By
Dr. Adel Sahib Al-Mayaly
Department of Surgery-Otolaryngology
The Larynx
Interesting synonyms of LarynxVoice box,
Watch dog of tracheobronchial tree
Introduction
The larynx is an organ that provides a protective sphincter at the inlet of the air passages.
It is also responsible for voice production ; beside that it is a respiratory organ.
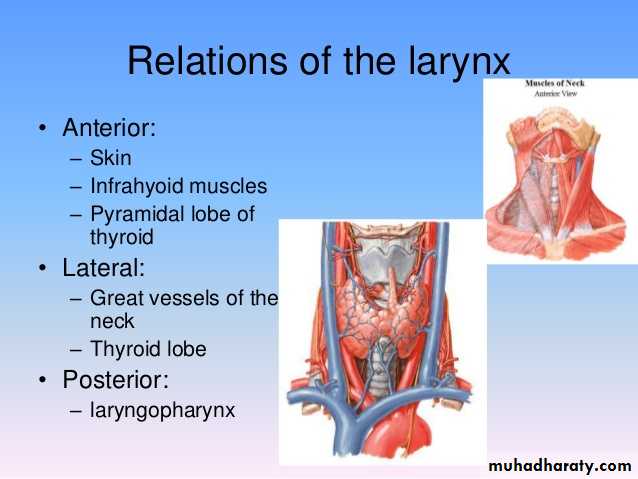
It is situated below the tongue and hyoid bone
and between the great blood vessels of the neck
