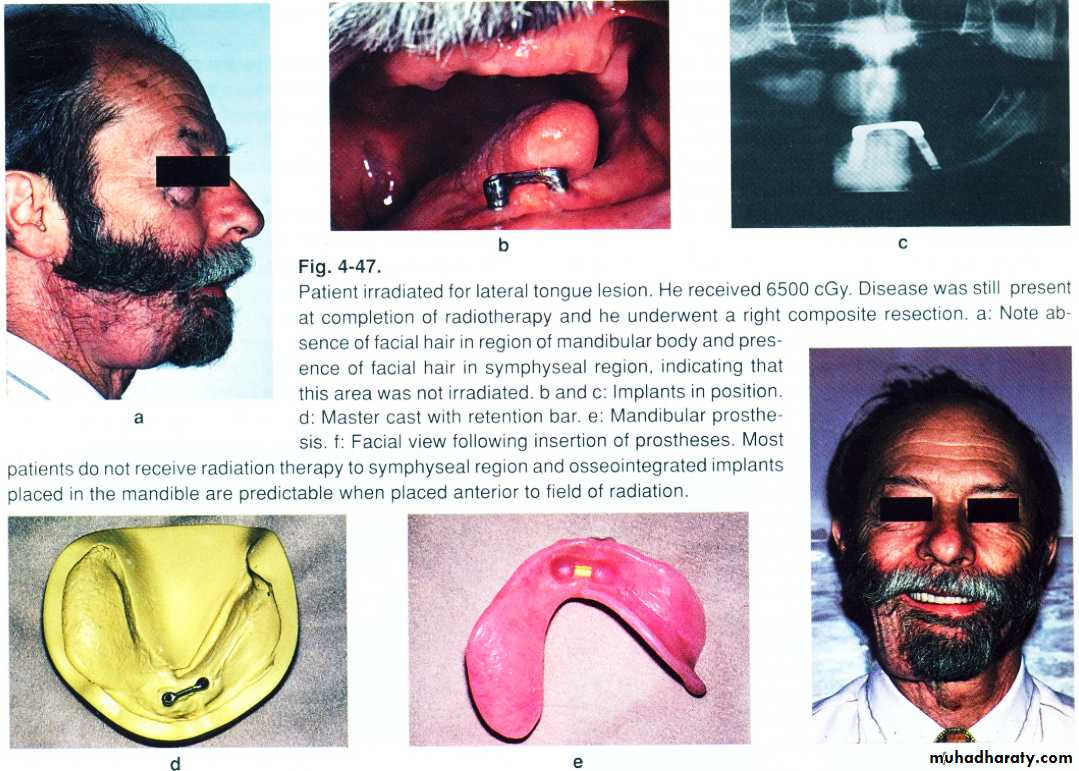
• The radiation therapy.
Disabilities associated with defects confined to the mandible
• Continuity defects, as in marginal mand. Resection… oblitration of buccal + lingual sulci
• Discontinuity defects .. deviation of mand.+tongue.
• Function rarely affected
Management of disabilities caused by mandibular defects
• Management of mandibular deviation:• Intermaxilary fixation.
• Physio-therapy.
• Mandibular guidance prosthesis:
• Buccal training flange.
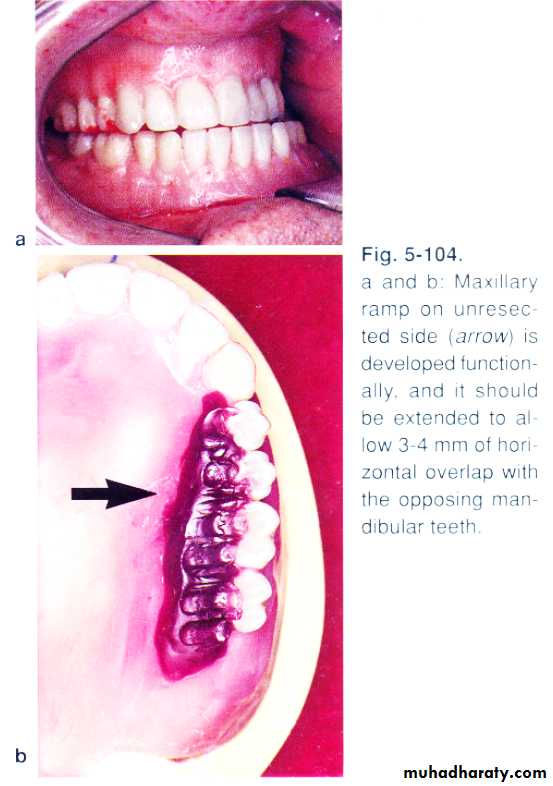
• Palatal ramp.
