• CEMENTUM
By/ M.Sc Sarah AHMEDاورال هستولوجي عملي
ثاني اسنان كركوك
19 / 11 / 2015
(500)
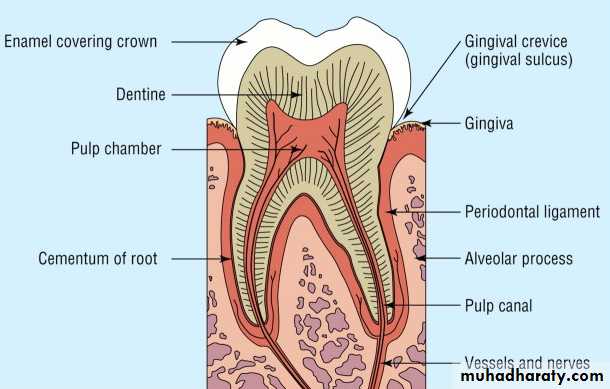
THE PERIODONTIUM
The peridontium consists of those tissues which surrounds , support the tooth and is composed of :
Gingiva
Periodontal ligamentCementum
Alveolar bone
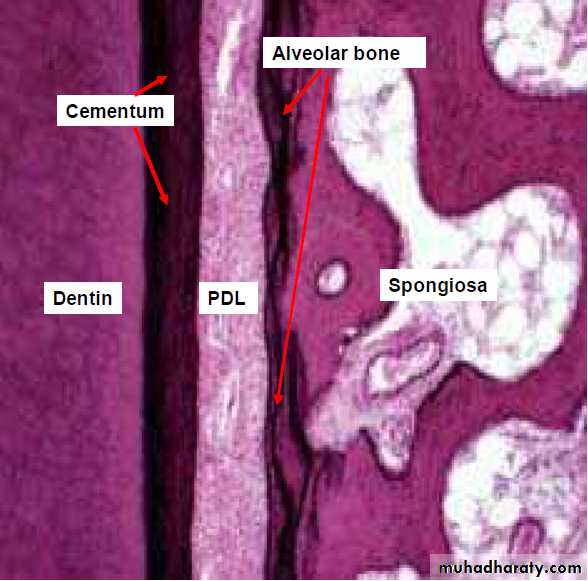
Cementum
Cementum is part of the periodontium
It is a hard avascular connective tissue that covers the roots of teeth
• It begins at the cervical portion of the tooth at the cemento-enamel junction and continues to the apex.Acellular cementum (20-50 m)
Cellular cementum (150-200 m)Physical Characteristics
2- Thickness
1-Color
Light yellow
Lighter in color than dentin
3- PermeabilityPermeable from dentin and PDL sides.
Cellular C is more permeable than acellular C.
Chemical Composition
45-50 % Inorganic substances
50-55% Organic substances
consists of calcium phosphate in the form of hydroxy-apatite crystals
collagen fibers embedded in a ground substance .
protein
Polysaccharides
Cementum contains the greatest amount of fluoride in all mineralized tissues
Cementogenesis
• It takes place in two phases:• Matrix formation
• Mineralization
• There are 3 cell types responsible for the cementogenesis:
• Cementoblasts
• Cementocytes
• Fibroblasts
• All of these cells are derived from the ectomesenchymal cells.
