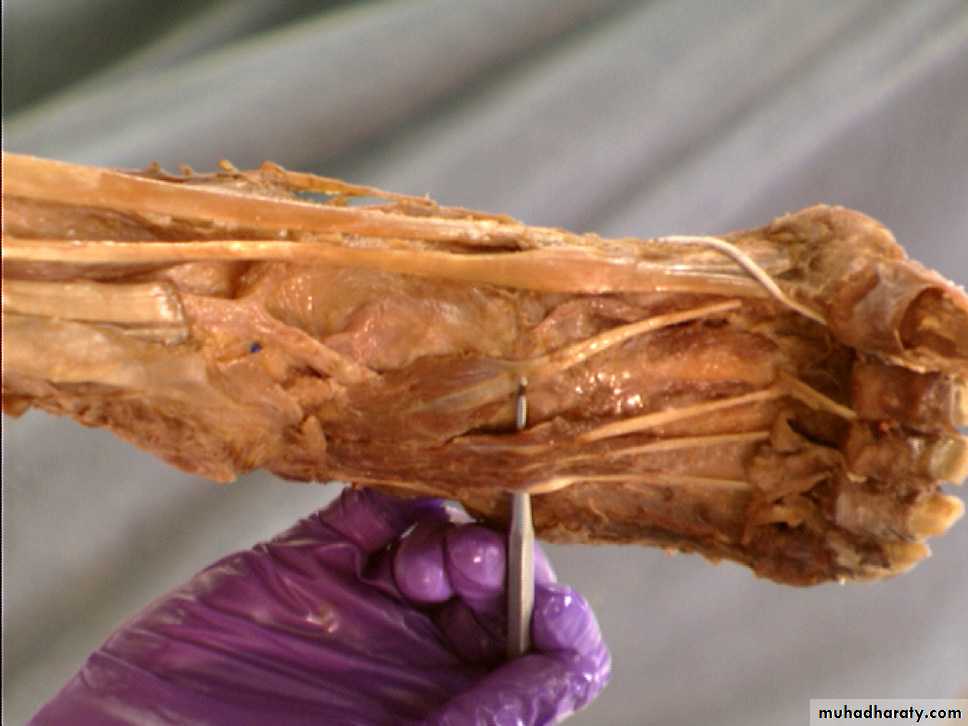
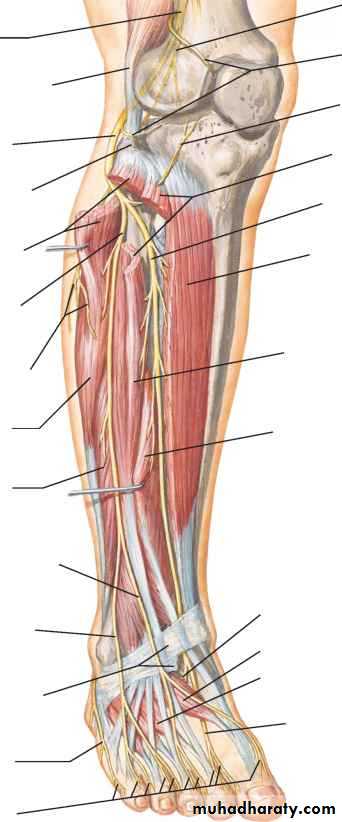
Front of the leg and dorsum of the foot
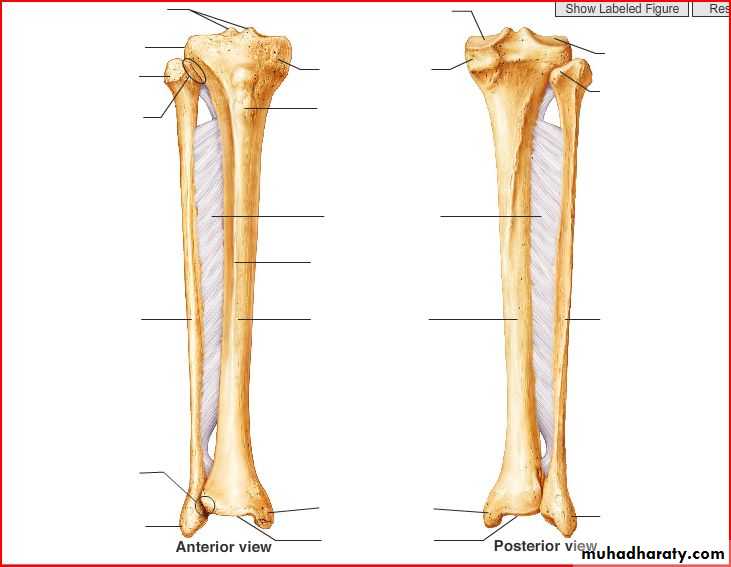
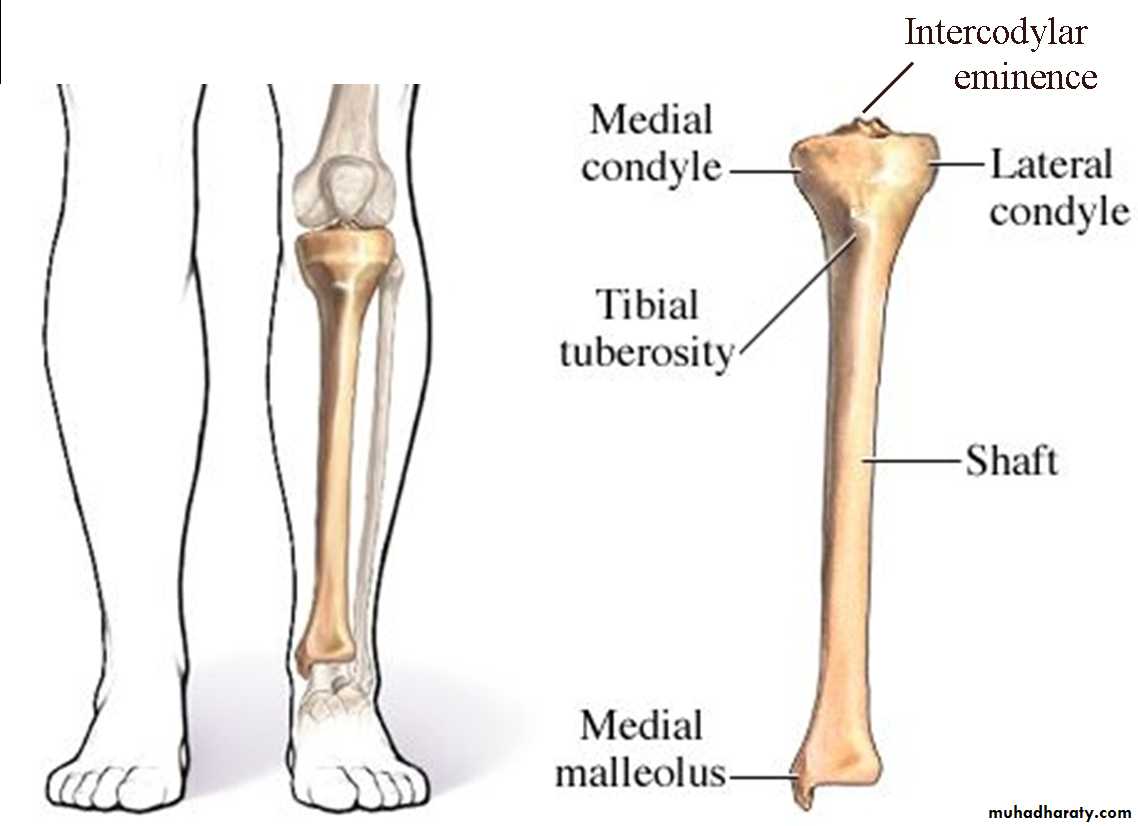
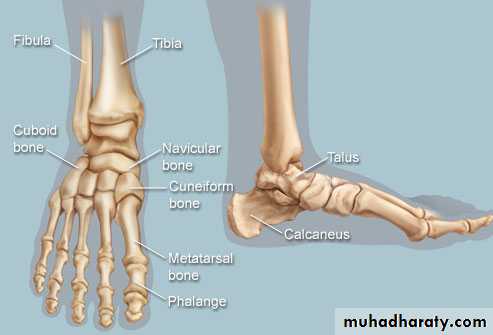
Tibia
A-Upper end , formed of :1- medial condyle
2- lateral condyle
3- inter condylar area
4-tibial tuerosity
B. shaft formed of :
3 border(ant, lat.,and med.)