It lies at the level of the fourth, fifth, and sixth cervical vertebrae.
Skeleton of larynx
Skeleton of larynx
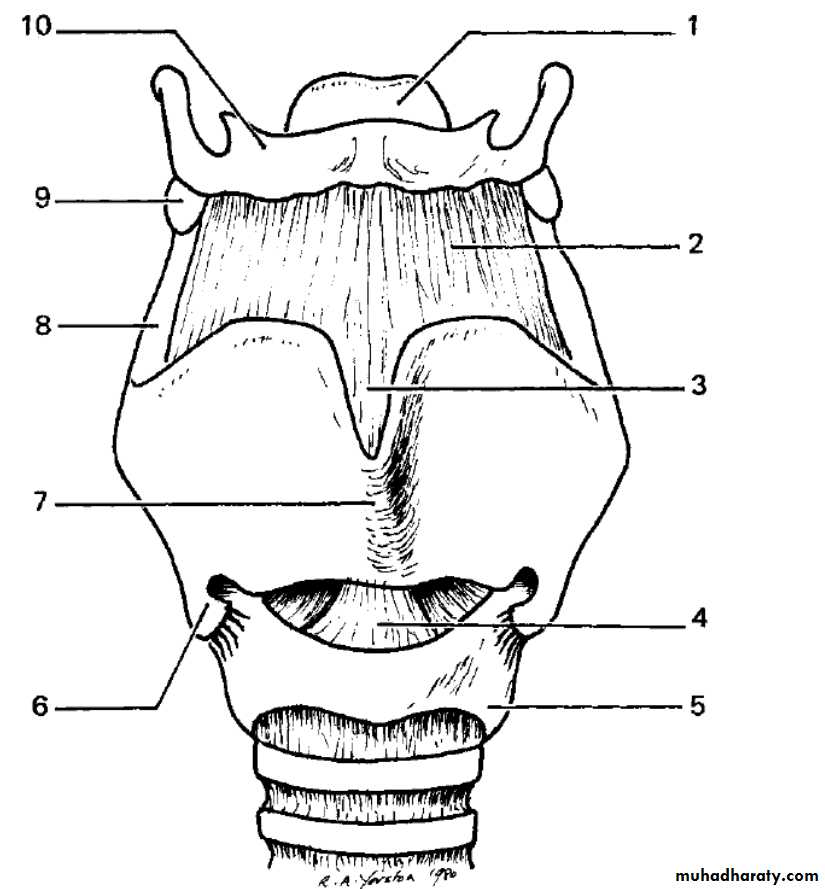
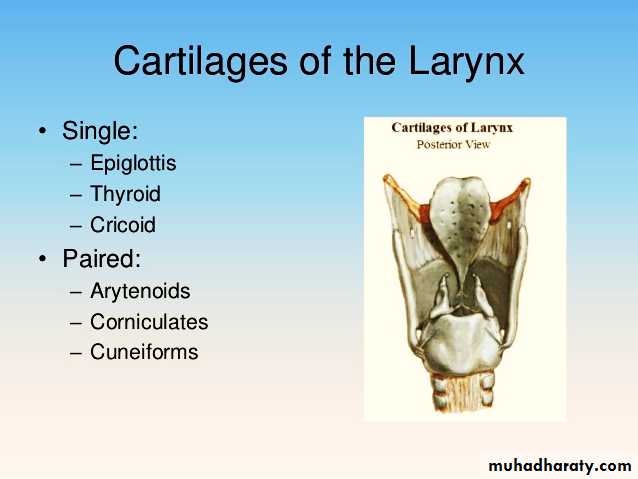
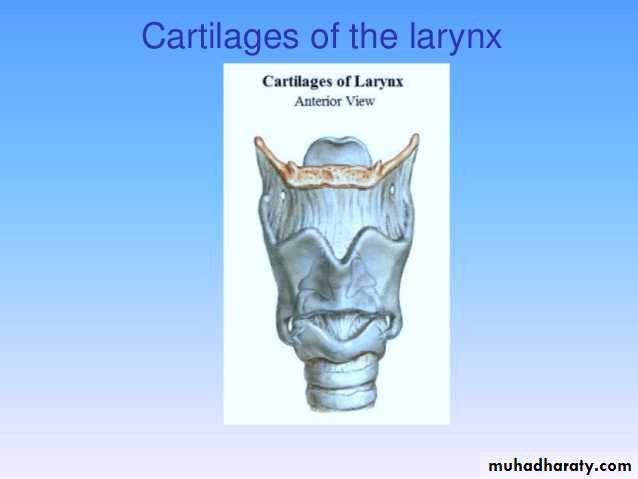
It is made up of 9 cartilages:- 3 paired & 3 unpairedPaired
Unpaired
Arytenoid
Thyroid
Corniculate
Cricoid
Cuneiform
Epiglottis
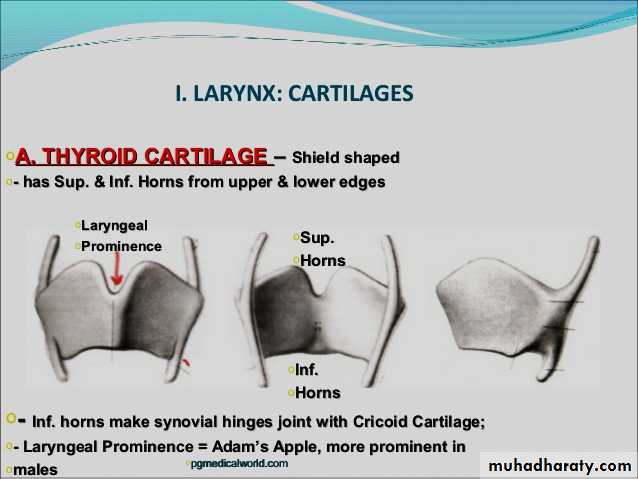
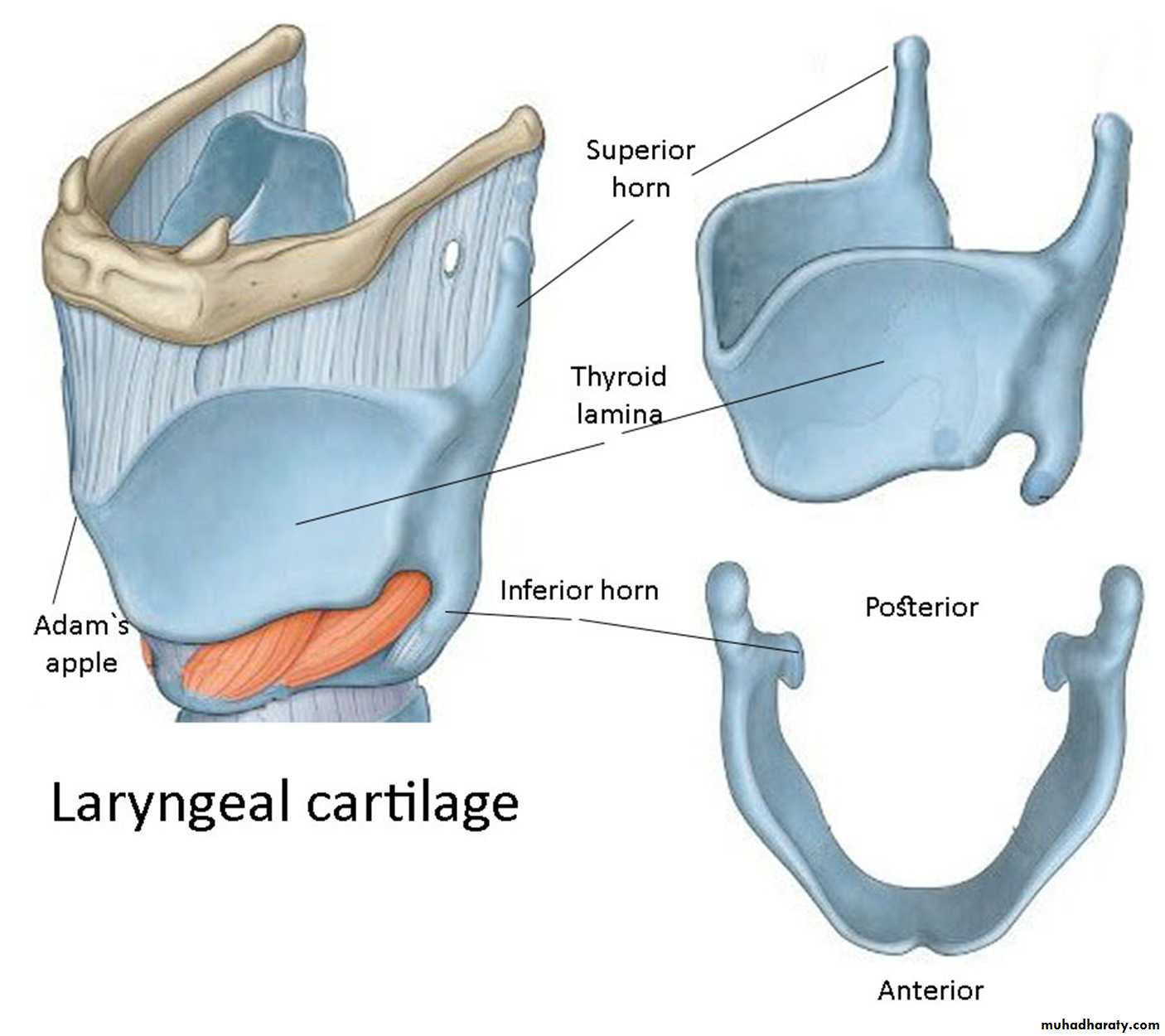
Thyroid cartilageShield
The biggest cartilage & it encircles the laryngeal lumen.It is made of 2 laminae of hyaline cartilages .
They join together anteriorly (Adam’s apple).
Diverge posteriorly.
Thyroid cartilage
Thyroid cartilage
Each lamina has superior, inferior & posterior borders.There are 2 prolongations from the superior & inferior borders (thyroid cornu).
The inferior cornu articulates with cricoid to form cricothyroid joint (synovial joint).