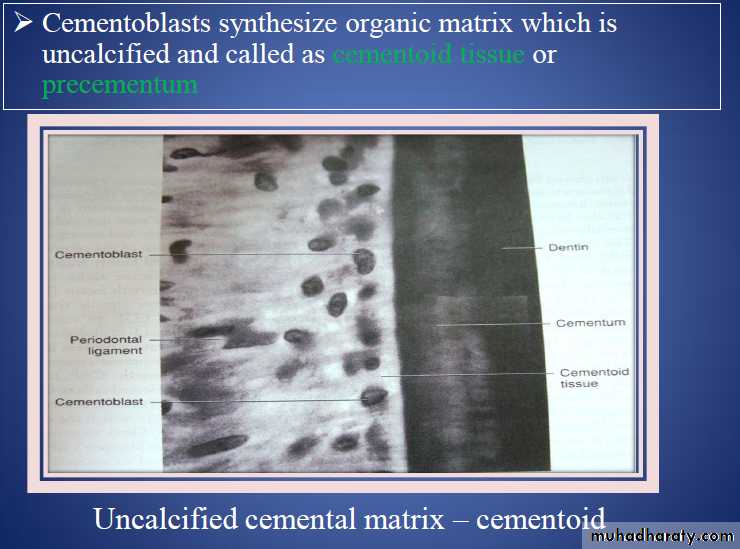
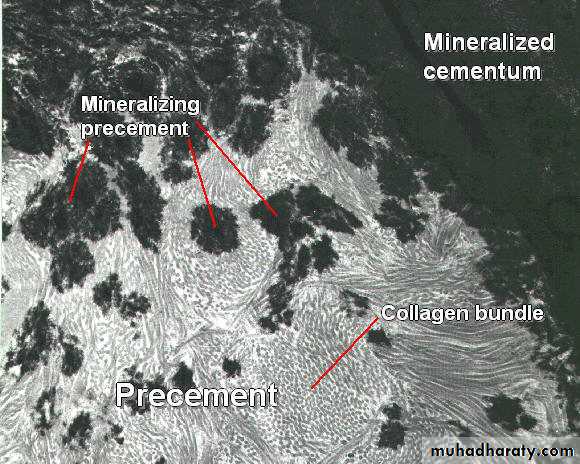
cementoid can be observed on cemental surface , covered by cementoblasts .
The mineralization begins after forming the first layer of matrix. (Cementoid)
Two types of cells are functionally concerned with cementum :* Cementoblasts
* Cementocytes
Cementoblasts line the root surface ,they contain numerous mitochondria, well developed Golgicomplex and large amounts of granular endoplasmic reticulum., and open-faced nucleus.
Cemento-progenitor cells synthesize collagen and protein polysaccharide.