3 surface( med., lat., and post)
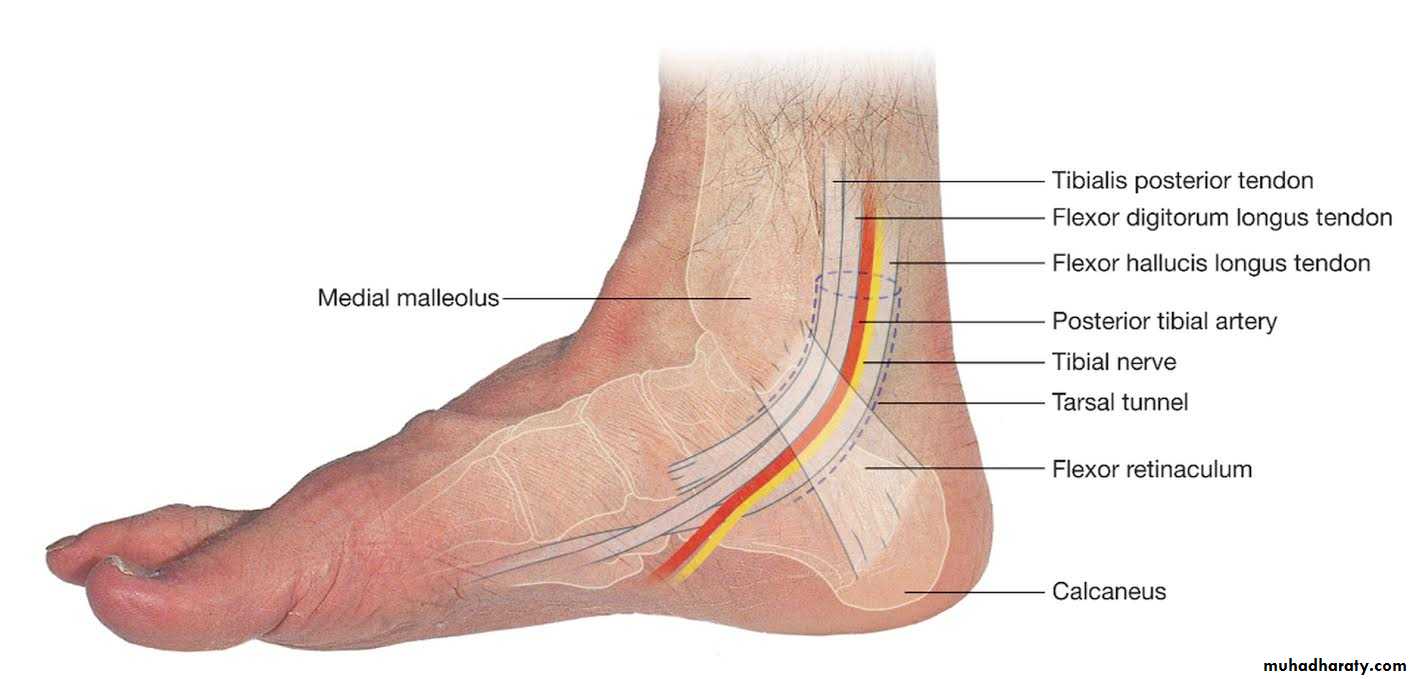
C- lower end, from its medial side , it forms subcutaneous projection called medial malleolus
fibula
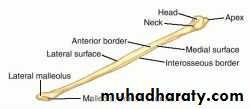
fibula
A-Upper end is formed of :
1- apex (styloid process 2- head 3- neck
B-shaft contins
3 border( ant., post.,and lateral)
3 surface(ant., post.,and
Lat.)
C-lower end :project laterally to form lat. Malleolus
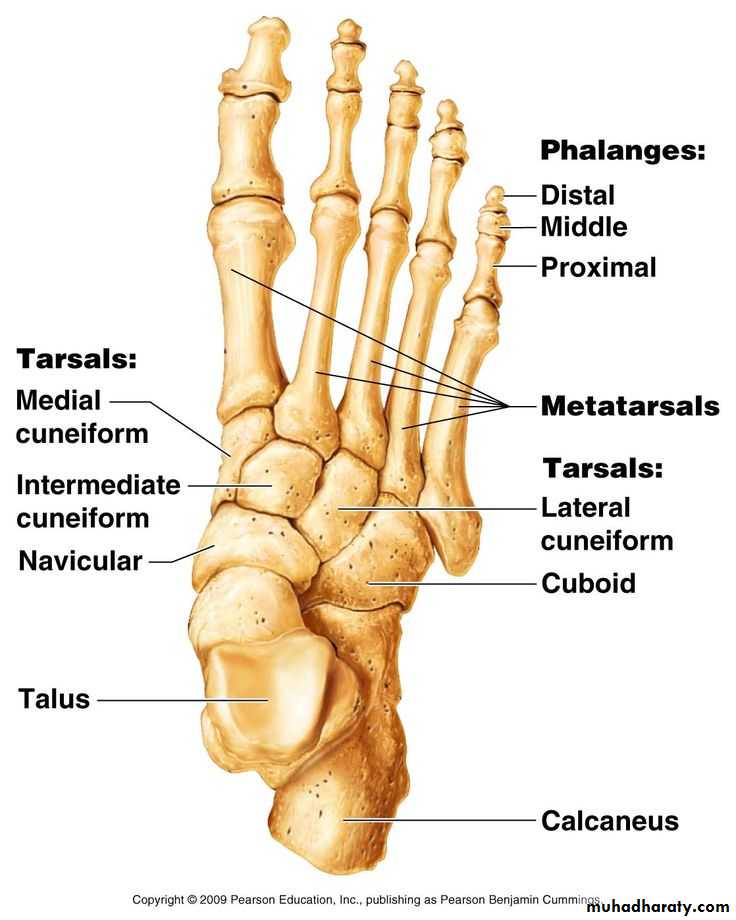
Skeleton of the foot
A- tarsus (7 in number)1-proximal raw(talus, calcaneus)
2-intermediat raw (navicular)
3- distal raw(3 cuneiform bones,medialy and cuboid bone ,laterally
B- metatarsus( 5 in number)each bone consists of , proximal end(base), shaft,and distal end (head)
C- phalanges(14 in number)
Big toe only consist of 2 phalanges
Bones of foot
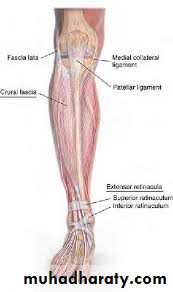
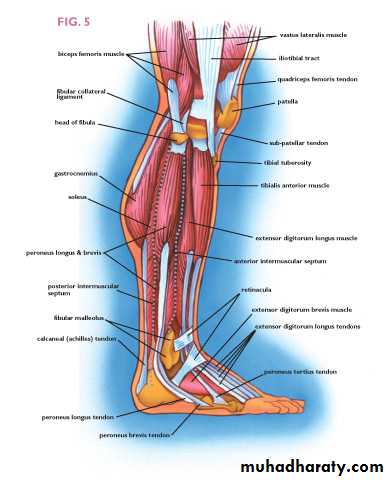
The deep fascia (crural fascia)
it attached to the patella, the patellar ligament and the tibial tuberosity..the crural fascia attached to the tibial condyles and the head of the fibula Inferiorly ,at the ankle joint , the deep fascia is thickened to form retinacula which act as a pulley to prevent displacement of the tendons of the muscles.