Thyroid cartilage
On each external surface of the lamina is an oblique line (for attachment of Muscles). Muscles attaching to the oblique line includeSternothyroid muscle (insertion)
Thyrohyoid muscle (origin)
Inferior constrictor muscle (origin)
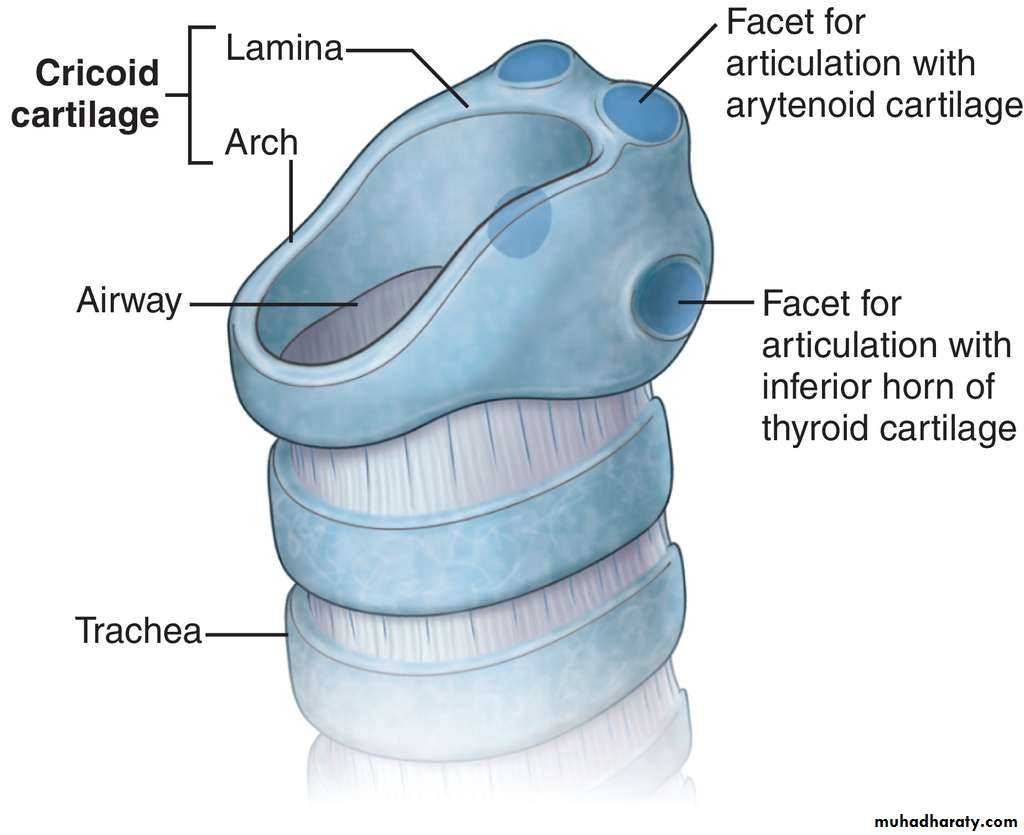
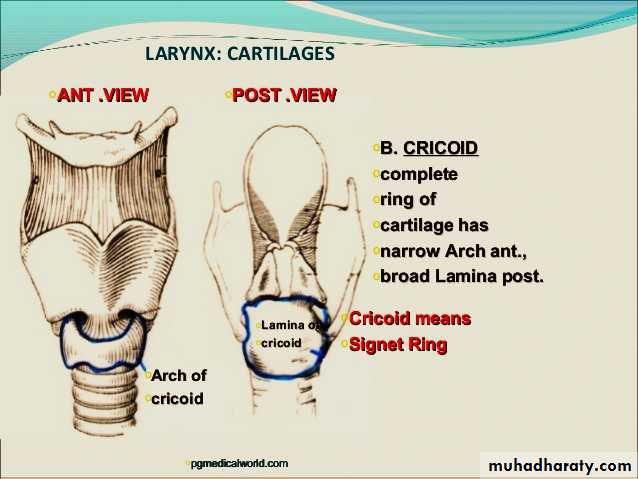
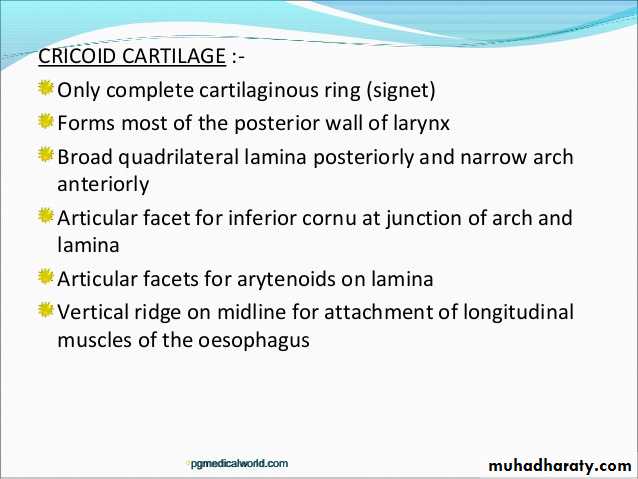
