
D.Rasha L2
1
Breast cancer
It is a most common malignant tumor in Iraqi female, also there are increase
incidence of breast cancer through out the world and despite advances in
diagnosis and treatment almost 1/3 of women who develop this cancer will
die of disease.
-
Risk factor :
There are well established risk factors which are:-
1.Geographic variation:-
There are differences among countries in the incidence and mortality rates of
breast cancer so this cancer is usually higher in north America and north
Europe than in Asia and Africa and this differences appear to be
environmental rather than genetics in origin.
2. Age:-
the risk of breast cancer is higher with life so it is uncommon under age of 30
years.
3. Genetics and family history :-
About 5-10% of breast cancers are thought to be related to specific inherited
mutations as:-
a. Germ line mutations of tumor suppressor gene P53 .
b. Germ line mutations of BRCA-1 gene which's located on chromosome
17q21 and this mutation having great majority of cases that there an inherited
predisposition to both breast and ovarian cancer.
c. Germ line mutation of BRCA-2 gene which is located on chromosome
13q12-13.
The BRCA-1 and 2 both are also tumor suppressor genes.
4- Prolonged exposure:-
To endogenous and exogenous estrogen especially in early decades of life. Ex.
In cases of early menarche, null parity, lowered cumulative months of

D.Rasha L2
2
lactation because these conditions prolonged the life time exposure to