GREAT SAPHENOUS VEIN
DEEP FASCIASER
IER
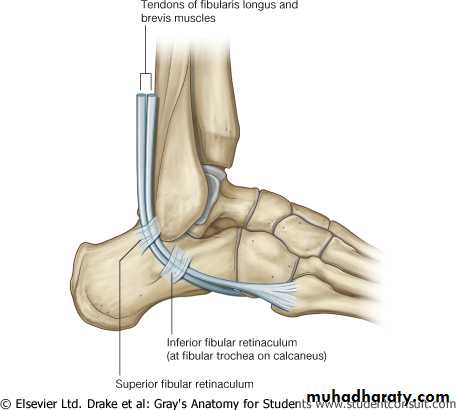
Superior peroneal retinaculumlateral Inferior peroneal retinaculum
-
Flexor retinacula
intermuscular septa
1-Anterior intermuscular septa:. It connects the deep fascia with anterior border of the fibula2-- The posterior intermuscular septa:. It connects the deep fascia with posterior border of the fibula
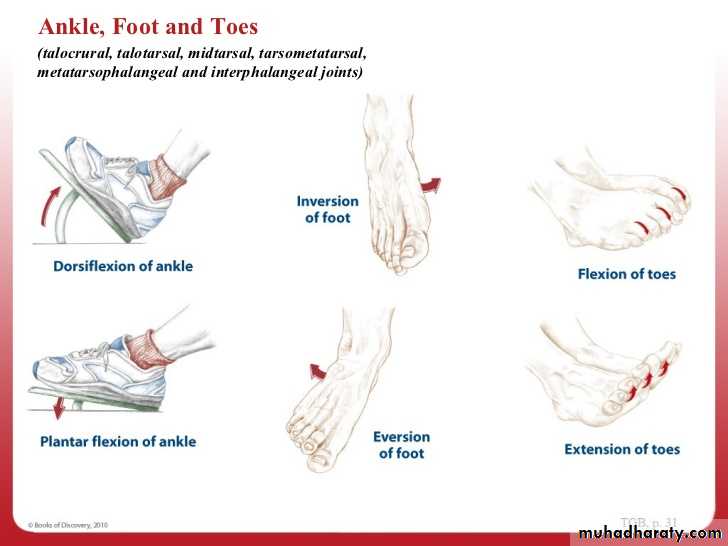
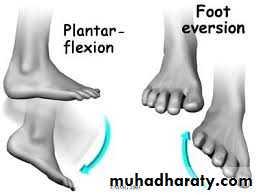
Movement at ankle j.
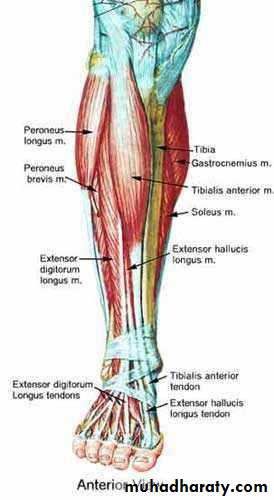
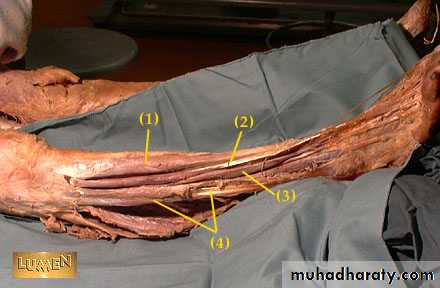
Anterior compartment of the leg
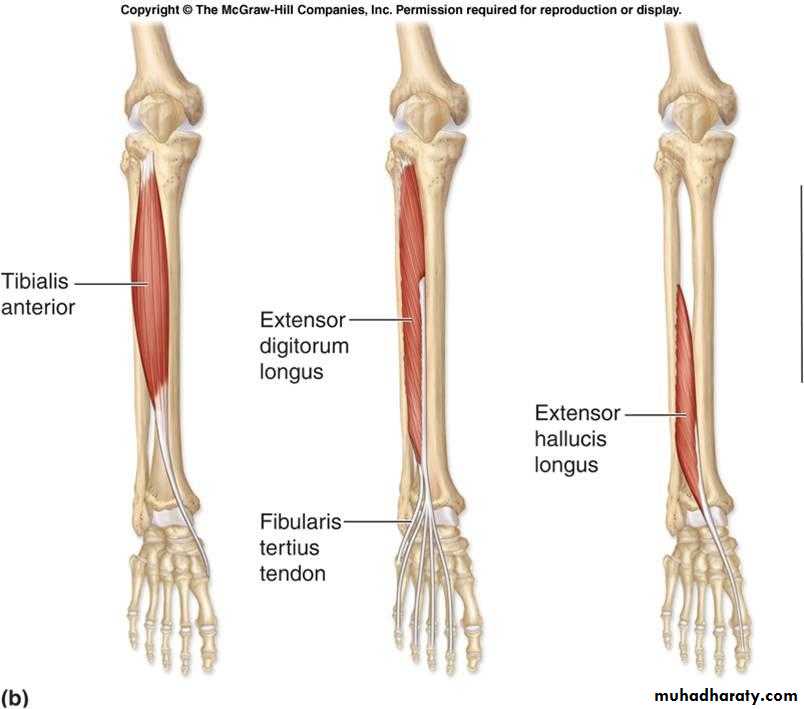
it contains the following muscles:,Tibialis anterior m.,.extensor hallucis longus m., extensor digitorum longus m., peroneus tertius m.Anterior compartment of the leg
1- TA. 2-EDL. 3 EHL. 4,PM
1-EHL2- EDL 3- PT 4- EDB
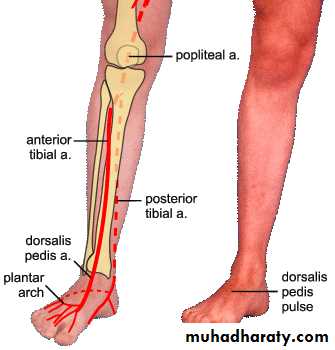
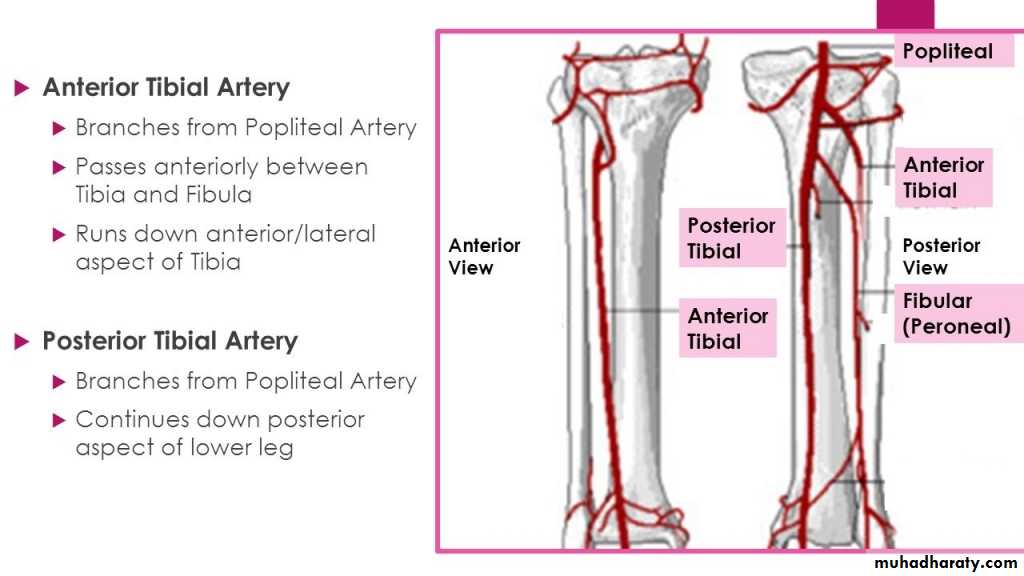
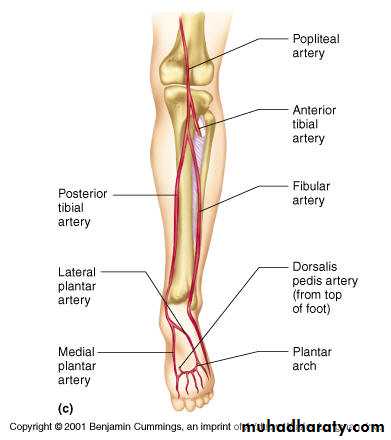
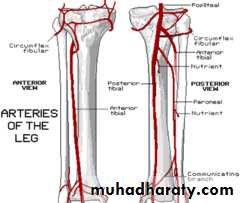
Anterior tibial arterya
Origin Arises from the popliteal artery at the lower border of the popliteus m.Termination It ends in the front of the ankle joint by becoming the dorsalis pedis artery midway between the malleoli
Anterior tibial artery
Branches:1- muscular branches to the muscles of the anterior compartment.
2- Anterior tibial recurrent artery passes upwards to the knee joint.
3- Medial and lateral malleolar arteries to the lateral and medial malleoli, the lateral one anastomosed with the perforating branch of the peroneal artery.
Anterior tibial recurrent
lateral malleolarMedial malleolar
Deep peroneal nerveIt gives :
articular branch to ankle joint
Muscular branches
Deep peroneal n.
