Lec.5 Biology
HistologyClassification of Connective tissue
Connective tissue classification is based upon three structural characteristics of the matrix:(1) The types of fibers
(2) The type of ground substance
(3) The structural arrangement.
According to these characteristics of the matrix, connective tissues are classified into:
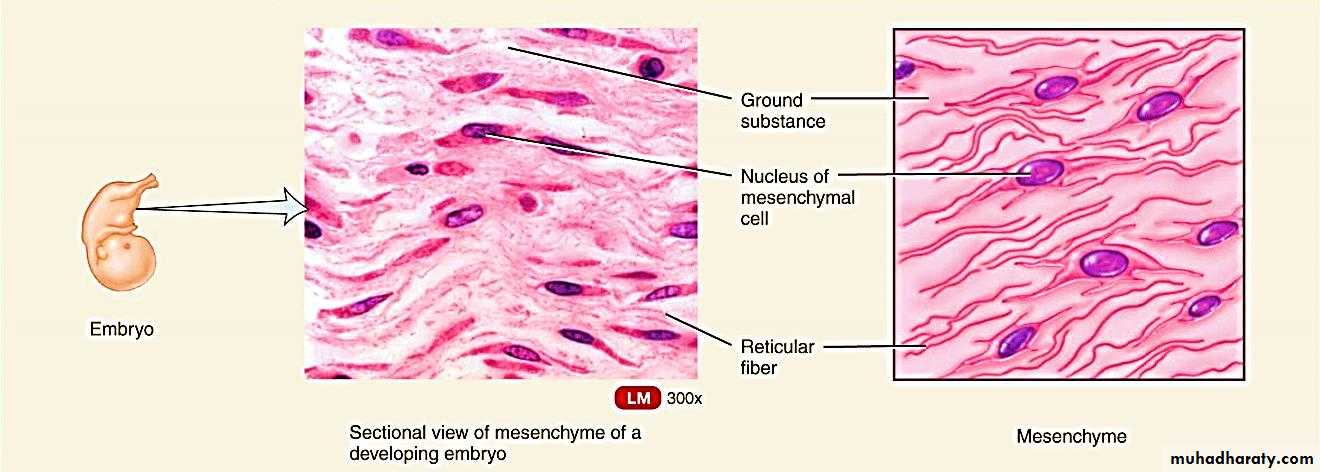
I. Embryonic connective tissue:Mesenchymal connective tissue (developing embryo & fetus)
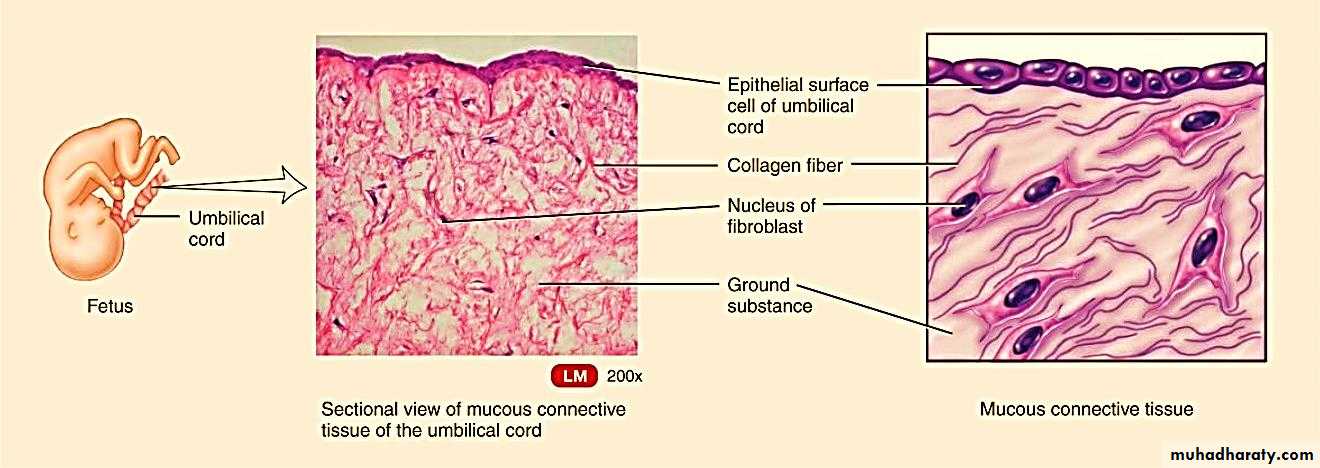
Mucus connective tissue (umbilical cord)
II. Connective tissue proper:
Loose connective tissueAreolar tissue
Adipose tissue
Reticular tissue
B. Dense connective tissue:
Regular dense connective tissue
Irregular dense connective tissue
Elastic connective tissue
III. Specialized connective tissue:
Bone
Cartilage
Blood
I. Embryonic connective tissue
Mesenchymal connective tissue: is the connective tissue of embryo, consists of mesenchymal cells in a gel – like amorphous ground substance containing scattered reticular fibers.