estrogenic peaks of MC and in cases of estrogen producing ovarian tumors .
Exogenous estrogen Ex: in cases of ERT (estrogen replacement therapy) used
previously to delay the onset of osteoporosis and protect against heart
disease and stroke.
The estrogen and progesterone play great role in causing breast cancer
because it appears to stimulate the production of growth factor by normal
and neoplastic breast epithelial cells, so in malignancy create an autocrine
mechanism of tumor development.
5- Pre-existing proliferative breast disease
, especially with atypical
hyperplasia.
6- Also there are less well-established risk factors such as
obesity, alcohol
consumption, cigarette smoking and high fat diet.
Morphology:-
About 90% of breast cancers are arises from ductal epithelial cells other minor
form from lobular epithelial.
So that breast cancer divided into:-
.I. Carcinoma in situ
-Ductal with or without Paget's disease.
-Lobular.
.
II. Invasive or infiltrative carcinoma.
-Ductal with or without Paget's disease.
-Lobular.
In addition to other rare types of breast cancer which are:-
1- Medullary carcinoma.
2- Colloid carcinoma.
3- Tubular carcinoma
D.Rasha L2
3
.
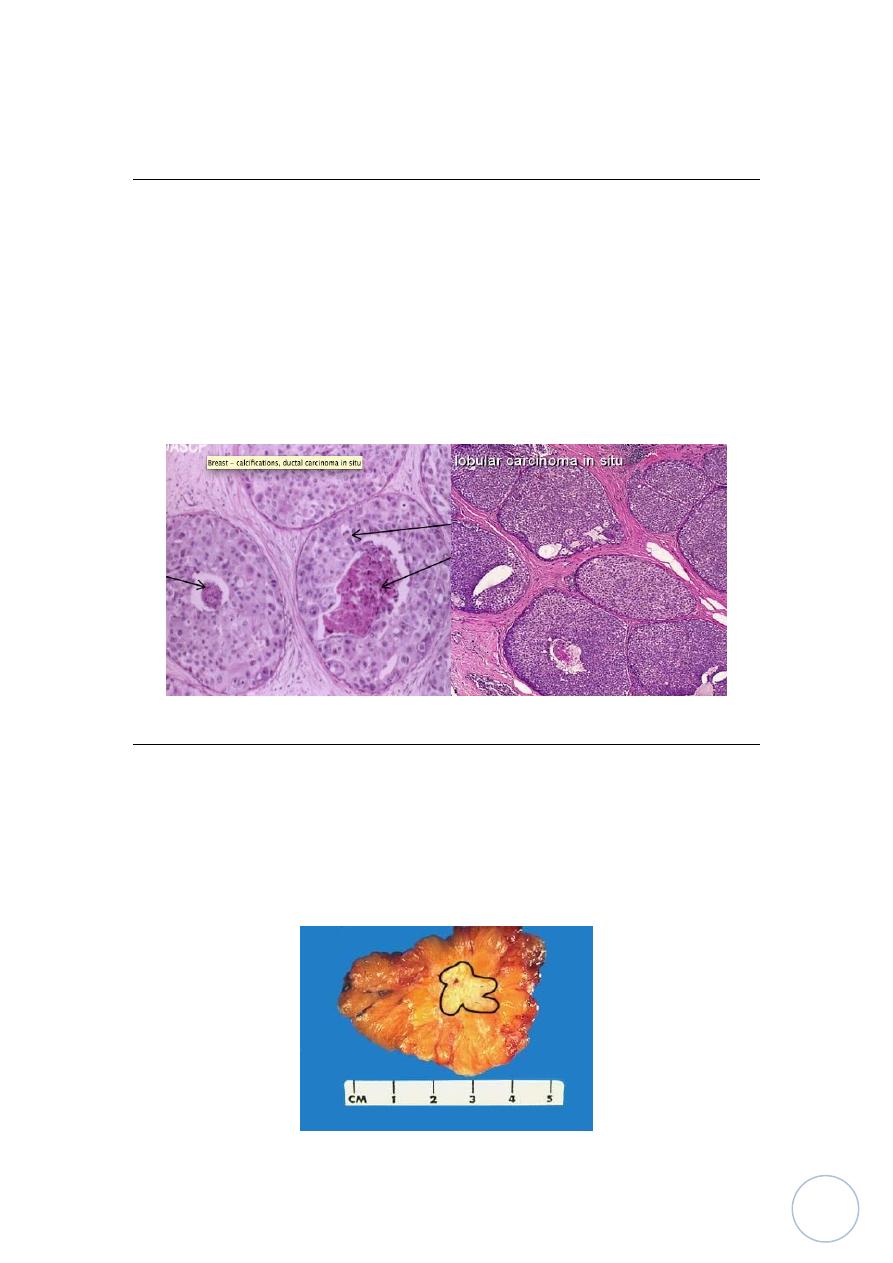
Carcinoma in situ:-
Also intraductal carcinoma are much more common than lobular carcinoma in
situ, it consists of dilated ducts filled by malignant cells that having criteria of
malignancy lose of myoepithelial cells layer but without invading the
basement membrane of ducts or stroma, in rare occasions it happened that