TA
EHL
Superfiscial peroneal n
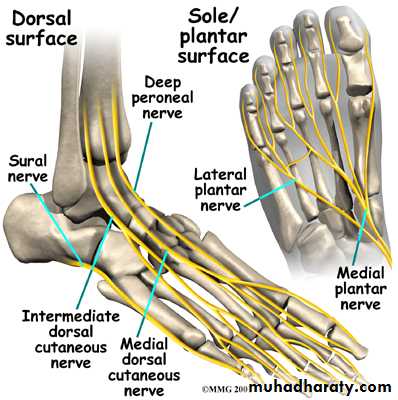
passes to the dorsum of the foot with the dorsalis pedis A. and terminates at lower border of inferior extensor retinaculum by dividing into lateral terminal branch (supplies extensor digitorum brevis and joints of the foot) and medial terminal branch (divides into 2 digital branch to supply adjacent sides between 1st and 2nd toesDE
medial terminal branch of DPN
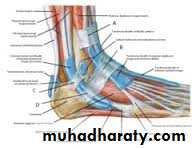
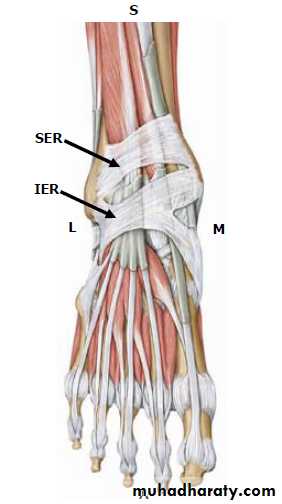
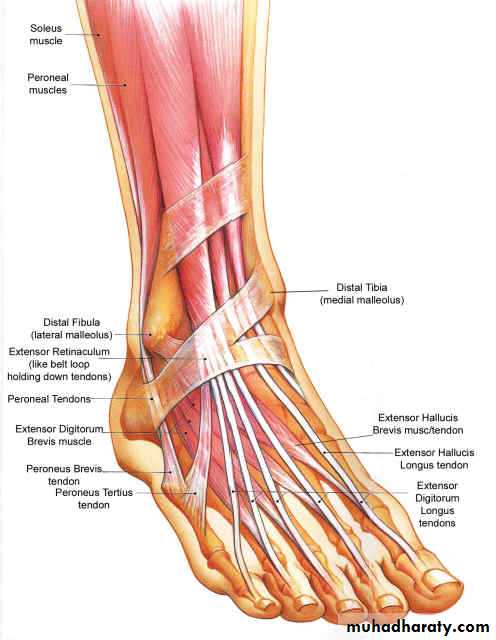
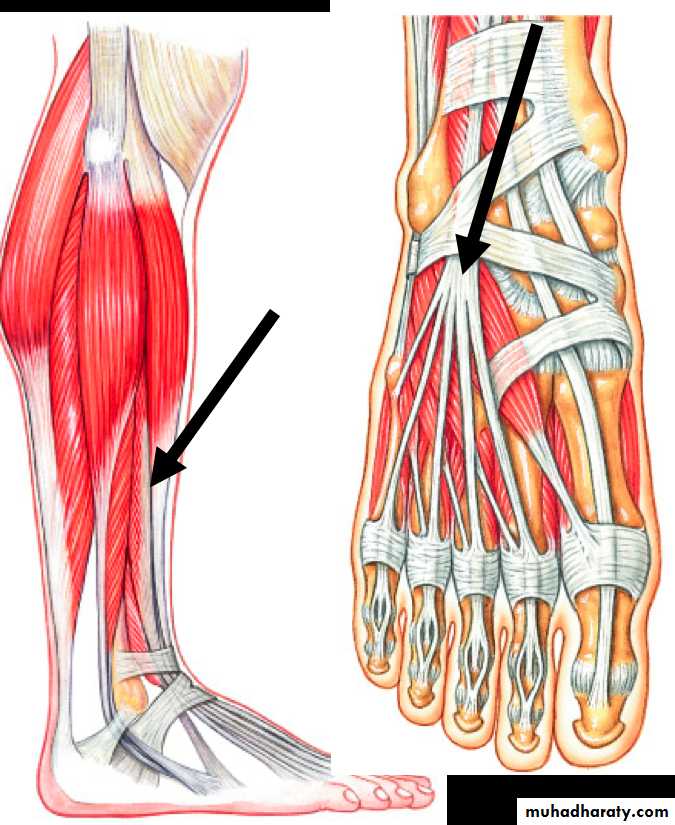
dorsum of the foot1- Superior Extensor Retinacula(SER): it is a thickening of deep fascia in front of lower part of leg ,attached to lower part of the anterior borders of tibia and fibula.
2- Inferior extensor retinacula(IER) it is a thickening of deep fascia (Y shaped)in the dorsum of the foot . its lateral end ( stem )attached to calcaneus while the medial end divided into 2 bands, the upper one attached to the medial malleolus ,the lower one attached to the deep fascia on medial
Structures pass deep to the ER
TAEHL
Anterior tibial vessels
Deep peroneal (Anterior tibial )n.
EDL
PT
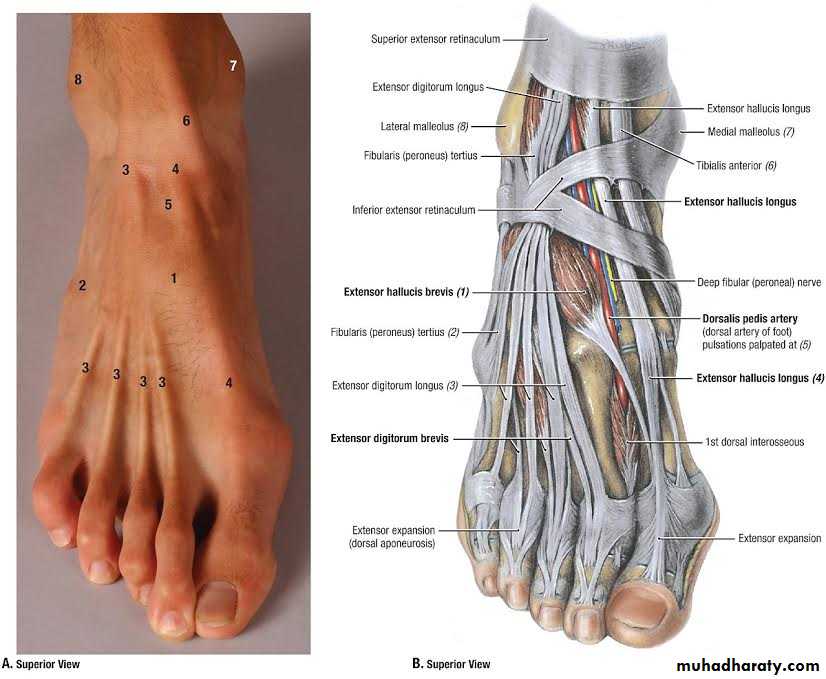
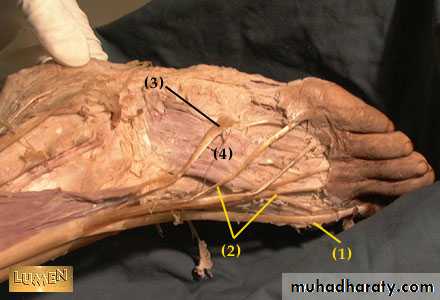
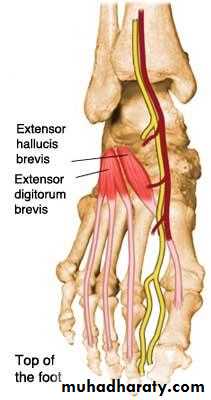
The muscles of the dorsum of the foot
is :Extensor digitorum brevis muscle: origin: at the superior surface of calcaneus
EHB
EDB
Extensor digitorum brevis
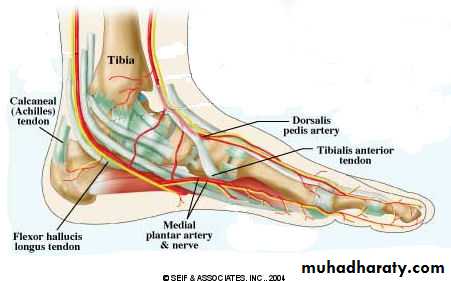
Dorsalis pedis artery
It is the continuation of the anterior tibial artery begins at the anterior surface of the ankle jointruns in the dorsum of the foot in line with the first dorsal inter digital cleft
At the proximal end of the 1st intermetatarsal space , the dorsalis pedis A. divided into arcuate and 1st dorsalmetatarsal arteries
Branches:
1- Lateral tarsal branch: runs laterally deep to EDB to supply it.