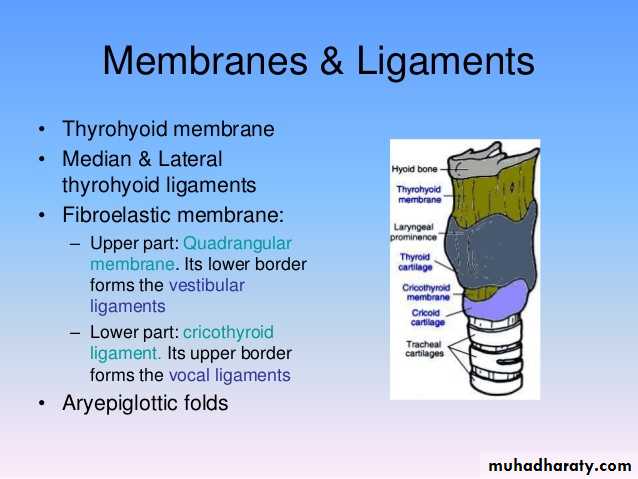
Cricoid cartilage
like signet ring .It is the only complete ring of cartilage in the walls of respiratory system.
It is made by lamina posteriorly & arch anteriorly.
The cricoid has two joints
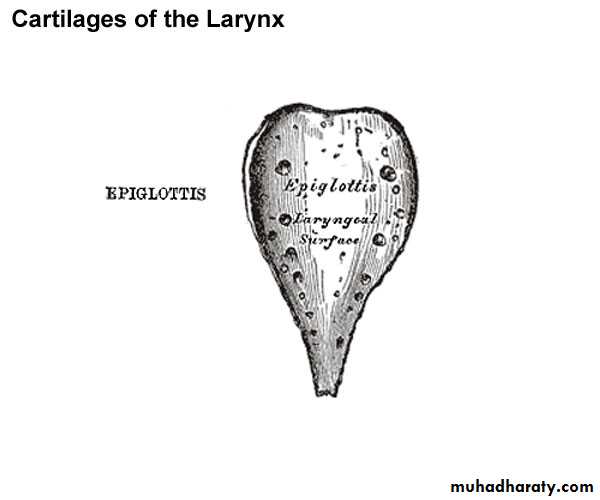
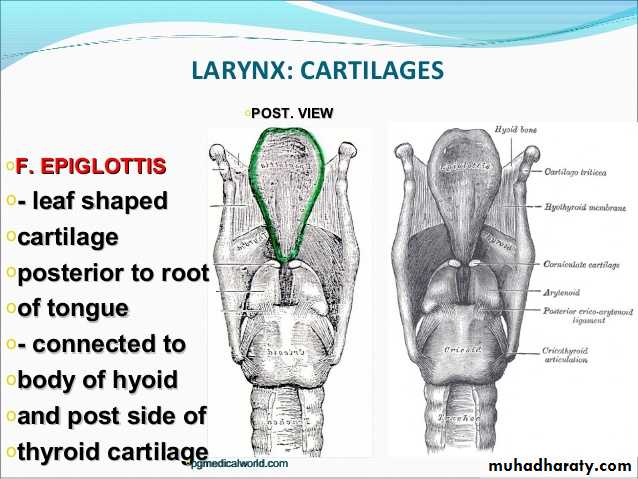
The epiglottic cartilage
leaf-shaped structureIt lies in the upper portion of the larynx.