anaplastic cancer cells extend into the epidermis of the nipple and areola
region to produce Paget's disease of the nipple.
While lobular carcinoma in situ consist of distended acini filled by anaplastic
tumor cells without invasion of BM or stroma.
Invasive carcinoma:-
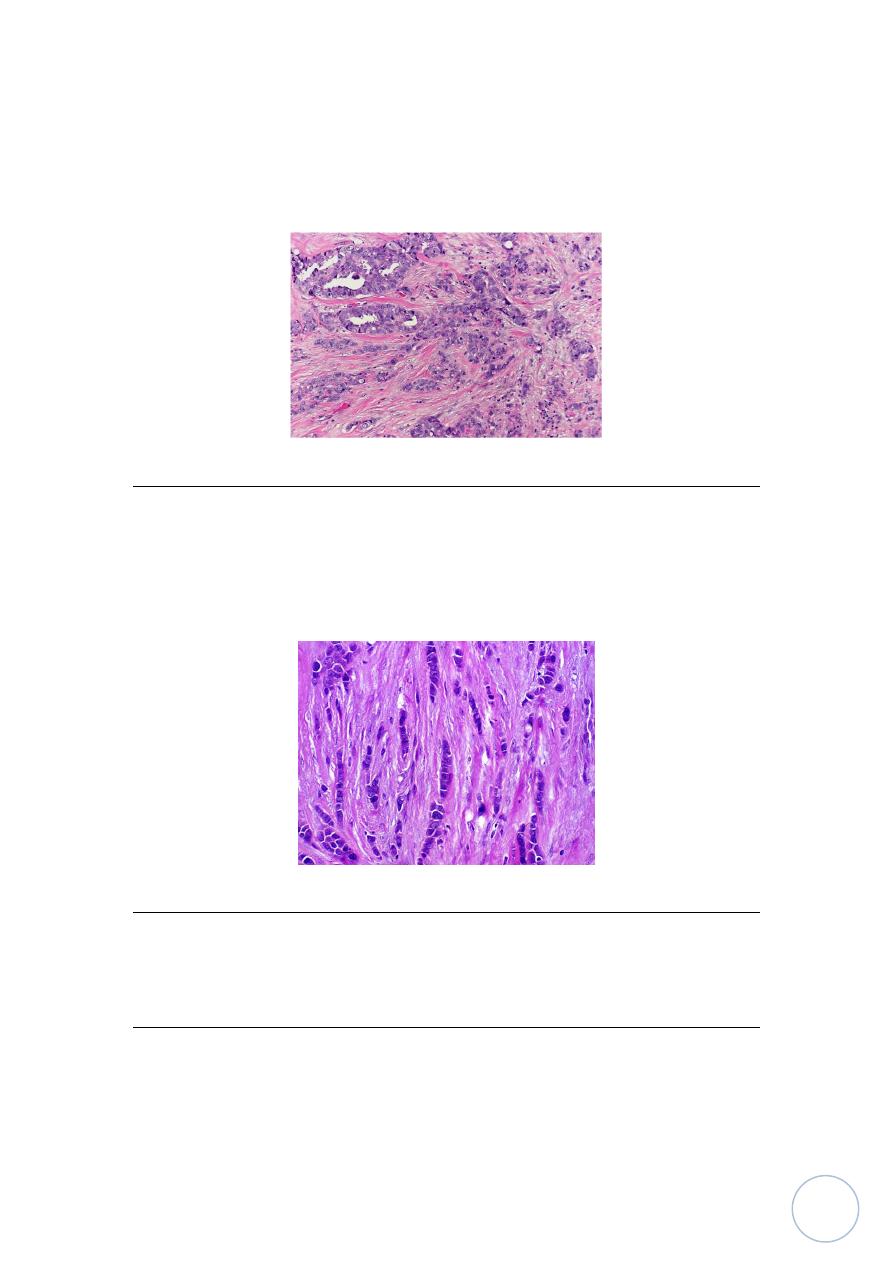
.I. Invasive ductal carcinoma:-
It's most common form of breast cancer clinically appear as strong hard mass,
so called scirrhous carcinoma having gritty texture on cut section with
retraction of fibrofatty tissue around it and this cause skin and nipple
retraction.
D.Rasha L2
4
Microscopically:
It's consisting usually of dense fibrous stroma in which there
are scattered nests and cords of large malignant ductal epithelial cells, these
nests also invade surround tissue as adipose tissue, perivascular
intralymphatic and perineural spaces.
.II. Invasive lobular carcinoma:-
Grossly it's usually rubbery in consistency, but sometimes it became hard and
scirrhous.
Microscopically:
It's consist of strands of malignant lobular cells dispersed in a
fibrous stroma, the cells are usually small and uniform.
.III. Medullary carcinoma:-
It represents about 1% of breast cancer, this tumor usually large 10 cm in
diameter, soft and fleshy rather than hard.
.IV. Colloid (mucinous) carcinoma:-
It's less common than medullary carcinoma, this tumor usually soft, and bulky.
Microscopically:
It's consisting of malignant cells filled by mucin found on
lakes of extracellular mucin.