• Occlusal equilibration.
Management of disabilities caused by mandibular defects
• Management of mandibular deviation:• Intermaxilary fixation.
• Physio-therapy.
• Mandibular guidance prosthesis:
• Buccal training flange.
• Palatal ramp.
• Occlusal equilibration.
Fixation indication:
Resection confined to mand.+ little soft tissue loss
Min. scar contracture+ enough soft tisssue for closure.Ms. Imbalance + compromised proprioception
contraindication:
Composite resection ; radical neck dessection ; radiotherapy ;1ry closure.Profound scar contracture ;worsened man. deviation
Physiotherapy :2 wks post surgical. How?
Maximum opening of man.
Grasp the chin ….move the man. Away from defect side
why?
reduce scar contracture +tris mus+ ms. Adhesion
Improve maxillary– mand. Relationship.
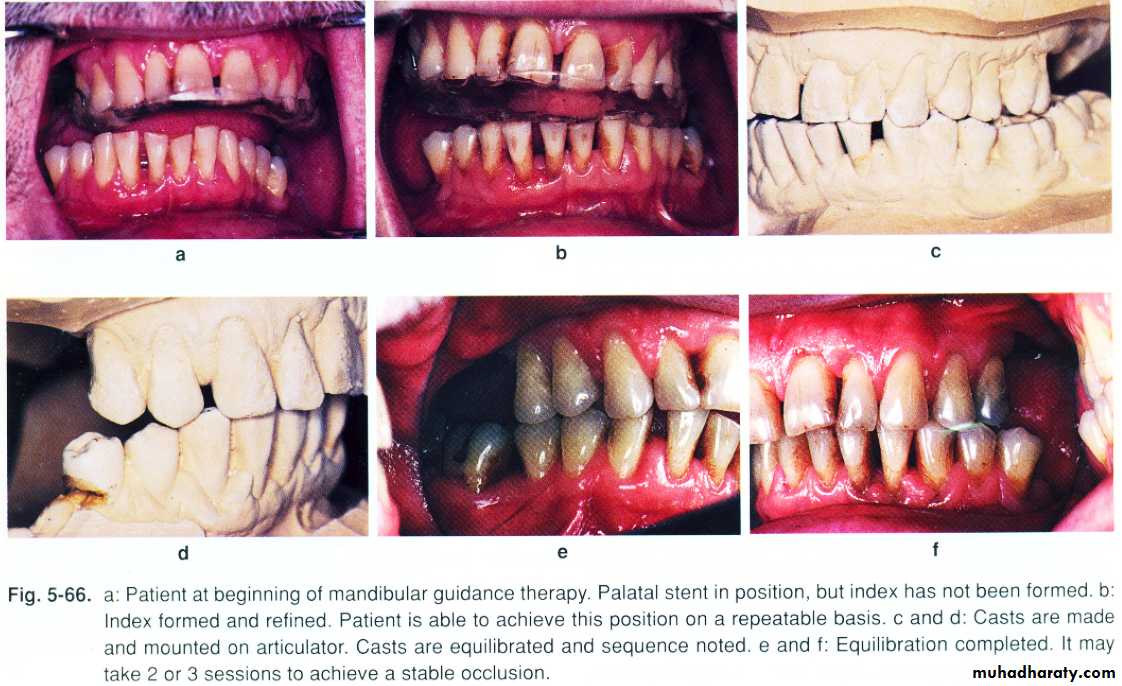
Man. Guidance therapy:As early as possible
Presence of the teeth is v. imp.
