Fifth stage
SurgeryLec-2
د.محمد نزار
13/4/2017
IRRITABLE HIPIrritable hip: is a term referred to transient synovitis of the hip in children; in which the child complain from pain and limping . it is the commonest cause of hip pain in children .
Boys affected twice as often as girls (2:1)
Clinically
The child is usually between 6-12 years old .
Presentation : pain and limping in otherwise healthy child .
The pain is felt in the groin and in the front of the thigh .
On examination : restriction of all movements with pain .
The symptoms subside spontaneously within 1-2 weeks so it is called transient .
Investigation
1- blood investigation : NORMAL .
2- x- ray finding : NORMAL .
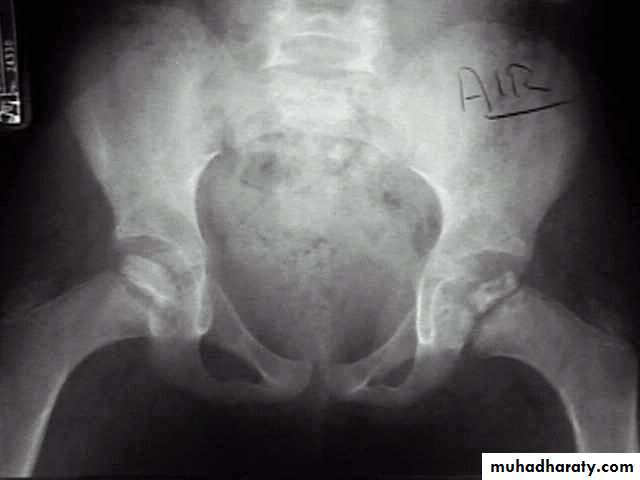
3- ultrasound ex. Of hip: MILD EFFUSION.
Differential diagnosis of pain and limping in children
1- transient synovitis (commonest cause) .
2- Perthes’ disease .
3- pyogenic infection(septic arthritis or osteomyelitis) .
4- T.B synovitis .
5-typhoid or brucillosis affecting the hip .
6-slipped femoral epiphysis .
7- Juvenile chronic arthritis .
Treatment
The child otherwise completely healthy .
1- in mild cases : rest in bed at home , analgesic anti inflammatory drugs .
2- in moderate to sever cases admission to the hospital rest in bed , skin traction , analgesic anti inflammatory drugs .
Weight bearing not allowed before acute attack is subside (usually take 1-2 weeks).
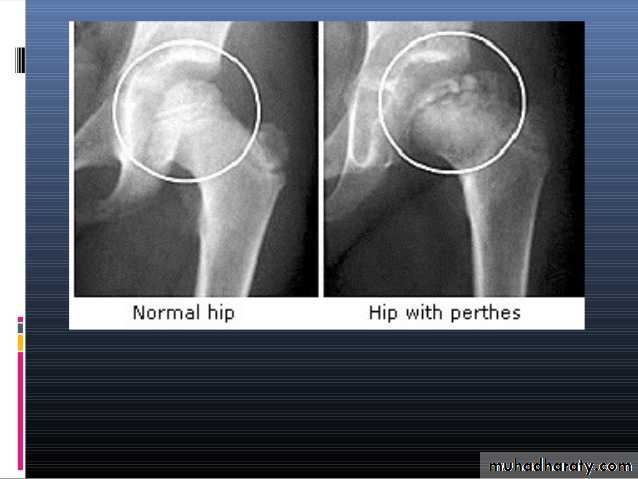
PERTHES’ DISEASE
Introduction
It is also called Legg – Calve’- Perthes’ disease .
It is painful disorder of childhood characterized by avascular necrosis of the femoral head .
It’s incidence is 1 : 10000 child .
More common in boys than in girls (4:1) .
Age incidence usually between 4-8 years
Pathogenesis
The precipitating factor of the disease is unknown .
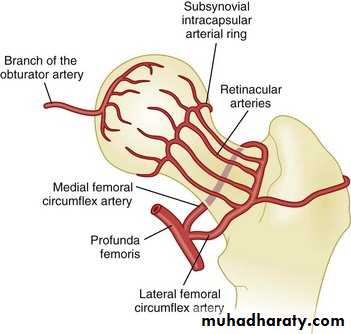
The main step in pathogenesis is ischemia of the femoral head .
Up to the age of 4 months the femoral head is supplied by:
1- metaphyseal blood vessels .
2- lateral epiphyseal vessels .
3- vessels in the ligamentum teres .
Pathogenesis (cont.)