Mucous connective tissue: it is found in umbilical cord, it contains fibroblasts, few macrophages and some lymphocytes. The ground substance is soft and jelly like containing fine collagenous fibers.
II. Connective tissue proper
A. Loose connective tissueLoose connective tissue is characterized by having a loose arrangement of fibers. It includes the following three tissues:
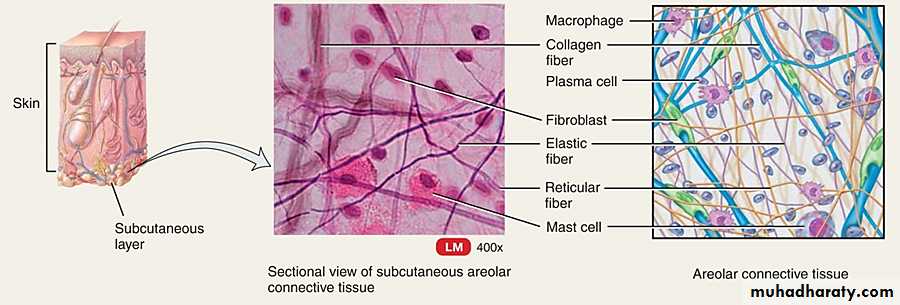
Areolar Connective Tissue
Areolar connective tissue is the most widespread connective tissue of the body. It is used to attach the skin to the underlying tissue. It also fills the spaces between various organs and thus holds them in place as well as cushions and protects them. It also surrounds and supports the blood vessels. The fibers of areolar connective tissue are arranged in no particular pattern but run in all directions and form a loose network in the intercellular material. All three fibers (collagenous, elastic and reticular) and several kinds of cells, including fibroblasts, adipocytes and cells of the immune system, are embedded in a semifluid ground substance.
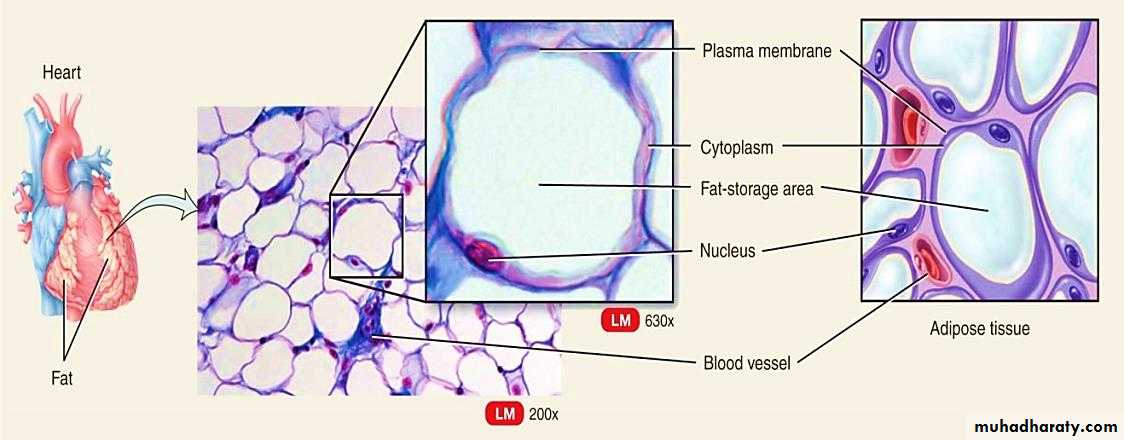
Adipose Connective Tissue