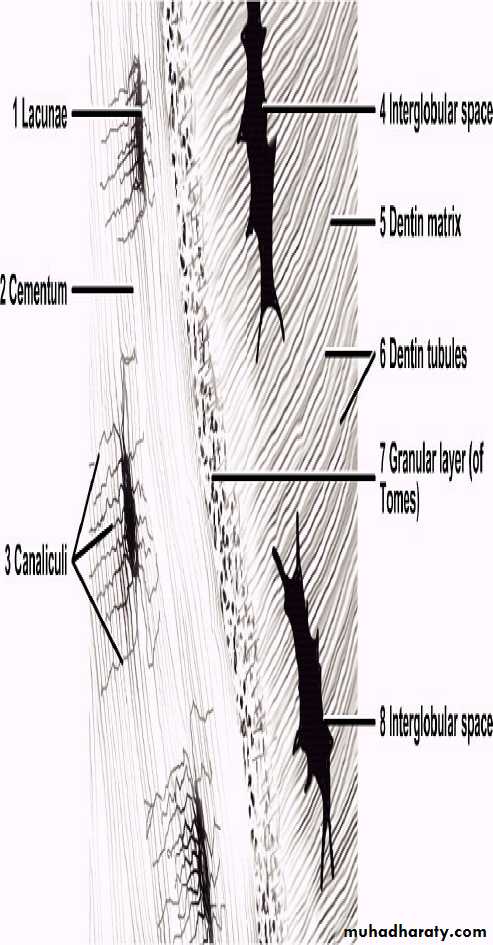
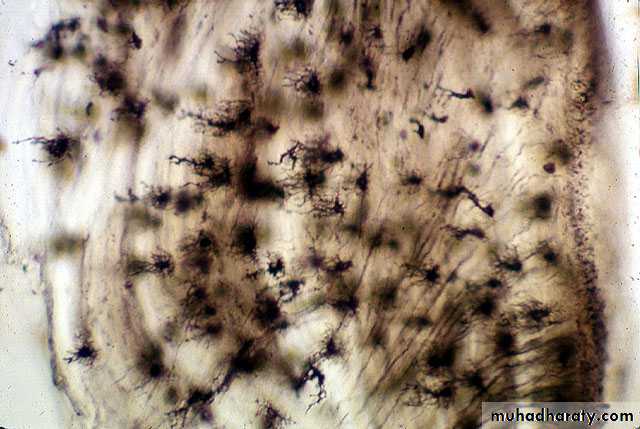
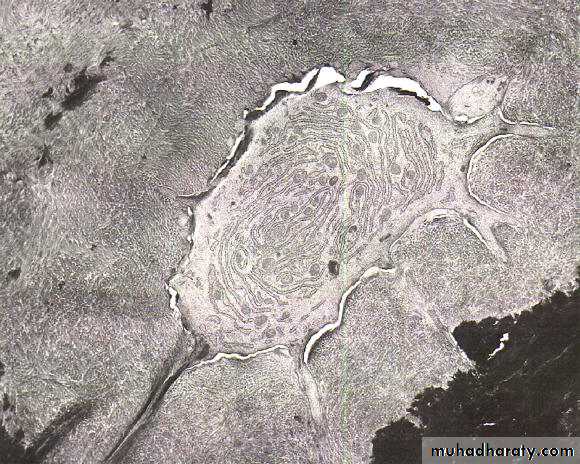
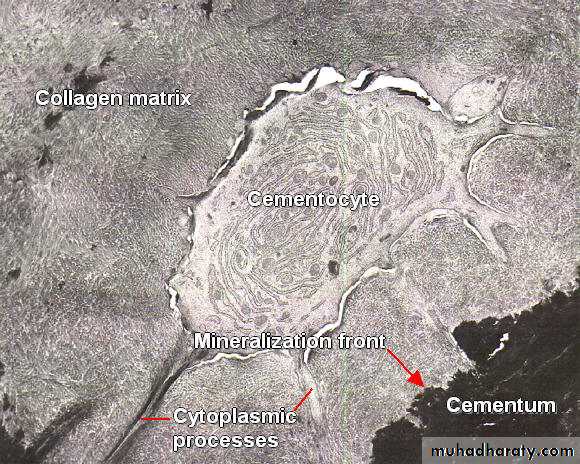
Cementocytesare seen located in lacunae in cementum matrix and typically have numerous processes lying in canaliculi .
Because cementum is avascular tissue, thus the processes of the cementocytes are oriented toward the periodontal ligament for nutrition .
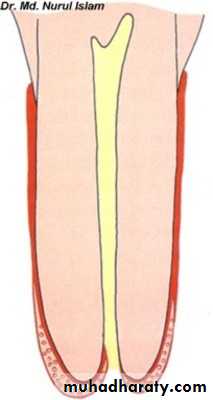
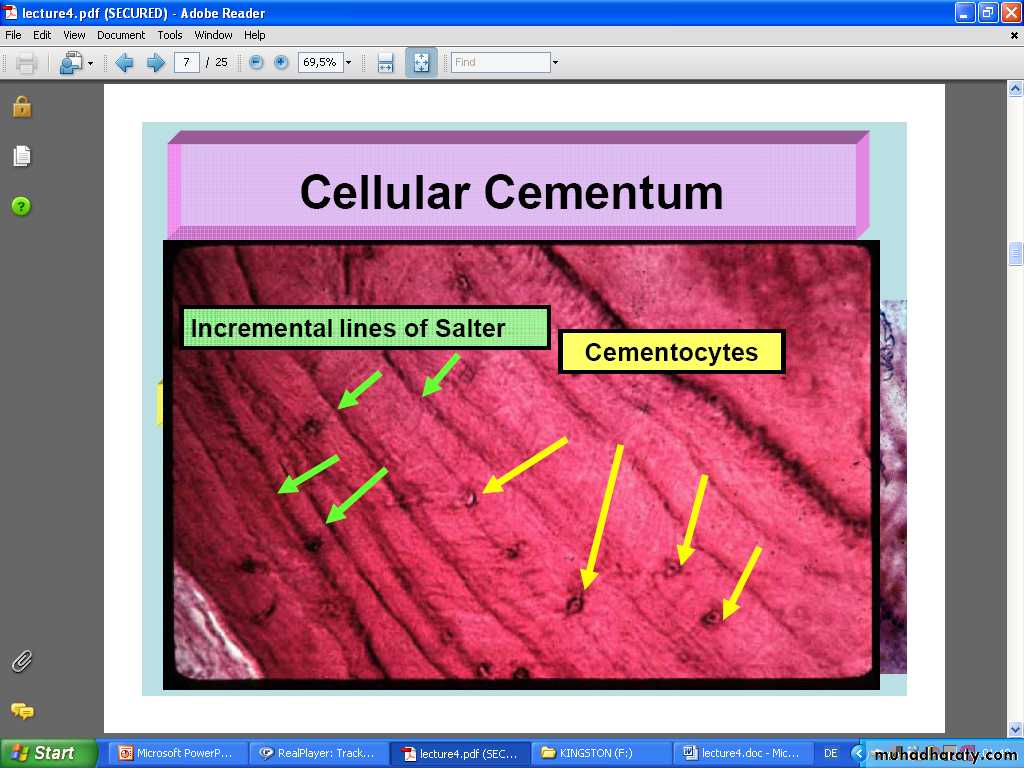
As a result of continuous phasic deposition of cementum, resting lines known Salter lines appear in cementum .
