
1
Endodontic failure
Causes:
I. Apical percolation:
i. Short root canal filling Retreatment
ii. Unfilled canal (missed canal)
II. Operative errors:
a. Root perforation:
i. Furcation perforation: -Biodentin
-MTA
-Amalgam
ii. Perforation of lateral wall:
1. Perforation of apical 1/3 surgery
2. Perforation of cervical 1/3 manage it like furcation perforation
3. Perforation of middle 1/3 -buccaly (surgery)
-palataly (extraction)
-mesial or distal (treat like another canal)
b. Overfilling:
i. Overfilling with G.p. follow up:
a. If asymptomatic leave it.
b. If painful with periapical infection Retreatment or surgical curettage.
ii. Overfilling with silver point: Retreatment.
c. Ledge formation, causes:
i. Straight instrument in curved canal.
ii. Jumping in instruments.
iii. Insufficient use of R.C. irrigant.
iv. No diagnostic radiograph.
Management: by prevention of occurrence.
d. Broken instrument:
i. Apical 1/3 sometimes leave it or apical surgery.
ii. Middle 1/3 bypass or apical surgery.
iii. Cervical 1/3 try to remove it.
ﻣﻌﺎﻟﺟﺔ
\
ﺧﺎﻣس اﺳﻧﺎن
د. ﻣﻌﺗز
)ﻣﻠﺧص م
1+2
(
20
\
4
\
2017
2
Custom made Post-Crown restorations
Parts:
1. Post.
2. Core.
3. Crown.
Functions:
1. Retention.
2. Protection.
Principles of preparation:
1. Conservation of tooth structure:
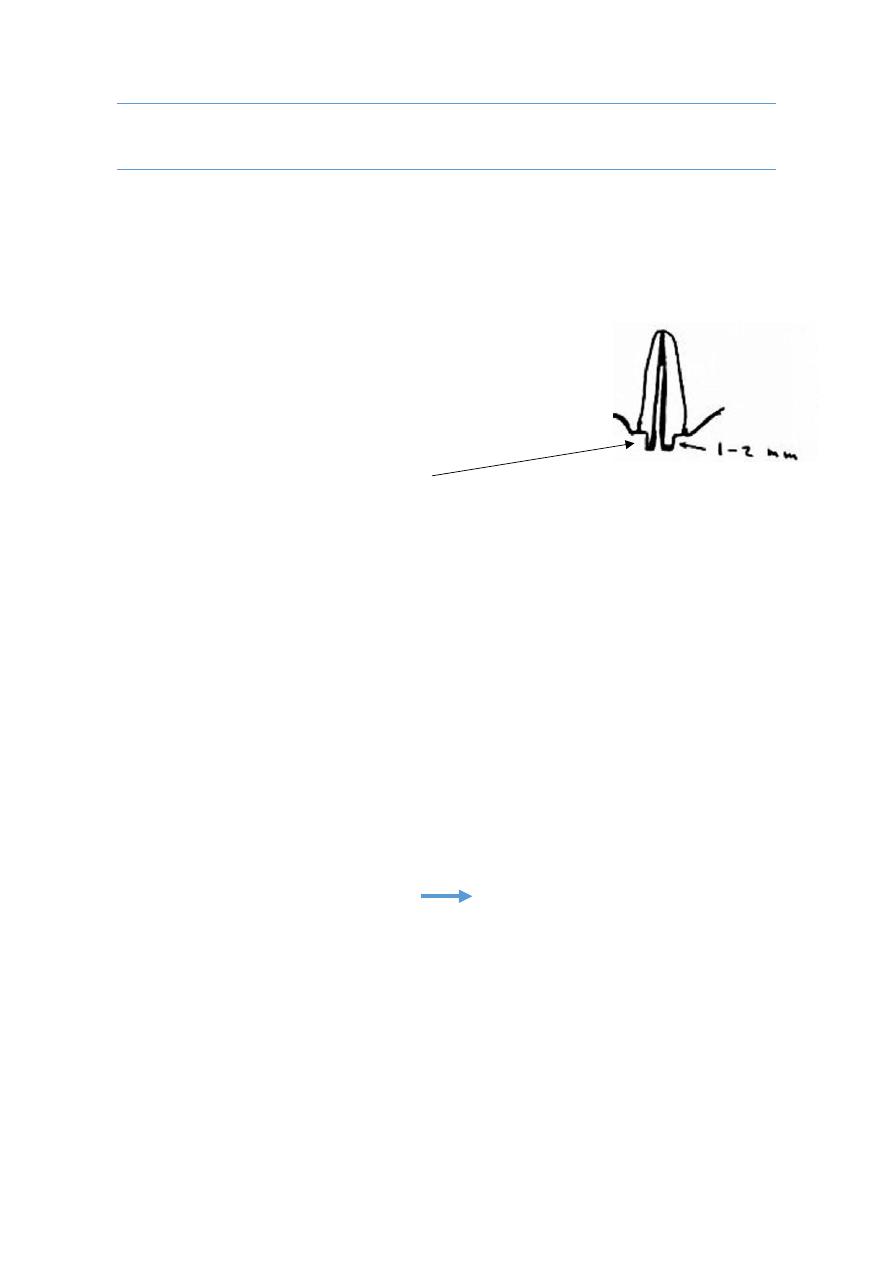
a. Coronal part:
1-2 mm dentinal (coronal) extension of tooth structure gives the best design.
b. Root canal: avoid over enlargement and weakening of tooth structure (enlarge the canal 1-2
sizes larger than the last file).
2. Retention form:
Factors affecting retention form of Post-Crown are:
a. Post length.
b. Post diameter.
c. Preparation geometry:
i. Surface area ( more surface area increases retention).
ii. Degree of taper (more taper reduces retention).
d. Post surface texture (rough post gives more retention than smooth post).
e. Luting agent.
3. Resistance form:
a. Rotational resistance:
i. Ferrulle effect.
ii. Antirotational lock.
b. Stress distribution:
i. Avoid over tapering of post wedging action.
ii. Post length (more post length increases stress distribution)
iii. Preserves tooth structure of gingival margins and at the apex.