2- Medial tarsal branch.
3- Arcuate artery
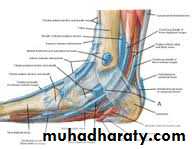
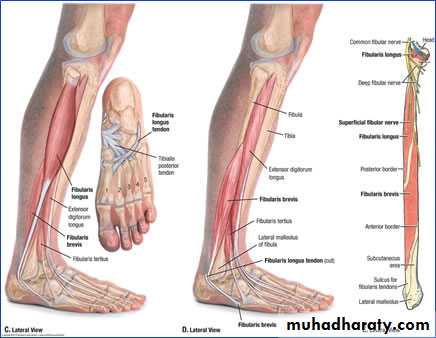
LATERAL SIDE OF LEG
Superior peroneal retinaculumextend from the back of lateral malleolus to lateral surface of the calcaneus
inferior peroneal retinaculum
extend from superior surfaces to lateral of the calcaneus
Its subdivided into two compartments by fibrous septa, the upper compartment transmit the tendon of PB while the lower compartment transmit the tendon of PL.
Lateral side of the leg
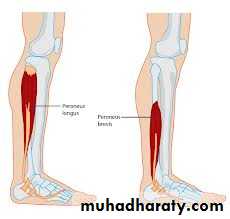
lie between the anterior and posterior intermuscular septa These are peroneus longus and brevis ms. supplied by the superficial peroneal nerve.and peroneal artery.
EDL
PLM
PBM
Peroneus longus m
Peroneus m
Superficial peroneal nerve
Descend in the peroneus longus m. to reach the peroneus brevis m. supply both muscles, then it descend between it and extensor digitorum longus m. pierce the deep fascia in the distal 1/3 of the leg and divides into medial and intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerves.The back of the leg
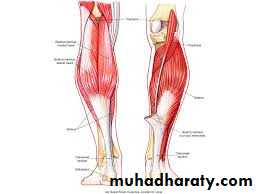
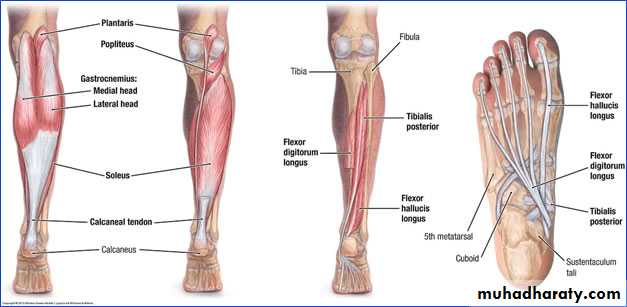
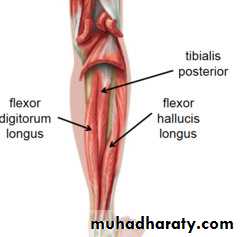
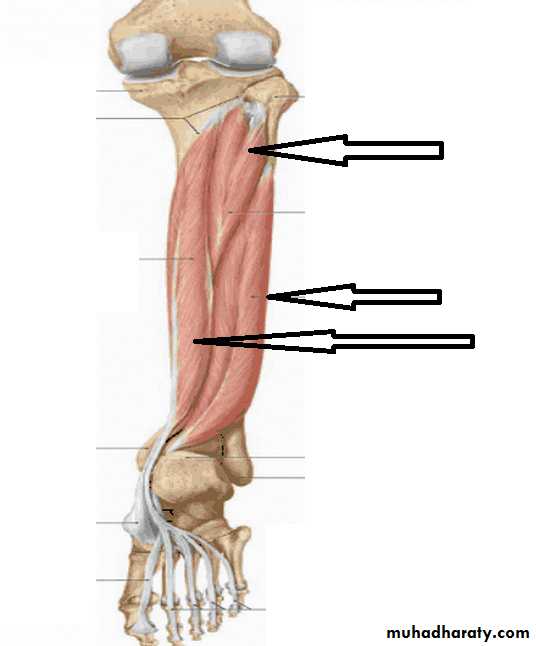
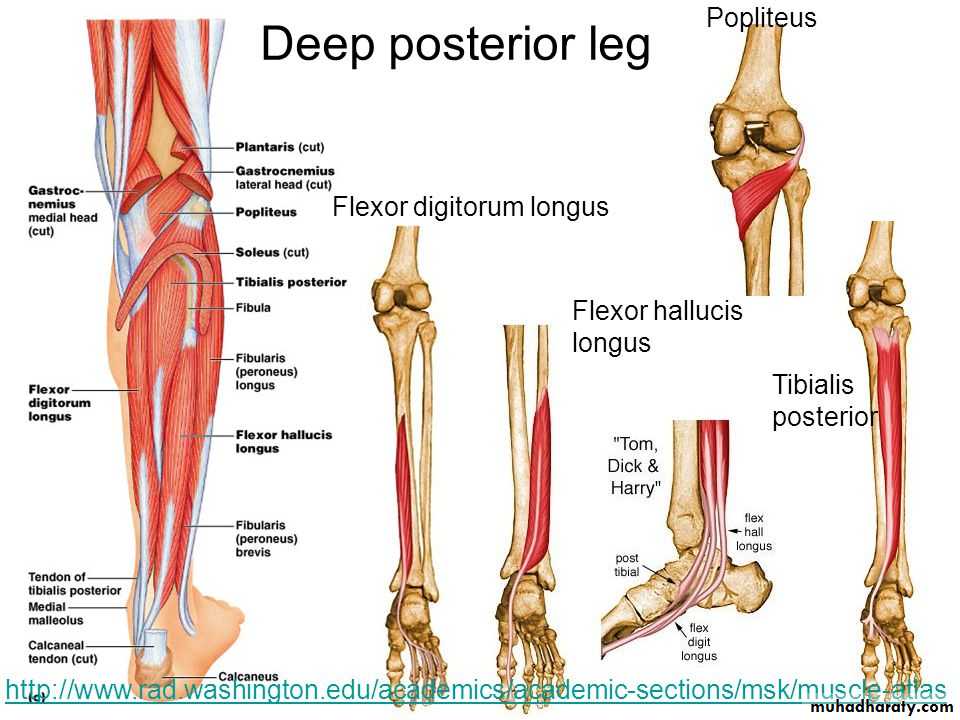
The transverse intermuscular septa divide the back of the leg into superficial posterior compartment and the deep posterior compartment, they supplied by the tibial nerveThe back of the leg
TP
FDL
FHL
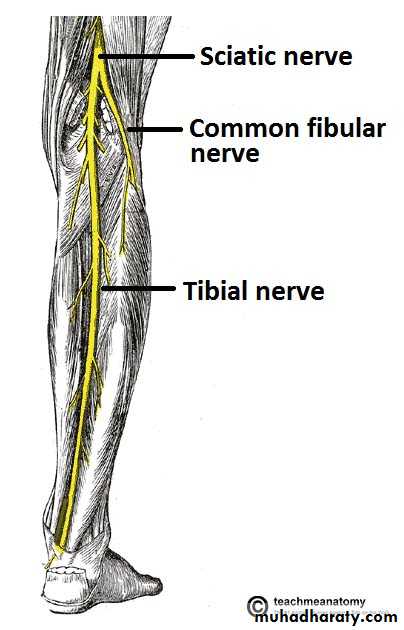
Tibial nerve
The princible nerve of the back of the leg is the Tibial nerve (L4,5,S1,S2,S3) passes under the tendinous arch of the solus muscle and descend under the transverse intermuscular septum superficial to the posterior tibial vessels. in the upper part of the leg it lies on the popliteus m. then posterior to the tibialis posterior m.
Tibial nerveterminate by dividing into medial and lateral planter n.