prolonged below into a slender process (STALK or petiole).
attached in the midline to the back of the laryngeal prominence
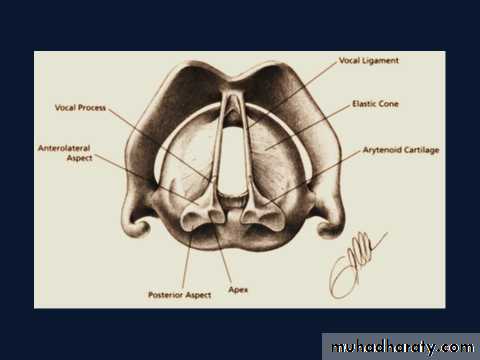
Arytenoid Cartilages
Each of the pair is a three-sided pyramid with anterolateral, medial and posterior surfaces.The inferior base has
1- forward projection, (vocal process); which provides attachment to the posterior end of the true vocal cords.
Arytenoid Cartilages
2- Lateral projection, the muscular process.It provides attachment to:-
Posteriorly: posterior cricoarytenoid muscle
Anteriorly: lateral cricoarytenoid muscle
Arytenoid cartilages
Articulations of Arytenoid cartilagesCricoarytenoid Joint:-
Is a synovial joint between the arytenoid cartilage and the lateral aspect of the lamina of the cricoid cartilage.
Cricothyroid joint:-
Is a synovial joint between the lamina of cricoid & inferior thyroid cornu
Interior of Larynx
The laryngeal cavity extends from the laryngeal inlet, through which it communicates with thelaryngopharynx, to the level of the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage.
3 regions
1-Supraglottis: from the tip of epiglottis to vocal cords.2- Glottis ((the vocal apparatus of the larynx) :- area of vocal cords.
3- Sub glottis:- from under surface of vocal cords to the 1st tracheal ring
Arteries of Larynx
They are branches of the superior and inferior thyroid arteries.1- The superior laryngeal artery;-accompanies
the internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve
2- Inferior laryngeal artery:-accompanies the inferior laryngeal nerve (terminal part of the recurrent laryngeal nerve).
Veins of Larynx.
1-The superior laryngeal vein:- usually joins the sup. thyroid vein2- The inferior laryngeal vein:- usually joins the inferior thyroid vein.
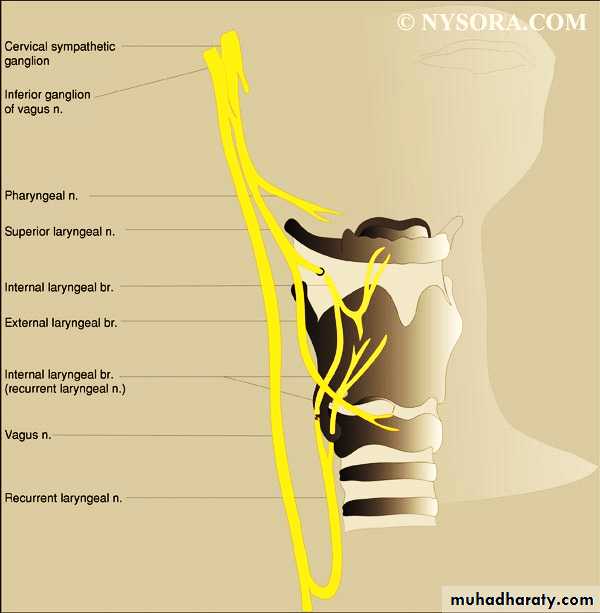
Nerves of larynx
The nerves of the larynx are the superior and inferior laryngeal branches of the vagus nerve
1-The superior laryngeal nerve:- from inferior vagal ganglion.