The metaphyseal blood supply gradually decline until by the age of 4 year it will disappear …. The vessels in the legamentum teres develop at the age of 7 years old ; so between the age 4-7 years the blood supply depend on the lateral vessels which run into the capsule of the joint , make them susceptible to stretching and pressure from an effusion of the joint .pathology
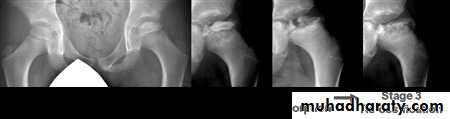
Pathological process take 2-4 years to complete .
Stage 1.. Ischemia and bone death .
Stage 2.. Revascularization and repair .
Stage 3.. Distortion and remodeling .
Clinical features
Typically a boy of 4-8 years complain from pain at the hip region associated with limping .
The attack take few weeks (more than 2 ) and it may recur intermittently .
The child’s general health is good .
At early stage the joint is irritable(all movements are restricted ) and their extremes are painful.
In late stages all movements are full apart from limitation in abduction and internal rotation
X-ray
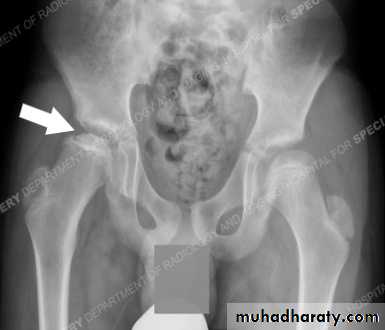
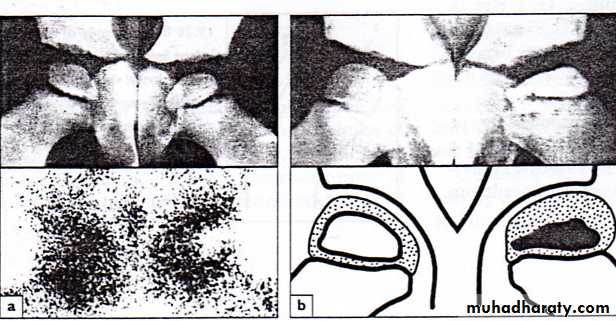
1- at the beginning the x- ray look normal some time we can see asymmetry of the ossific centers ; bone scan is helpful at this stage (showing the avascular area) .
2- later on the increase density of the ossific nucleus will be clear ; and there is increase in the joint space .
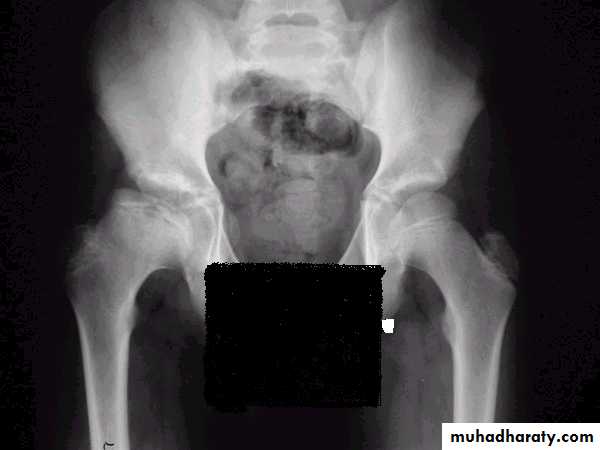
3- fragmentation of the epiphysis .
4- flattening and lateral displacement of the epiphysis .5- widening of the metaphysis .
6- in sever and advance cases the head become mushroom shape .
prognostic factors
1- age : below 6 years good prognosis .2- sex : girls carry bad prognosis than boy
3- the greater the involvement of the femoral head the badest is the prognosis .
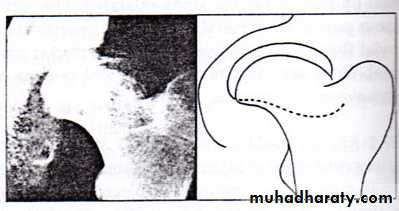
Criteria of ahead at risk
1- progressive uncovering of the epiphysis
2- calcification of the cartilage lateral to the ossific nucleus .
3- radiolucent area at the lateral edge of the epiphysis .
4- sever metaphyseal resorption .
Treatment of perthe’s disease
As long as the head is irritable the child should be kept in bed with skin traction and the hip is in little flexion and external rotation . Once the irritability is subside which usually take three weeks then movements is encouraged .Further treatment :
A – symptomatic treatment . B – containment.
Symptomatic treatment :
Include : pain control by simple analgesic and periods of traction and rest .Regular assessment should be taken every few months i.e. (supervised – neglect) way.
Sport and heavy activities should be avoided
containment :
It mean taking active step to seat the head of the femur as fully as possible in the acetabular socket.This achieved by :
A – holding the hip widely abducted in plaster or in removable abduction splint and the position maintained for at least one year .
B – operation by varus osteotomy of the femur or osteotomy of the innominate bone