The posterior tibial artery
Branches in the leg:
1- peroneal artery :
a-muscular b- Nutrient branch to the fibula.
c- Perforating artery d- The peroneal artery ends by giving posterior lateral malleollar
Art . Of leg
Flexor retinaculum
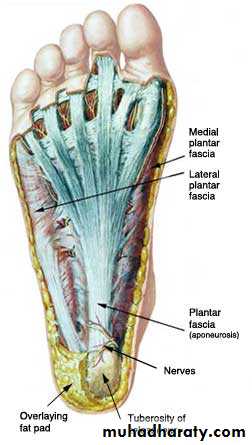
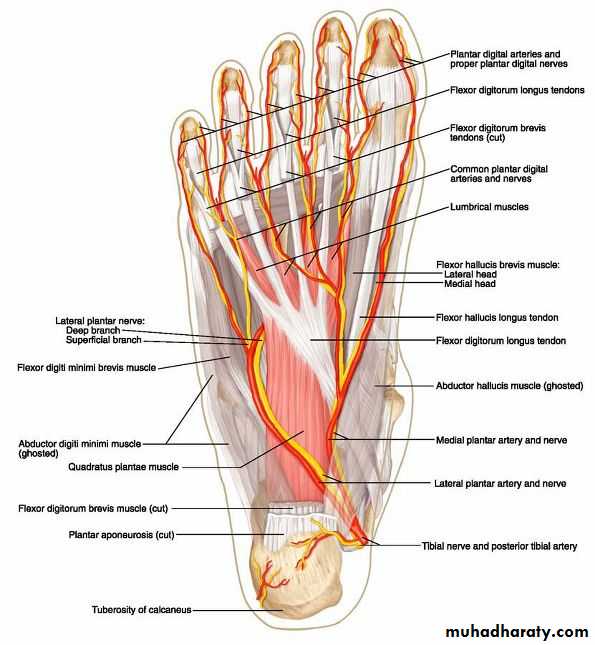
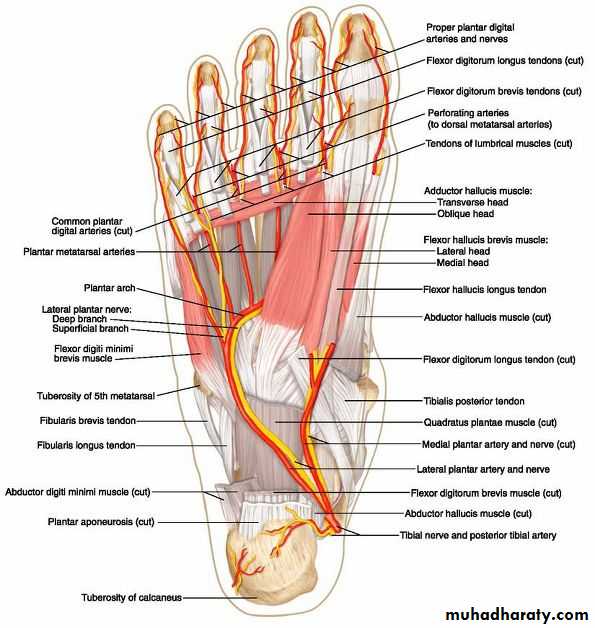
Sole of the foot
Deep fascia (planter fascia)Planter aponeurosis
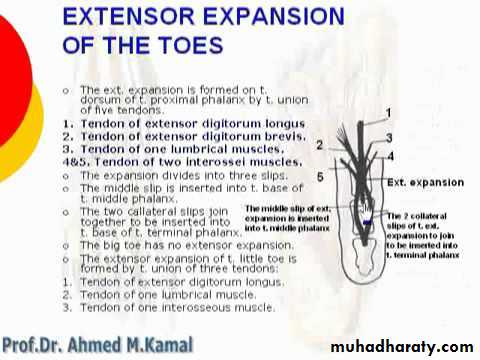
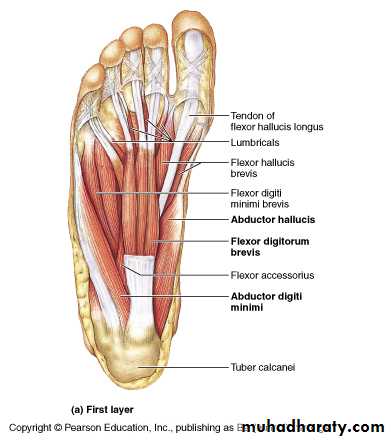
The great toe compartment
This compartment contains the abductor hallucis and flexor hallucis brevis muscles, the medial planter nerve and vessels, and the first metatarsal bone.The compartment of the little toe
It lies under the lateral planter fascia and is bounded by the lateral intermuscular septum medially and the by the attachment of the fascia to the dorsum of the fifth metatarsal bone laterally. It includes the abductor and flexor digiti minimi muscles and the fifth metatarsal bone.
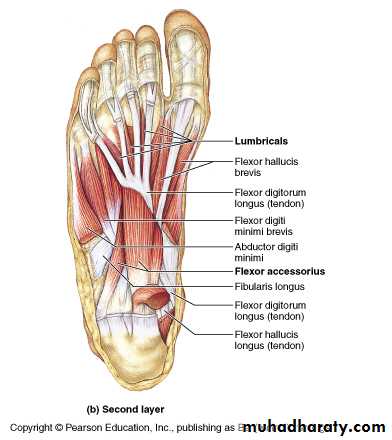