The nerve divides into two terminal branches within the carotid sheath.
1- The internal laryngeal nerve(sensory & autonomic)
Supply the mucosa above the vocal cords
Nerves of larynx
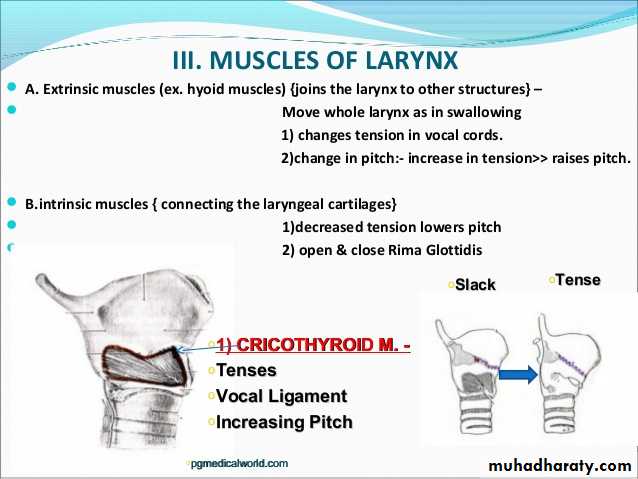
1- The external laryngeal nerve:- supplies the1- Cricothyroid muscle (external tensor of vocal cords).
2- Inferior constrictor muscle.
Inferior (Recurrent) laryngeal n.
It is the primary motor nerve of the larynx.It supplies all the intrinsic muscles except the cricothyroid,
It also provides sensory fibers to the mucosa below the vocal cords.
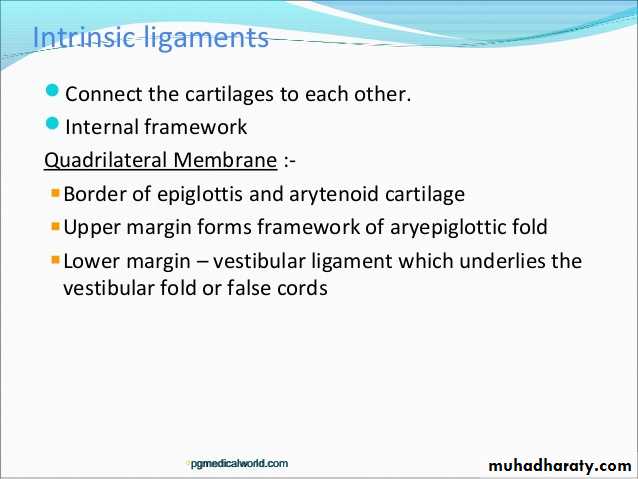
The vocal folds
The vocal folds are the sharp-edged folds of mucosa overlying the vocal ligaments and they are the source of the sounds (tone) that come from the larynx
Each vocal fold contains a:-
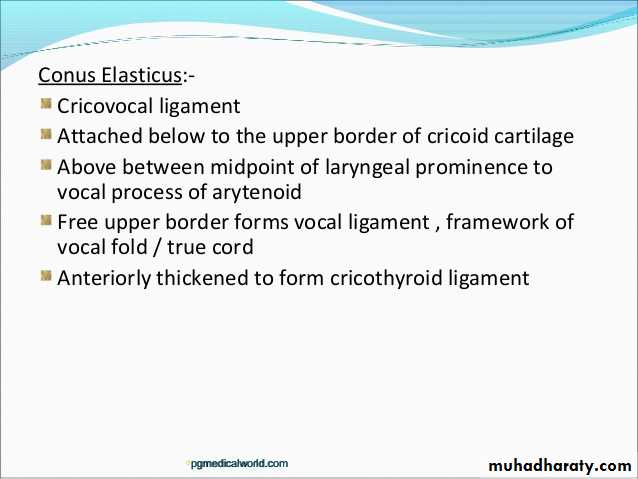
1- Vocal ligament, consisting of thickened elastic tissue.
2- Vocalis muscle:-medial fibres of thyroarytenoid muscle.