To get acceptable occ. Relationship + proper proprioceptive mechanismtypes of man. Guidance prosthesis:
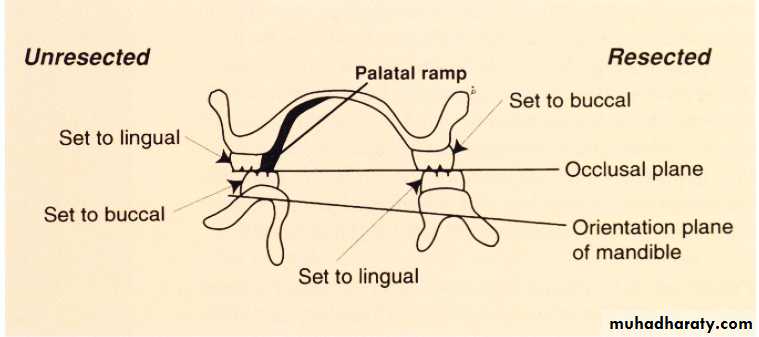
Buccal training flange (lower)………man. Can be manipulated to proper max..man. Relation + pt. can,t bring man. To occ. b\c lack of motor controlPalatal ramp (upper)…sever deviation b\c more adjustable
Palatal stent……..most of teeth presentocclusal equilibration
• Reduce mand. Deviatio, and frontal plane rotation.• 2. Reestablish occlusal stops to reproduce C.R
Prosthetic rehabilitation
Partially edentulous pt.
Completely edentulous pt.
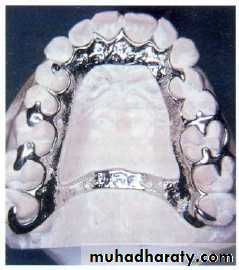