Cementocytes
• Cementocyte lacuna•
Cementocyte
Cementocyte canaliculiCementocyte process
Incremental lines of Salter
Dentin
Incremental LinesIncremental lines of Salter.
Incremental lines of Salter
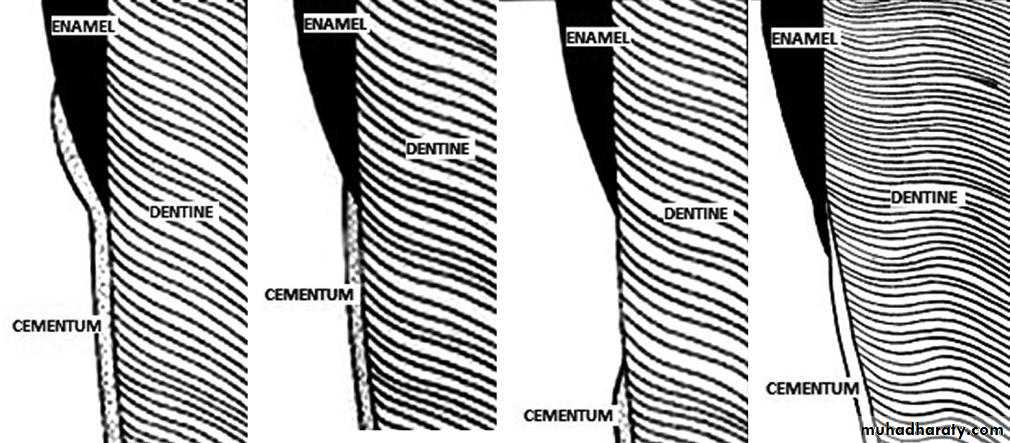
Cementoenamel Junction (CEJ)four TYPES OF RELATIONSHIP
In about 60% cases cementum overlaps the cervical end of enamel.In approx. 30% of all teeth cementum meets the cervical end of enamel.
In 10% cases enamel and cementum do not meet which can cause accentuated sensitivity because of exposed dentin.
