SEMESTER / 2
Experiment No. (3)Digital to Analog converter (DAC)
Introduction:
Digital-to-analogue conversion is an essential function in data processing systems. D/A converters provide an interface between the digital output of signal processors and the analogue world. Multistep ADCs employ interstage DACs to reconstruct analogue estimates of the input signal. Each of these applications imposes certain speed, precision, and power dissipation requirements on the DAC,A digital to analog converter (DAC) is a circuit that converts a digital signal into analog signal. The input signal may be in the serial or parallel form.
The simplest form of DAC requires a wide range of resistance values weighted according to their digital value. A DAC with an R-2R ladder network eliminates these complications at expense of an additional resistor for each bit.
Procedures:
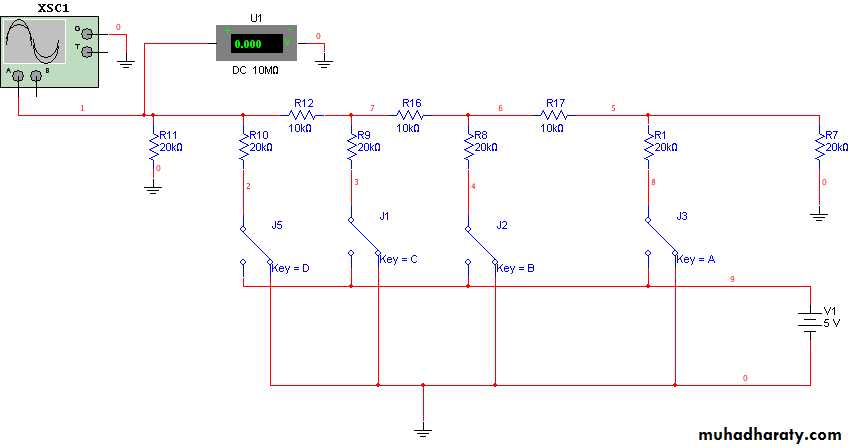
Item (1):Connect the R-2R ladder network shown in fig.1. record Vo with respect to increasing digital code inputs (D, C, B, A) as listed in table (1).
Fig (1)
Digital Input (D,C,B,A)
Output Voltage(VO)
0000
0 mV
0001
0010
0011
01000101
01100111
10001001
10101011
11001101
1110
1111Table (1)
Item (2):Connect the input switches (D, C, B, A) of the DAC to the outputs of 4-bit counter as shown in fig.2. Apply 50 KHz TLL level clock signal to the counter. Draw from the scope the output Vo.
R- 2R Ladder
A
B
C
D
Vo
50 KHz TTL
Q3
Q2
Q1
Q0
4-bit Counter
74191
77
Fig (2)
Report:
Analyze the R-2R ladder network of fig.1.Calculate the resolution of the DAC shown in fig.1.
Determine the accuracy of the DAC shown in fig.1.