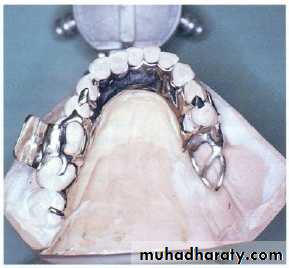
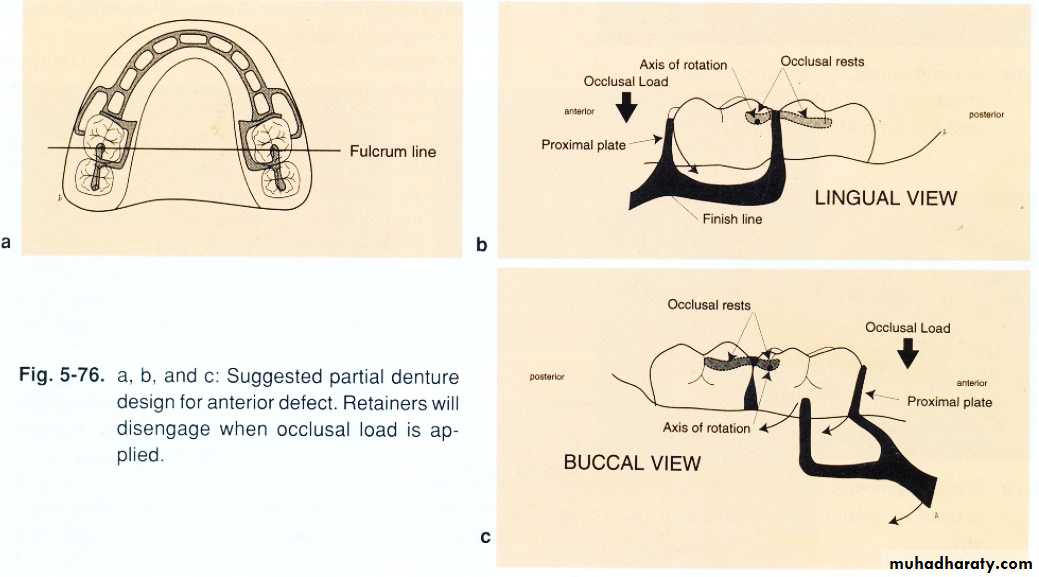
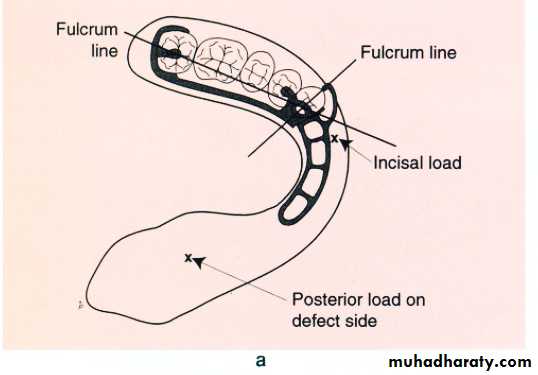
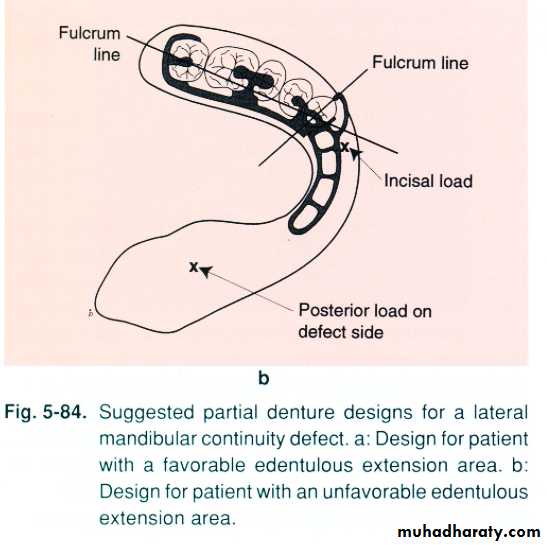
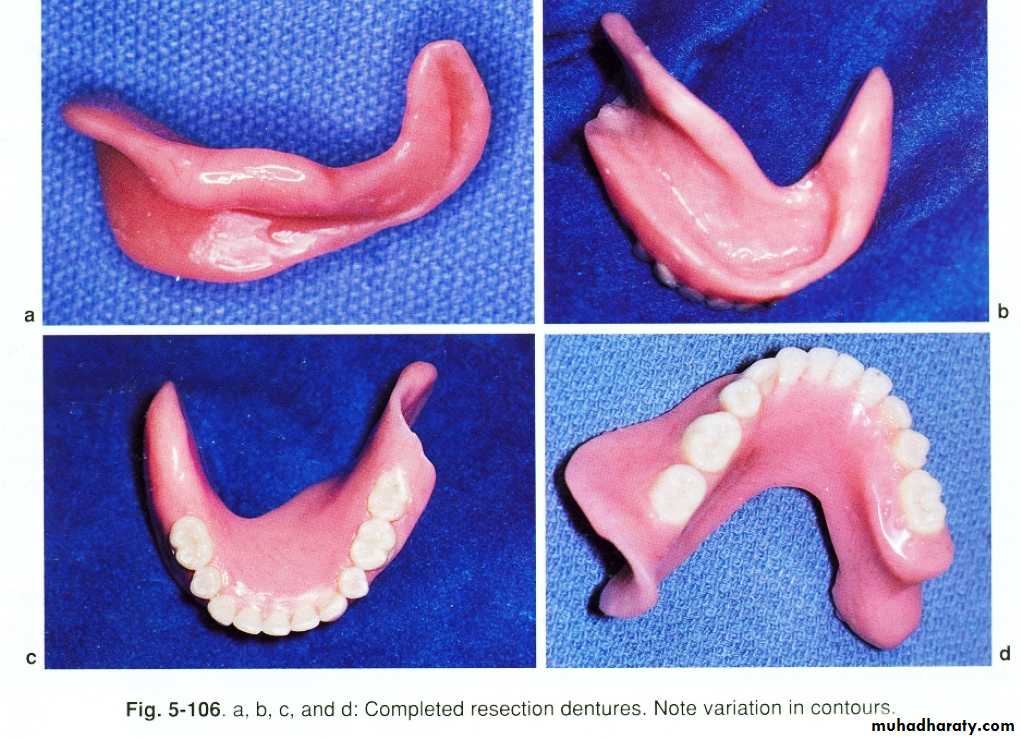
Partially edentulous pt.Latral discontinuity defects…fulcrum line ,design,steps, altered cast technique (for final imp.), altenative cast technique (pick_up imp.), occ.(proper ICP at C.O ,occ. Ramp lingual to max. teeth
Continuity defects ( latral +anterior)….. conventional RPD or implant_retained
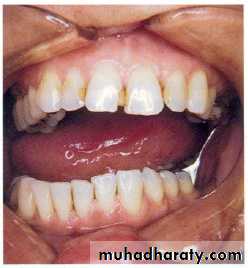
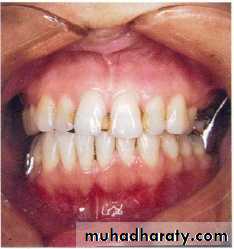
Completely ed. Pt. :