The cells of adipose (fat) tissue are characterized by a large internal fat droplet, which distends the cell so that the cytoplasm is reduced to a thin layer and the nucleus is displaced to the edge of the cell. These cells may appear singly but are more often present in groups . When they accumulate in large numbers, they become the predominant cell type and form adipose (fat) tissue. Adipose is widely distributed in the body, especially under skin and around internal organs.Reticular tissue:
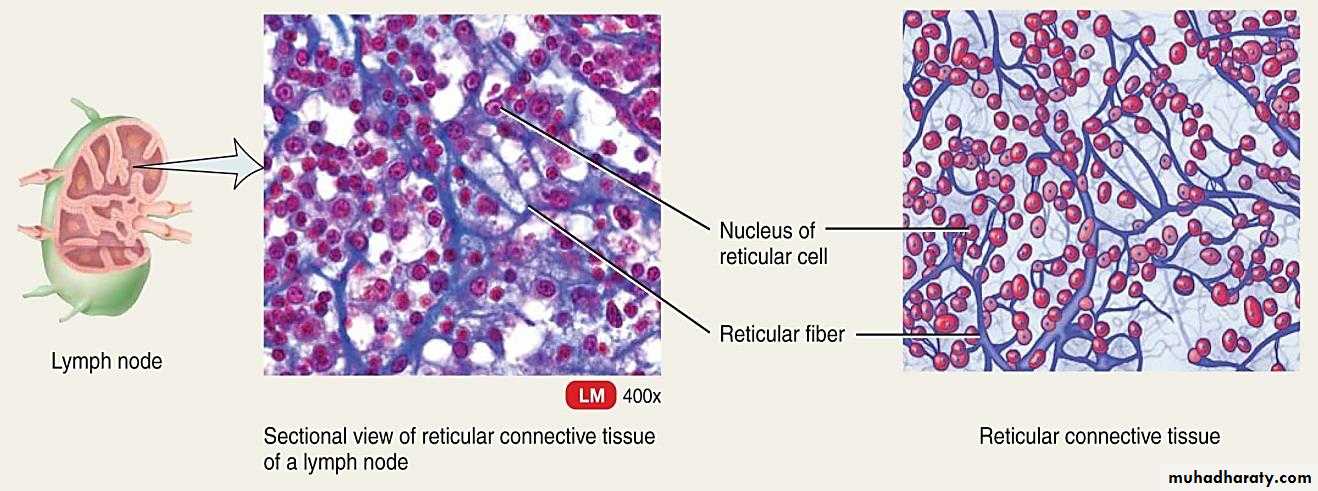
It consists of reticular cells, these are star in shape, has long cytoplasmic extensions and the network of reticular fibers formed by them. Reticular tissue is located in the liver, lymph nodes, spleen, and the bone marrow.
B. Dense Connective Tissue
Dense connective tissue is characterized by having a dense arrangement of fibers. It includes the following three tissues:Dense Regular Connective Tissue
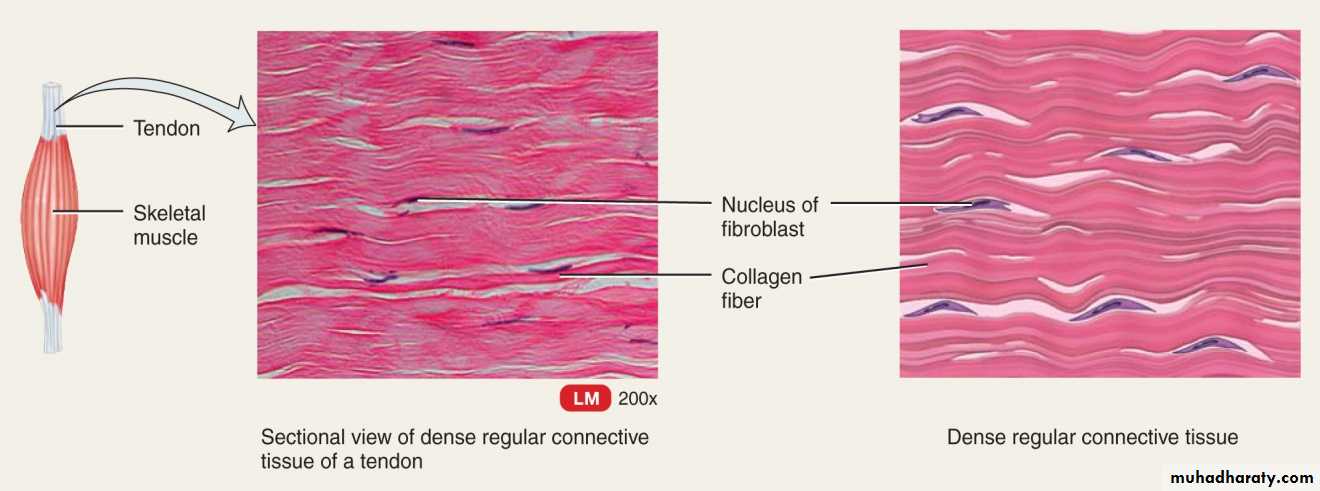
The matrix of dense regular connective tissue consists of dense bundles of parallel (regular arrangement) collagenous fibers. The bundles of collagenous fibers are surrounded by a small quantity of ground substance. The structural cells are called fibroblasts and are found in rows between bundles of collagenous fibers. Dense regular connective tissue is mostly found forming tendons.Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