In about 1.6% of cases enamel overlaps cementum
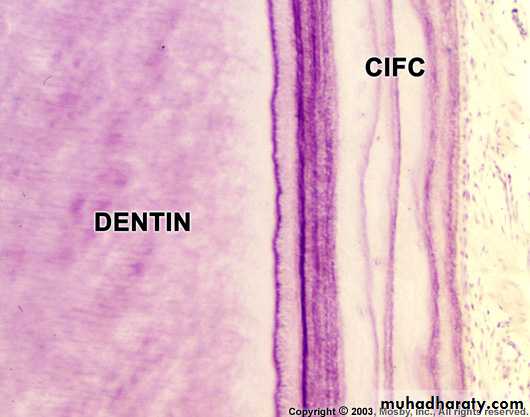
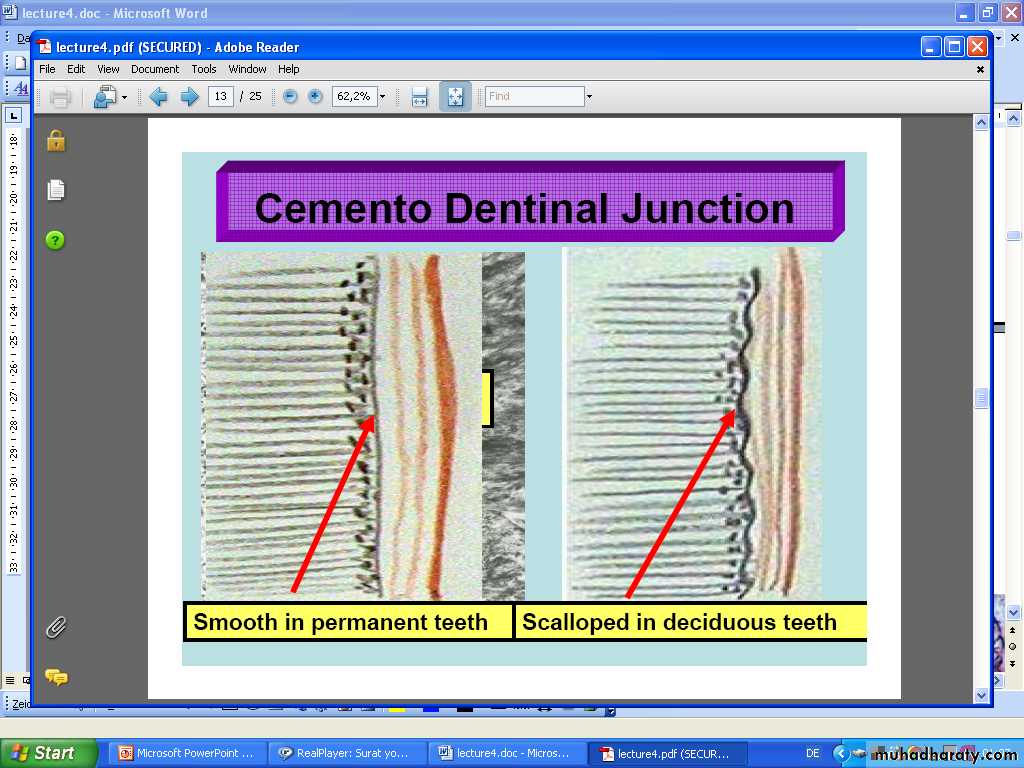
Cementodentinal junction
• The dentin surface upon which cementum is deposited is relatively smooth in permanent teeth.• The cementodentinal junction in deciduous teeth, however, is sometimes scalloped.
Permanent teeth
Deciduous teethDefinition
Bone is specialized C.T with calcified intercellular substanceAlveolar bone is specialized part of maxillary and mandibular bone that forms the primary support structure for teeth
Structure of alveolar bone
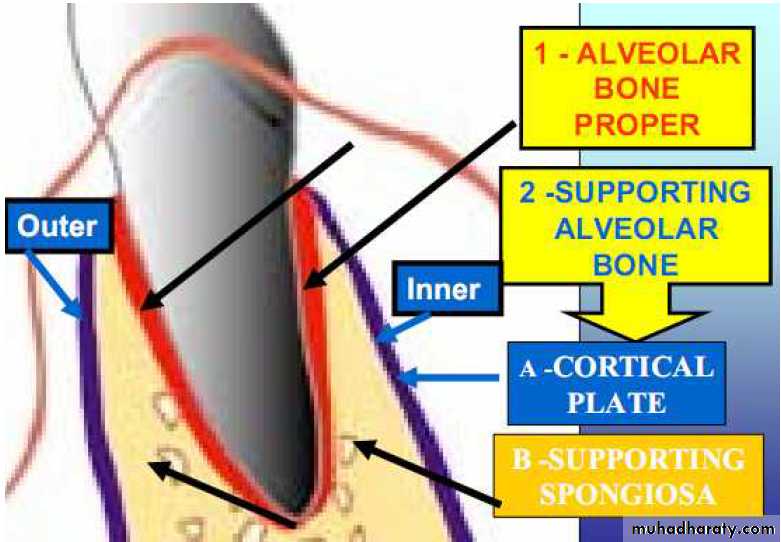
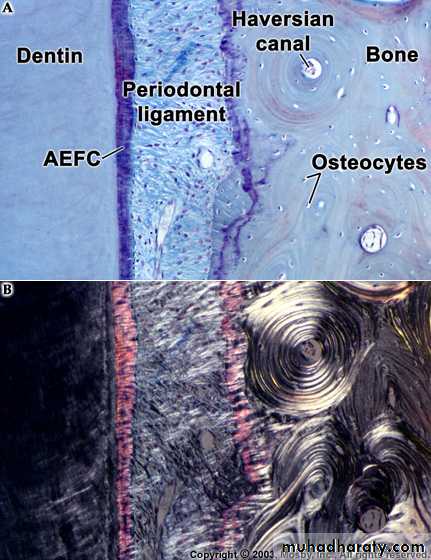
Alveolar bone proper
It surrounds the root of the tooth and gives attachment to the periodontal ligament fibres.It consists of
Lamellated bone
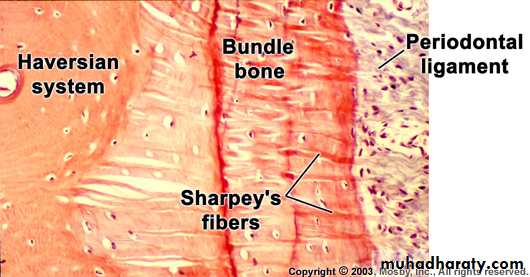
Bundle bone
Lamellated bone consists of osteons.