Ant. Discontiuity defects are impossible to restore.Lateral discontinuity defects
Depend on:
• Extent of soft tissue and bony resection
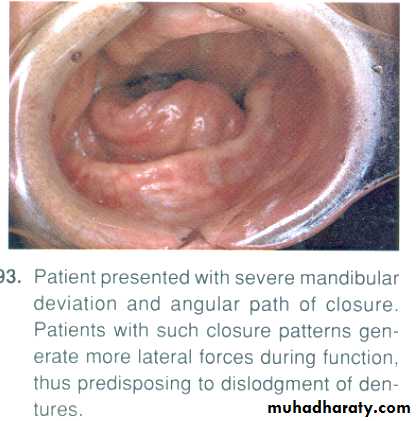
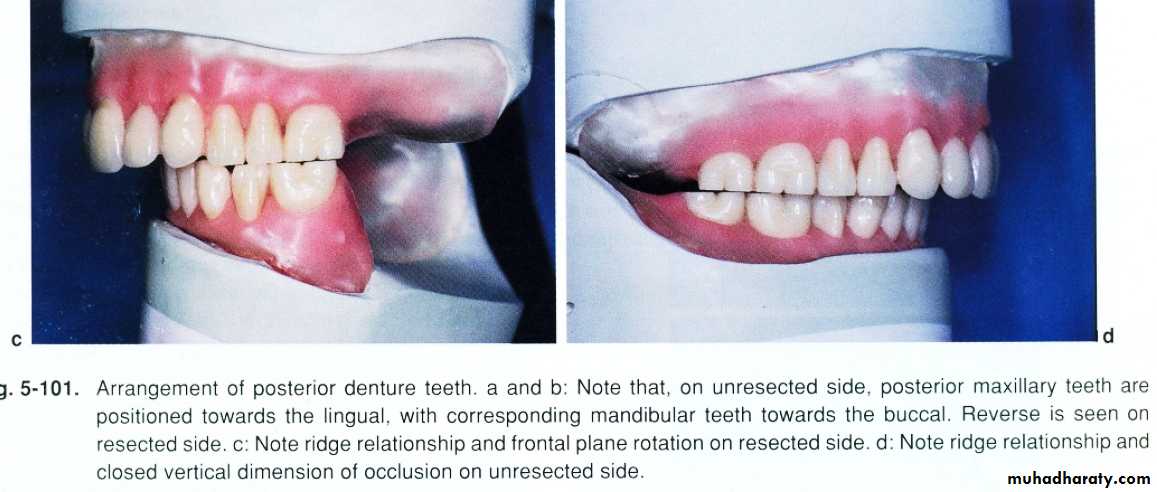
• Tongue mobility in directions which stabilize C.D …….tongue immobility is adv. b\c it allows aggressive extention of lingual flange in non_surgical side….increasing the stability.• Man. Dev. Instability of C.D + application of occ. Forces on unresected side reduce ret.
• Compromised motor + sensory lip control cause…cheek biting ; salivary drooling ; and lips retracted post. So lingual positioning of C.D teeth.