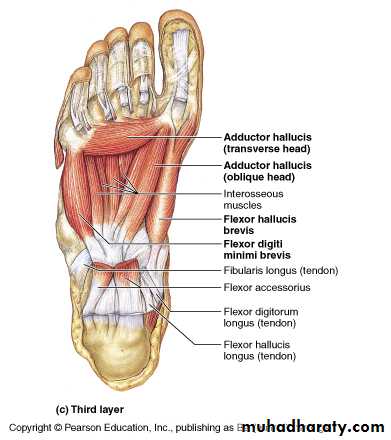
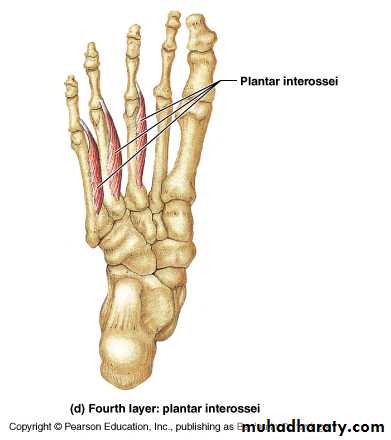
The central compartment of the sole
It lies deep to the planter aponeurosis, bounded on either side by the medial and lateral intermuscular fascia which passes from the margins of the aponeurosis to the planter interosseous fascia. It contains the flexor digitorum brevis muscle, the tendons of the flexor digitorum longus and its associated muscles ( quadratus plantae and four lumbrical muscles), the tendon of the flexor hallucisFrolich, Human Anatomy, Lower LImb
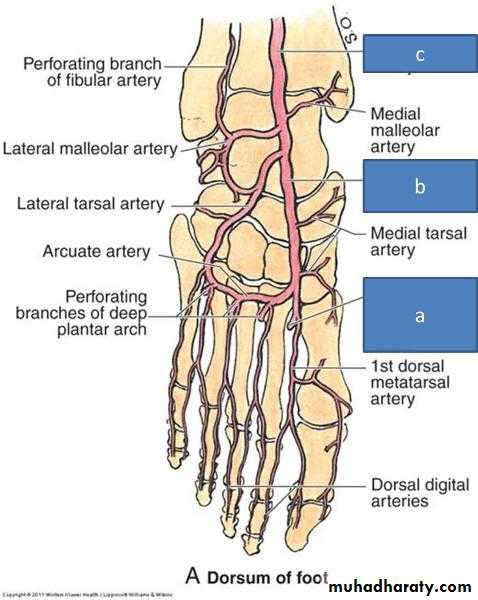
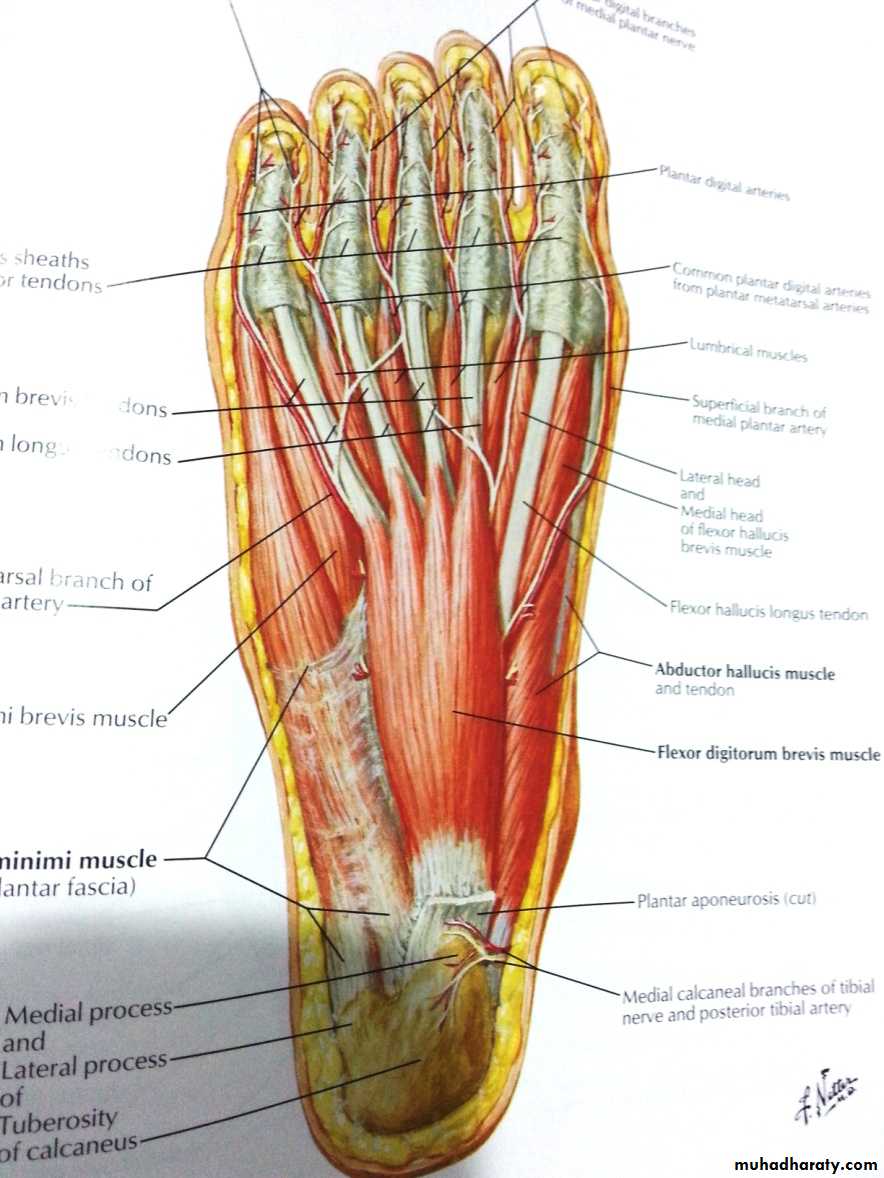
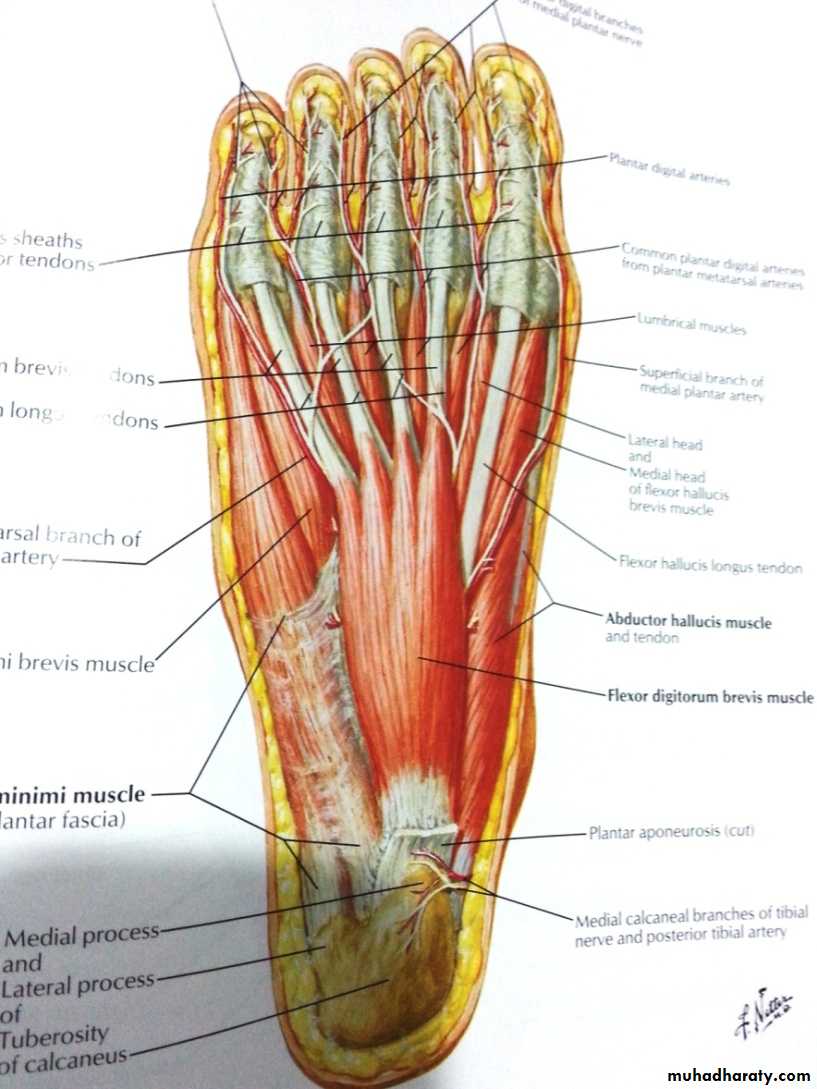
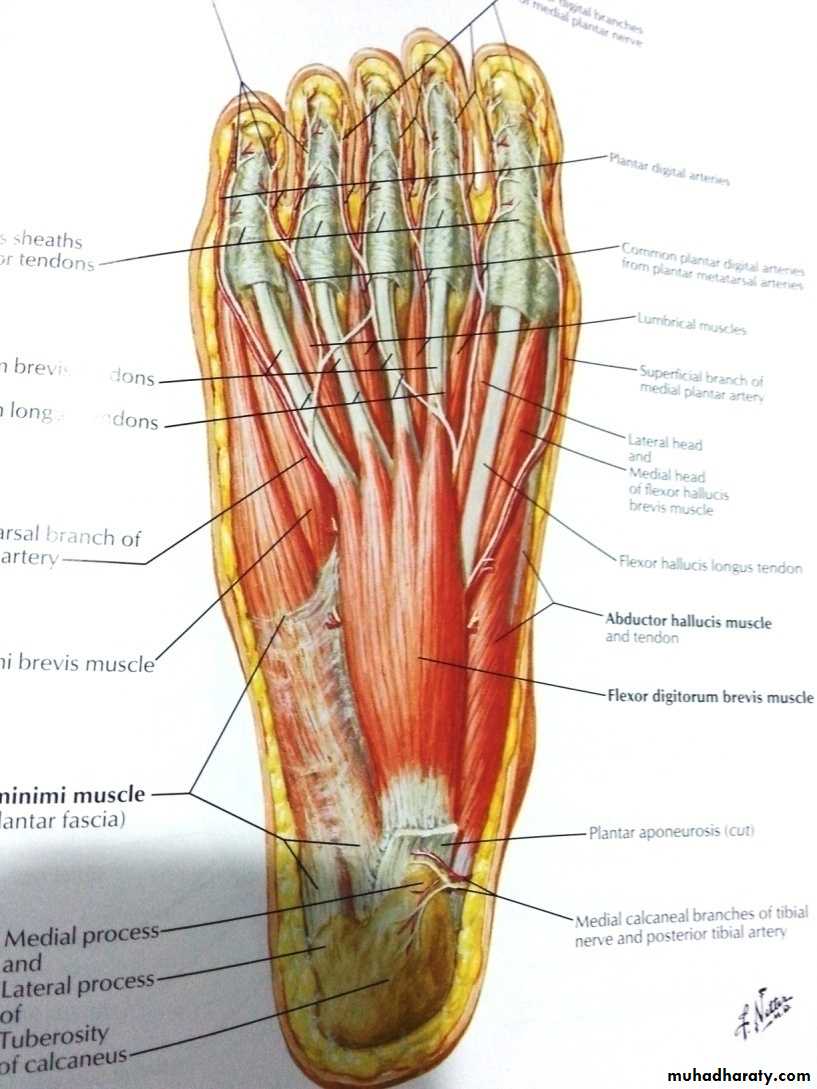
Arteries of the sole of the foot
The medial planter arteryLateral planter arteryThe planter arch :
The planter arch
It is formed from the lateral planter artery, the arch completed medially by its union with the deep planter branch of the dorsalis pedis artery. The arch gives:four planter metatarsal s.
The proper digital artery to the lateral side of the little.