Concentric lamellae along with a central blood vessel form an osteon.
Bundle bone
Part of the alveolar bone where periodontal ligament fibres are inserted (attached).Bundle – bundles of fibres
Sharpeys fibres – principal fibres of the periodontal ligament that are embedded in the bone or cementum.
Sharpeys fibres are seen perpendicular to the bundle bone.
Other fibrils are less and are arranged parallel to the bundle bone surface
Radiographically is more radiodense due to presence of thick bone without trabeculations and is called as “lamina dura”
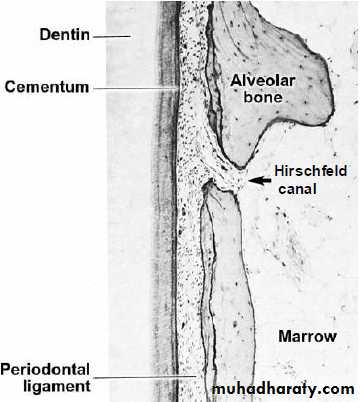
Alveolar bone proper has many openings for blood vessels and nerves – is perforated and is called as “cribriform plate”
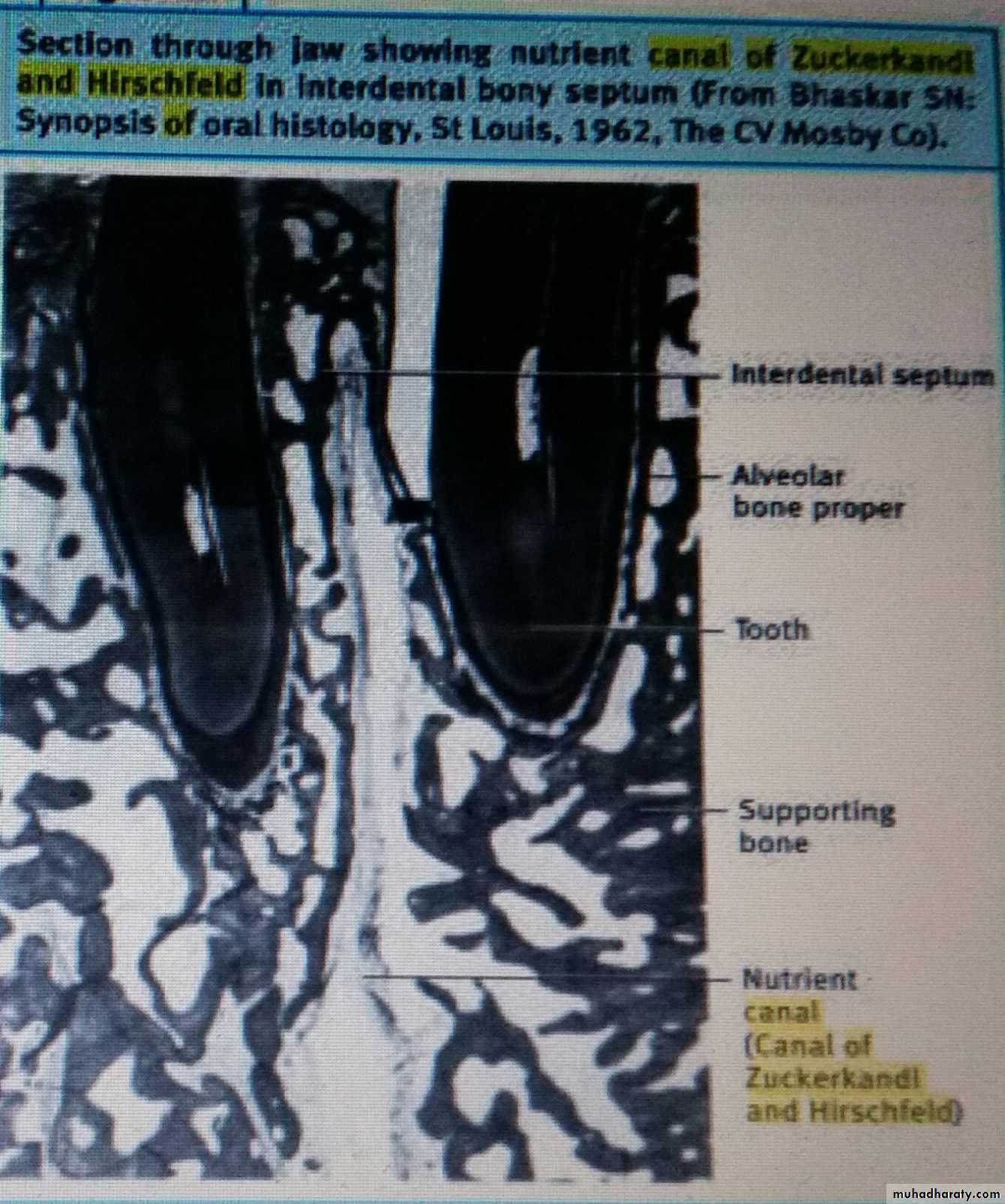
Interdental and interradicular septa have canals known as canals of “ zuckerkandl and Hirschfeld”