D.Rasha L2
5
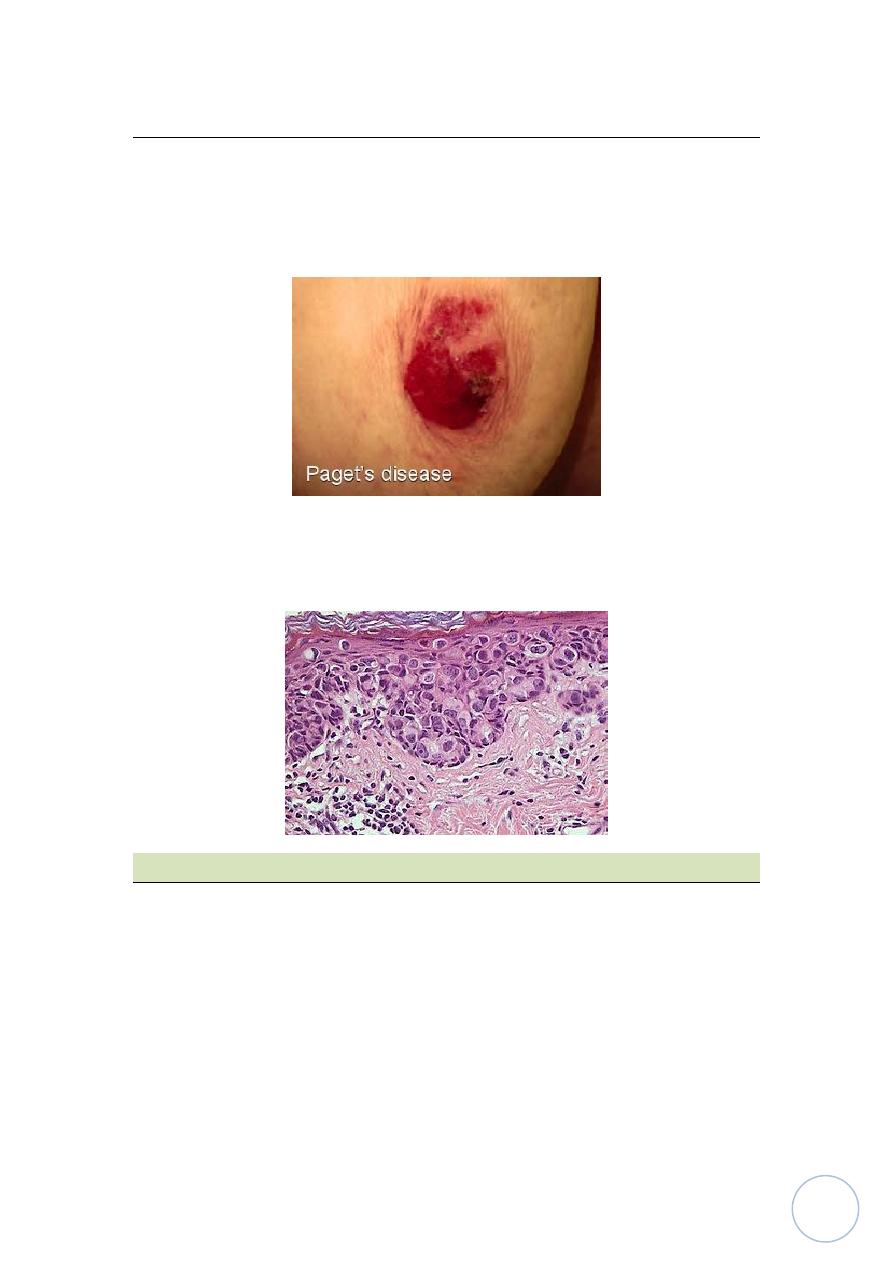
Paget's disease:-
It occurs with ductal carcinoma in situ or invasive in old age group present
with fissured, ulcerated nipple and areola with oozing, inflammatory
hyperemia and edema not respond to anti-inflammatory dermatological
treatment, there may or may not be palpable mass in the breast.
Microscopically:
It appears as malignant cells called Paget's cells invade the
epidermis which are large hyperchromatic cells, the nuclei surrounded by
clear halo.