• radiotherapy
Steps
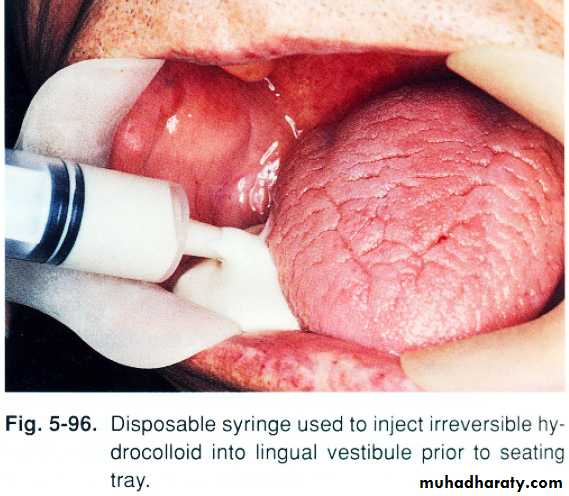
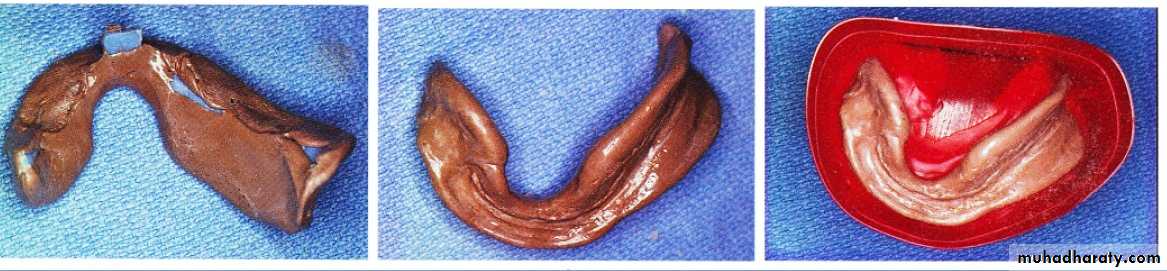
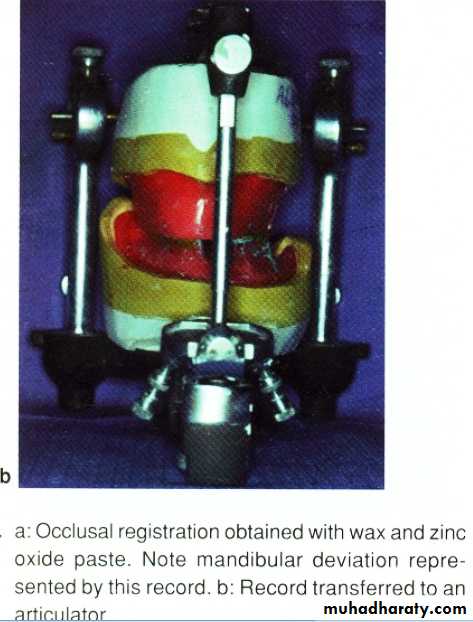
Impression(1ry +2ry)..adaptation;support; stability; proper lip support..Centric registration..occ. Rim is wide in unresected side b\c man. Dev.and support of upper lip reduced to reduce effect of man. Dev. And retrusion…………..V.D difficult b\c altered proprioception; trismus; man. Dev.; ms. Imbalance; ……..so phonetic methods and swallowing are used instead of neuroms. Methods.
Occ. Schem +latral registration
Non_anatomic post. Teeth used.
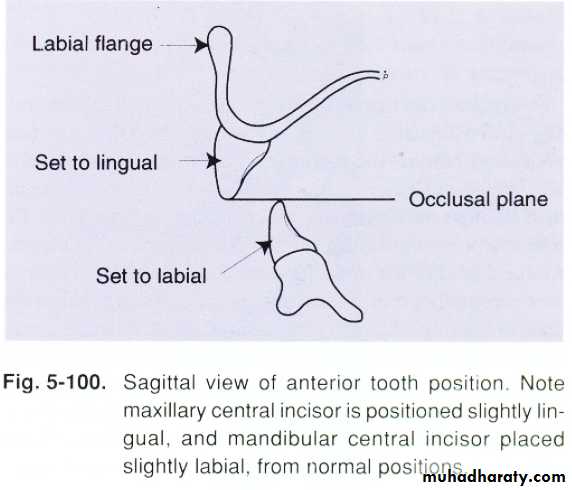
Ant. Max. Teeth lingually positioned for esthetic.
Protrusion done by most pt.(incisal guidance not affected).
Lingual inclination of man. On defect side nessacitate thickining of the flange to support lip.