Cribriform plate Vs Lamina dura
Supporting alveolar bone
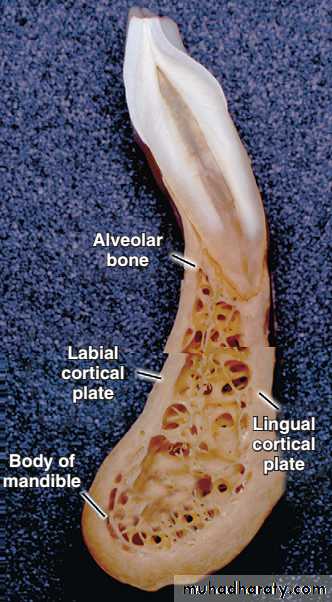
It consists of two parts –Cortical plates (Outer and inner)
Spongy bone
Cortical plates: these are made up of compact bone & form the outer and inner plates of alveolar bone.
Cortical bone varies in thickness in different areas – it is thicker in the mandible than in the maxilla and thicker in the premolar-molar region than in the anteriors.
Spongy bone: it fills the area between the cortical plates and the alveolar bone proper.
It contains trabaculae of bone and marrow spaces.Types of spongy bone (spongiosa) :-
Type I: the trabaculae are regular and horizontal. This is seen most commonly in the mandible.
Type II: irregularly arranged delicate and numerous trabaculae. This is seen most commonly in the maxilla.
The spongy bone is very thin or absent in the anterior regions of both the jaws.