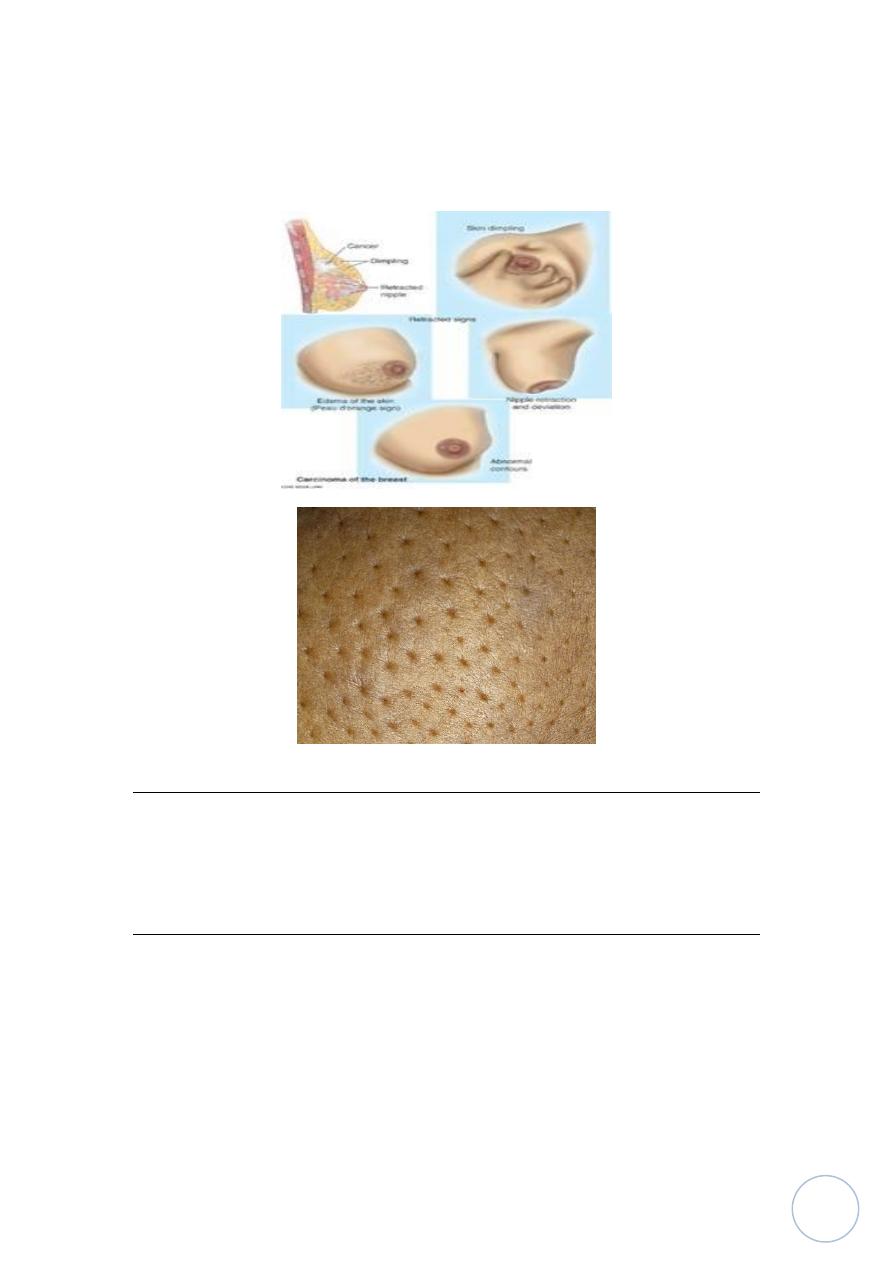
Clinical features of invasive carcinoma:
The most common features of patient with breast cancer is presence of hard
mass at the beginning it is movable, with time it becomes fixed to underlying
pectoral muscles or overlying skin causing skin retraction, dimpling and nipple
retraction, the spread to lymphatic pathway of skin causing edema of skin of
breast features called peaud' orange (orange peel) because of edema of skin
around hair follicles.Sometimes in pregnancy because of rapid progression of
tumor cause acute inflammatory reaction with swelling, redness and
tenderness, so called inflammatory carcinoma.
D.Rasha L2
6
Spread of disease is usually lymphatic, hematogenous and nodal metastasis
usually begin early at axillary LN and in about 2/3 of cases first presentation
with axillary LN metastasis
.
How to diagnose breast cancer:
breast cancer is sometimes found after symptoms appear, but many women
with breast cancer have no symptoms, this is why regular breast cancer
screening is so important.
Tests and procedures used to diagnose breast cancer include:
1-breast examination:
the clinician exam of both breasts and armpit for any
lump or abnormality.