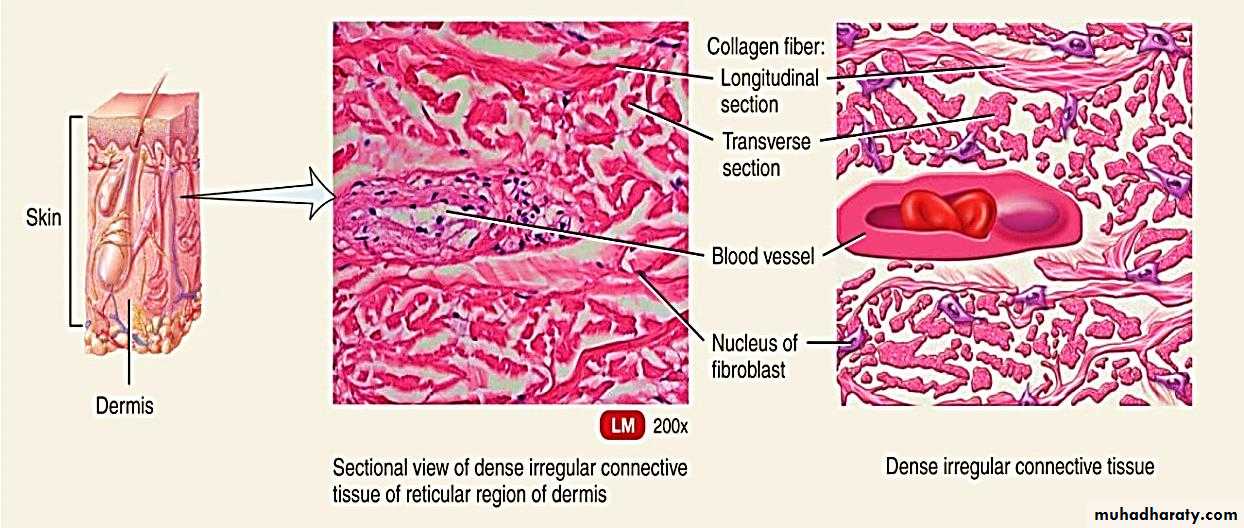
The matrix of dense irregular connective tissue consists mostly of irregularly arranged collagenous fiber bundles with a small quantity of ground substance. An irregular arrangement means that the bundles (groups of collagenous fibers) are interwoven in many directions . Fibroblasts are dispersed among the bundles of collagenous fibers. Tissue locations include the dermis (skin) , connective tissue sheets surrounding muscles (fasciae) and some organs such as the liver and lymph nodes.Elastic Connective Tissue
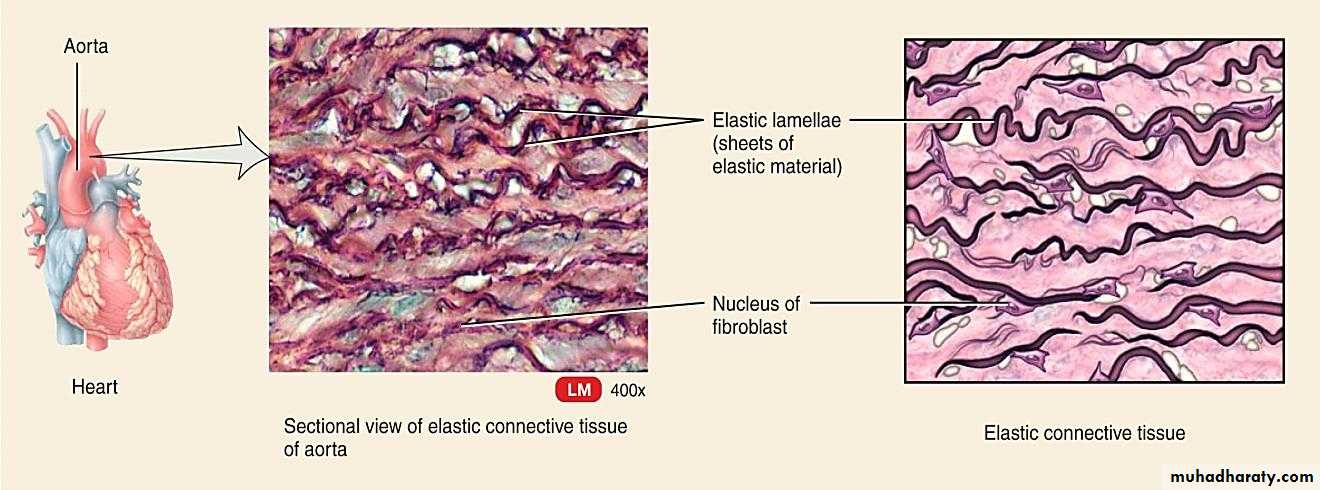
Elastic connective tissue may be considered a special type of dense regular connective tissue. This is because its matrix consists mostly ofdensely arranged elastic fibers, not collagenous fibers. Scattered collagenous fibers are located in small spaces among the elastic fibers.
Fibroblasts are found throughout the tissue. Elastic connective tissue locations include the vocal cords, walls of large arteries, walls of respiratory airways, and ligaments.