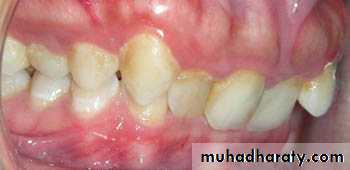
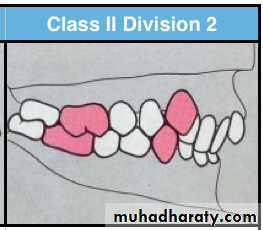
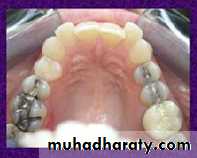
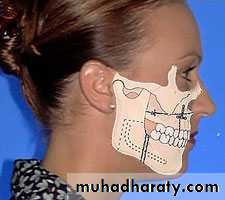
Class II division 2 malocclusion
Features of class II division 2 malocclusion:Extraoral features:
1- profile is straight to convex.2- shape of head mesocephalic to dolichocephalic.
3- no hyperactivity in mentalis muscle.
4- normal mentolabial sulcus.
5- normal or hypoactive upper lip.
Intraoral features:
1- Excessive lingual inclination of maxillary central incisors overlapped on the labial by the maxillary lateral incisors.In some cases both maxillary central and lateral incisors are lingually inclined and overlapped by canines on laterals.
2- U shaped or square palatal arch.
3- Deep overbite and minimal overjet.
4- With extreme overbite the incisal edge of lower central incisor may contact the soft tissue of palate.
5- In absence of overjet manibular labial gingiva get traumnatized by lingualy inclined maxillary incisors.
Features of class II division 2 malocclusion:
Class II division 2 malocclusion is either dental or skeletal
1- dental class II division 2 is corrected by orthodontic treatment (extraction or non extraction method)2- skeletal class II division 2
a- Growth modification (growing patient)b- Dental camouflage ( extraction or non extraction)
c- Orthognathic surgery with orthodontic treatment (moderate to severe class II cases)
Treatment of class II division 2
Dental class II division 2 malocclusion:
Extraction or non extraction treatment is depend on the severity of mesial drift of the maxilary first molarSlight mesial drift (mesial crown tipping) with minimal crowding ------ non extraction with distalization of maxillary first molar
Sever mesial drift (roots and crown are mesially positioned) ----- extraction is indicated to obtain space.
Skeletal class II division 2
Three treatment approach are available1- growth modification
2- dental camouflage3- orthognathic surgery( with orthodontic treatment)
Growth modification (orthopedic treatment)
The goal of growth modification is to enhance the un acceptable skeletal relationship by modifying remaining facial growth pattern of the jawsOptimum timing : prepubertal growth spurt ( active growth period)
Two types of orthopedic appliances usedHeadgear (extra-oral force)
Functional appliances (removable or fixed)Headgear : it deliver an extra-oral orthopedic force to compress the maxillary sutures and modify the pattern of bone apposition at these sites
Two types
1- face bow (maxillary excess)2- J hooks (maxillary anterior retraction and intrusion)
Functional appliances
Class II functional appliances are designed to position the mandible in a downward and foreward to enhance its mandibular growth patternIndication : mandibular deficincy
typs:1- removable Functional appliances ( activator, bionator, twin bloc, frankyl II )
2- fixed functional appliances ( herbst, Jasper jumper)
Indication1- adult
2- mild to moderate class II cases
3- minimal dental crowding
4- acceptable facial esthetics
5- usually require extraction
Dental camouflage without extractionis rare in cases of skeletal classII
Mild skeletal class II cases
Mild excessive overjet
Adequate space available
Maxillary molar distalization
Dental camouflage
Sever class II skeletal discrepancy
Orthognathic surgery is considerd.
Done only after cessation of growth.
Presurgical orthodontics should be considered in all cases
Maxillary prognathisim – partial maxillary retropositioning (most commonly done)
Mandibular retrognathism – intraoral sagittal split osteotomy.
Orthognathic surgery
Indicated in adults with no growth potentialmandibular advancement
Indication : skeletal class II caces with mandibular deficiencyThe intraoral sagittal split ramus osteotomy is the popular technique for surgical mandibular advancement.
Orthognathic surgery
Maxillary impaction (Le Fort 1 maxillary osteotomy)
Indication : Vertical maxillary excessAnterior maxillary sub-apical set back
Indication : maxillary excess in antero-posterior dimentional mid-face protrusion ( no vertical excess)Orthognathic surgery
Combined surgical approaches : maxillary and mandibular
Indication : maxillary excess and mandibular deficiencyOrthognathic surgery