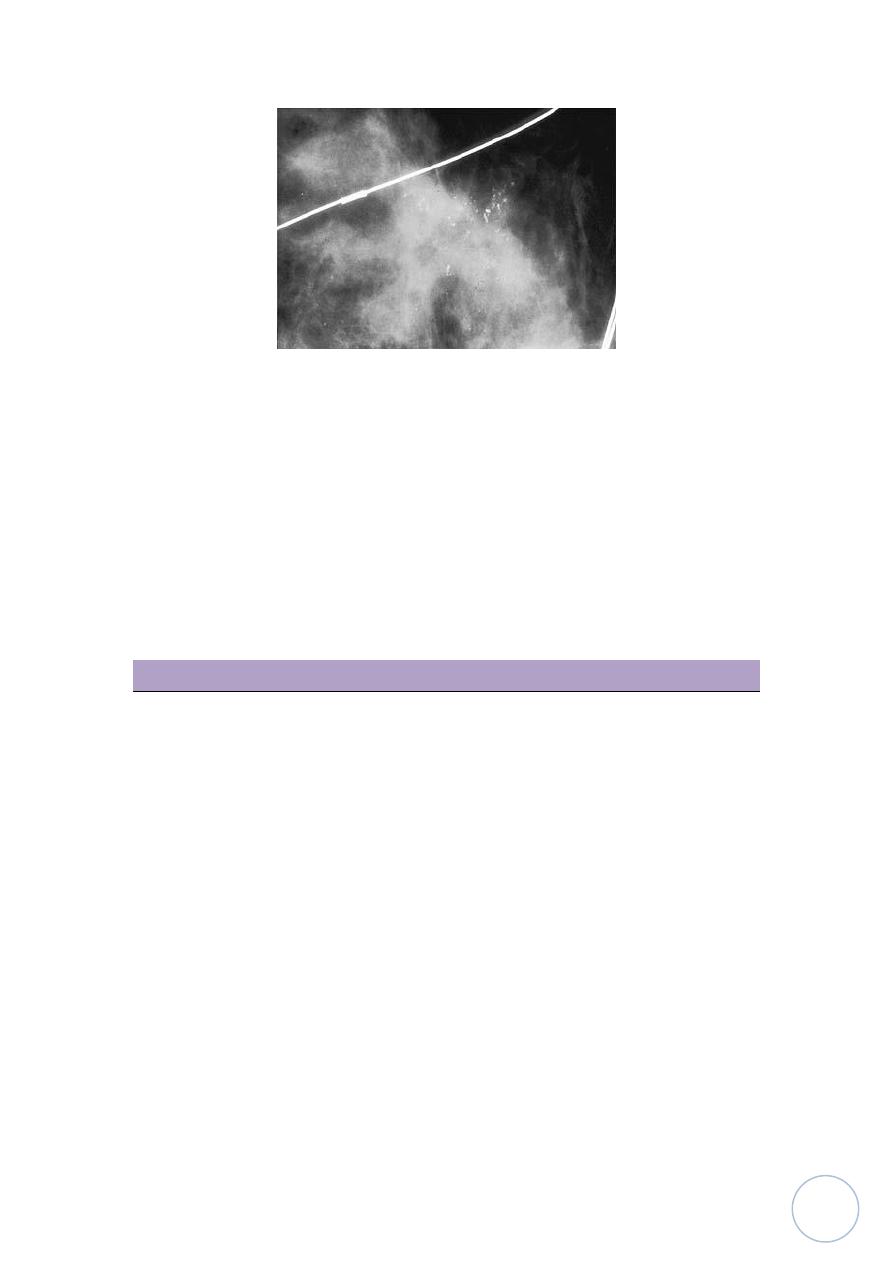
2-mammogram:
is an special x-ray for breast used to screen for breast cancer.
D.Rasha L2
7
3-breast U/S:
U/S can be give definite presence of breast lump and determine
weather it is solid mass or fluid filled cyst.
4-biopsy :
a biopsy is the only definitive way to make a diagnosis of breast
cancer, this achieved by either:
a- FNAB
fine needle aspiration biopsy whether blind or U/S guide FNA.
B- surgical excision biopsy :
to be examined and give diagnosis if it is benign or
malignant lesion, biopsy can give information about type of cancer, it is grade,
stage and IHC study on cells as estrogen and progesterone receptors which
are determined the treatment options.
Male breast:-
The disease of male breast are usually rare however there are 2 more
common conditions which are:-
1- Gynecomasta:-
Which is analog to fibrocystic disease of female breast this condition occur as:
a- Physiologic one in puberty and in extreme old age.
b- Pathological caused by excesses of estrogen in the body and increase
sensitivity of breast to estrogen occur in liver cirrhosis because of decreased
metabolism of estrogen, estrogen- secreting tumors and estrogen therapy.
2- Carcinoma:-
It's very rare tumor with a frequency ratio to breast cancer in the female of
1:125 it occurs in advanced age.