Each planter metatarsal artery gives perforating branches which passes through the interosseous space anastomosed with the corresponding branch of the dorsal metatarsal artery.
.gives off numerous muscular
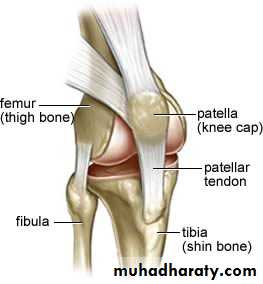
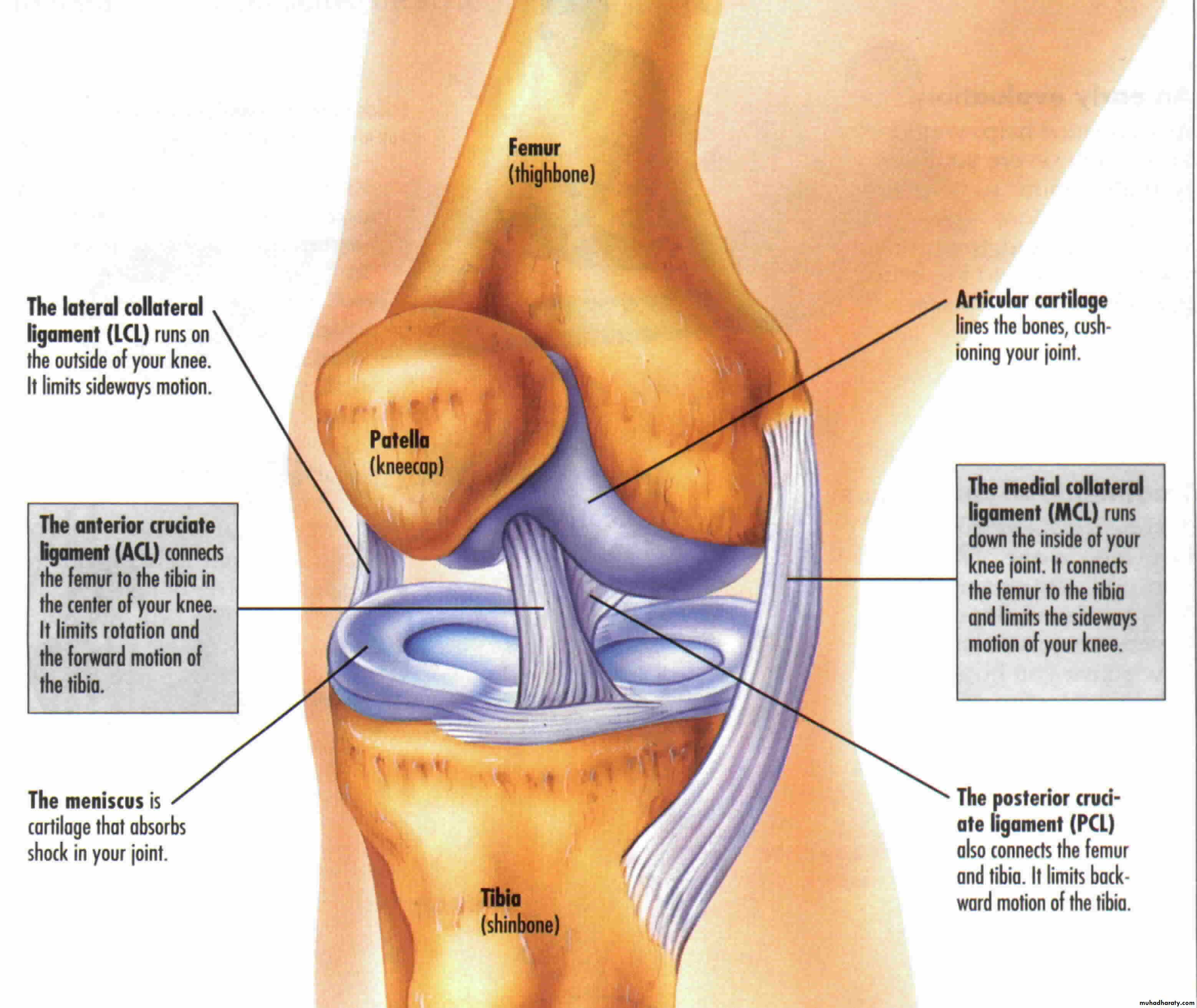
The knee joint
It is a synovial joint of the hinge type, it is unstable joint but this overcome by certain mechanism:1- expansion of the upper end of the tibia and lower end of the femur.
2- Presence of the strong collateral ligament and tendons.
3- Strong capsule.
4- Presence of the intra-articular ligaments.
The capsule is strengthened by number of ligaments
include:1- lateral and medial patellar retinacula
2- Iliotibial tract.
3- The ligamentum patellae which is a continuation of the quadriceps femoris tendon run on the patella to reach the tibial tuberosity.
4- Oblique popliteal ligament it is the posterior reinforcement of the capsule of the joint and it is extension from the tendon of the semimembrenosus m.
5- Arcuate popliteal ligament arise from the back of the head of the fibula and runs medially over the popliteus m.
6- Collateral ligament they are tibial and fibular collateral ligaments. They are very strong ligaments.
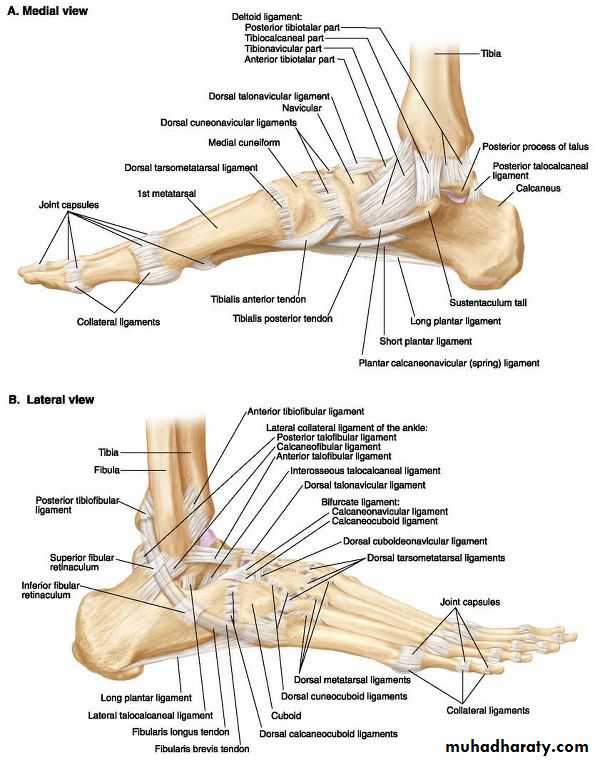
Ankle joint
This is a hinge type of joint between the trochlea of the talus with the distal end of the tibia and medial malleolus medially and the lateral surface of the body of the talus with the lateral malleolus laterally
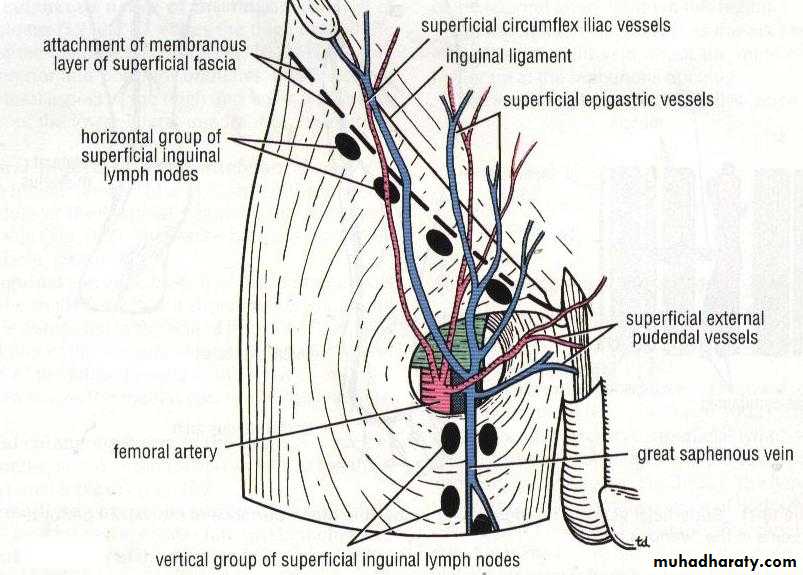
Superficial Inguinal Lymph Nodes
Horizontal GroupVertical Group
58